SLE pharmacology
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Topicals
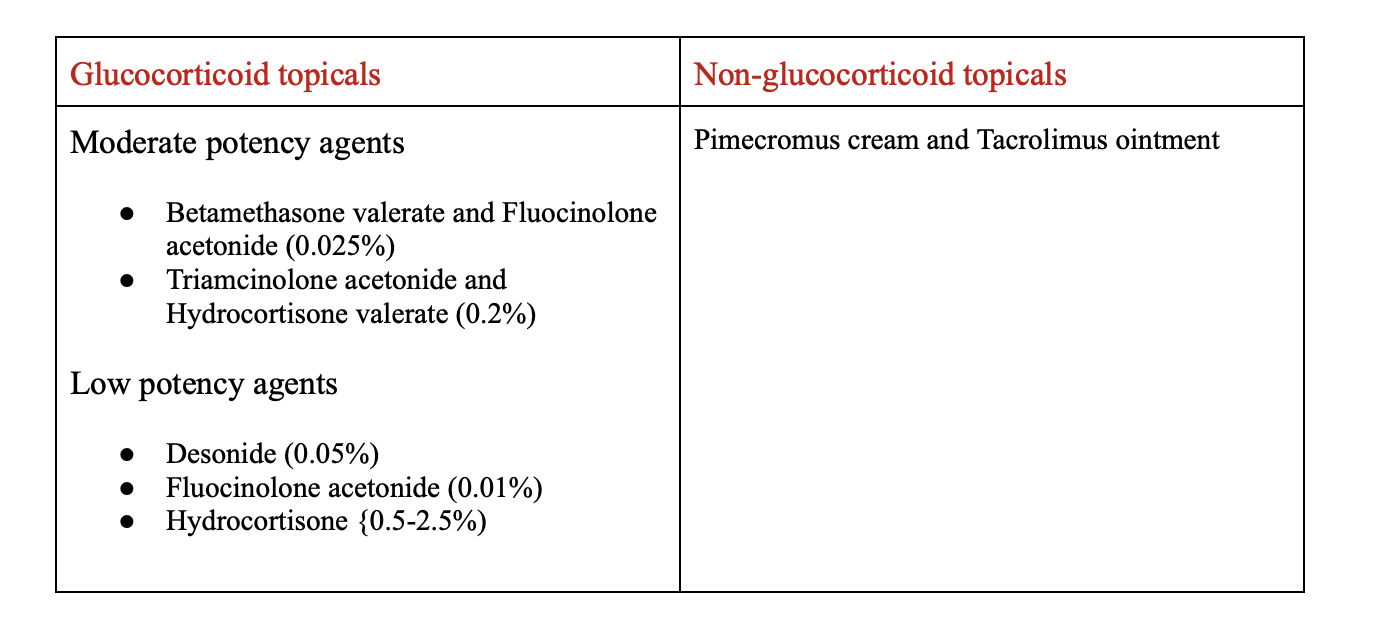
Clinical pearls:
Low potency options should be used on the face in a short-term capacity only
Moderate strength are used on the body long term
Calcineurin inhibitors have no time limit for use on the face
NSAIDs
MOA: inhibit COX 1 and COX 2 enzymes decreasing the production of inflammatory mediators
Use: control mild to moderate symptoms of inflammation depending on patient response
BBW: Cardiovascular thrombolytic events and GI bleeding ulceration or perforation
ADR: Renal impairment, pulmonary hypertension, decreased hematology
Monitoring:
electrolytes every 6 months
BP every 12 months
Glucocorticoid’s
MOA: Decreases inflammation by suppression of migration leukocytes and reversal of increased capillary permeability
Use: Used to suppress immune response and therefore inflammatory response
ADR: CNS/behavioral effects, GI effects, Ocular effects
Monitoring: Adrenal insufficiency
Clinical Pearls:
Lowest possible dose to control symptoms should be used
For flares methylprednisolone pulse therapy (250-1000mg for 1-3 days) followed by an oral taper
tapering:
If a patient’s disease is controlled but they’re taking more than 5 mg of prednisone per day, the goal is to gradually reduce (taper) the dose to below 5 mg and completely stop prednisone within 6 months.
If the patient can’t get off prednisone (down to 0 mg) without their disease flaring, then you should start or increase other immunosuppressive medications so the disease can be controlled without long-term steroid use.
Chloroquine(CQ)
Aralen
MOA: Inhibit Prostaglandin synthesis
Use: modulate the immune system and prevent activation of dendritic cells
Dose: Max dose 2.3mg/kg/day
ADR: Blue-grey skin pigmentation, hypoglycemia, abdominal cramp
Monitoring: CBC with diff at baseline
Azathioprine(AZA)
Imuran
MOA: Blocks purine synthesis
Dose: 2-3mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses
BBW: Malignancies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
ADR: pancreatitis, liver toxicity, infections
Monitoring:
CBC with diff
LFTs
SCR
Is safest drug for SLE in pregnancy
Methotrexate(MTX)
Trexall, Rheumatrex
MOA: Inhibit purine and thymidylic acid synthesis decreasing immune response
Dose: 20-25mg SubQ or oral once WEEKLY
BBW: embryo-fetal toxicity, bone marrow suppression, serious infections, toxicity(GI toxicity, hepatic toxicity, pulmonary), hypersensitivity, and dermatologic reactions
ADR: dermatological toxicity, diarrhea, increased liver enzymes
Monitoring:
CBC with diff
LFT monthly for 3 months then every 3 months thereafter
Anakinra
Kineret
MOA: Antagonist of the interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor.
Dose: 100mg SubQ or IV daily
Use: Adjunctive or alternative to immunosuppressants and used to lower steroid need
ADRS: Increase LFTs, hyperkalemia, hypernatremia
Monitoring:
CBC every month ×3 months, then q3 months ×3 months, then q6 months ongoing
Anifrolumab
Saphnelo
MOA: IgG1-kappa monoclonal antibody that blocks the biologic activity of type 1 interferon receptors
Dose: 300mg IV infusion every 4 weeks
ADR: Antibody development, infection, hypersensitivity reactions
Pearls: Zoster vaccine prior to starting
Belimumab
Benlysta
MOA: IgG1 antibody; Decrease the ability for autoreactive B-cells to mature and cause damage
Dose:
IV dosing: 10 mg/kg/dose q 2 weeks x 3 doses then q 4 weeks
SC dosing: 200 mg week
ADR: Diarrhea, Nausea, Infections, PML
Monitor: Hypersensitivity and suicide ideation
Pearls: Takes 2-4 months to see results
Colchicine
Colcrys
MOA: inhibiting β-tubulin polymerization into microtubules;
this prevents activation, degranulation, and migration of neutrophils
Dose: 0.6-1.2mg daily; decreased with 3A4/PgP inhibitors
ADR: GI effects, Myalgia
Monitor:
Eye screening baseline then every 4-6 months
EKG at baseline and as needed
Cyclophosphamide(CYC)
Frindovyx
MOA: prevents cell division by cross-linking
DNA strands and decreasing DNA synthesis.
Dose: 750mg-1000mg/m2 IV monthly for 6 months
ADR: Bone Marrow suppression, hepatotoxicity, pulmonary toxicity
Monitor:
CBC and SCr qweek for 1 month then monthly
Urine pregnancy test prior to each infusion
Urinalysis every 6 months following course
Pearls:Can cause permeant infertility
Cyclosporine(CNI)
Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune
MOA: MOA: Inhibition of production and release of interleukin II
Dose: 3-5mg/kg/day by mouth in 2 divided doses
BBW: Hypertension, Nephrotoxicity, Immunosuppression
ADR: infections, diabetes, neurotoxicity
Monitor:
CBC & LFT monthly for 3 months then every 3 months.
SCr, Potassium, Magnesium every 2 weeks for 3 months then monthly
Lipid every 6 months.
Dapsone
Aczone
MOA: Inhibit neutrophil movement and the lack of the ability to initiate inflammatory processes
Use: refractory skin disease
Dose: 50mg daily (max 150mg) in 2 divided doses
ADR: Hypersensitivity reactions, hepatic effects, blood dyscrasias
Monitor:
CBC, LFT q week for 4 weeks—> 4 weeks for 3 months—>every 3 months.
G6PD testing before starting
Hydroxychloroquine(HCQ)
Plaquenil
MOA: Inhibits locomotion of neutrophils and chemotaxis of eosinophils; impairs complement-dependent antigen-antibody reactions.
Dose: 200-400mg /day in 2 divided dose start at 5mg/kg
ADR: QT prolongation, hypoglycemia, retinal toxicity
Monitor:
CBC, LFT, SCr at baseline and then as needed.
Eye screening at baseline then annually no later than 5 years after.
EKG at baseline then as needed
Pearls: Typically first line for SLE
Takes 2-4 months to see results
Continue therapy even if remission is reached
IVIG
Use: used for patient with low platelet or RBC counts
Dose: 2g/kg given over 2-5 days consecutively monthly
BBW: Thrombosis and acute renal failure
ADR: Abdominal pain, chest pains, hypertension
Monitor:
CBC at baseline then monthly before infusion.
LFTs and chemistry panel prior to infusion
Lenalidomide
Revlimind
MOA: TNFa inhibitor
Dose: 5 mg every day PO
BBW: Embryo fetal toxicity, hematological, and VTEs
ADRs: hypokalemia, edema, rash
Monitoring:
CBC, LFT, SCr, TSH at baseline then every month for 3 months
Urine pregnancy test 2 weeks prior and before infusion adminstration, every week *4 weeks, then every 2-4 weeks, then 4 weeks after d/c treatment
Not really used due to risk; often for refractory cases
Leflunomide
Arava
MOA: inhibits pyrimidine synthesis
Dose: 10-20mg every day
BBW: embryo-fetal toxicity, hepatotoxicity
ADR: Diarrhea, Infection, interstitial lung disease
Monitor:
CBC with diff, LFTs, SCr monthly for 3 months then every 3 months
Mycophenolate mofetil(MMF or MPAA)
Cellcept
MOA: T-cells become less responsive and therefore decrease immune response
Dose: 2-3g by mouth daily in 2 divided doses
BBW: Infections, embryo-fetal toxicity, malignancies
ADR: Edema, GI effects, hypertension
Monitor:
CBC every 2 weeks after each dose change then once stable once yearly.
Urine Pregnancy screening 8-10 days after baseline and at subsequent visits
Obinutuzumab(anti-CD20)
Gazyva
MOA: Anti-CD20 medications that specifically cause cell death to B-cells that would be autoreactive
Dose: 1 gram IV on Day 1 and at weeks 2, 24, 26 and 52
BBW: Hepatitis reactivation, PML
ADR: Skin rash, hyperkalemia, hypernatremia
Monitor:
CBC with Diff at 3 months then every 6 months
IgG levels assessed every 6 months
Rituximab(anti-CD20)
Rituxan
MOA: Anti-CD20 medications that specifically cause cell death to B-cells that would be autoreactive
Dose: 1 gram IV on Days 1 and 15
BBW: Infusion reactions, hepatitis b reactivation, PML, Mucocutaneous reactions
Monitor:
CBC with Diff at 3 months then every 6 months
IgG levels assessed every 6 months
Tacrolimus(CNI)
Prograf
MOA: suppresses cellular immunity
BBW: Mortality in liver transplants, malignancies and serious infections
ADR: Diabetes, nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity
Monitor:
CBC with Diff, LFT monthly for 3 months then every 3 months.
Creatine potassium and magnesium every 2 weeks for 3months then monthly