Addition Reactions- Alkenes and Alkynes
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
nucleophillc
Alkenes and alkynes are generally ___________, so they react with electrophilic compounds.
∏-bond attacks an electrophile to form a carbocation on the more substituted carbon. The nucleophile attacks.
general mechanism of electrophilic addition to alkenes
Markovnikov Rule
The addition of a proton acid to the double bond of the alkene results in a product with the acid proton bonded to the carbon atom that already holds a greater number of hydrogens (least substituted position)
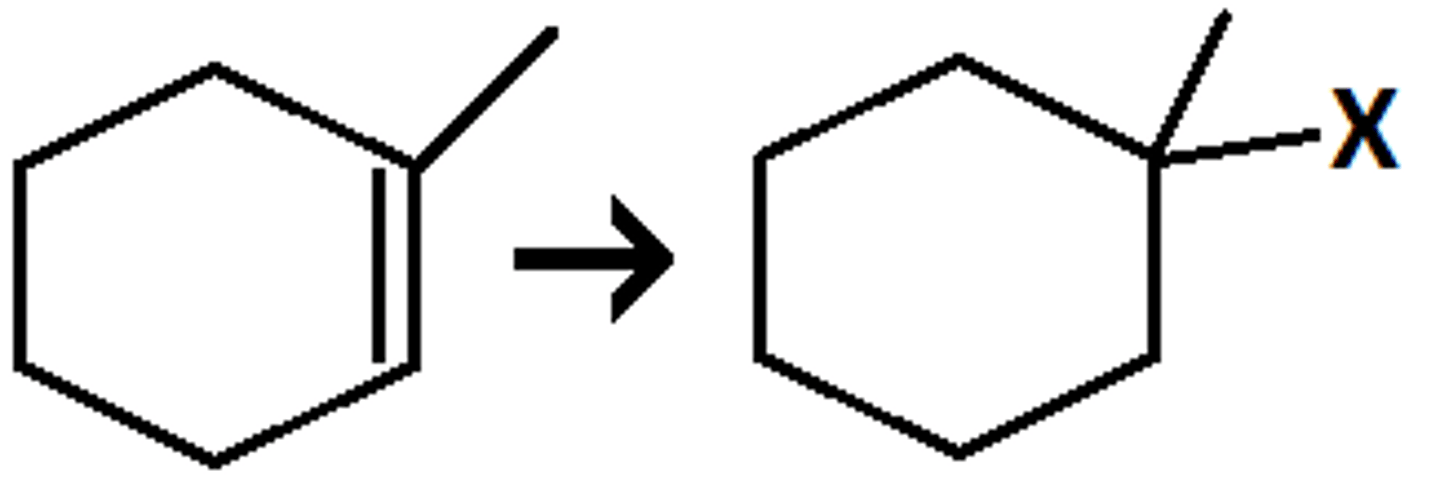
Anti-Markovnikov
electrophile adds to the less substituted carbon
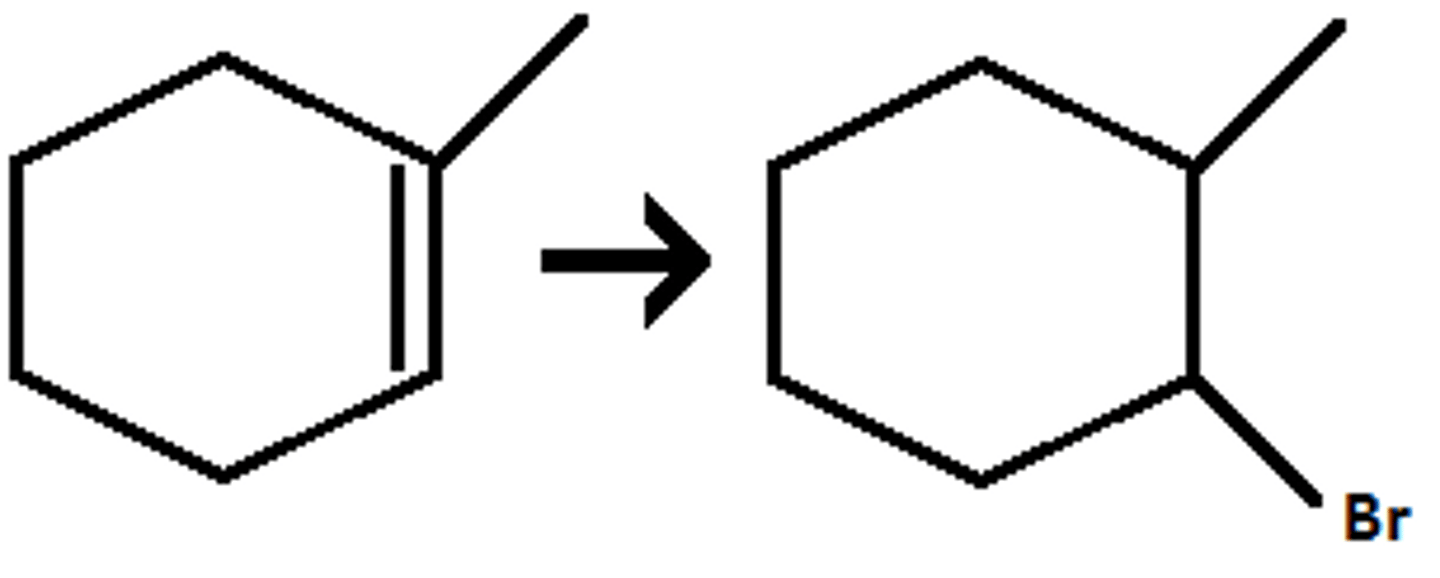
-Alkene-->Alcohol
-add H and Br
-Maokovnikov addition
Reaction Coordinate for addition of Alkenes
1. alkene attacks H on H2SO4
2. proton is added to less substituted carbon (positive charge is on more substituted carbon)
3. H2O attacks positive charge on alkene
4. H2O is deprotonated by H2O
alkene + H2SO4, H20 (Mechanism)
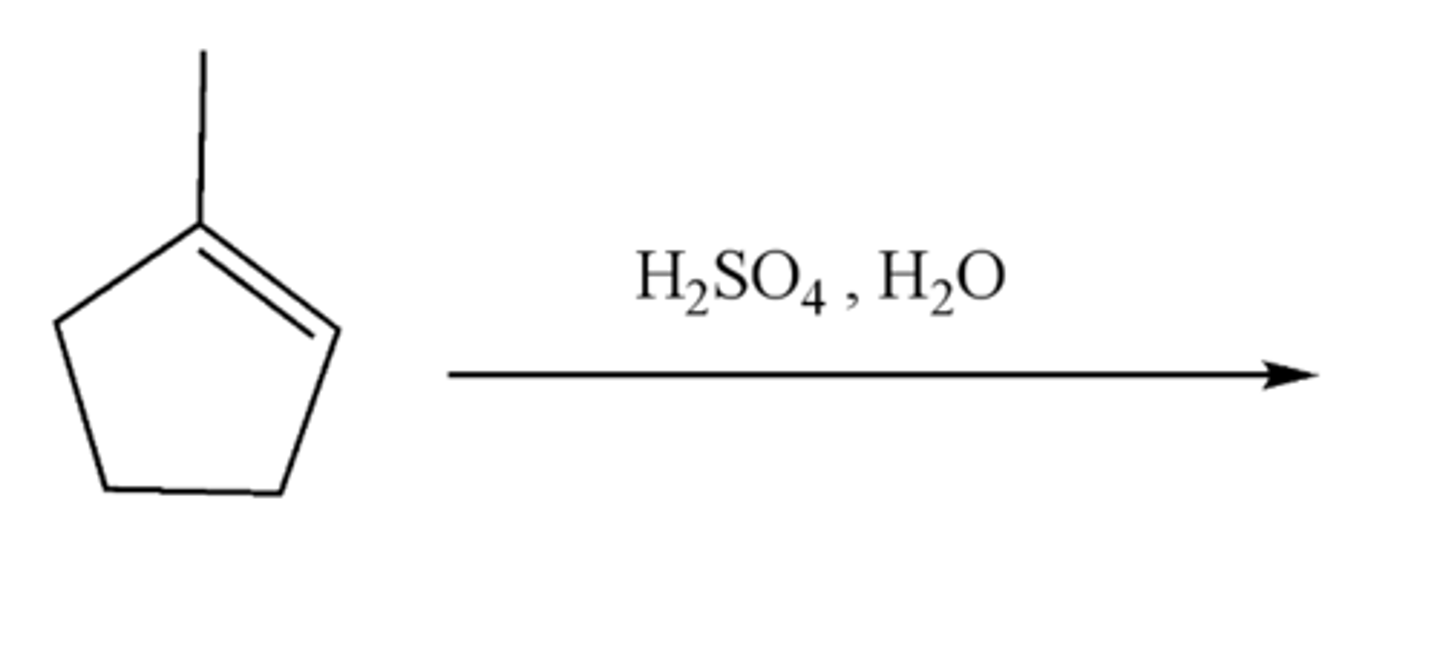
-Alkene-->Alcohol
-OH and H are added
-major product: Maokovnikov
-minor product: Anti-Markovnikov
alkene + H2SO4, H20 (products)
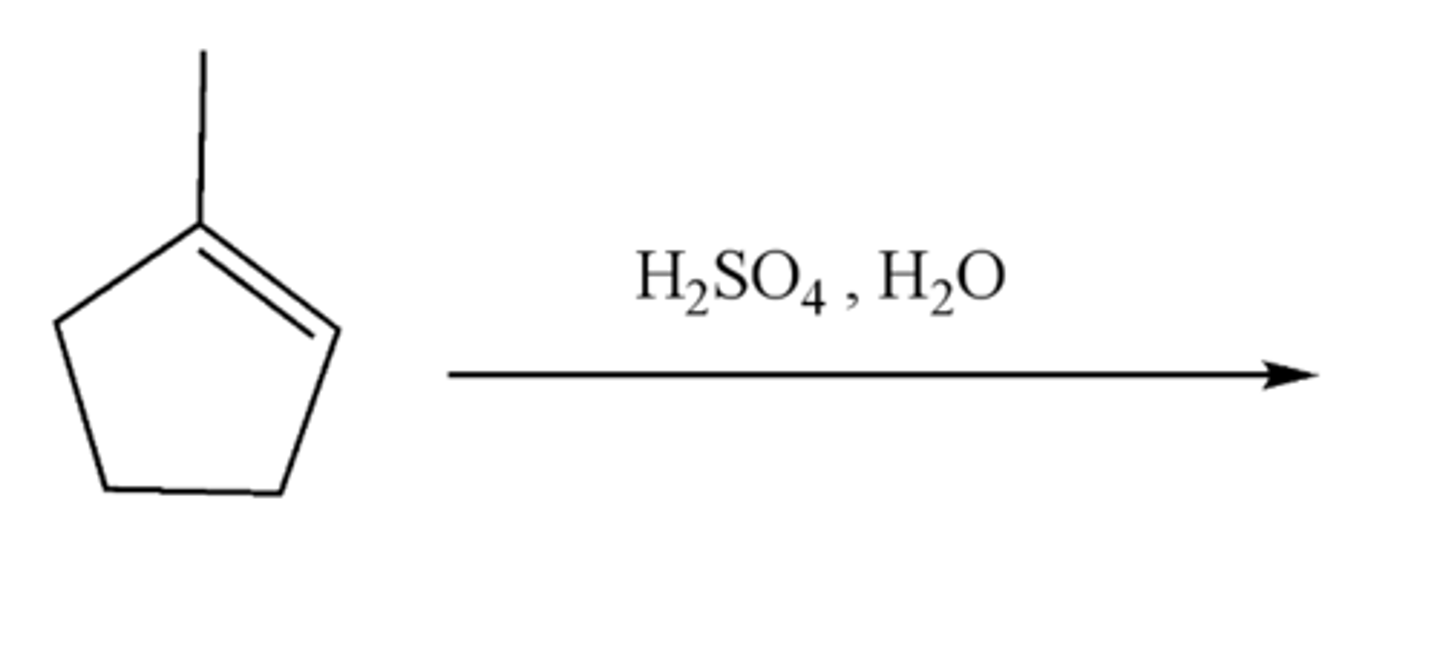
-Alkene-->Alcohol
-OH and H are added
-Markovnikov product
Alkene + 1)Hg(OAc)2 2)NaBH4 (products)
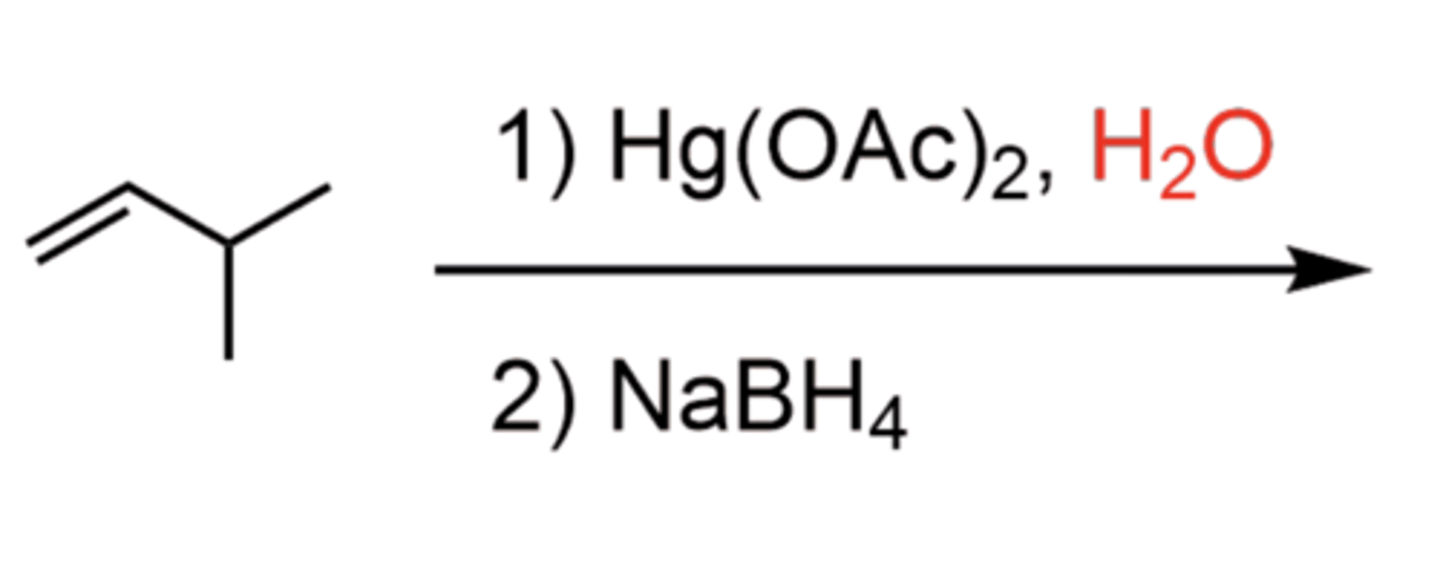
1. Oxymercuration to form 3-membered ring
2. Add H2O to open the ring (SN2-like)
3. Demercuration with NaBH4
Alkene + 1)Hg(OAc)2 2)NaBH4 (mechanism roadmap)
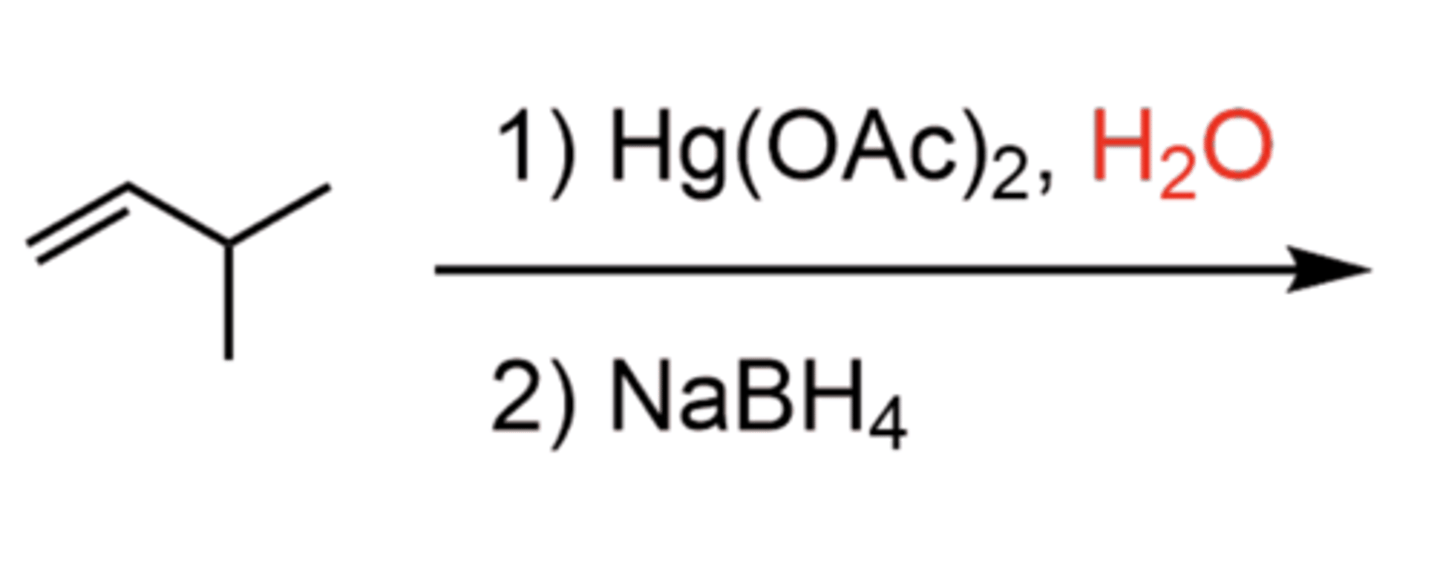
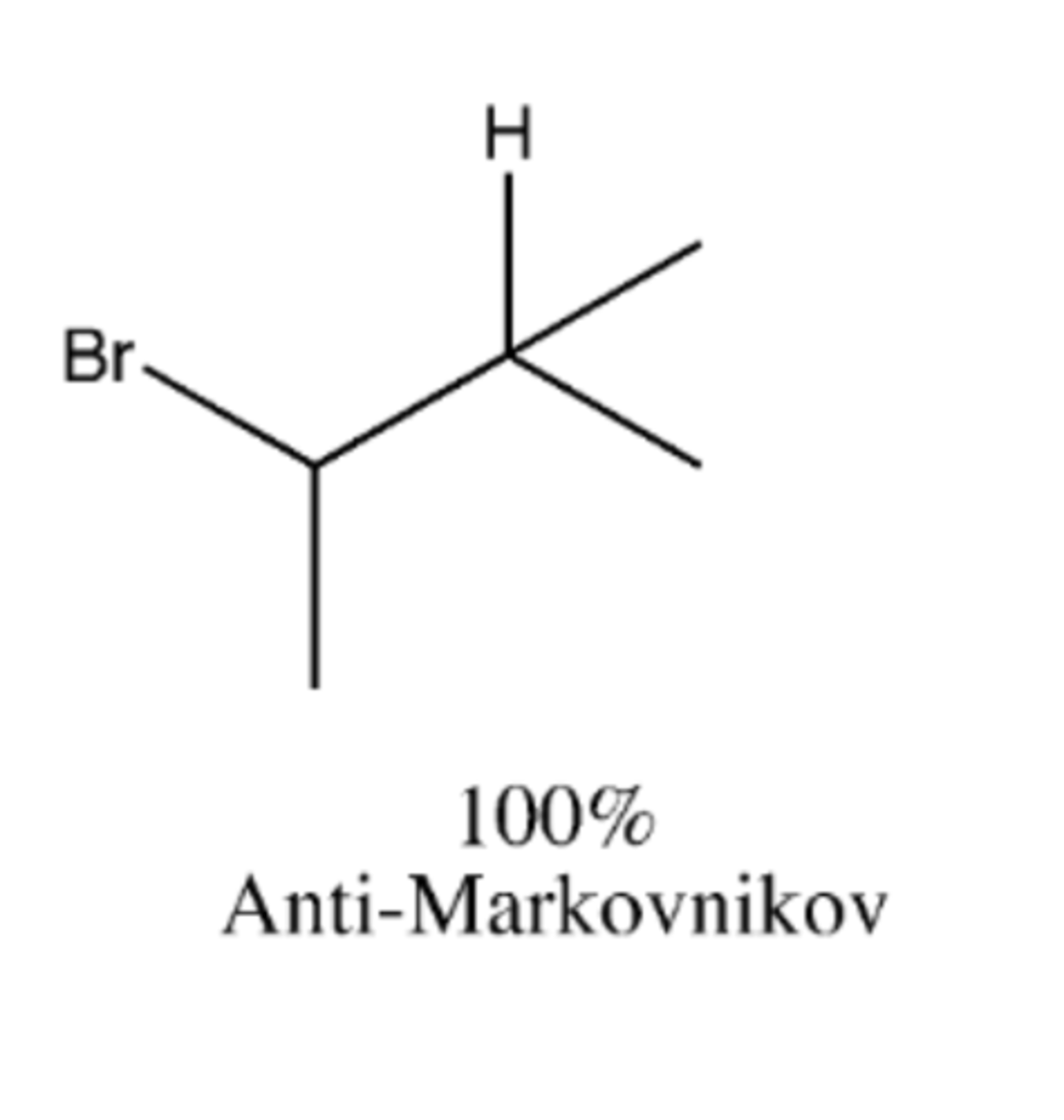
-Alkene-->Haloalkane
-Br and H added
-Anti-Markovnikov
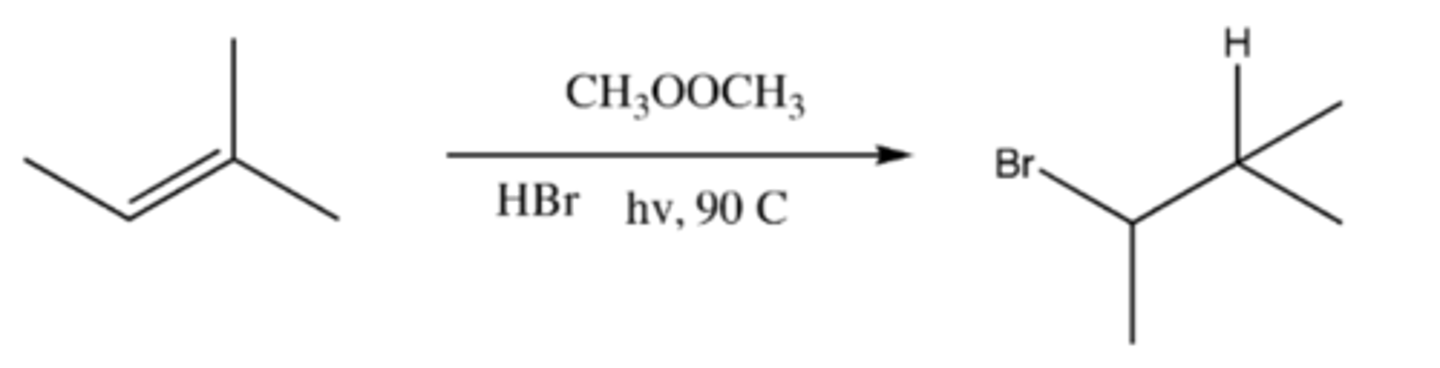
alkene + CH3OOCH3 + HBr + hv, 90 C (product)
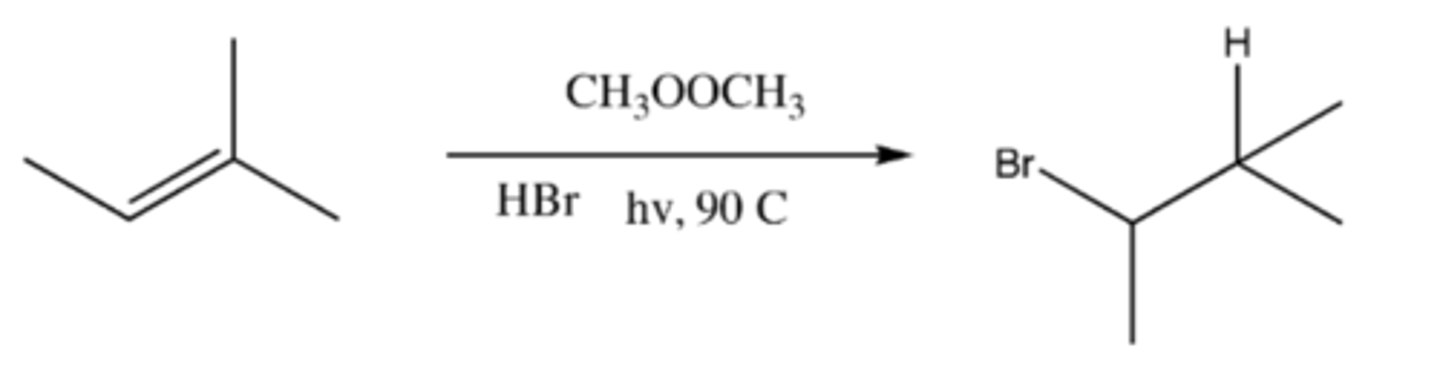
-Initiation: CH3OOCH3 splits to form 2 OCH3 radicals
-Propagation 1: OCH3 radical + H-BR --> HOCH3 + Br radical
-Propagation 2: Br radical + alkene --> radical bromo-alkane
-Termination: Radical Bromo-alkane +H-Br --> Bromo-alkane + Br radical (electron from hydrogen joins with radical)
alkene + CH3OOCH3 + HBr + hv, 90 C (mechaism)
3° > 2° > 1° > methyl
Stability of Radicals
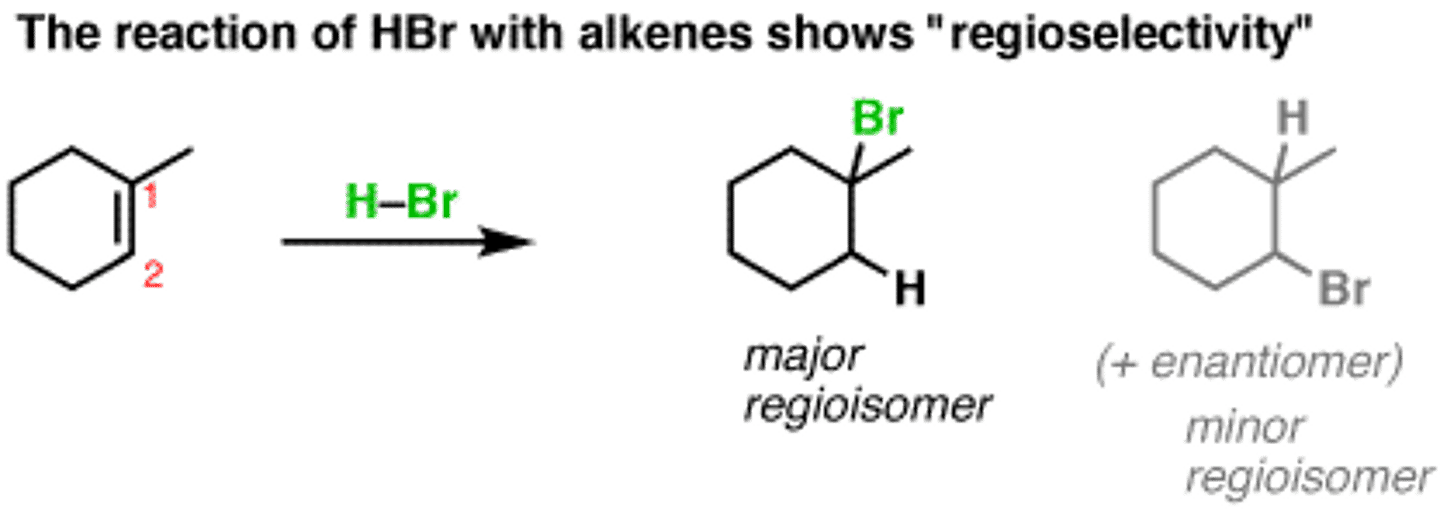
Regioselective
A reaction in which one direction of bond making or breaking occurs preferentially over all other directions
syn addition
An addition in which two groups add to the same face of the double bond
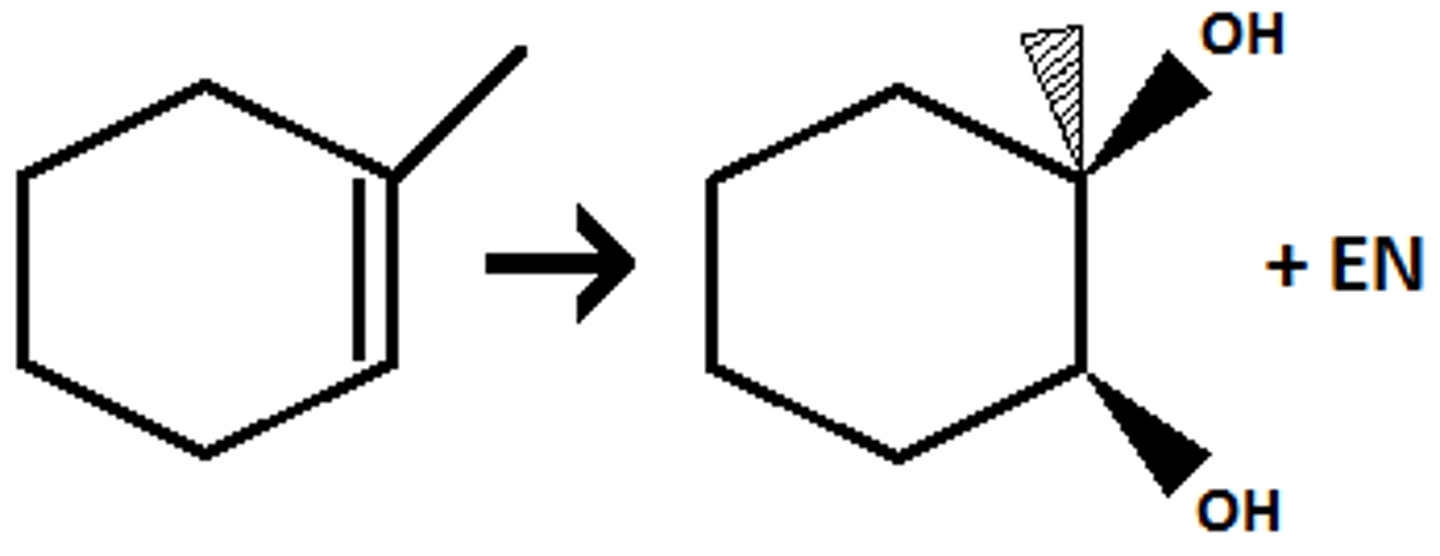
anti addition
an addition in which two groups add to opposite faces of the double bond
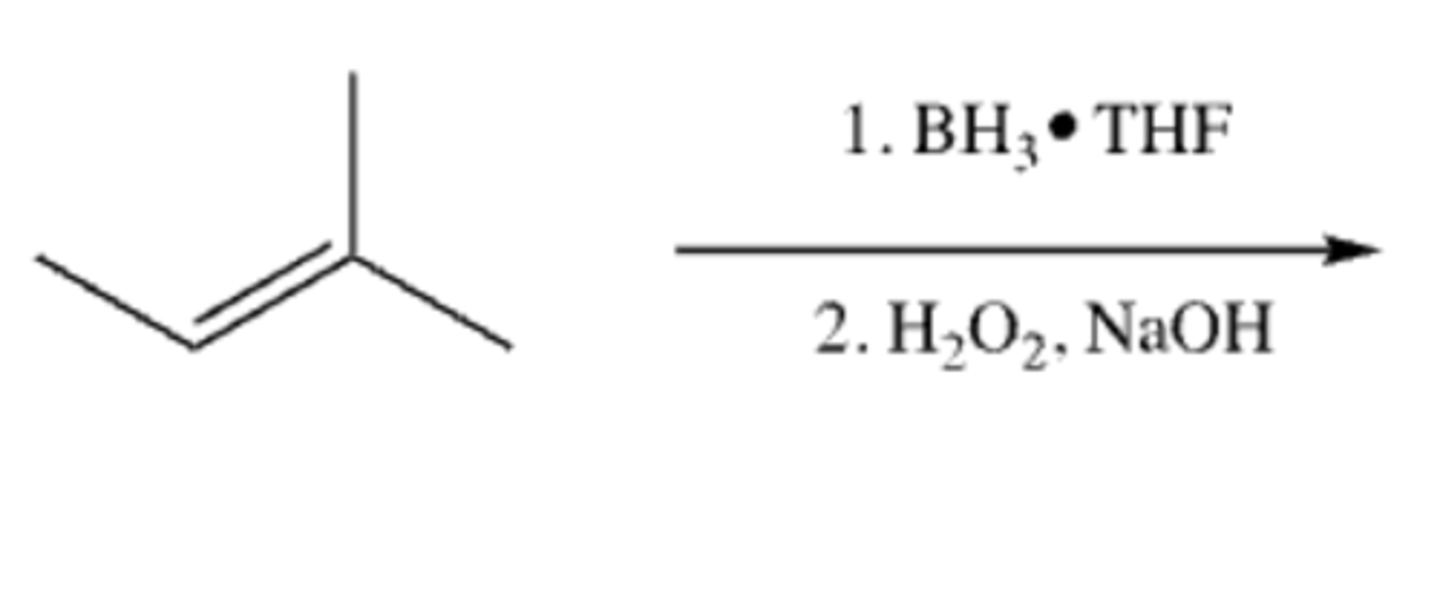
Alkene-->Alcohol
-Add H and OH
-Anti-Markovnikov
-syn addition
alkene + 1)BH3·THF 2)H2O2, NaOH
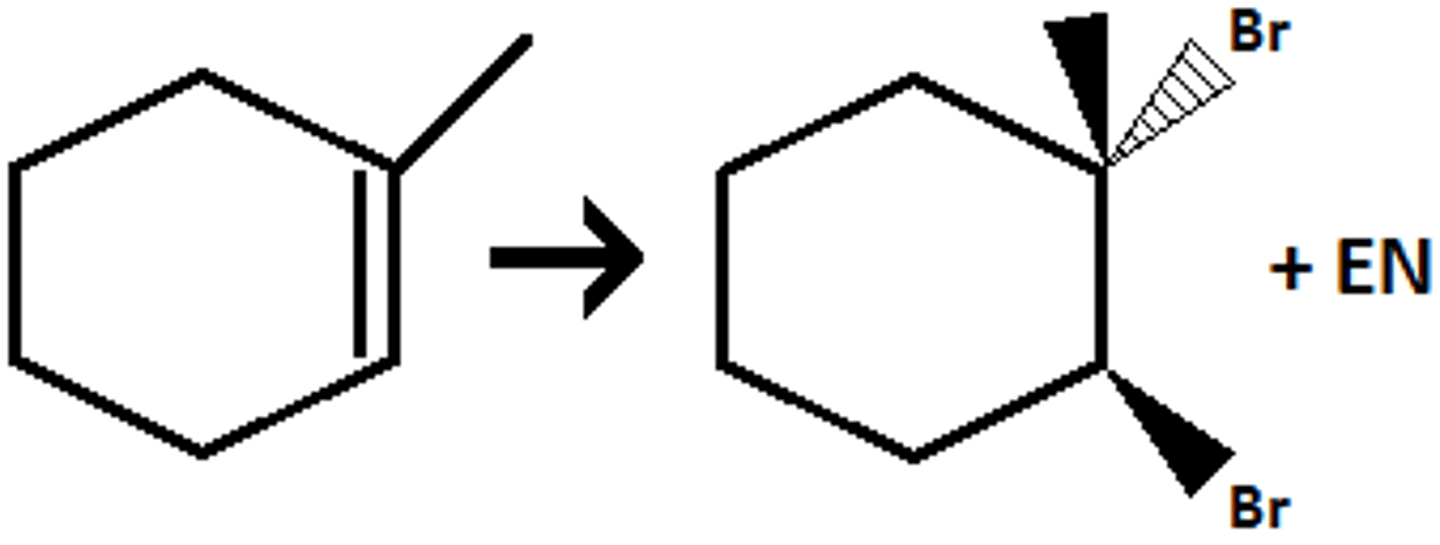
-Alkene--> Dibromide/Dicloride/Diiodine
-Anti addition
-syn addiotion
alkene + diatomic halogen (product)
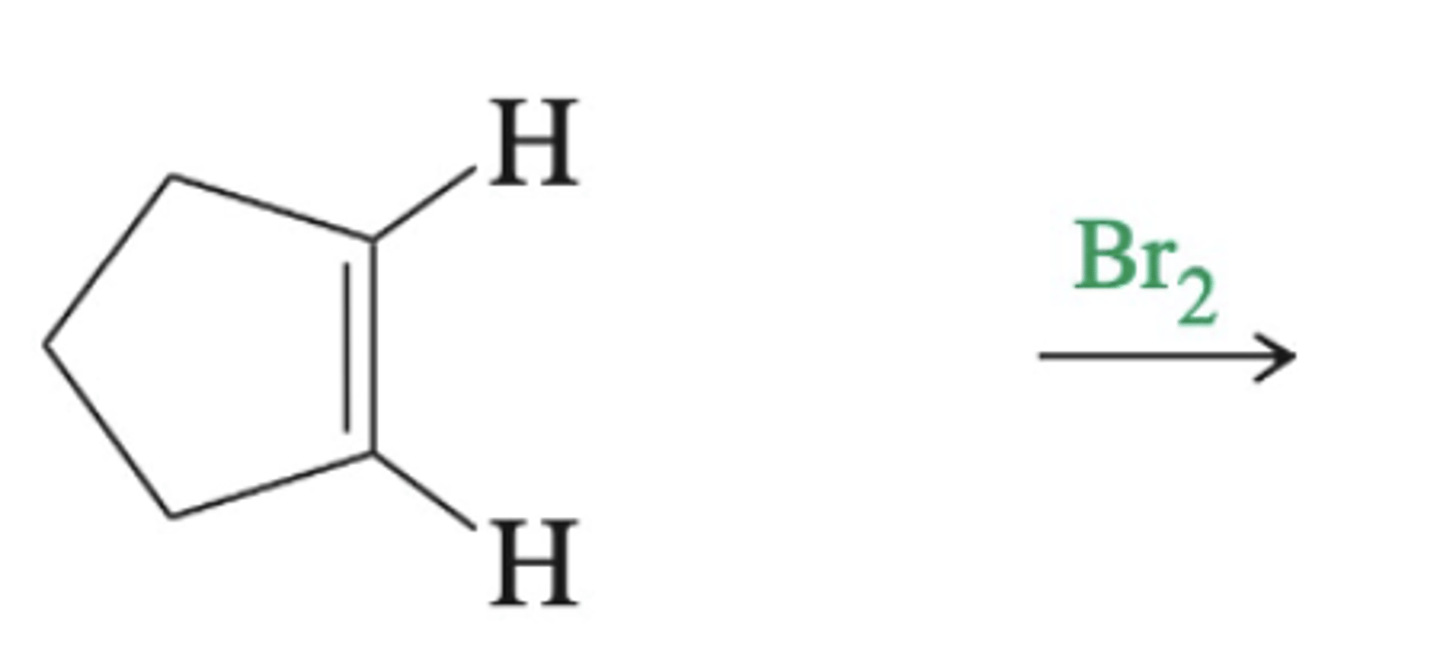
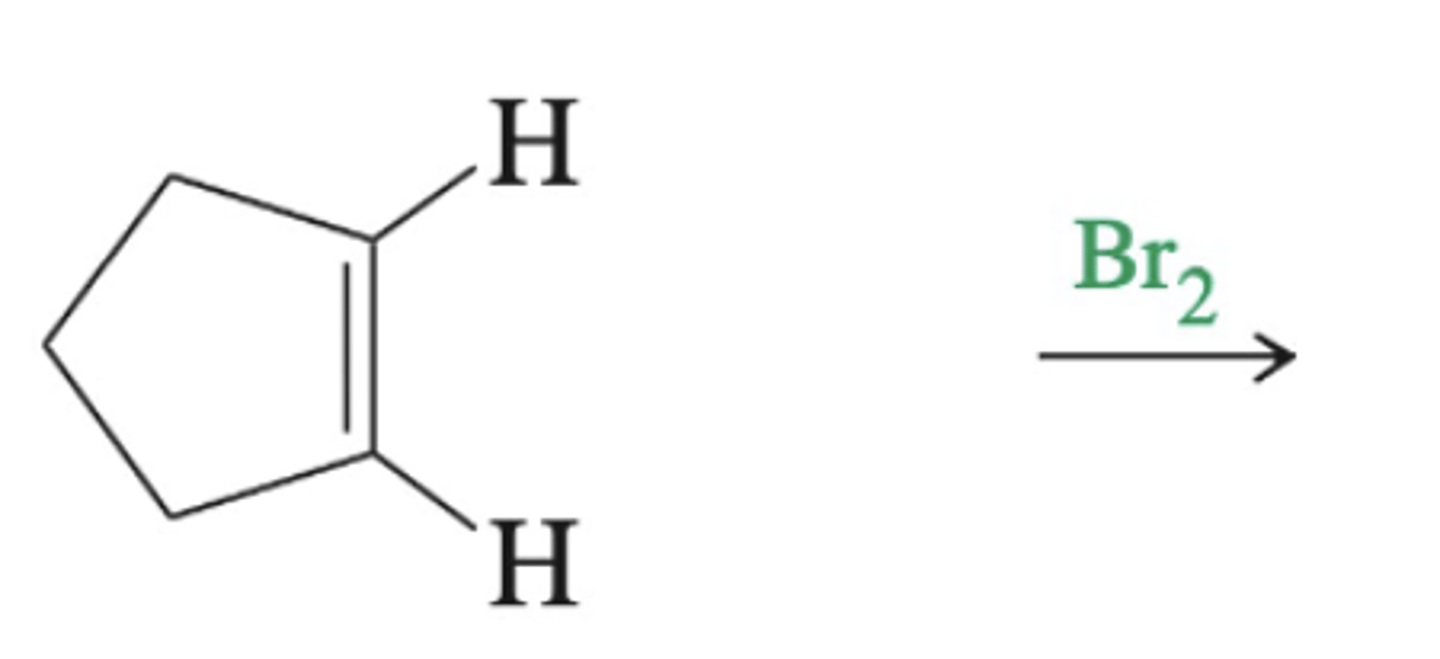
-Formation of bromonium Intermediate and anti products
-practice this
alkene + diatomic halogen (mechanism)
Halohydrin
an alcohol with a halogen on an adjacent carbon atom
-Alkene--> Halohydrin
-add Br and OH
-Regioselkectivity: OH to more substituted carbon
-Stereoselectivity: anti addition
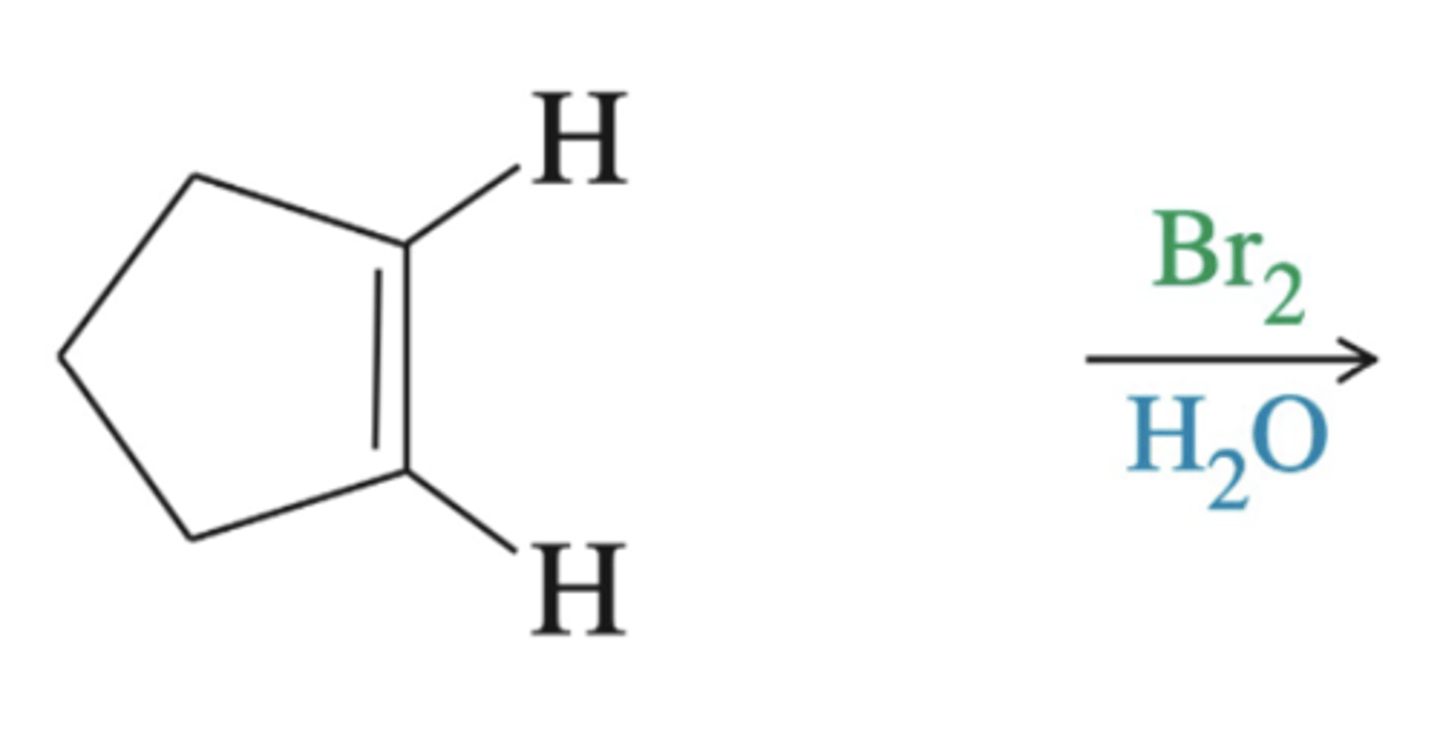
alkene + Br2, H20
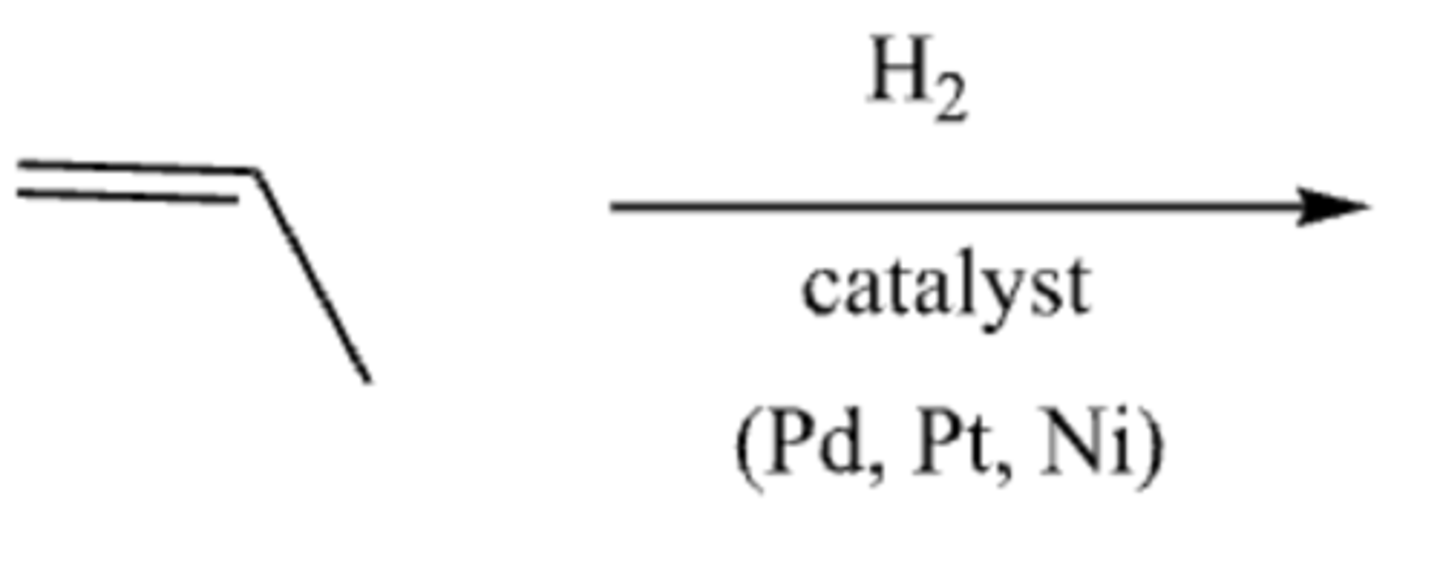
-Alkene-->alkane
-adds two H
-syn addition
alkene +H2 + Pt/Pd/Ni (catalyst)
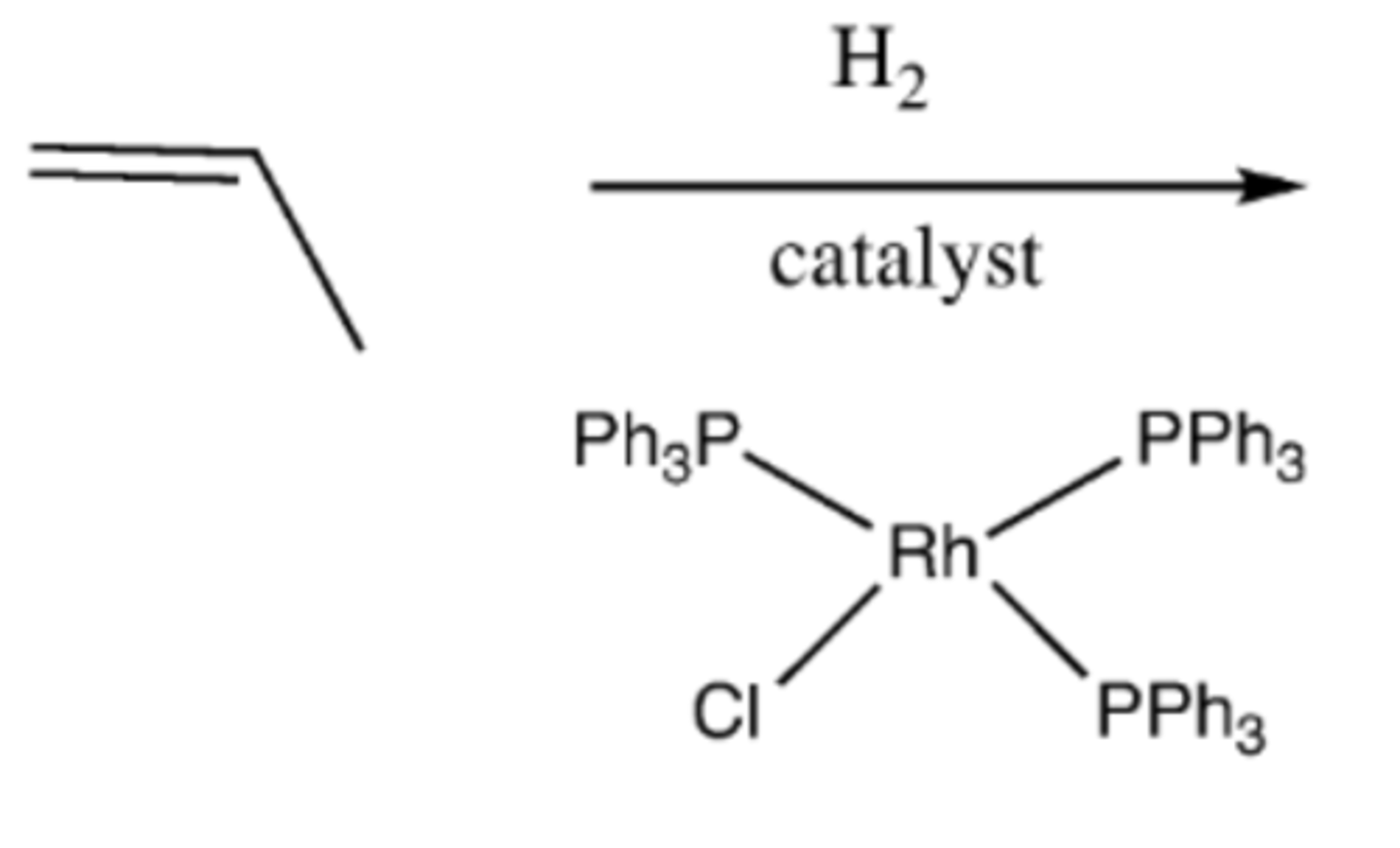
-Alkene-->alkane
-adds two H
-syn addition
alkene +H2 + Wilkinson's catalyst
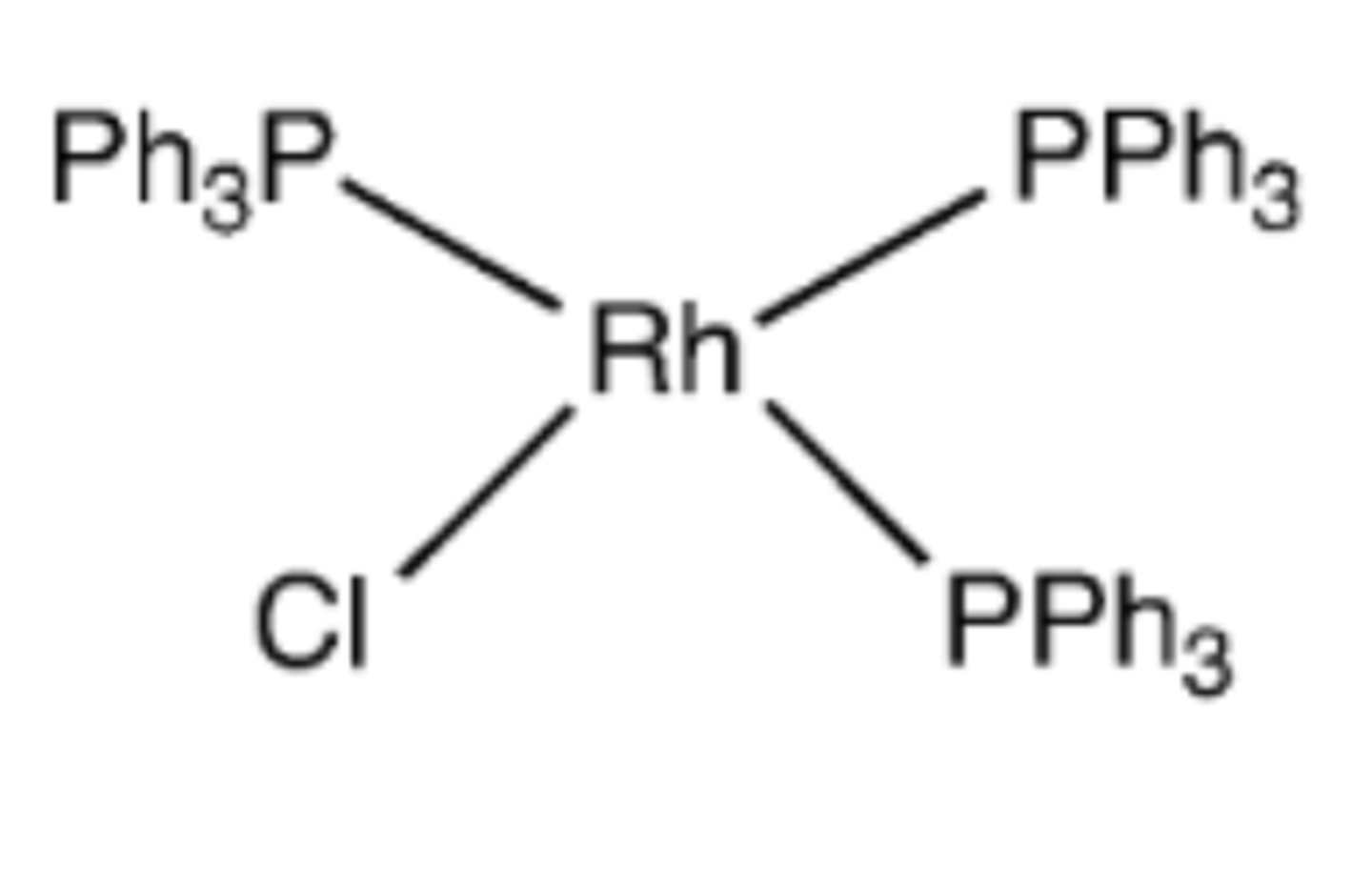
NBS, hv
Wilkinson's catalyst
-forms a cyclopropane
-syn addition
-mechanism: pi bond attacks carbene and electrons from carbene attack other carbon from the pi bond
alkene + carbene (CH2 N2)
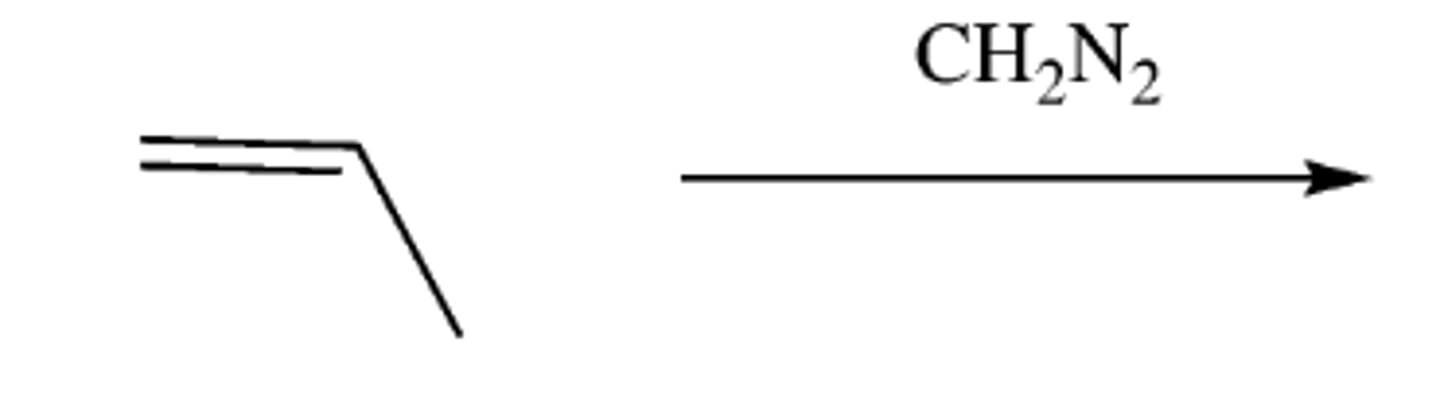
-forms cyclopropane
-syn addition
-mechanism: 2 C-C bonds are formed at the same time
alkene + CH2I, Zn, CuCl
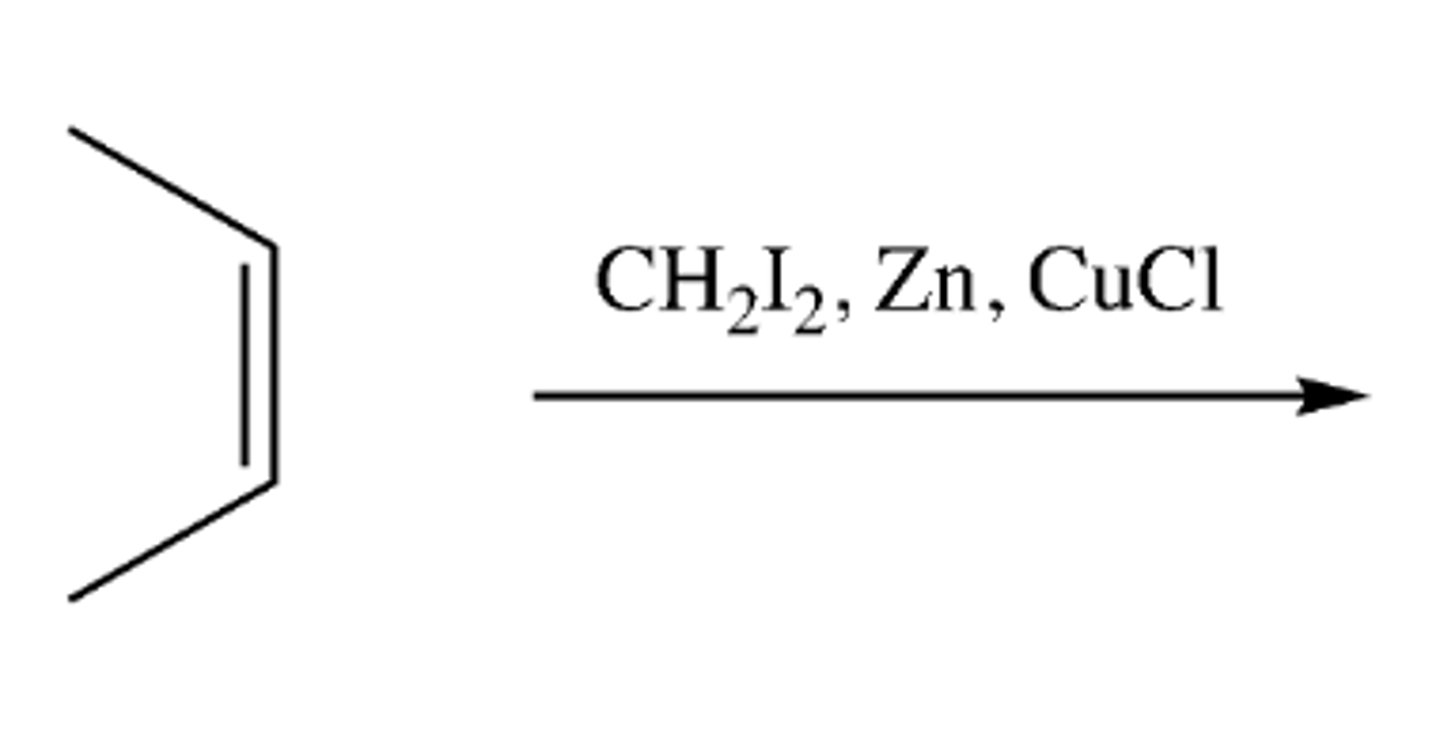
-forms cyclopropane with 2 Br groups
-practice mechanism
alkene + CHBr3, KOH/H20
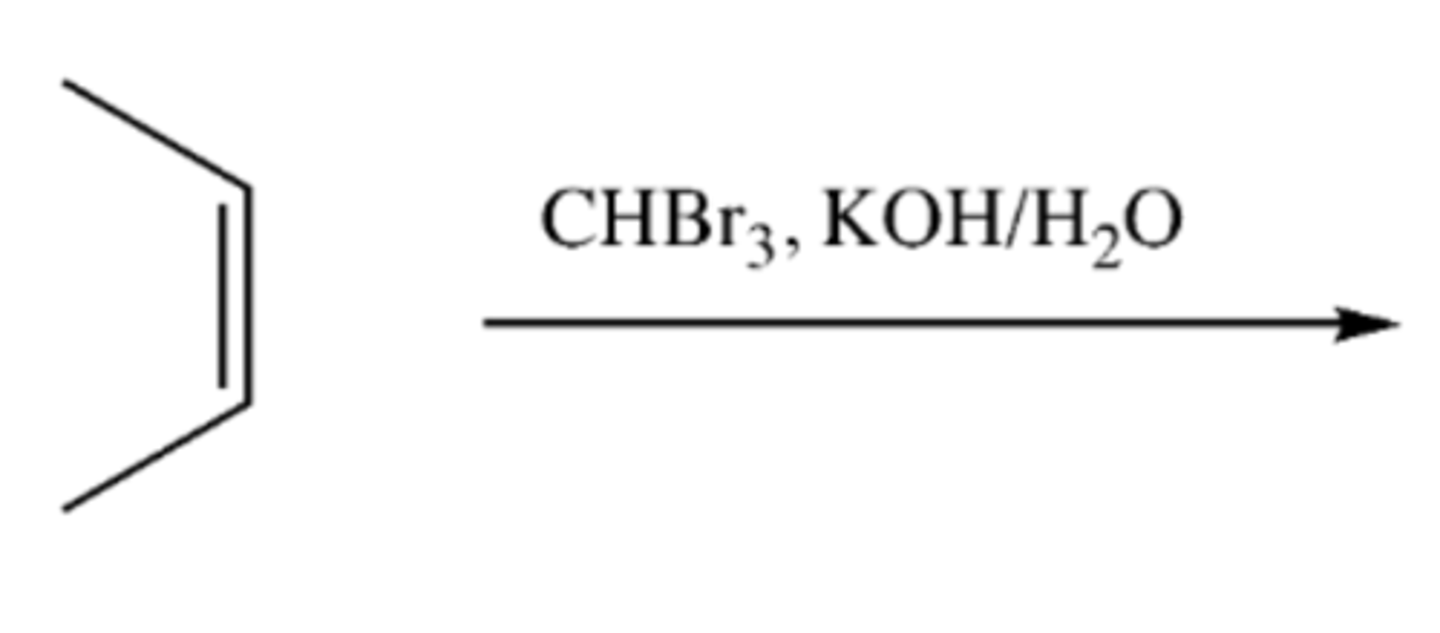
-Alkene--> Diol/Glycol
-2 OH groups added
-syn addition
-don't need to know mechanism
alkene + (1) KMn)4 (2) NaOH
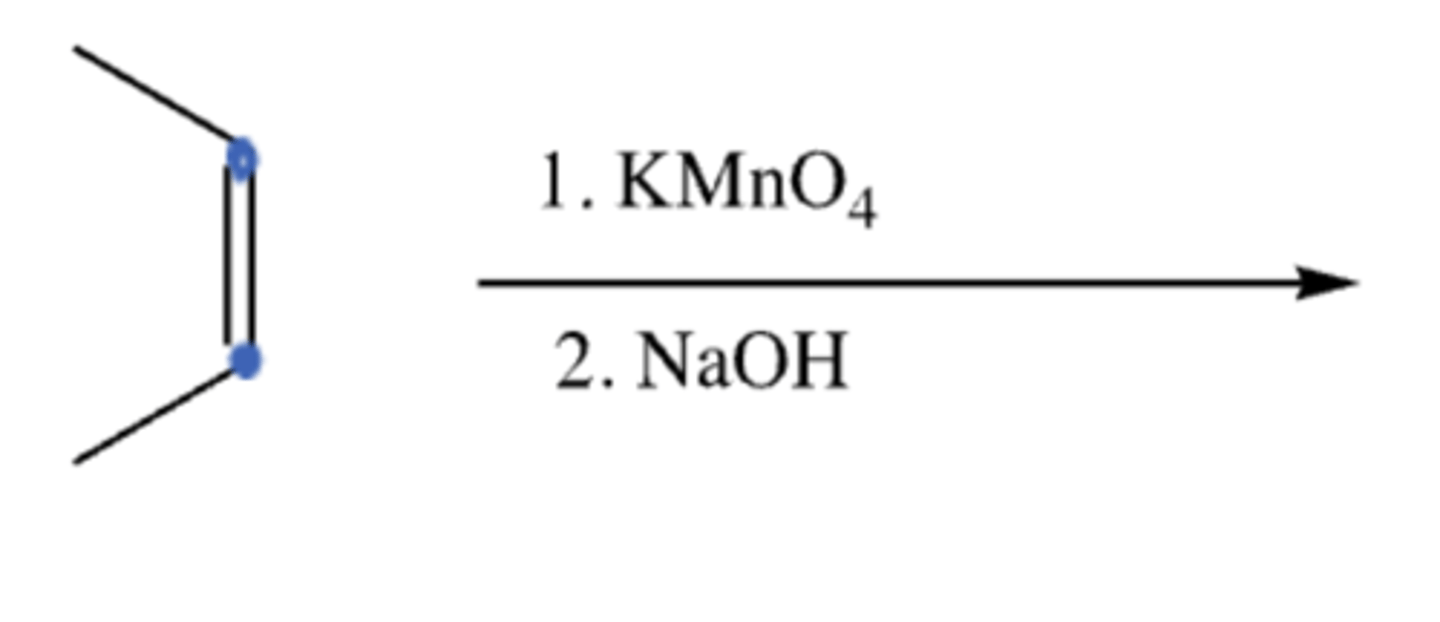
OsO4
KMnO4 is often used instead of ______ becuase it is a cheaper, milder reagent.
-Alkene--> Diol/Glycol
-2 OH groups added
-syn addition
-don't need to know mechanism
Alkene + OsO4 +H2O2
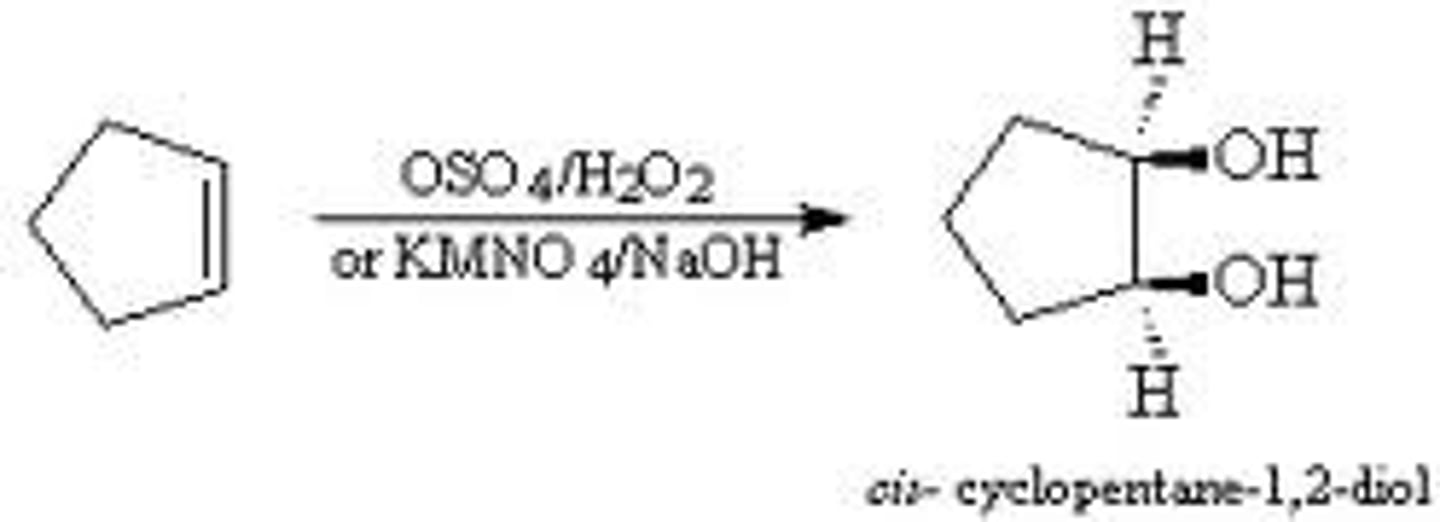
-Alkene--->Epoxide
-Practice mechanism!!
alkene + peroxyacetic acid

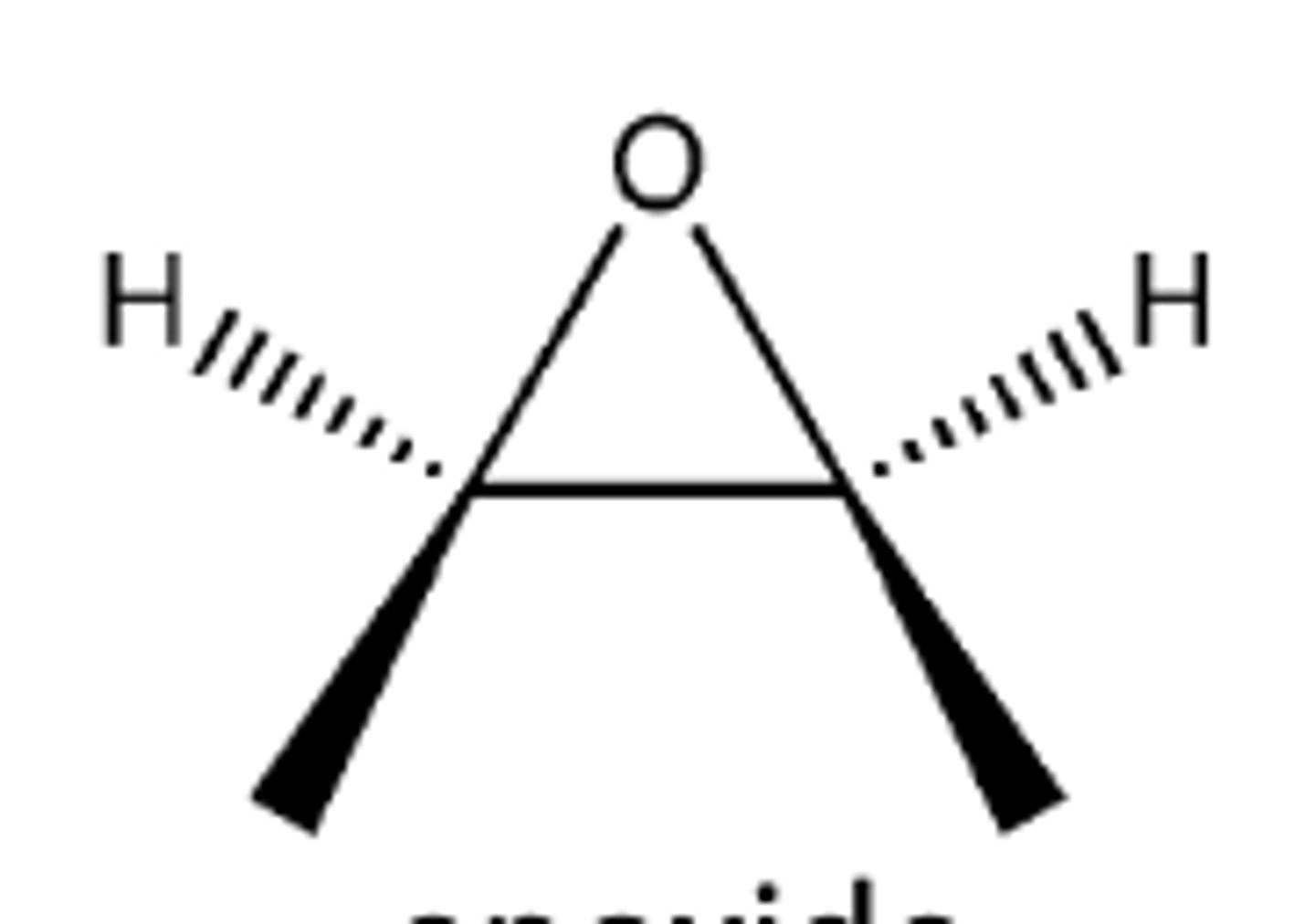
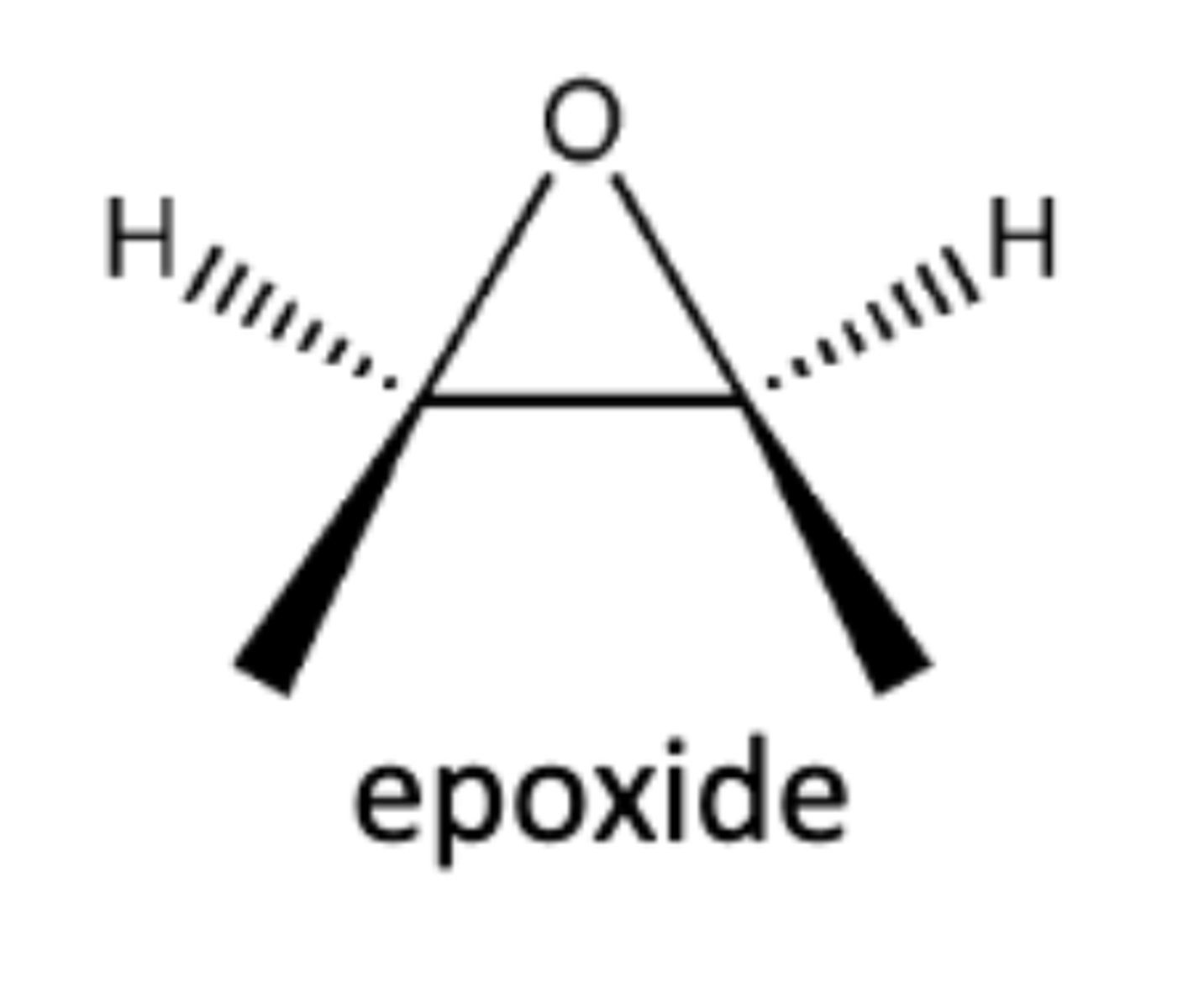
epoxide
Mechanism:
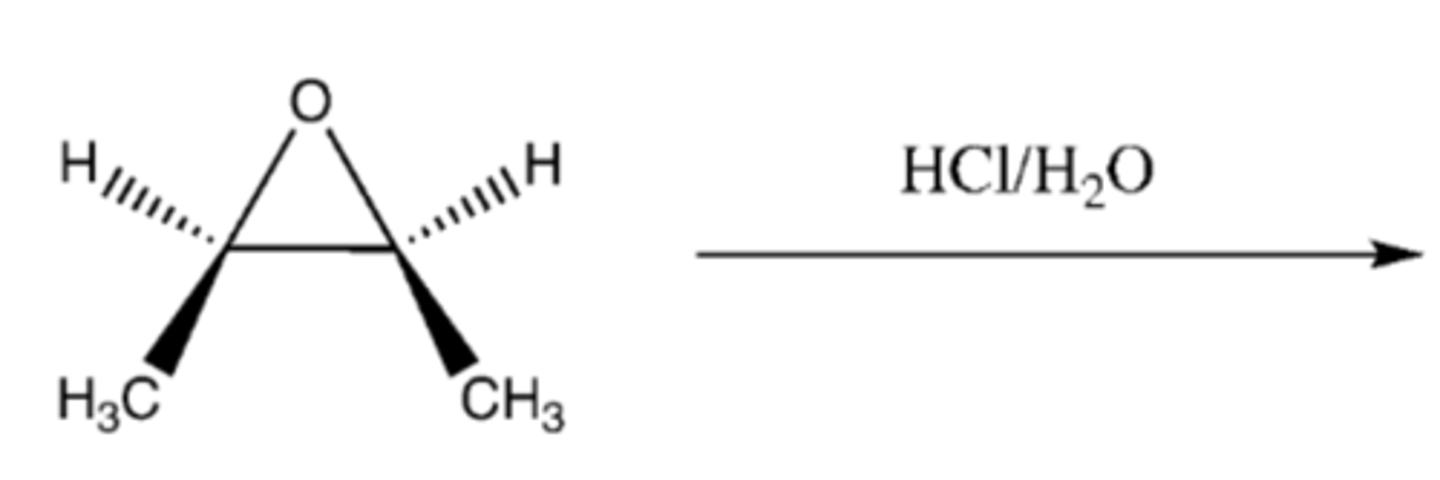
1) lone pairs from oxygen attack H from H-Cl
2) H2O attacks carbon adjacent to oxygen SN2 style
3) OH3+ group is deprotonated by
-OH groups are anti
-practice mechanism!!
epoxide + HCl/H2O
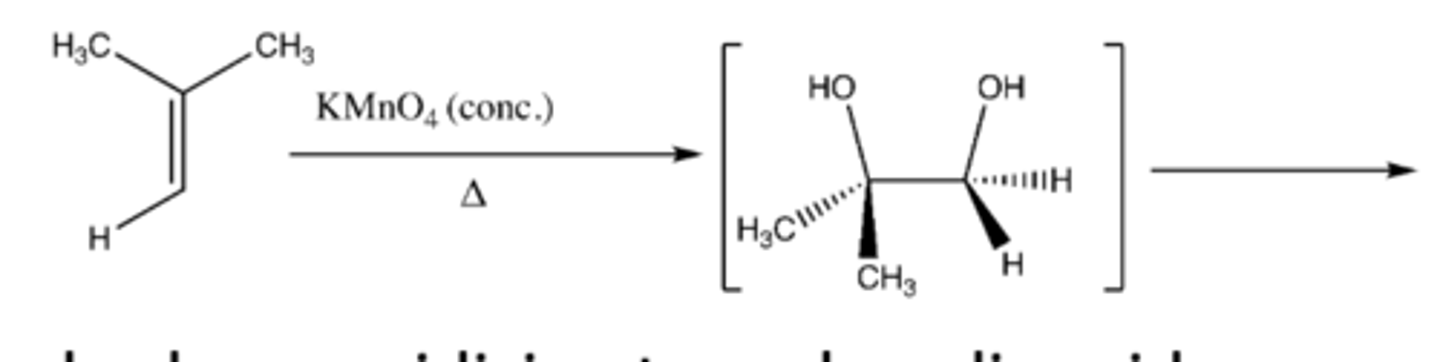
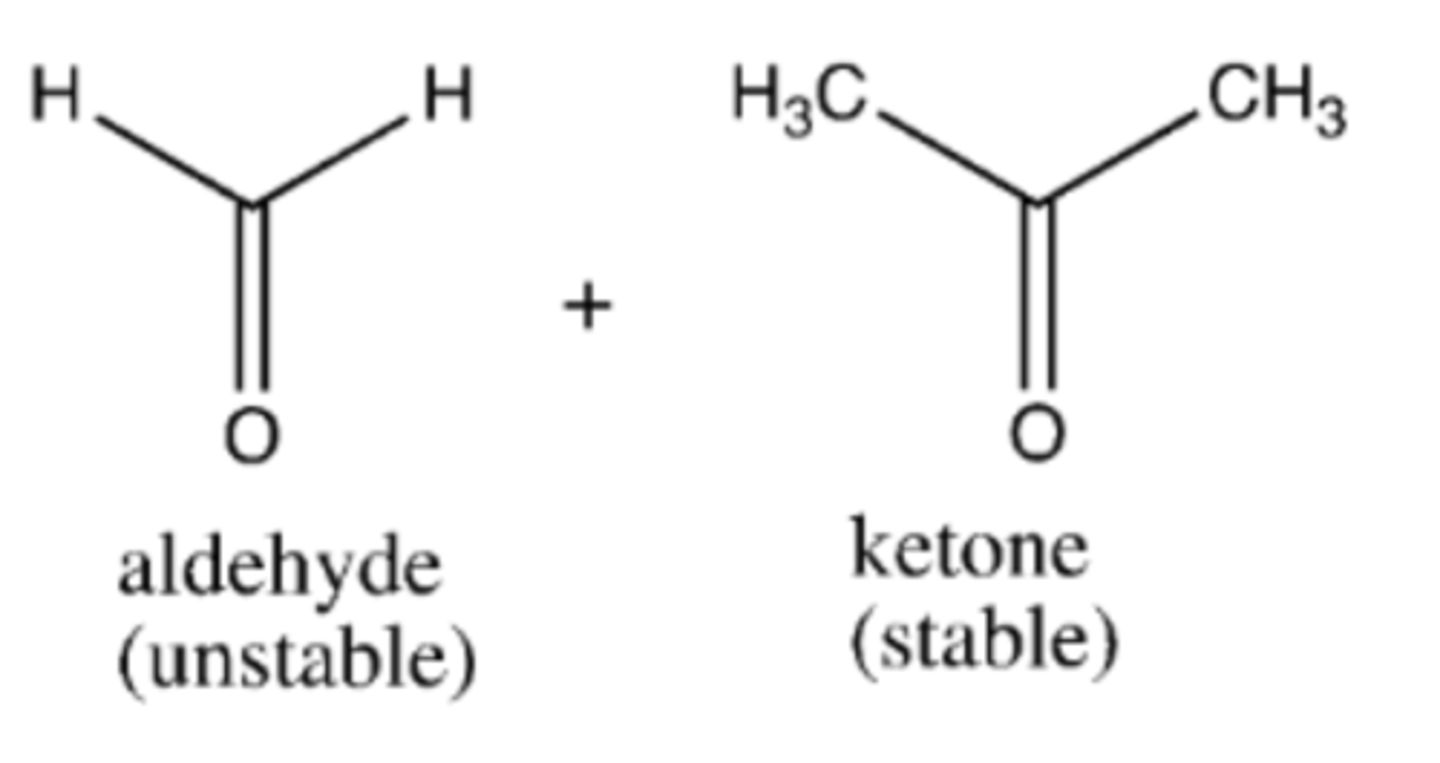
-Alkene-->Ketones/Aldehydes
-forms a stable ketone and an unstable aldehyde
-aldehyde keeps oxidizing to carboxylic acids
alkene + KMnO4 (conc) and heat
-split pi bond in half
-carbon that once had pi bond now has a pi bond attached to an oxygen
-practice mechanism
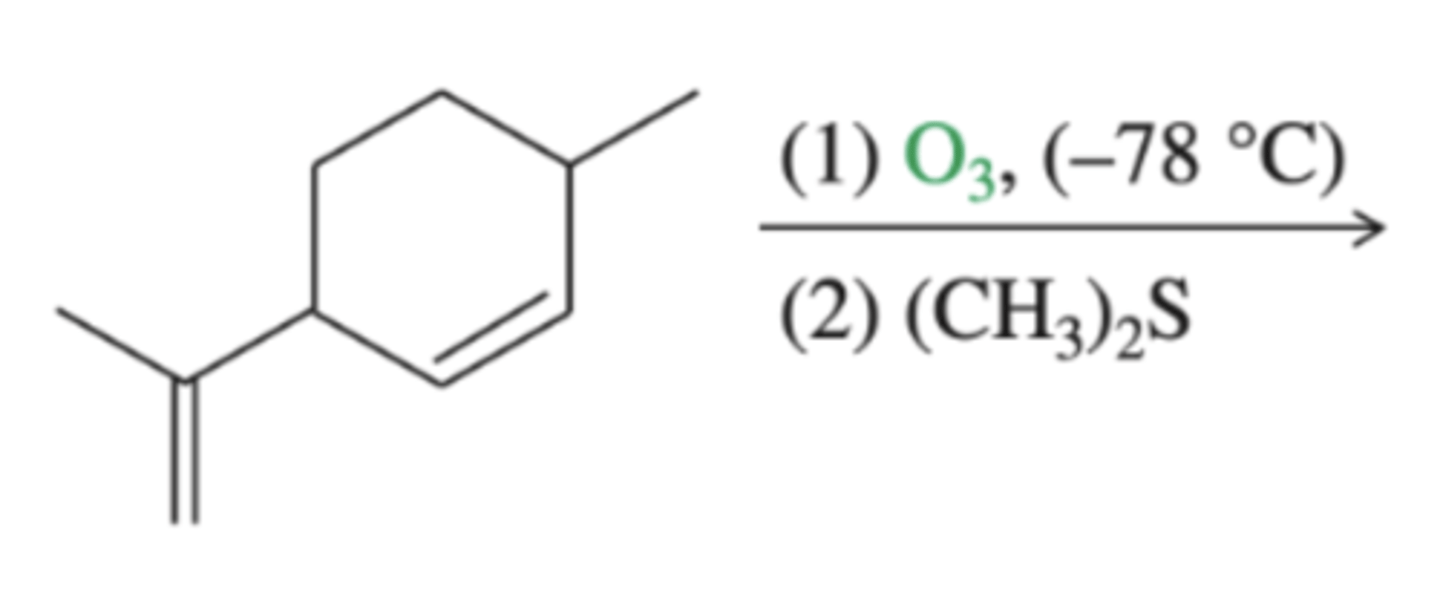
alkene + (1) O3 (2) (CH3)S (also known as DMS)
alkynes (also known as acetylenes)
-hydrocarbons that contain CC triple bonds
-similar chemistry to alkenes
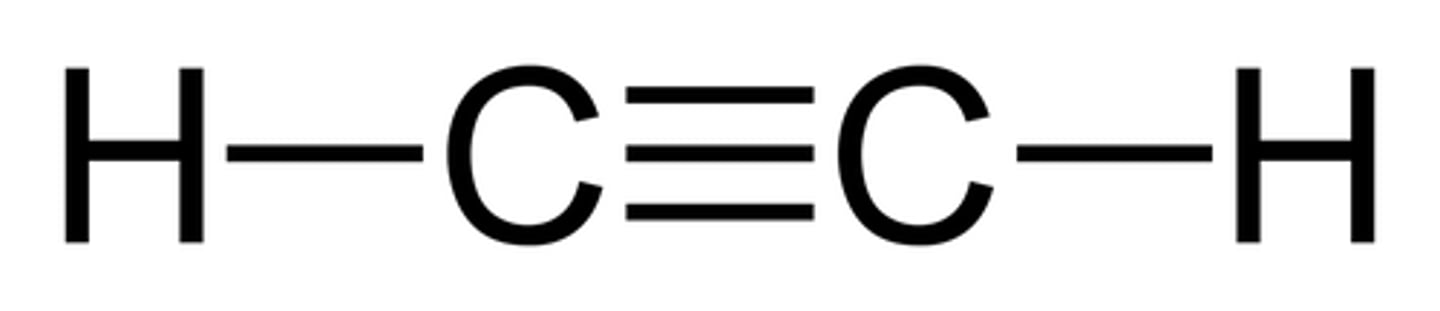
-Similar to alkenes: find the longest continuous chain that includes the triple bond and change the -ane to -yne
-The position of the triple bond is designated by its lower-numbered carbon atom
Naming Alkynes
-alkynes have much more acidic proton because C(sp)-H carbons have more s character and stabilize conjugate bases (anions) better than C(sp2)-H
Acidity of Alkynes
-alkene-->alkyne
-mechanism: double elimination (loss of LG, base attacks H and pi bond forms)
-can be deprotonated by STRONG BASES [(NaNH2) sodium amide]; hydroxide ions are NOT strong enough to deprotonate these weak acids
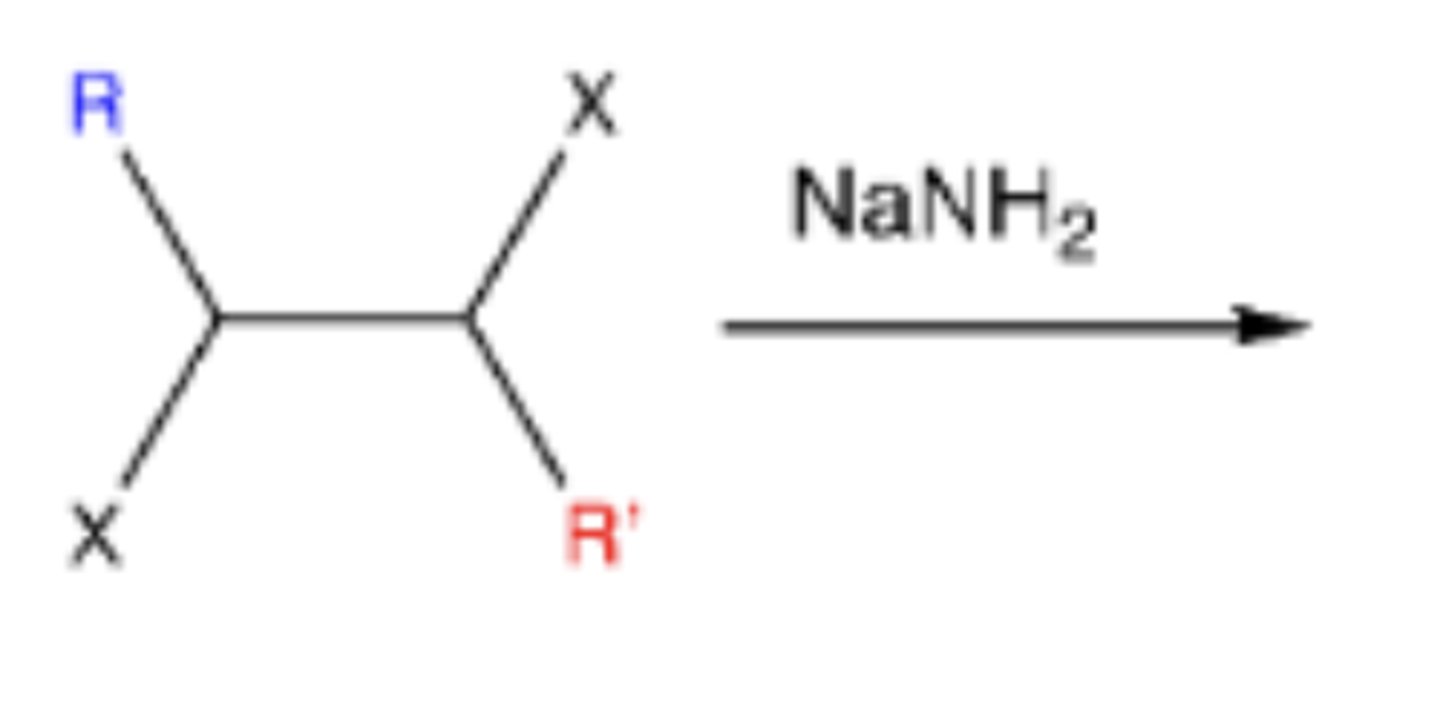
vicinal dihalide + NaNH2
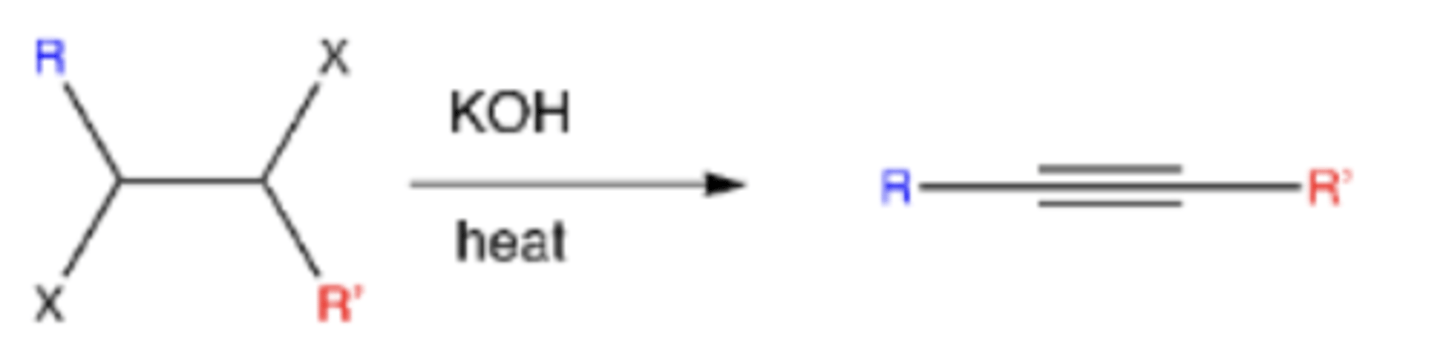
-alkene-->alkyne
-mechanism: double elimination (loss of LG, base attacks H and pi bond forms)
-second elimination is very slow (you need heat for the second elimination to occur)
vicinal dihalide + KOH and heat
strong
acetylide ions are _____ nucleophiles; hidden within acetylene
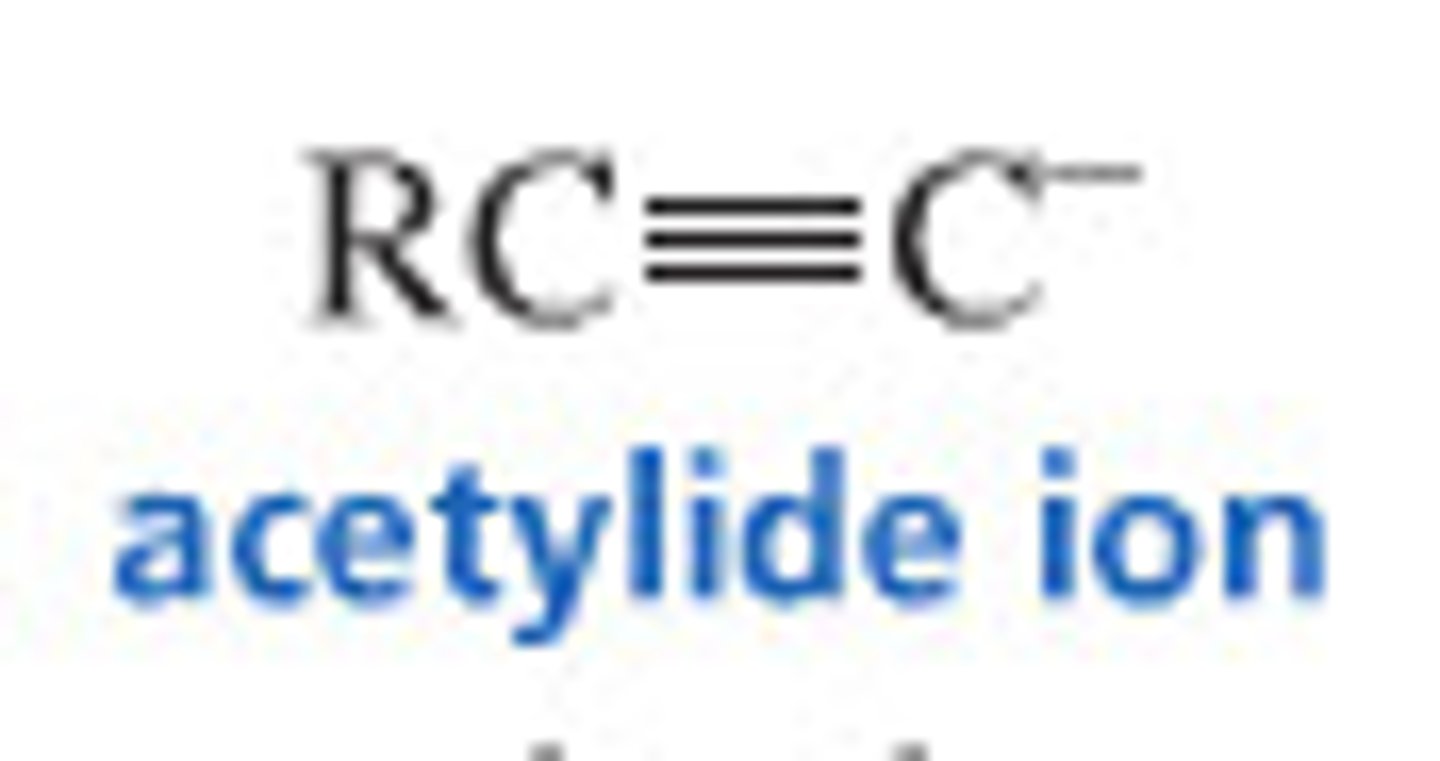
-synthesis of alkylated acetylenes
-R-X must be a methyl or primary alkyl halide
-mechanism:
1. NH2 attacks H on acetylene to form acetylide ion
2. acetylide ion attacks R and R-X bond breaks (X- is formed)
acetylene + (1) NaNH2 (2) R-X
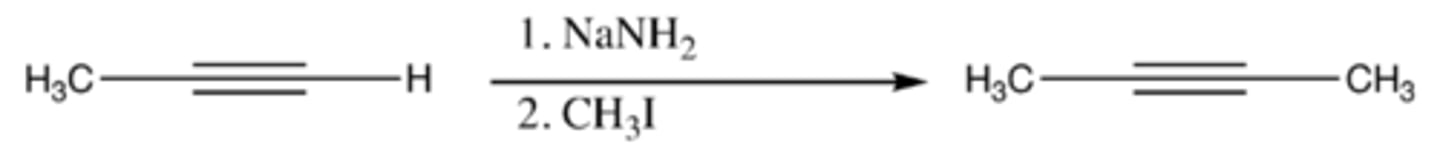
carbonyls
_______ are quite electrophilic substrates that are attacked by nucleophiles
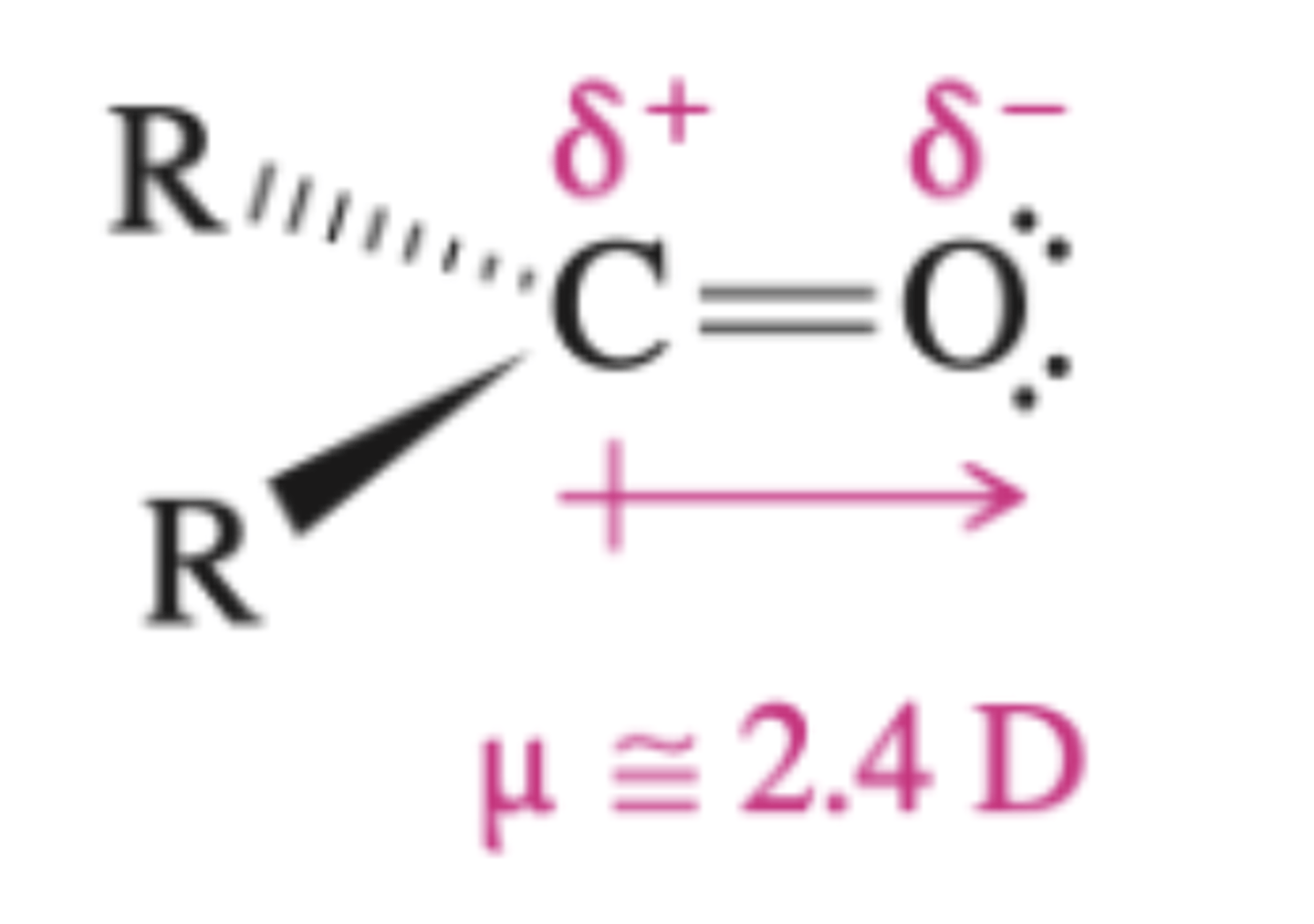
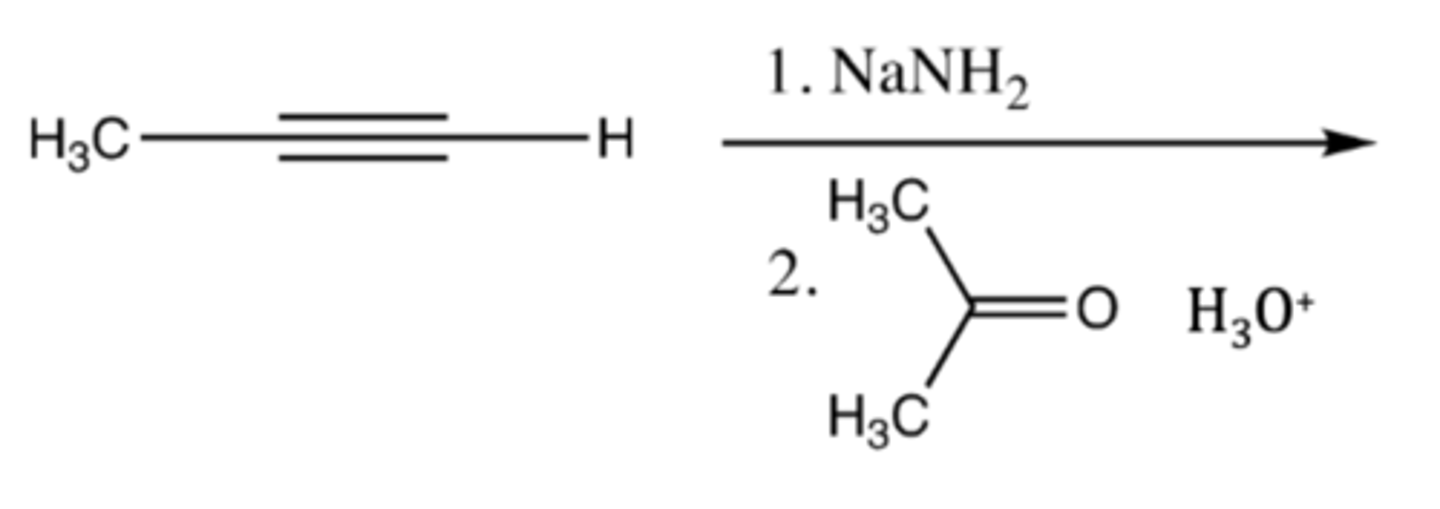
Mechanism:
1. 1. NH2 attacks H on acetylene to form acetylide ion
2. acetylide ion attacks electrophilic part of carbonyl (pi bond electrons are transferred to oxygen)
acetylene + (1) NaNH2 (2) carbonyl
2, 4
For additions to/across alkyne pi-bonds, convert a pi-bond to __ sigma bonds (or 2 pi-bonds to __ sigma bonds)
-Alkyne-->alkane
-4 H's added
-similar to alkene hydrognation
-can't stop the reaction at the alkane stage
alkyne + (1) H2 (2) Pt, Pd, or Ni
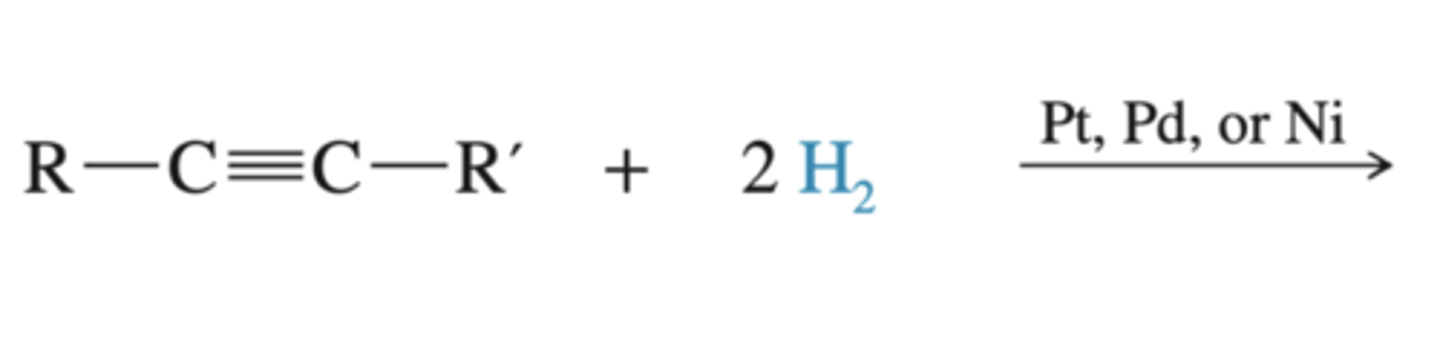
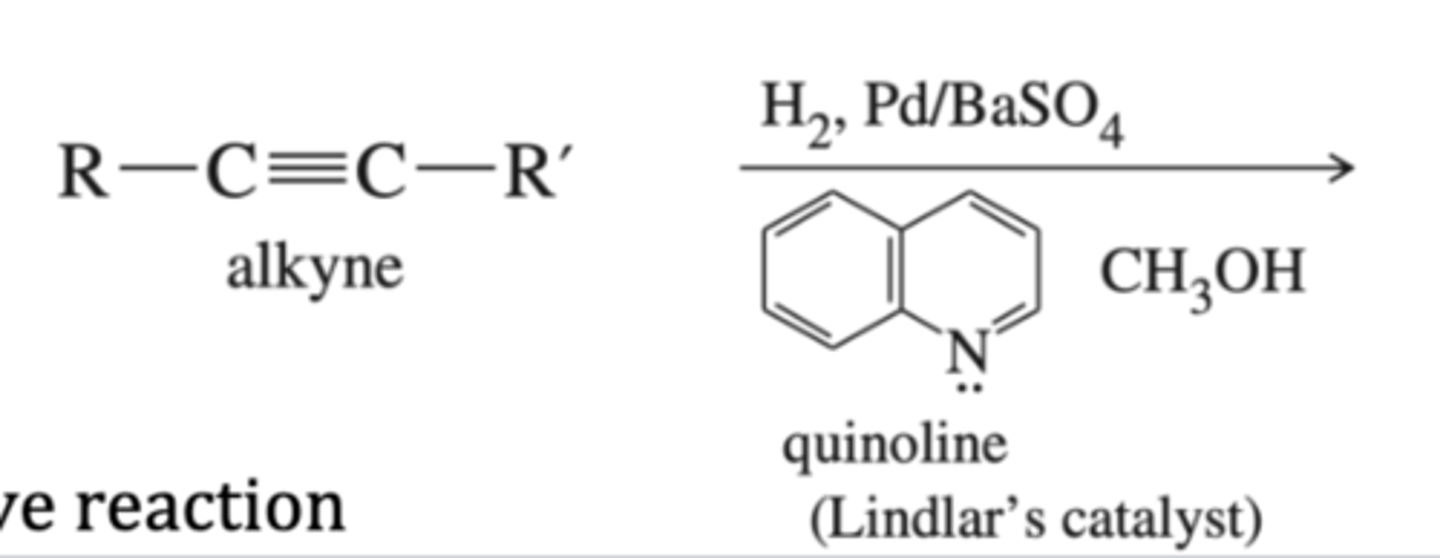
-Alkyne-->Alkene
-2 H's added (partial hydrogenation)
-forms CIS alkene
alkyne + Lindlar's catalyst
-Alkyne-->alkene
-2 H's added
-TRANS alkene formed
alkyne + Na/NH3
-Alkyne-->Dibromoalkene
-froms cis and trans alkene
-Non-selective, hard to control
alkyne + Br2
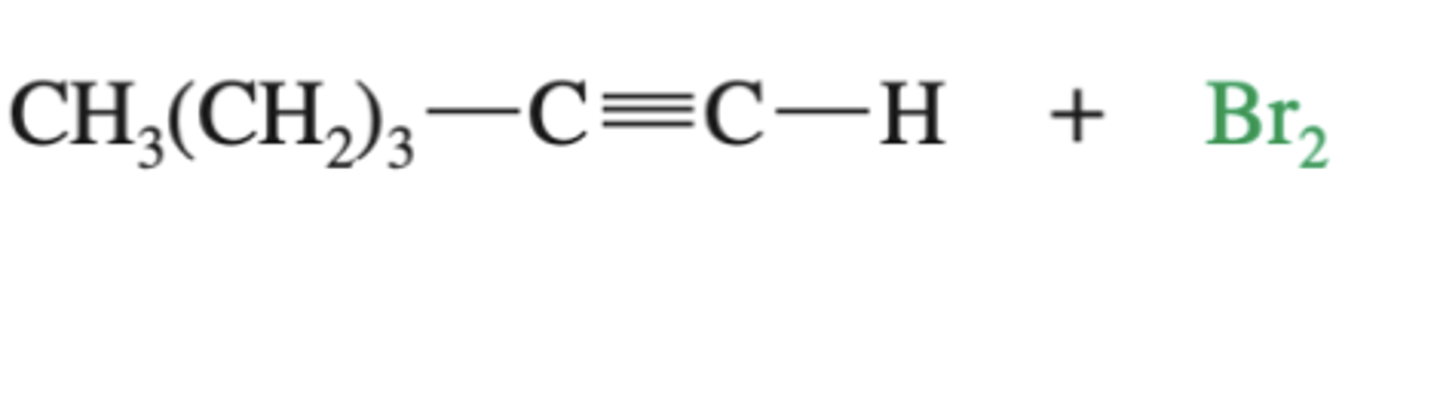
-alkyne-->terachloroalkane
-4 Cl groups added
-does not stop at alkene
alkyne + 2Cl2
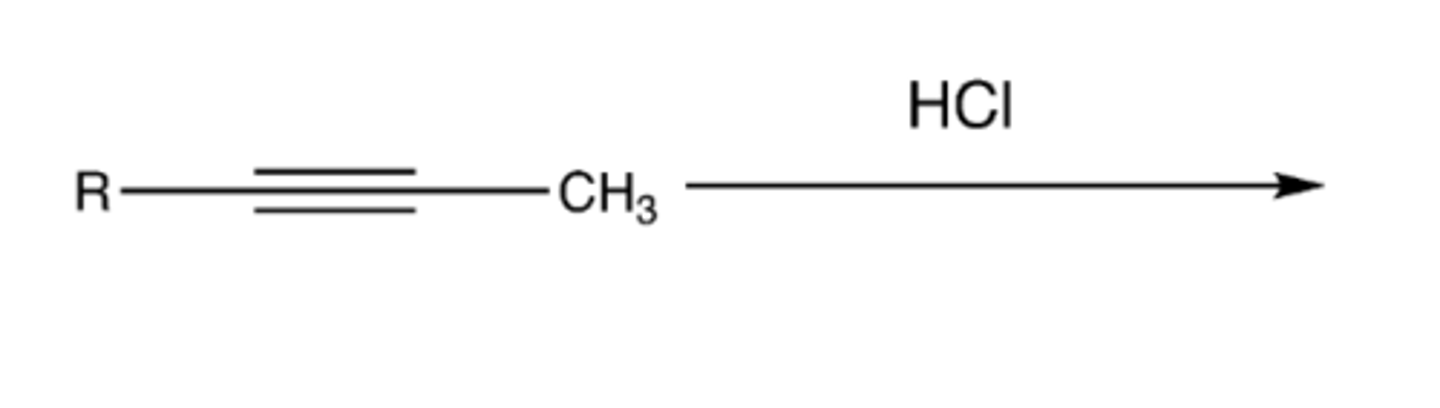
-Alkyne-->Alkene
-Addition of H and Cl
-Markovnikov addition
-Mix of cis/trans (Z/E) alkene
-practice mechanism!!
alkyne +HCl
E
trans
Z
cis
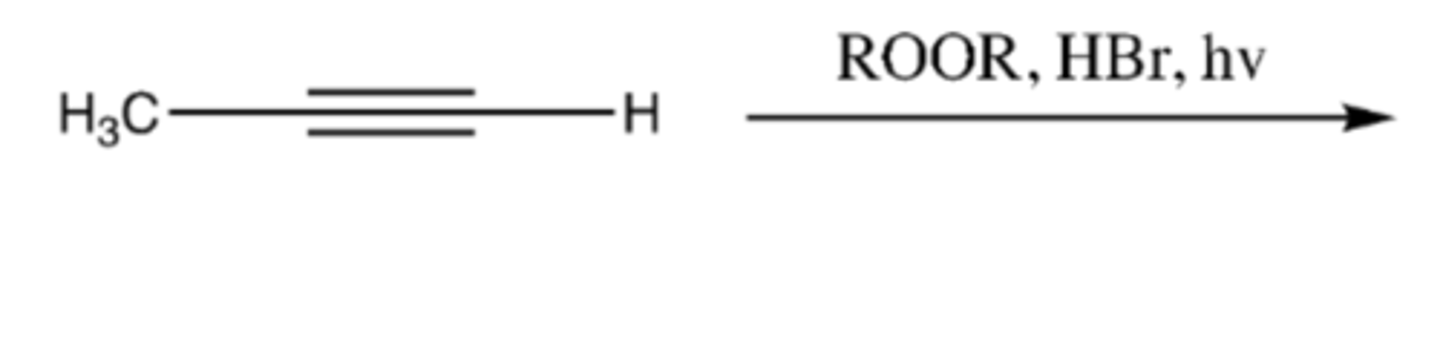
-Alkyne-->Alkene
-H and Br added
-anti-Markovnikov addition
-mix of E/Z
-Practice mechanism: free radical
alkyne + ROOR, HBr, hv
-alkyne-->enol-->keto
-enols are unstable and can isomerize to the keto form in the presence of HCl/H2O
-practice mechanisms
alkyne + 1. H2O 2. HgSO4, H2SO4
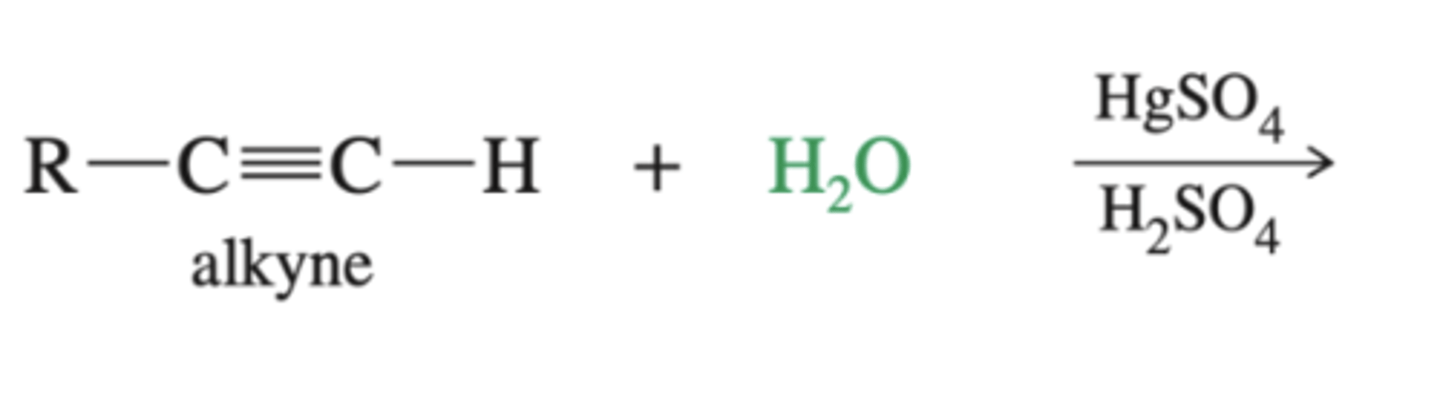
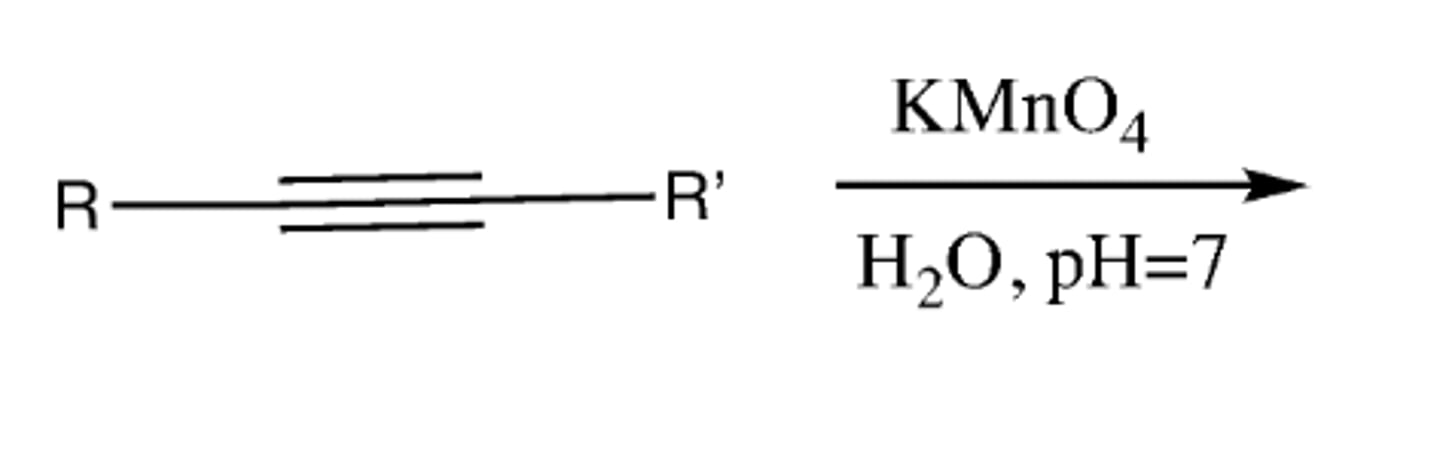
-Alkyne-->diketone
-if solution is too warm or basic, the diketone is oxidized
alkyne + KMnO4, H2O, neutral
-Alkyne-->diketone-->carboxylate salts
-alkyne + KMnO4
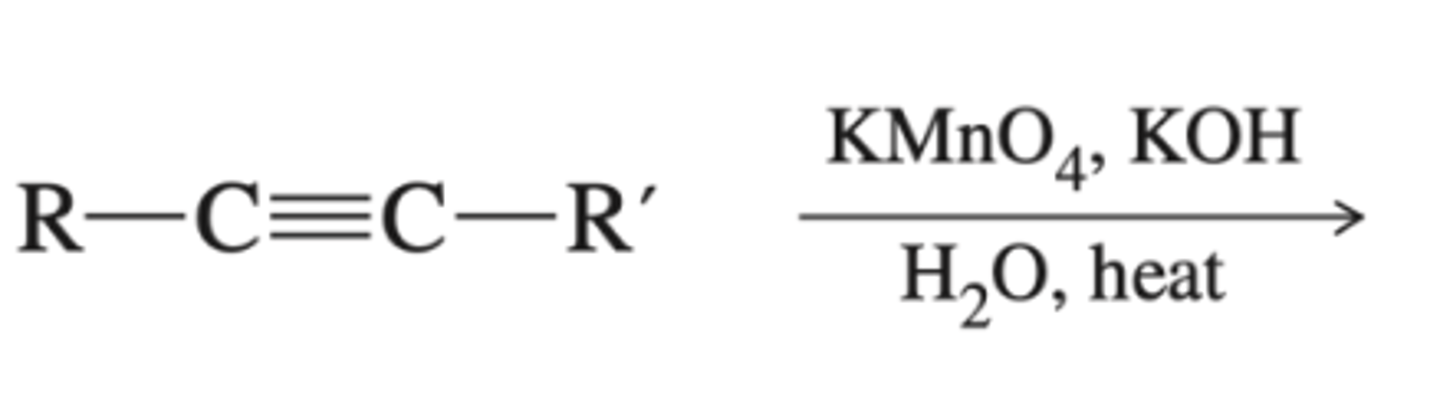
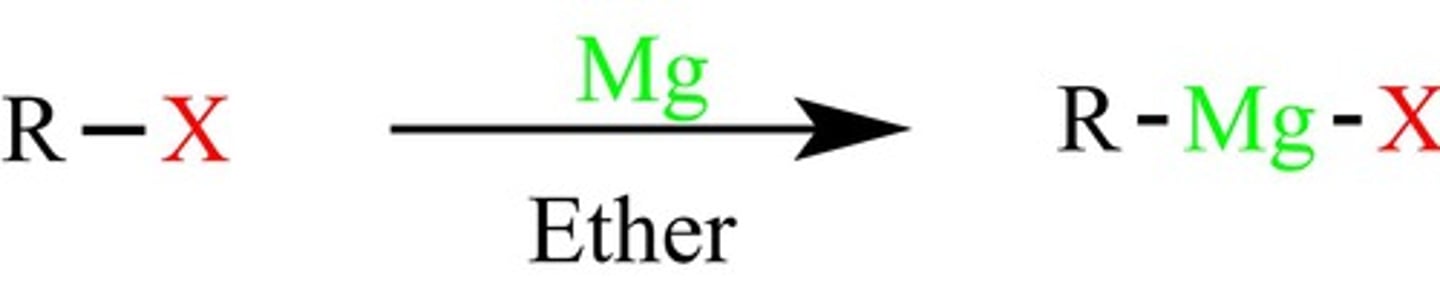
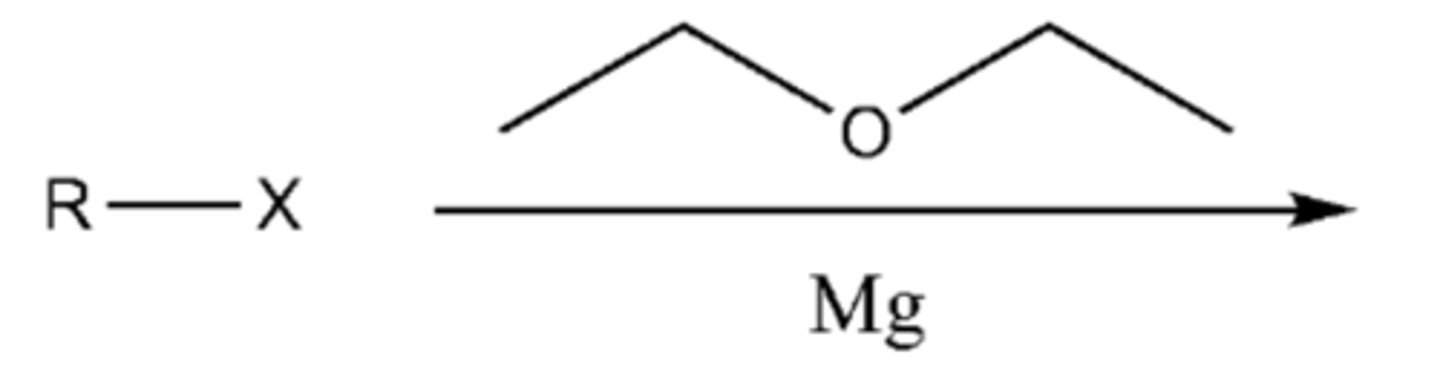
Grignard reagent
An alkyl magnesium halide that converts carbonyls to alcohols by adding alkyl groups (forms C-C bonds)
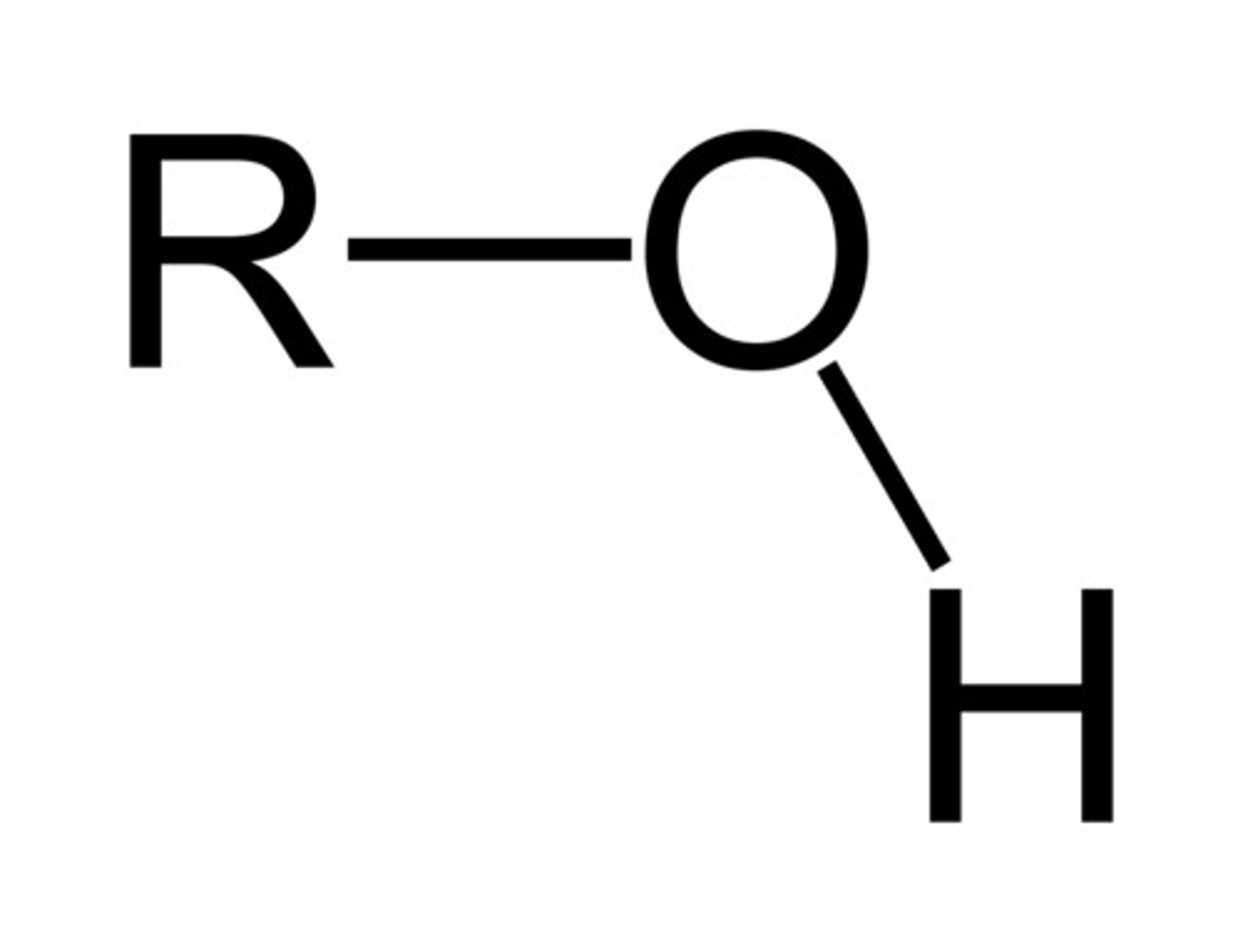
alcohol
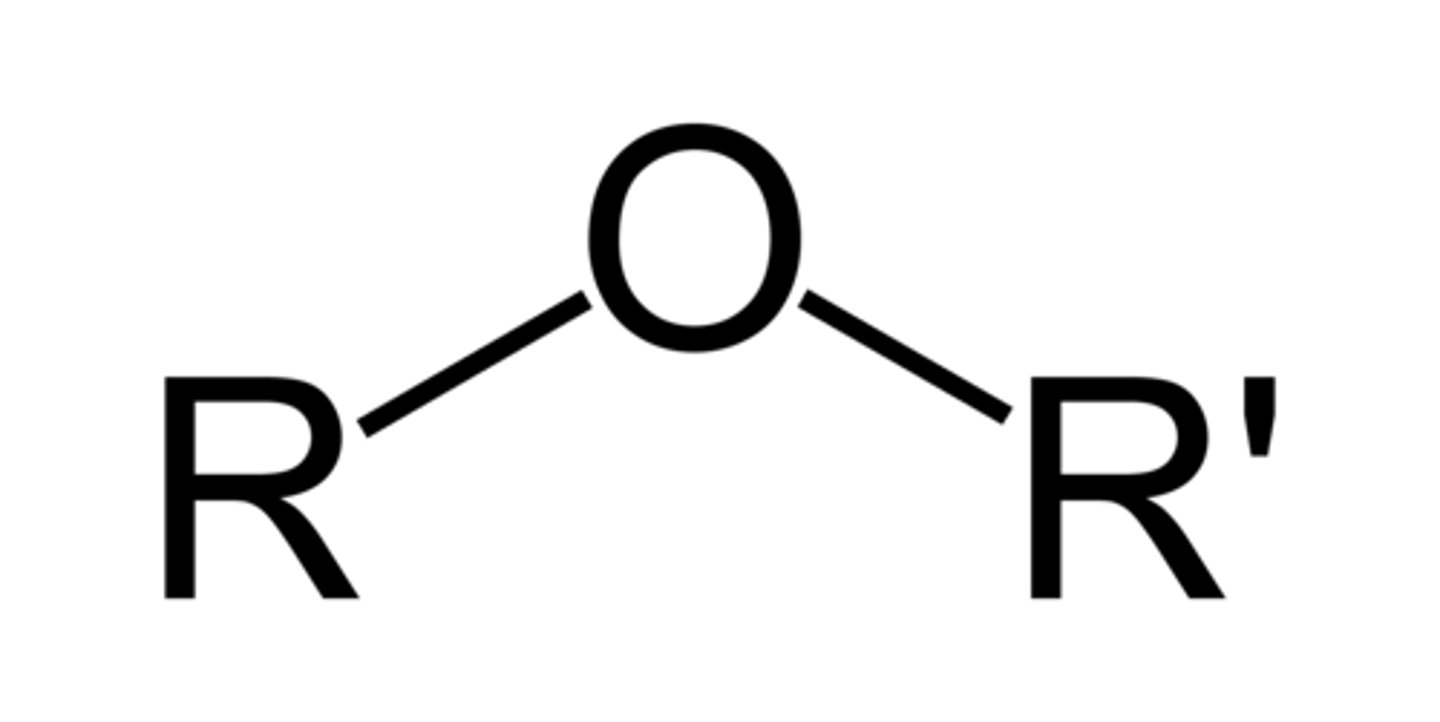
ether
aldehyde
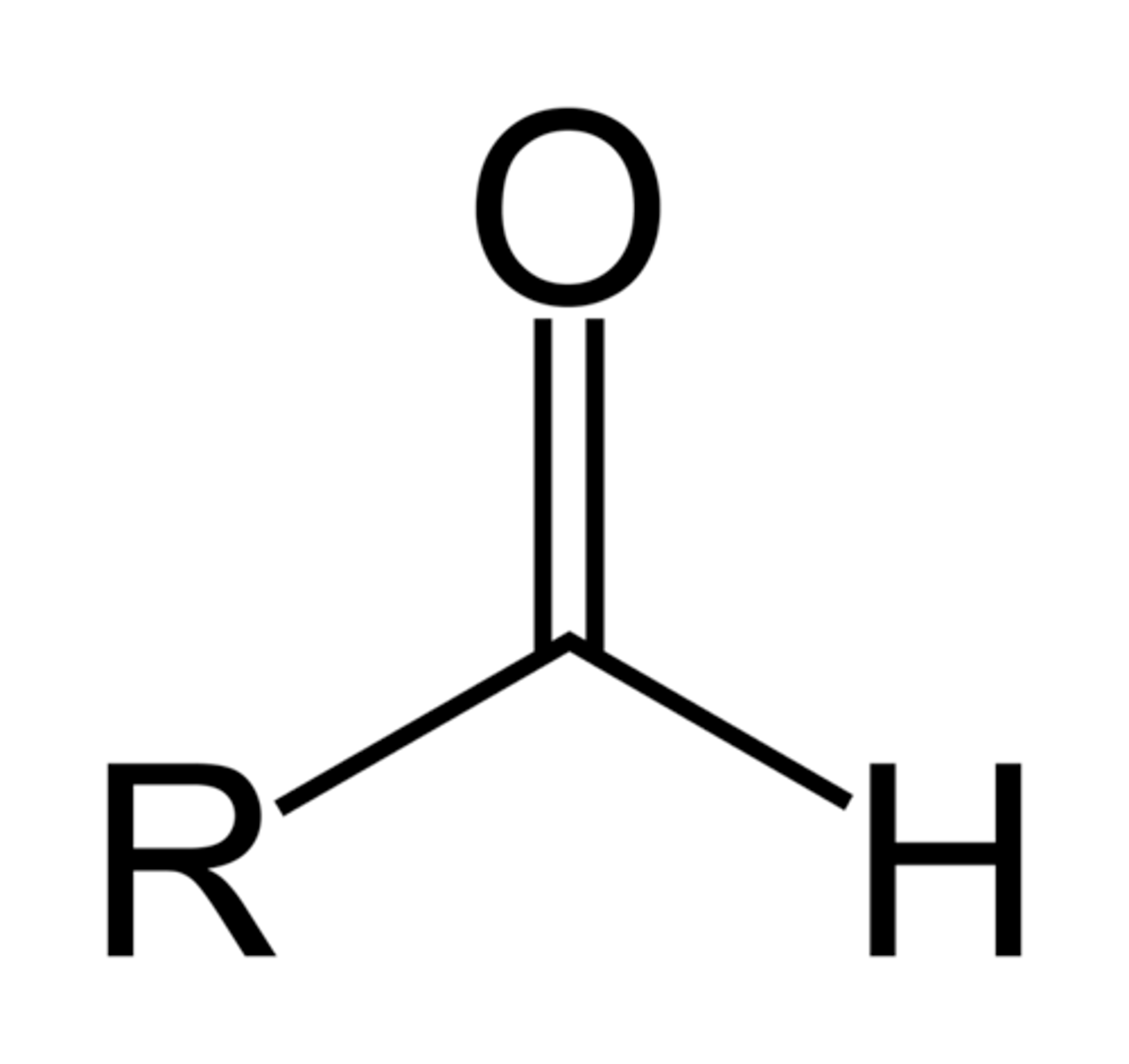
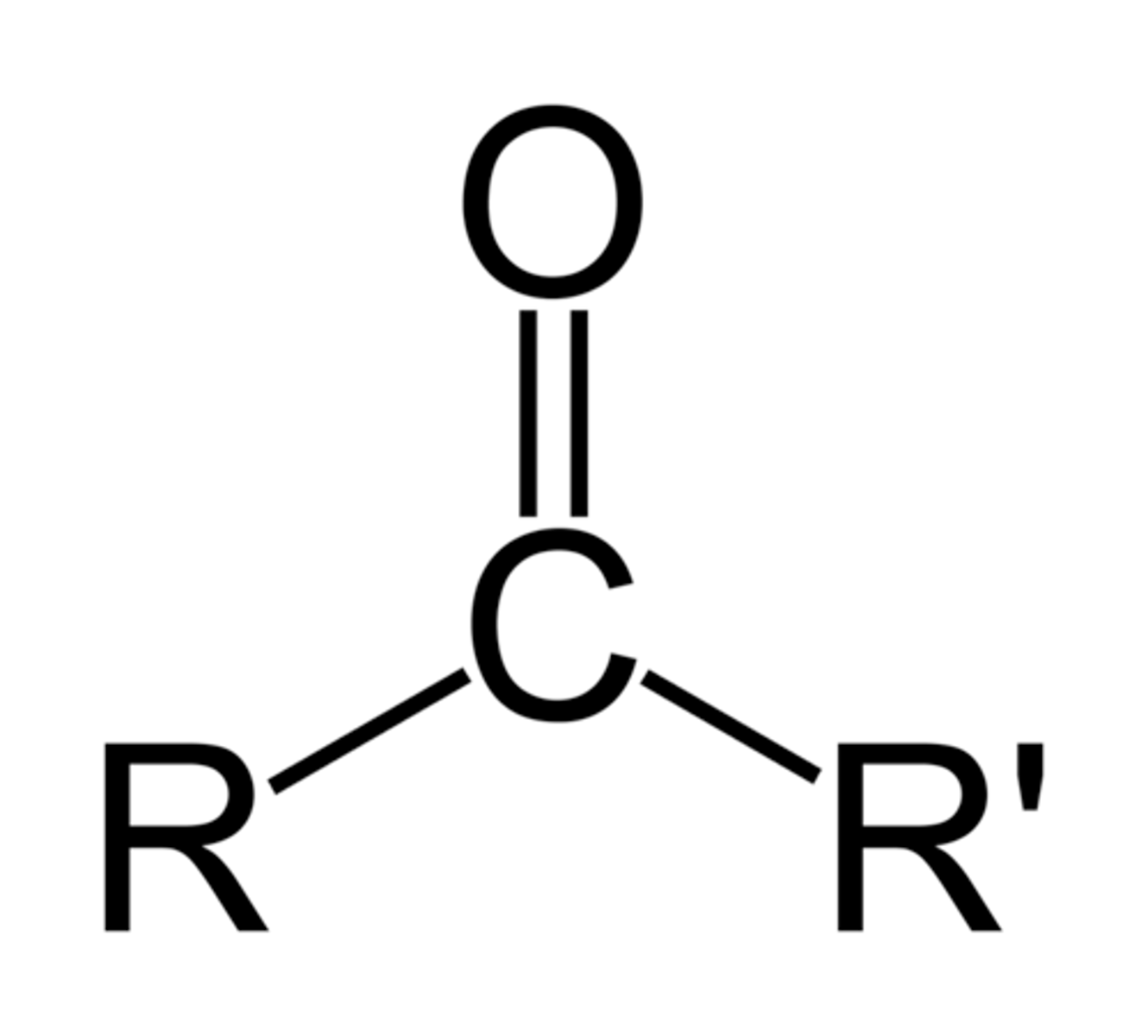
Ketone
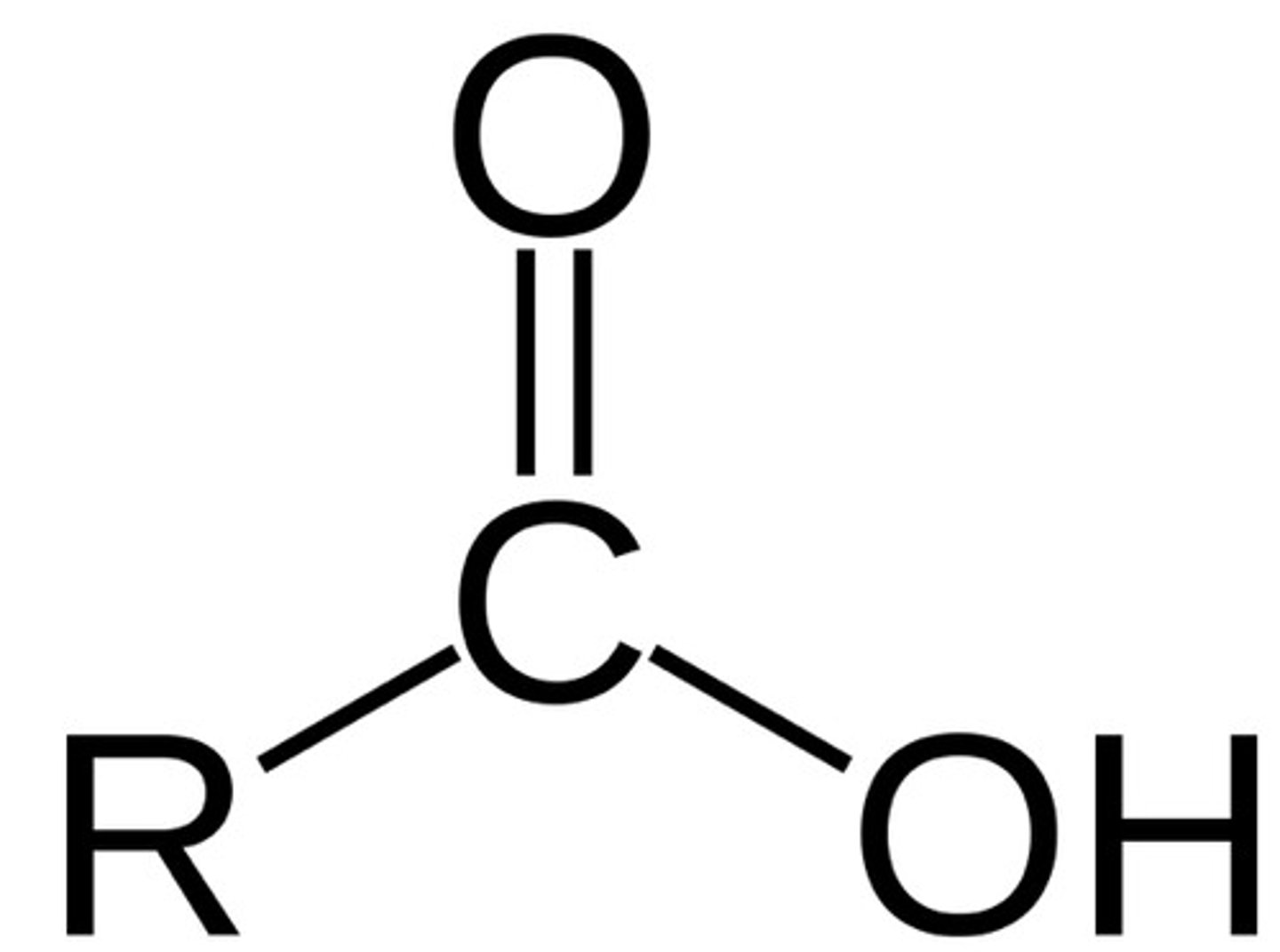
Carboxylic acid
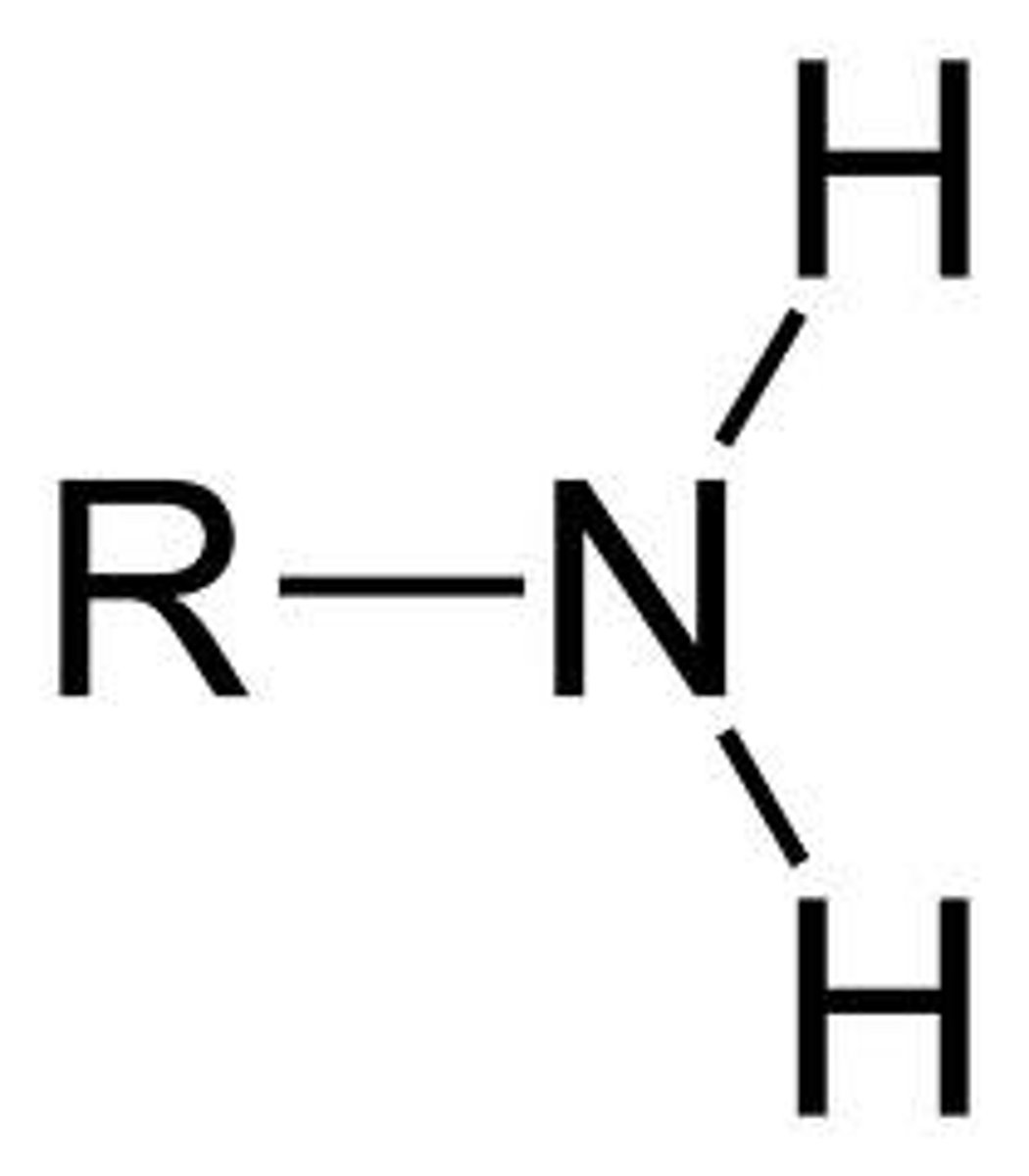
Amine
Amides
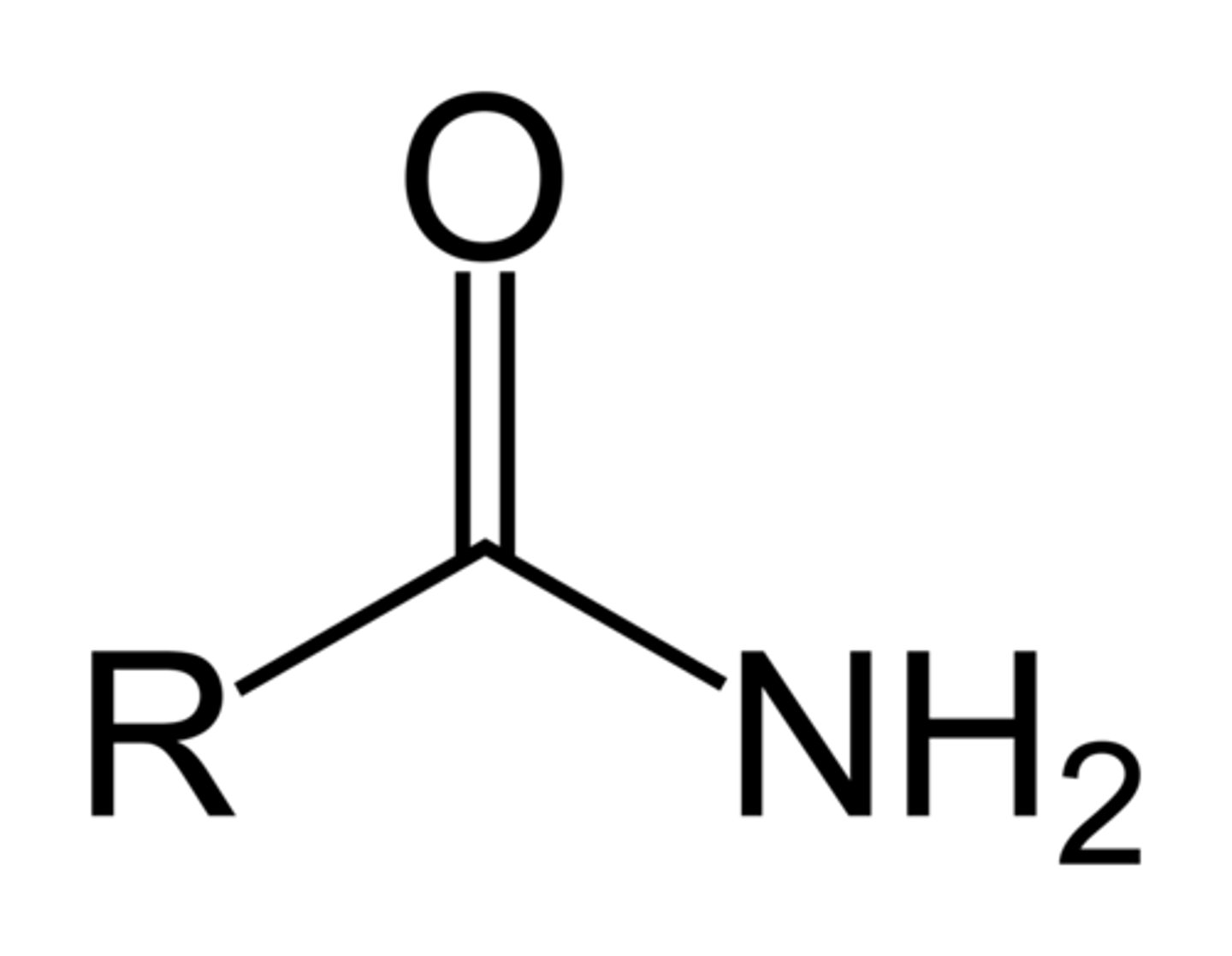
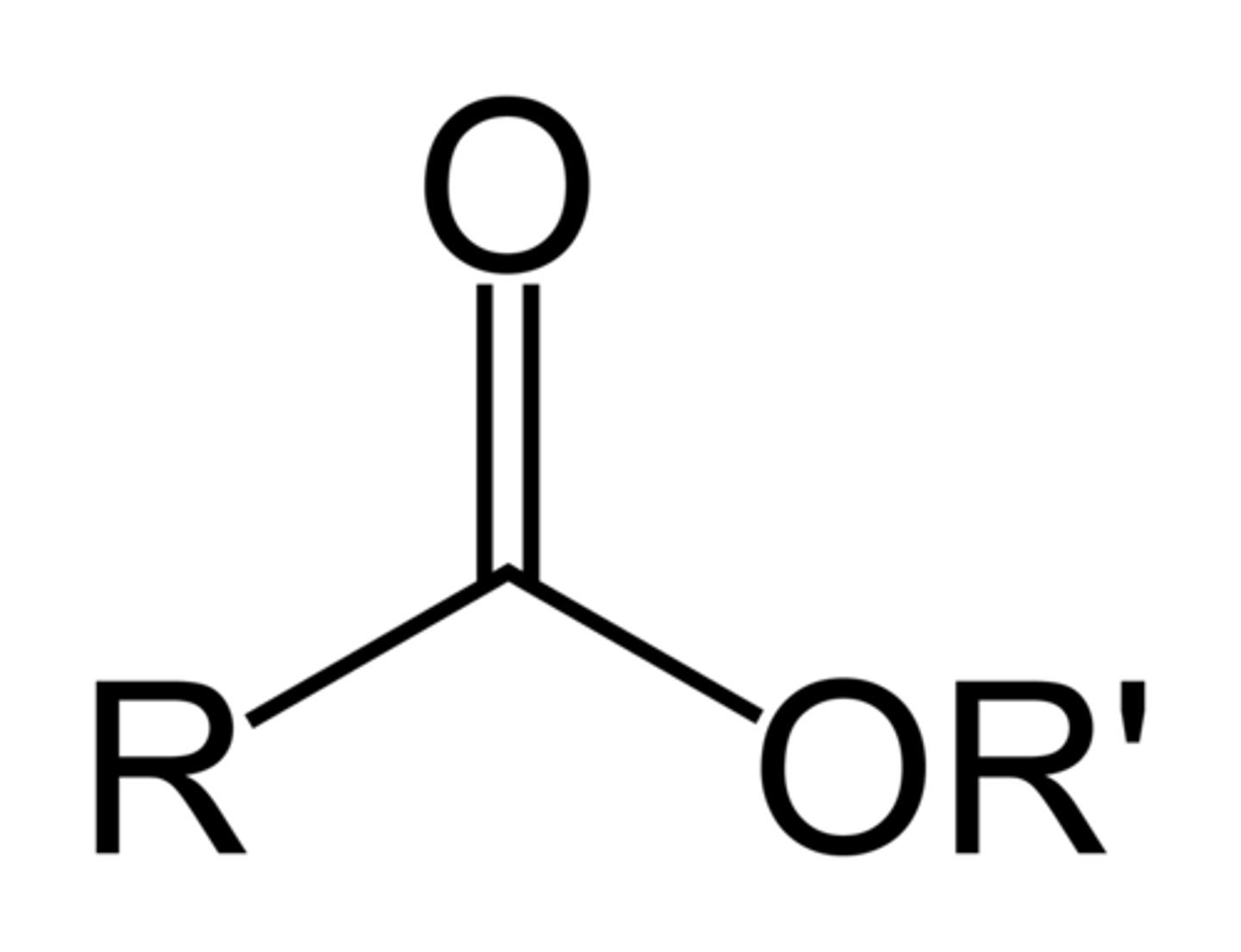
ester
-forms Grignard reagent (R-Mg-X)
-Metals are electropositive and the C-M bond is polarized with a partial positive on the metal)
-R reacts like a carbon nucleophile (Can form C-C bonds)
-
Gringard reagent + acetone
Gringard reagent + acid chloride
Gringard +Ester
ethers, epoxides
Gringards do not typically react with ________, but they do in the presence of ________
-forms alcohol with OH and R group anti to each other
epoxide + (1) RMgBr, ether (2) HCl, ether
NaBH4
hydride reagent that converts carbonyls to alcohols by adding H- ions
carbonyl
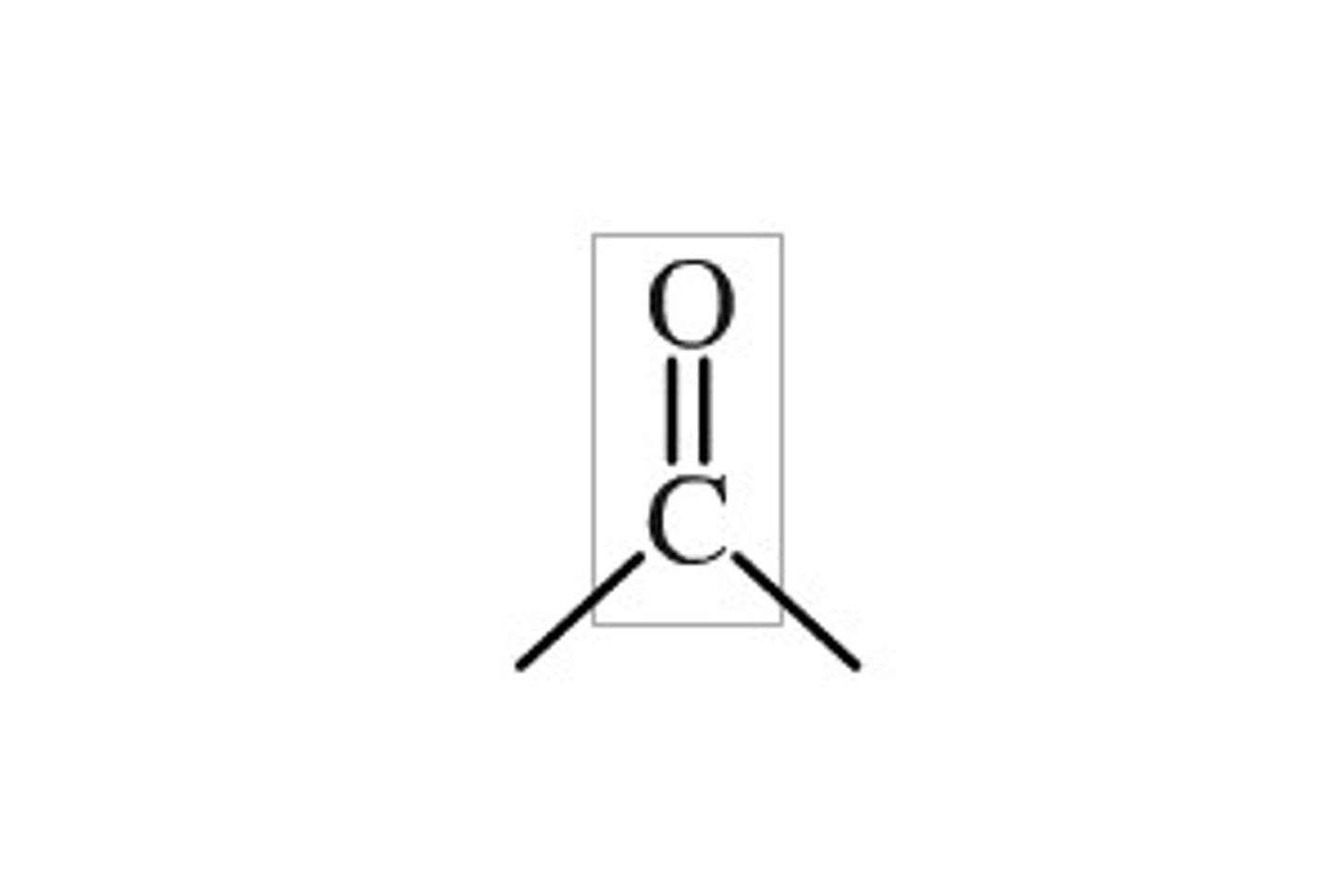
ketones, aldehydes,
NaBH4 reacts only with ________ and ________, ________ and ________ ________ are not reactive enough.
-produces a small amount of Br2
-forms alkyl halide
1. strong acid + H2O
2. (1) Hg(OAc)2 (2)NaBH4
preperation of Markovnikov alcohol from alkene
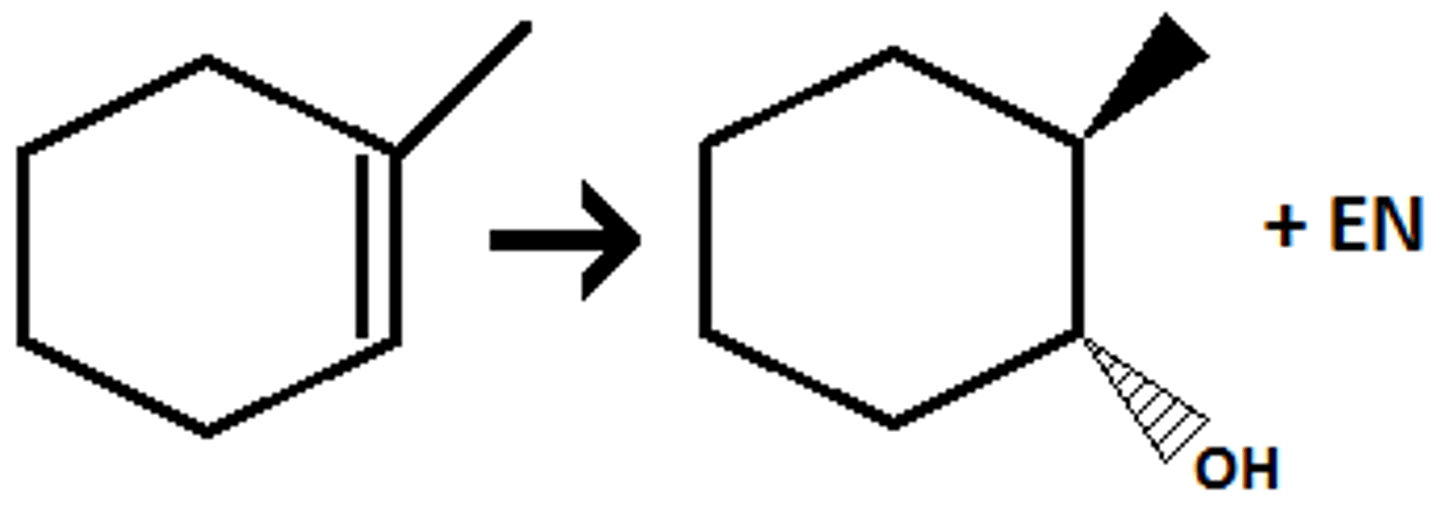
(1) BH3 THF (2) H2O2, NaOH
preperation of Anti-Markovnikov Alcohol, syn addition from alkene
cMPBA, peroxyacetic acid
preparation of epoxides from alkenes
CH3OOCH3, HBr, hv, 90 C (free radical chain reaction)
preparation of Markovnikov alkyl halide
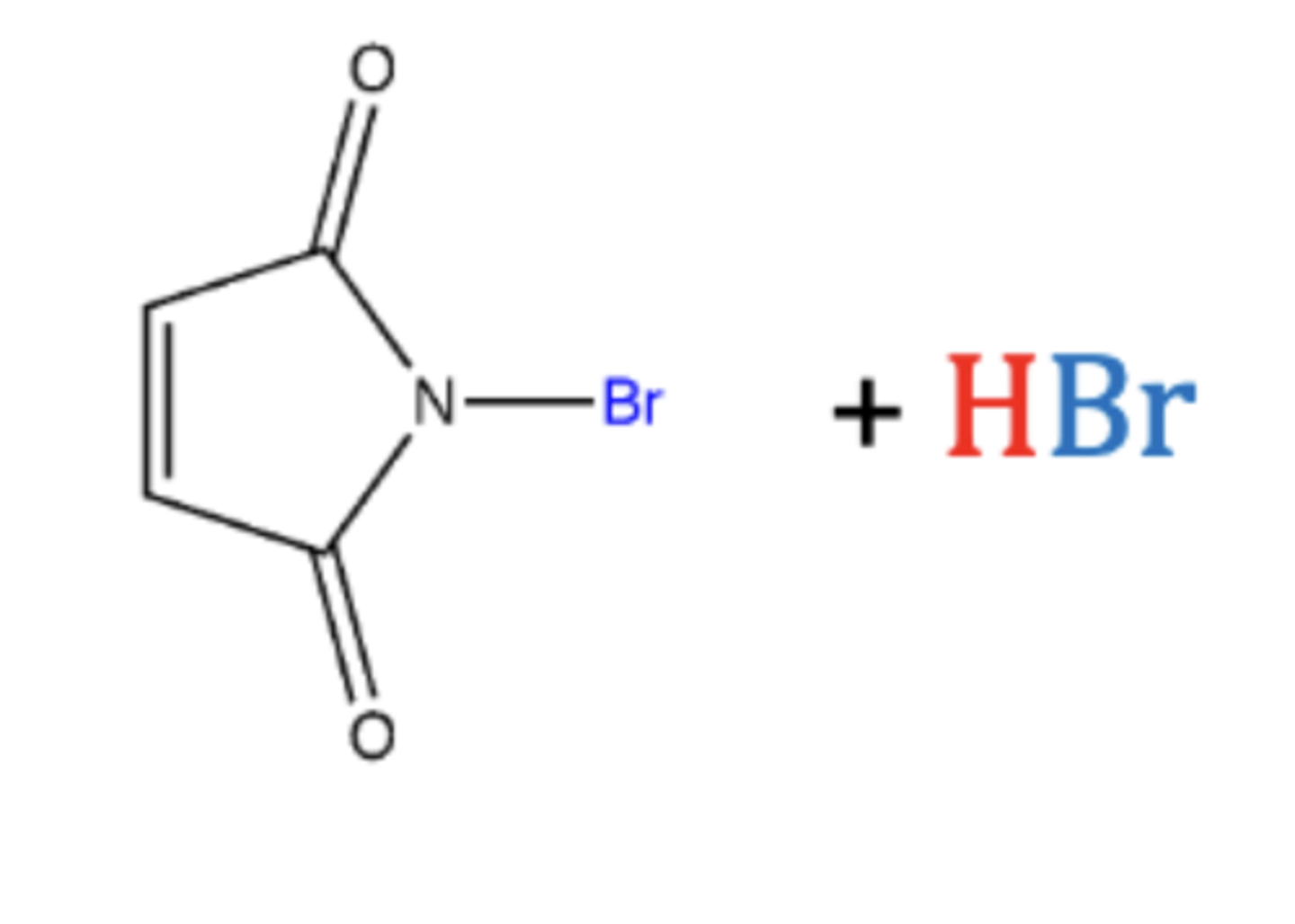
-NBS, hv
-free radical chain reaction
Preparation of alkyl halides (reagents)
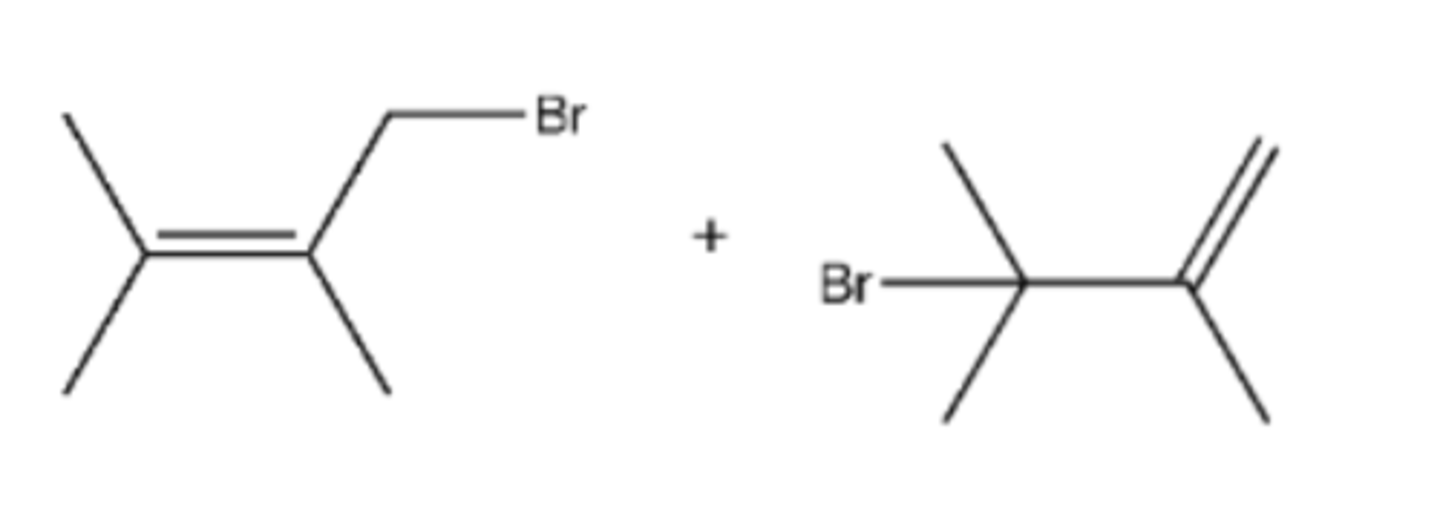
Br2
Preparation of anti dibromide from alkene
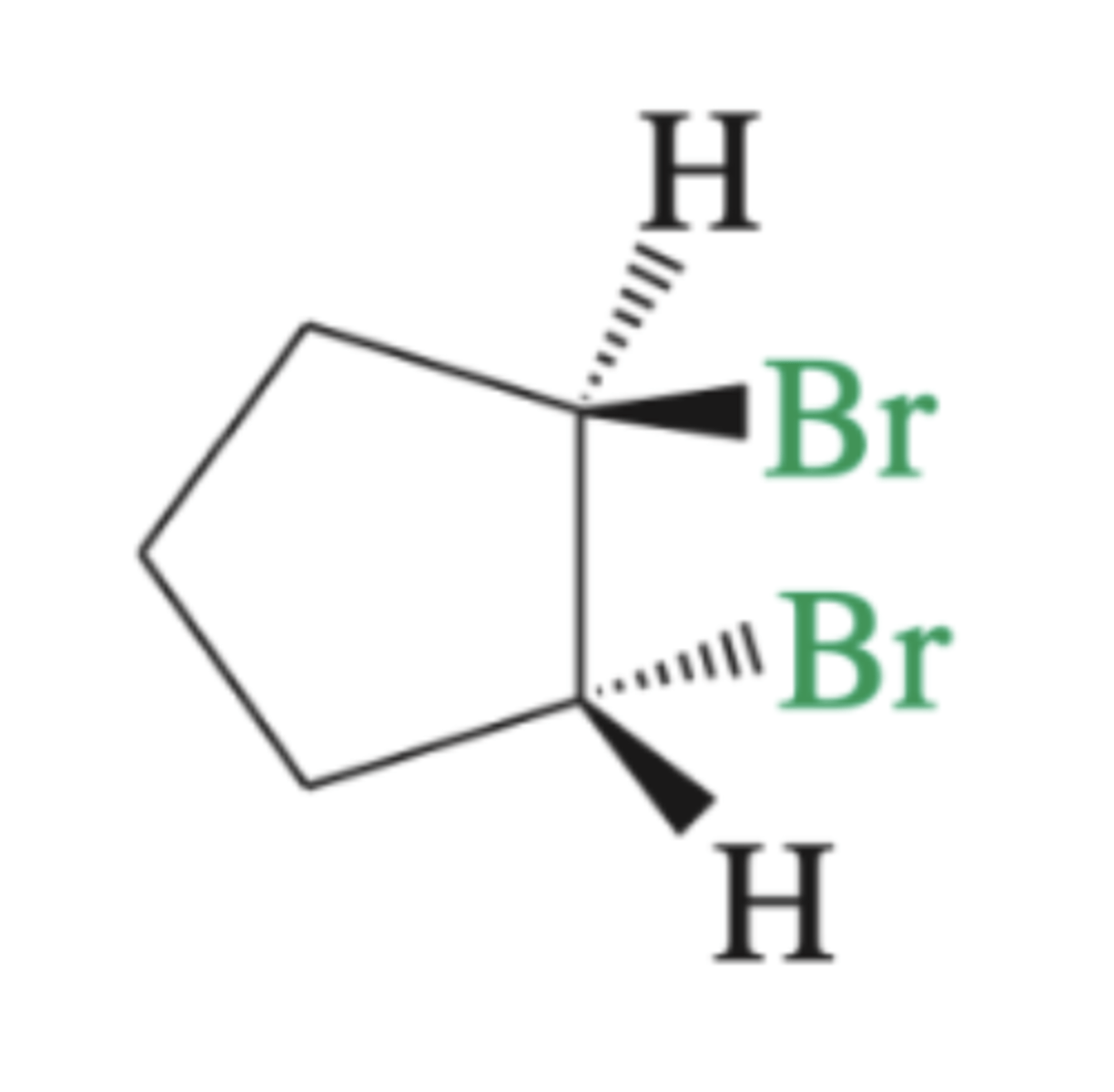
Br2, H2O
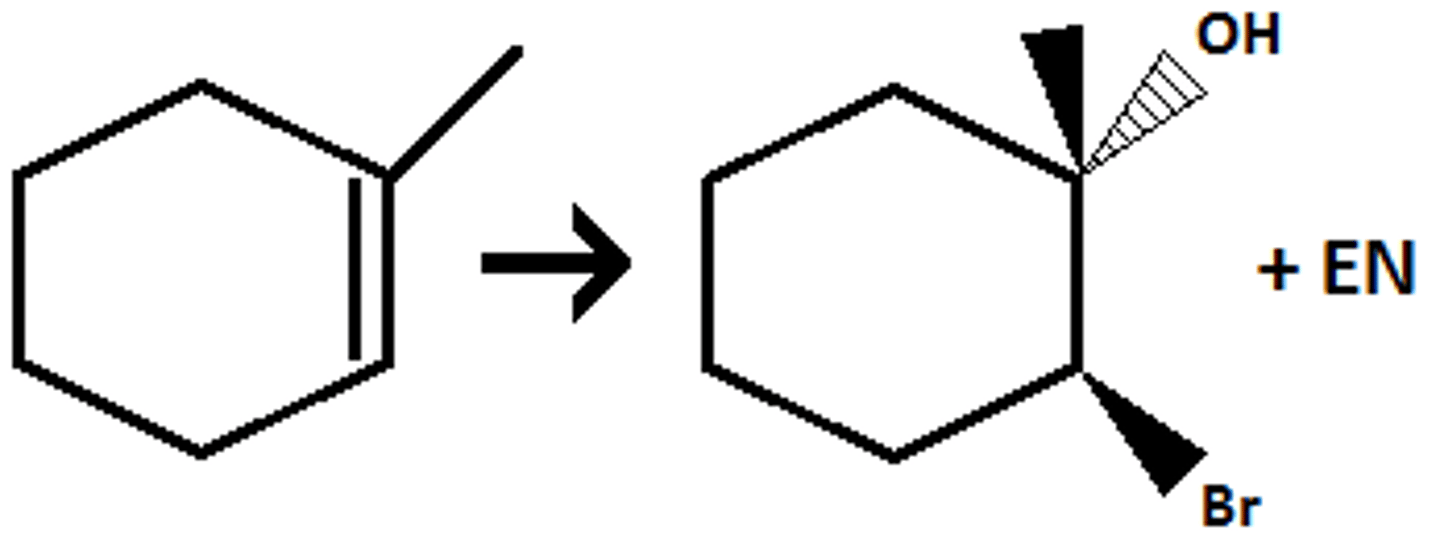
Preparation of a halohydrin from alkene (OH to more substituted C, anti addition)
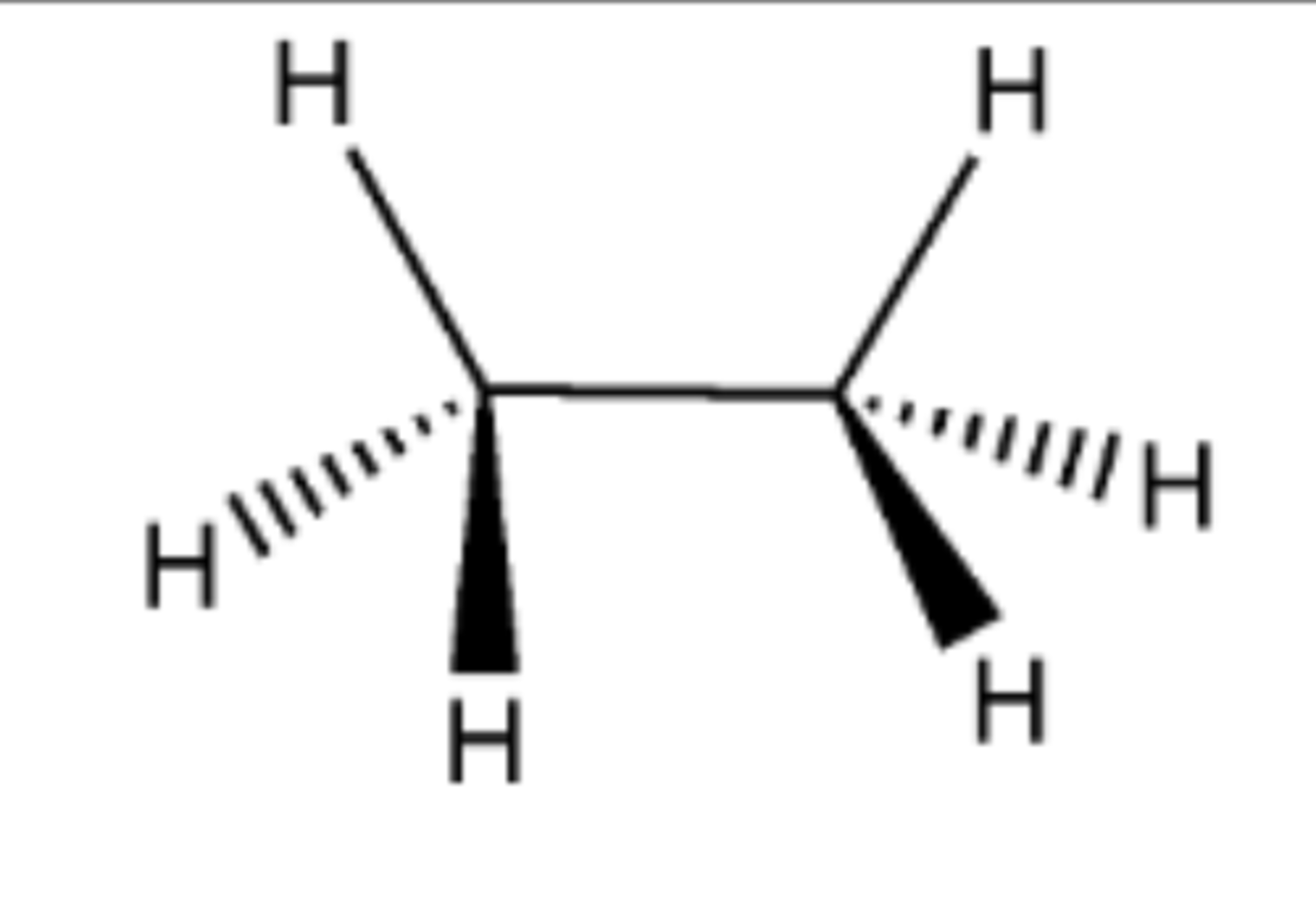
H2+ catalyst (Pd, Pt, Ni, or Wilkinson's)
Preperation of alkane from alkene (syn addition of 2 H)
CH2N2 (carbene) or CH2I2, Zn, CuCl
Preperation of cyclopropane from alkene
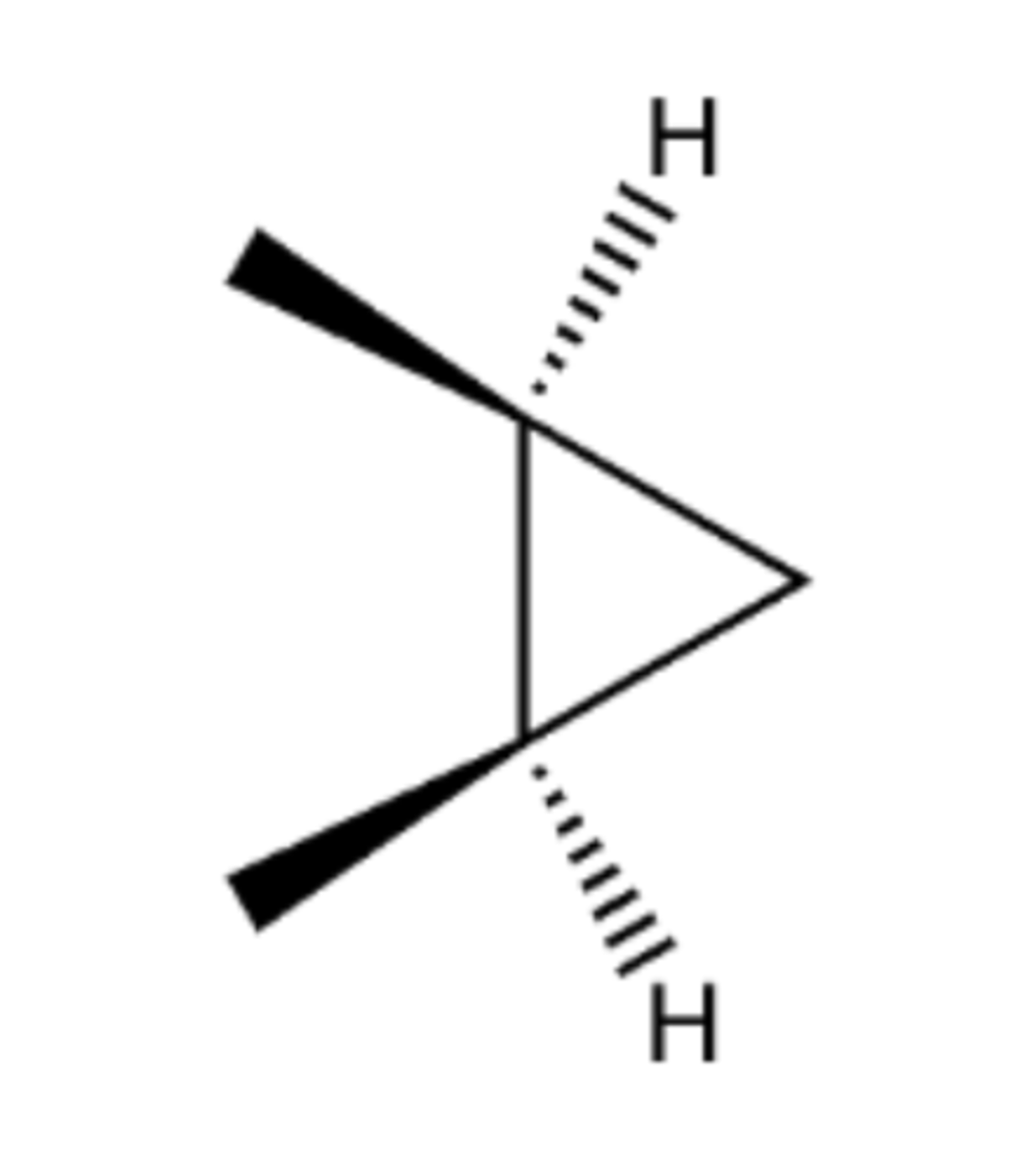
CH3Br3, KOH/H2O
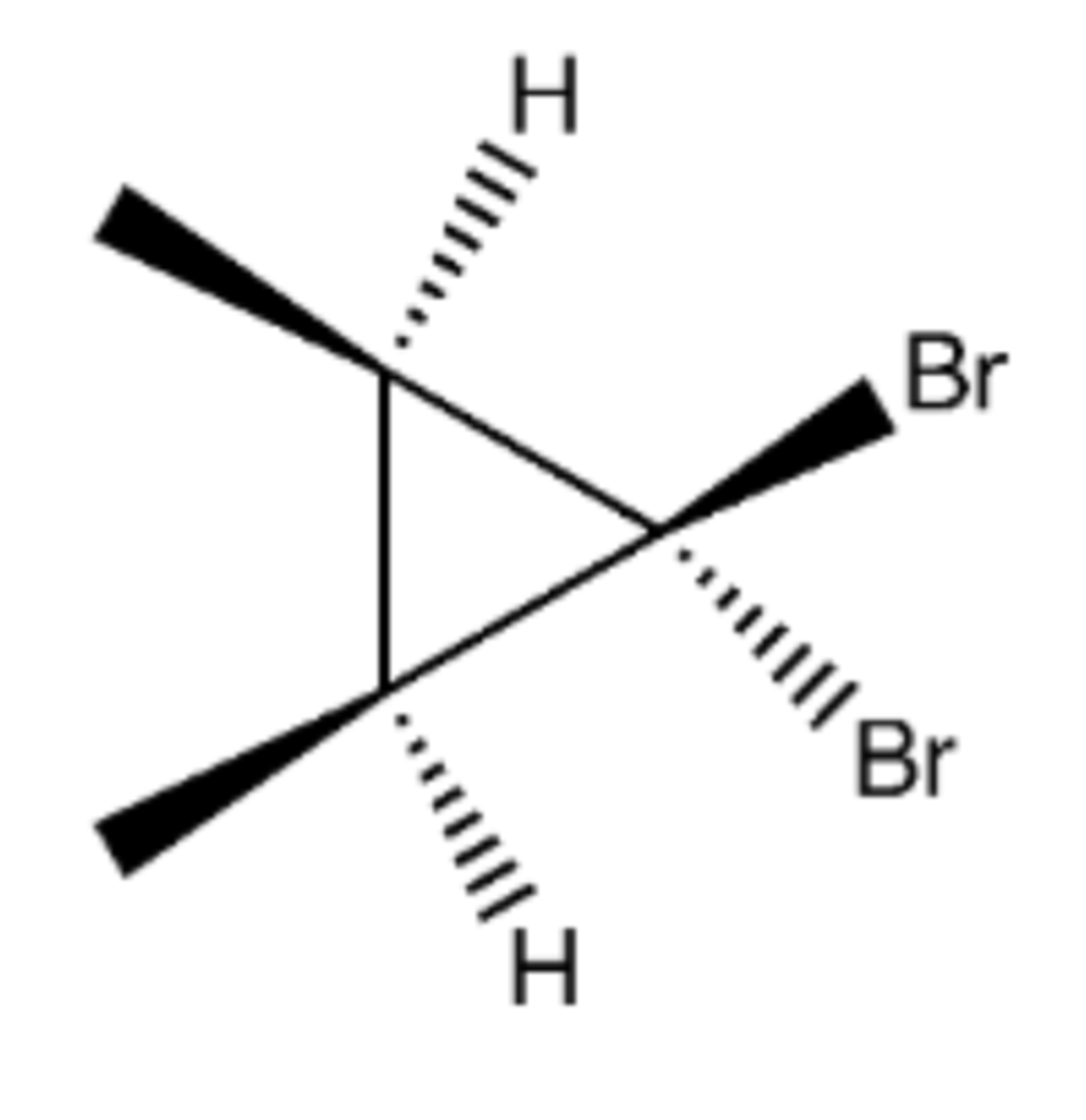
Preparation of cyclopropane with 2 Br groups attached from alkene
1. OsO4, H2O2
2. (1) KMnO4 (2) NaOH
Preparation of syn Diols/Glycols from alkene
(1) mCPBA (2)HCl/H2O
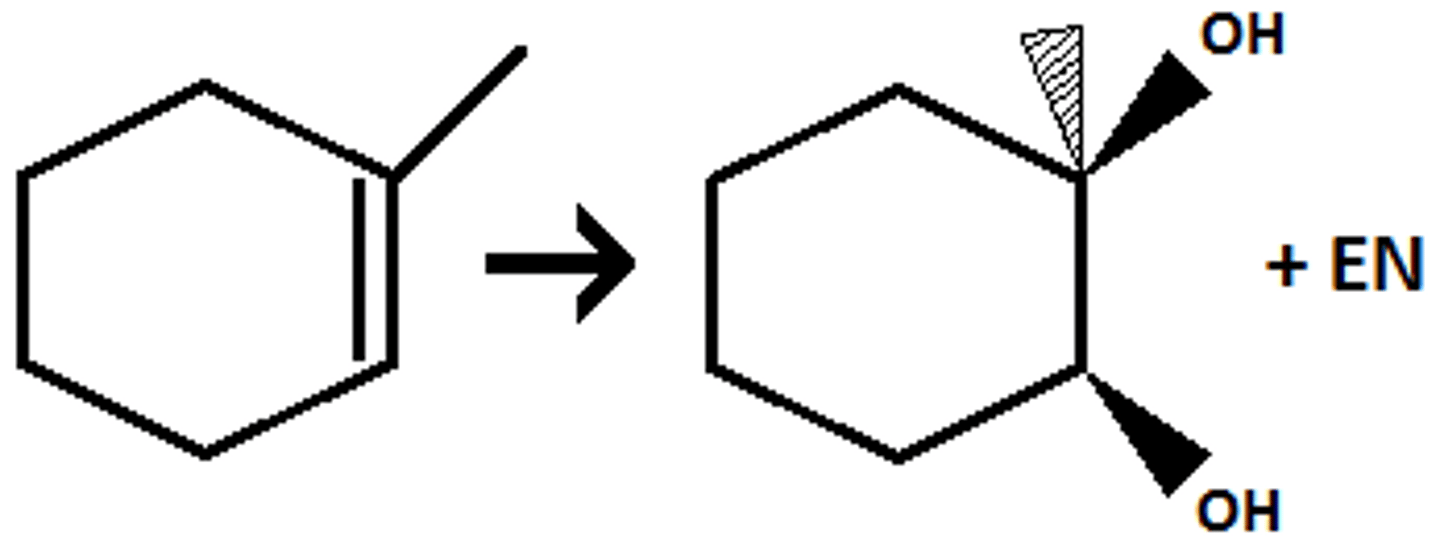
preparation of anti Diols/Glycols from alkene
1. KMnO4 (conc.), heat
2. (1) O3, (-78 C) (2) (CH3)S
preparation of ketones/aldehydes from alkenes
(1) NaNH2 (2) R-X (X=halide)
Preparation of alkylated acetylene from acetylene
(1) NaNH2 (2) carbonyl
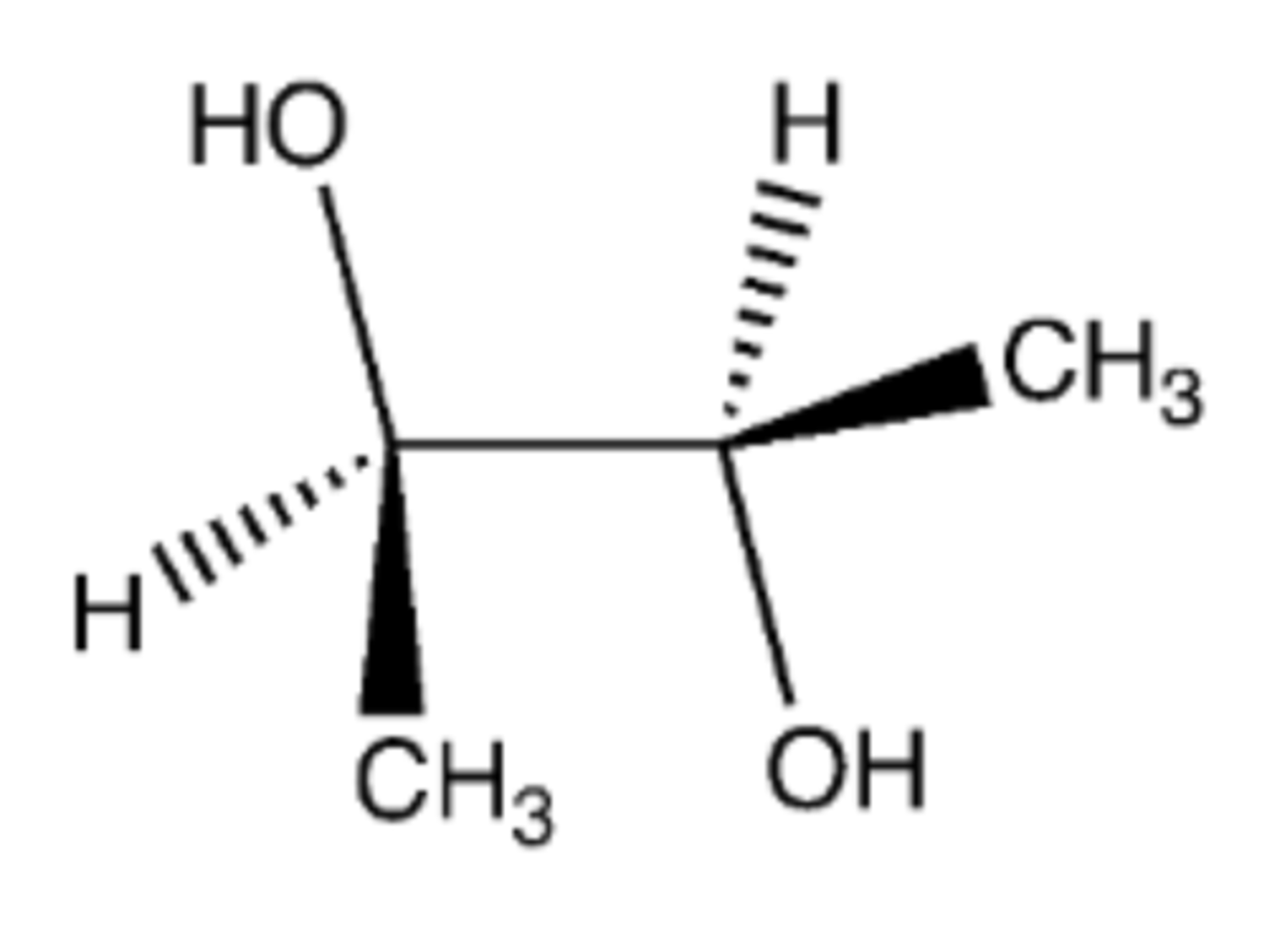
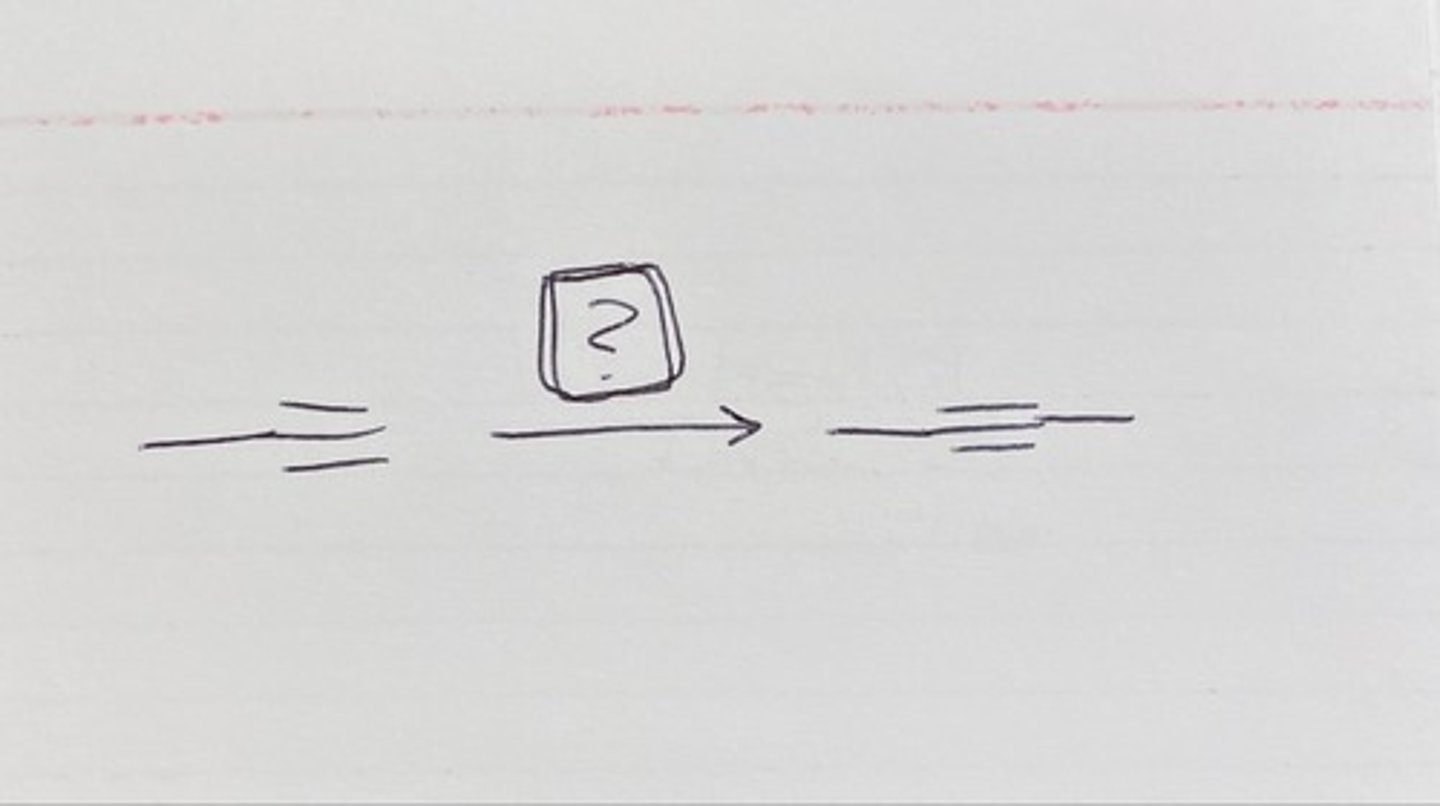
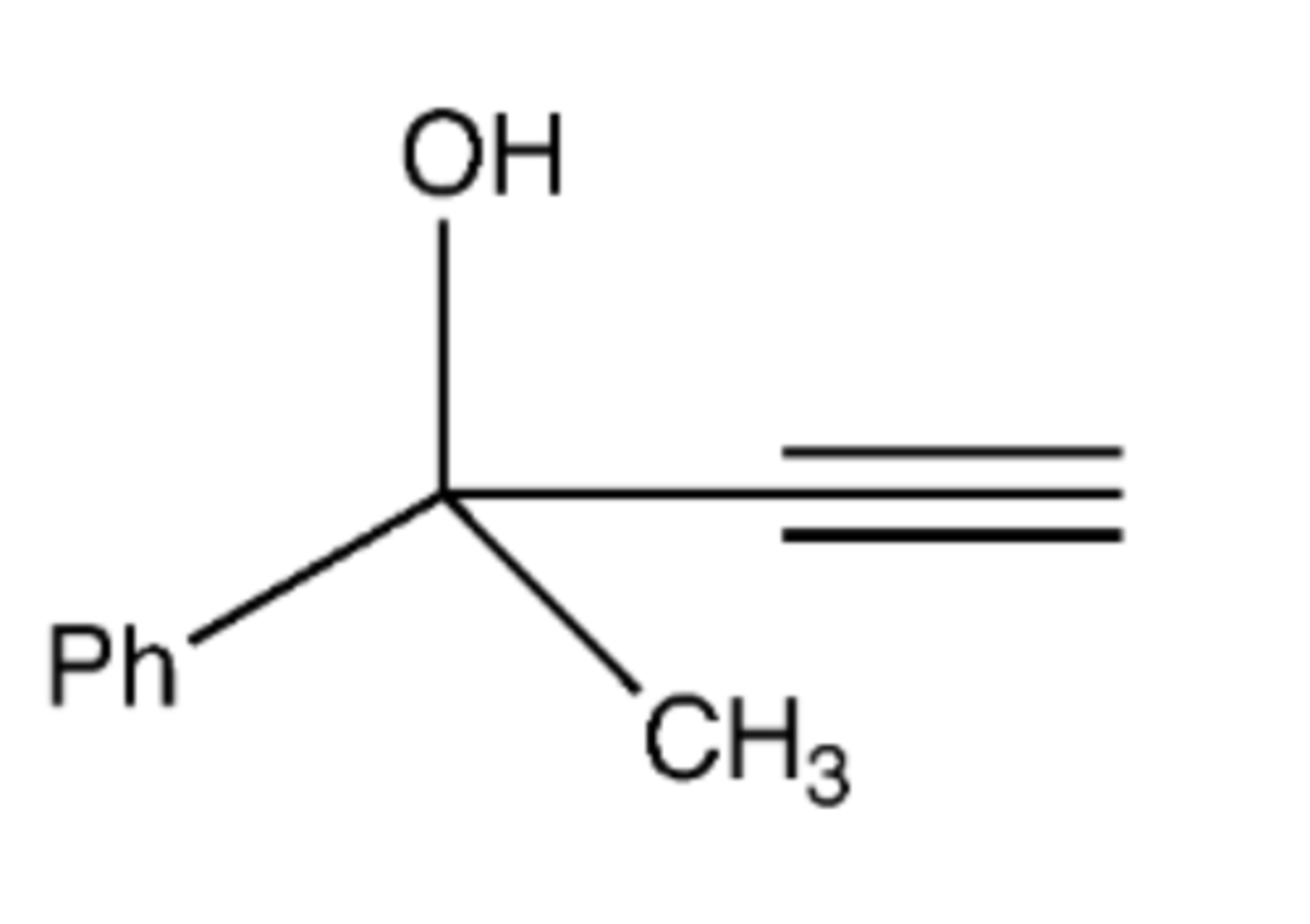
Preparation of this molecule
H2, Pt/Pd/Ni
Preperation of an alkane from an alkyne
H2, Lindlar's catalyst
Preparation of a cis alkene from an alkyne
Preparation of a trans alkene from an alkyne
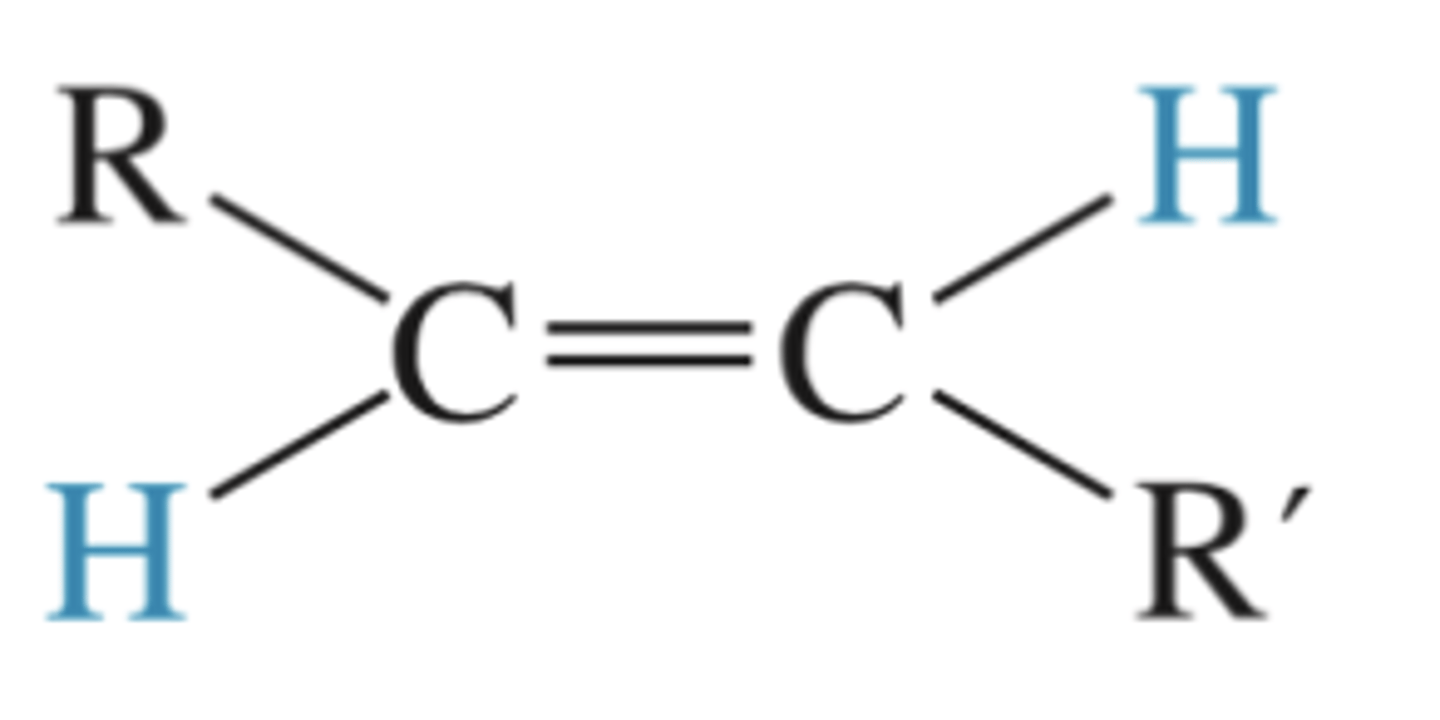
H-X (X=Cl, Br, I)
Preparation of a Markovnikov halo alkene from an alkyne (mix of cis and trans)
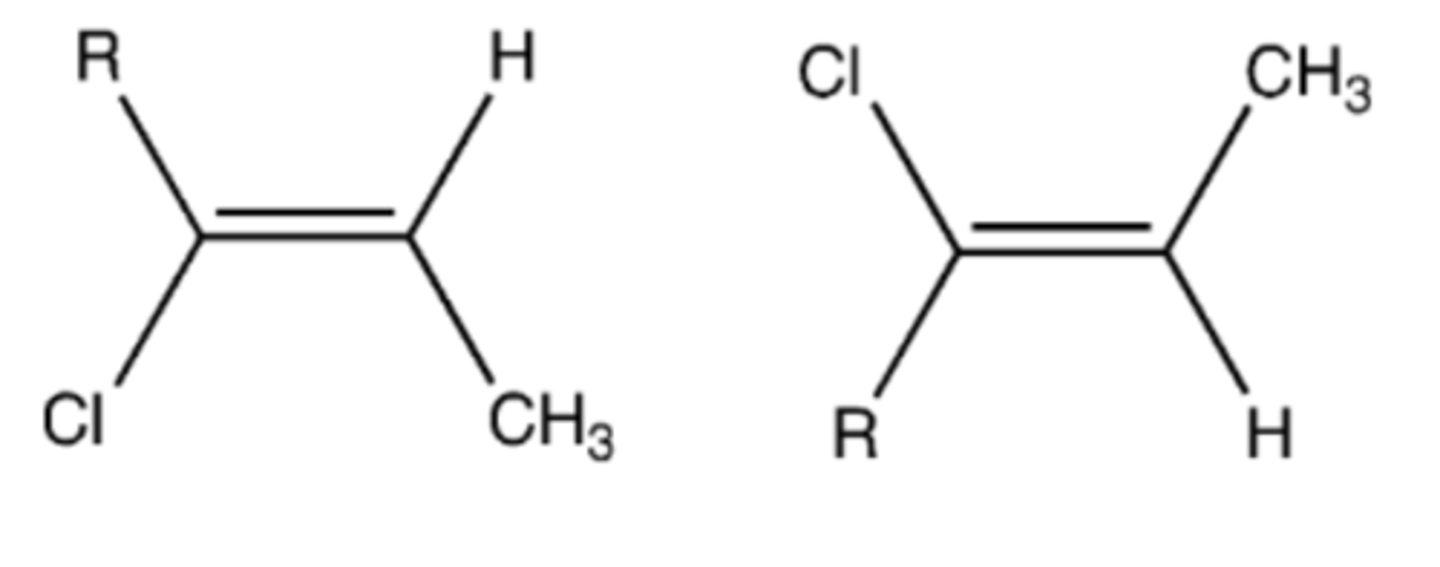
ROOR, HBr, hv (free radical chain rxn)
Preparation of an anti-Markovniokov halo alkene from an alkyne (mix of cis and trans)
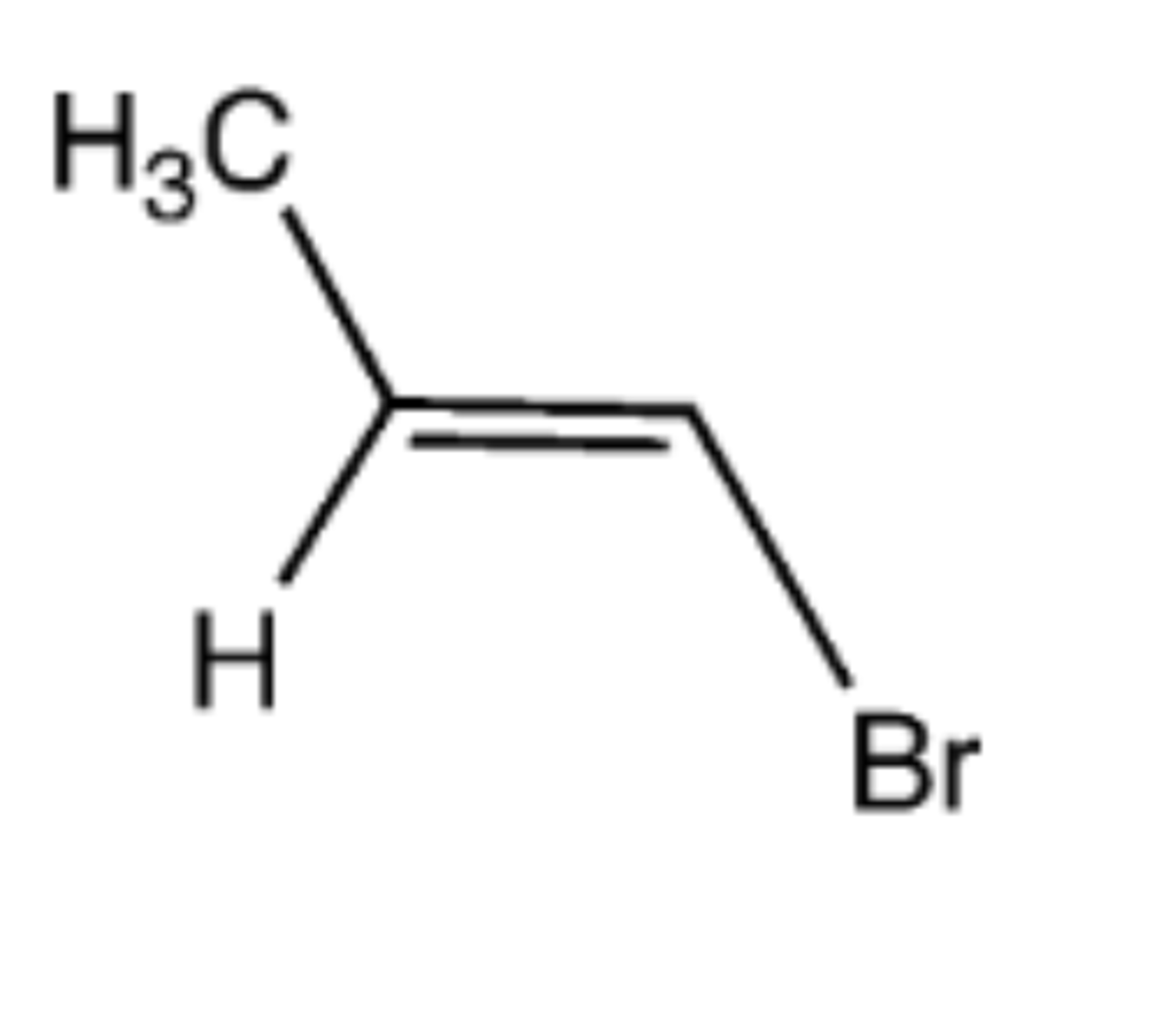
1. (1) HgSO4, H2SO4 (2) HCl/H2O (enol intermediate)
2. acid or base
Preparation of ketone from alkyne
KMnO4, H2O, neutral (pH=7)
Preparation of a diketone from alkyne
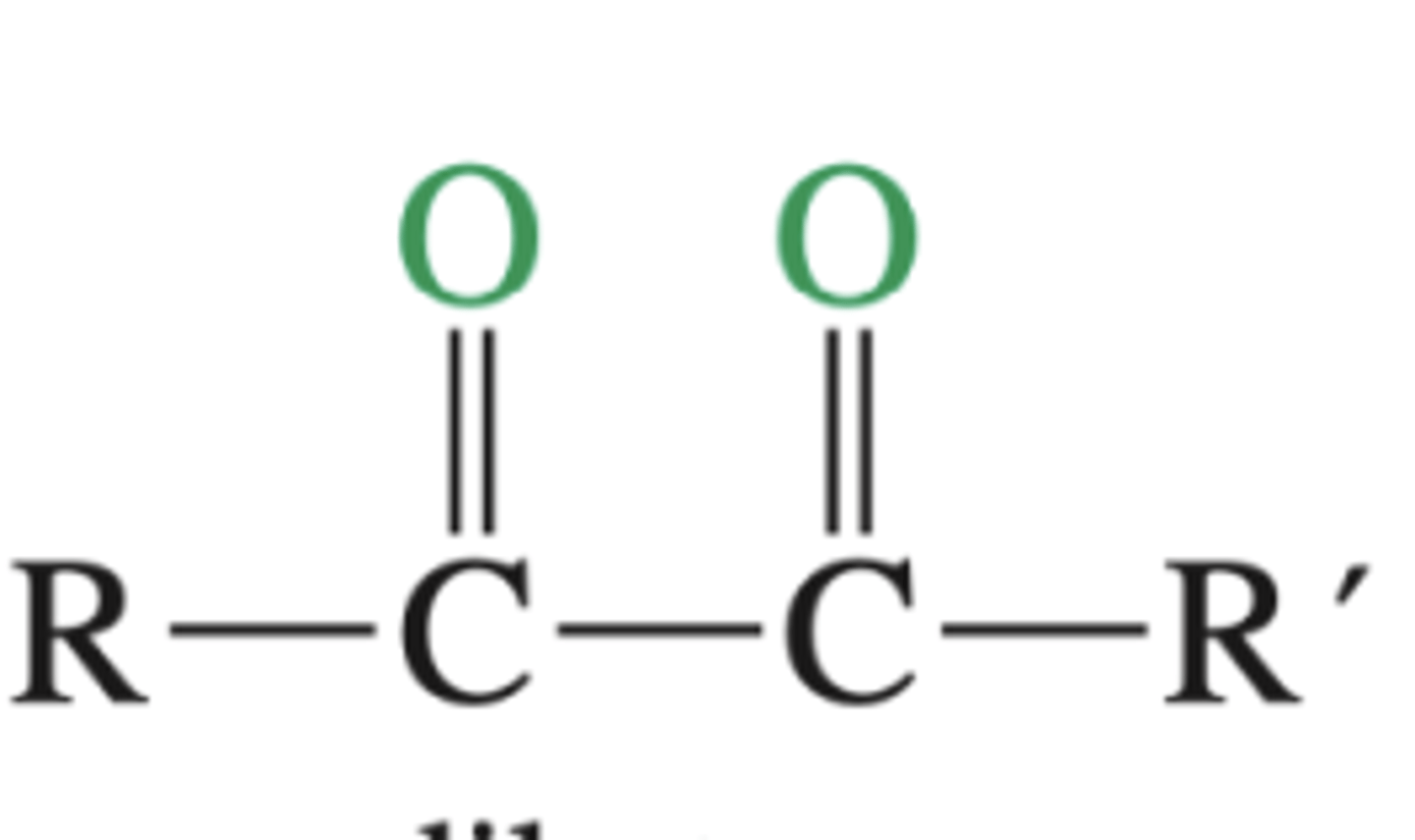
KMnO4, H2O, heat or basic (pH>7)
Preparation of carboxylate salts from alkyne