inorganic chemistry: Group 7
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
state/appearance RTP | characteristics of ← | colour in solution | |
|---|---|---|---|
fluorine | |||
chlorine | |||
bromine | |||
iodine |
state/appearance RTP | characteristics of ← | colour in solution | |
|---|---|---|---|
fluorine | yellow gas | very reactive, poisonous | |
chlorine | pale yellow/green gas | reactive, poisonous, dense | pale green |
bromine | red/brown liquid | dense, volatile | orange |
iodine | grey solid | shimmery, crystalline, sublimes into purple vapour | dark brown |
what is the structure and bonding of halogens
simple molecular (strongly covalent bonded molecules, weak intermolecular forces)
Each molecule contains two halogen atoms joined by a single covalent bond.
colours down the group get _______
colours down the group get DARKER
m/b points ______ down the group and why…
m/b points INCREASE down the group
the molecules become larger
the intermolecular forces become stronger
more energy is needed to overcome these forces
Chlorine, bromine and iodine react with _____ and non-______ to form compounds
metals and non-metals to form compounds
which group are the halogens in
group 7 → 7 electrons in outer shell
reactivity _____ down the group and why
reactivity DECREASES down the group
halogens have 7 electrons in outer shell, means they have to gain one, have to attract it
it gets harder to attract the extra electron the further away it is from the nucleus (more shells/larger atomic radius)
the rate of reaction will be _____ down the group
The rate of reaction is slower for halogens which are further down the group
equation, Sodium + chlorine →
Sodium + chlorine → sodium chloride
2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s)
properties of halogens as you go DOWN the group and simple def why (3)
high boiling/melting points → stronger intermolecular forces
less reactive → electron to be attracted further away from nucleus bc more shells
darker colour
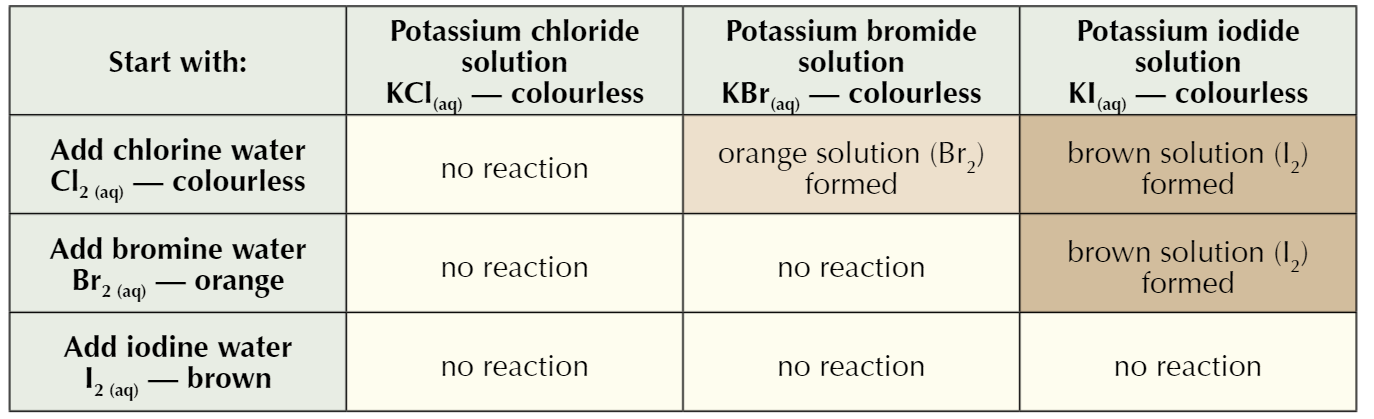
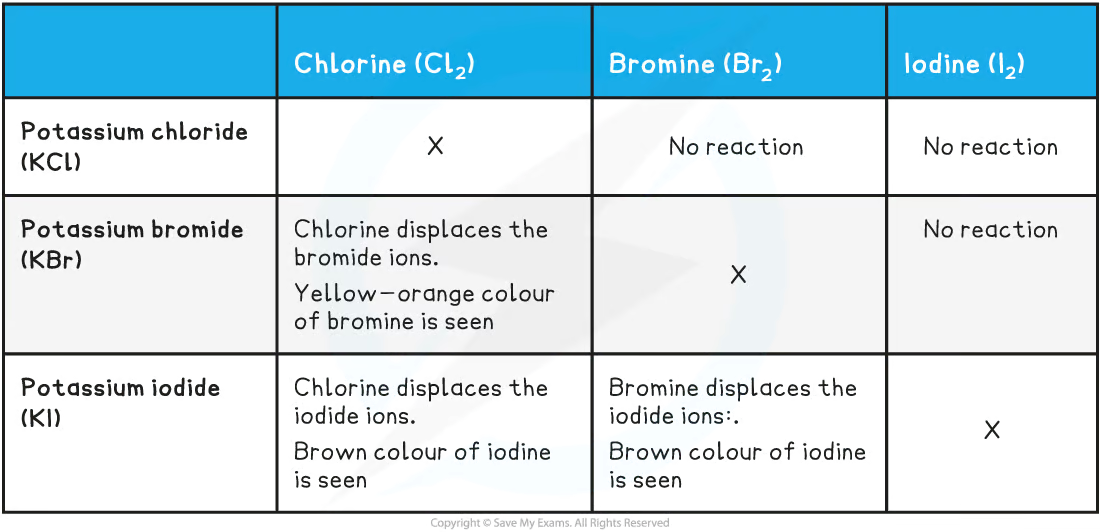
what is a halogen displacement reaction
A halogen displacement reaction: when a more reactive halogen displaces a less reactive halogen from an aqueous solution of its halide
more reactive element pushes out less reactive element
rank reactivity of Br2, Cl2 and I2
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
reacts with | potassium chlorine solution | potassium bromide solution | potassium iodide solution |
|---|---|---|---|
chlorine water (green) | |||
bromine water (orange) | |||
iodine water (brown) |
the same table but inverted - makes you think
reacts with | chlorine | bromine | iodine |
|---|---|---|---|
potassium chloride solution | |||
potassium bromide solution | |||
potassium iodide solution |
why is fluorine most reactive
Fluorine is the smallest halogen, which means its outermost shell is the closest to the positive nucleus of all the halogen
Therefore, the ability to attract an electron is strongest in fluorine making it the most reactive
describe halogen displacement reaction in terms of electrons
chlorine + iodine with ions
cl2 + 2I - → 2cl- + I2
electrons are passed from the iodine to the chlorine