HB TOPIC 2- NERVOUS SYSTEM
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Define Nervous system
define
2 types
communication network and control centre of the body
Central Nervous system and Peripheral Nervous system
Difference between CNS and PNS
CNS- brain and spinal chord
PNS- Nerves connecting the central nervous system with limbs and organs
Define Neuron
define
specialised cell that transmits signals by generating electric currents
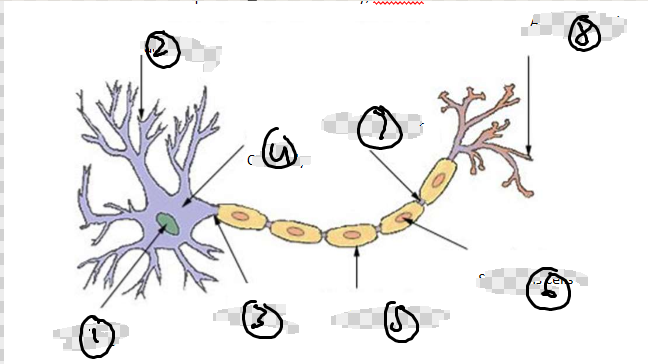
Label Parts of Neuron
Nucleus
Dendrites
axons
cell body
myelin sheath
Schwanns cells
Nodes of Ranvier
Function of Dendrites
extensions of cytoplasm that deliver messages/ never impulses from surrounding neurons to cell body
Function of axons
long extensions of cytoplasm that carry messages away from body
Role of Myelin Sheath
define
role
white lipid layer covering most axons
Speeds up transmission by…
acting as an insulator
protects axons from damage
speeds up nerve impulses
3 types of neurons CLASSIFIED BY FUNCTION
list them
function
sensory/ receptor- carry messages from receptors to CNS
Motor/ effector- carry messges from CNS to muscles/glands
Interneurons- link sensory and motor in CNS
List type of nerve cells by structure
Multipolar
Bipolar
Unipolar
Pseudonipolar
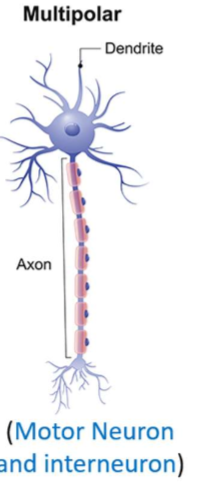
Structure of Multipolar Neurons
structure
which are common
one axons, multiple dentrites
interneurons and motor
Structure of Bipolar Neurons
structure
examples
one axon and one dendrite
sensory neurons and interneurons
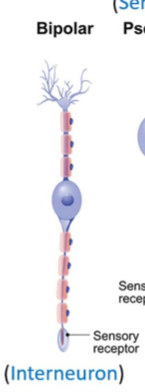
structure pf pseudonipolar neurons
structure
examples
one cell body to the side of the axon, one extention connects to dendrite and the other to axon terminals.
Sensory neurons
Define nerve fibres
long extensions of cytoplasm from cell body (usually axon)
Define nerve
bundles of nerve fibres held tg by connective tissue
Neurotransmission
define
transfer of a message from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of another
Define synapse
Gaps between adjacent neurons where signals are passed across
Define electrochemical change
change in electric voltage caused by changes in ion concentrations in and out of neuron
define potential difference
potential for positive and negative ions to come together and release energy
How does extracellular fluid start before nerve impulses?
pos/neg
concentration of Na+ and Cl-
Permeability of each
Starts positive
10x Na+ outside- slightly permeable due to limitied sodium leakage channels
High concentration of Cl ions- highly permeable through protein channels
How does intracellular fluid start?
pos/neg
concentration of?
permeability of each
Negative
high concentration of K+, - highly permeable due to pottassium leakage channels
high concentrations of organic ions- inpermeable
Define Membrane potential
difference in charges between outside and inside of cell membrane
Resting membrane potential define
unstimulated neuron with potential difference of -70mV (inside of cell is 70mV less than outside)
Steps of Neurotransmission
Neuron at rest
Stimulus
Threshold and depolarization
Repolarization
Hyperpolarization
Return to resting potential
Step 1- Neuron at rest
resting potential at -70mv
na+ ions are outside membrane and k+ ions are inside the membrane
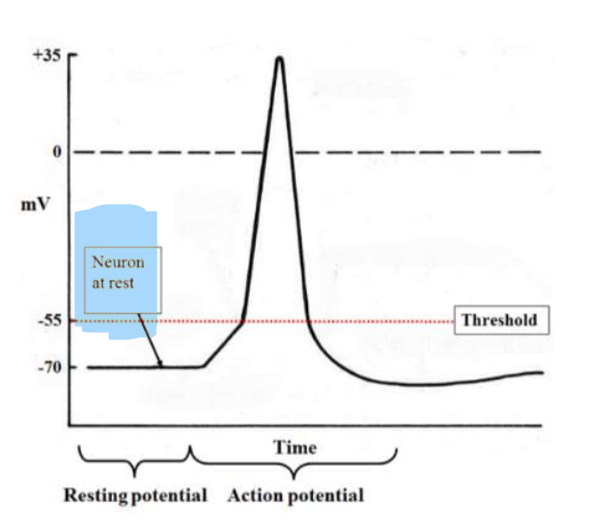
Step 2- Stimulus
causes gated sodium channels to open= some na+ ions into the cell
results in cell becoming more positive inside
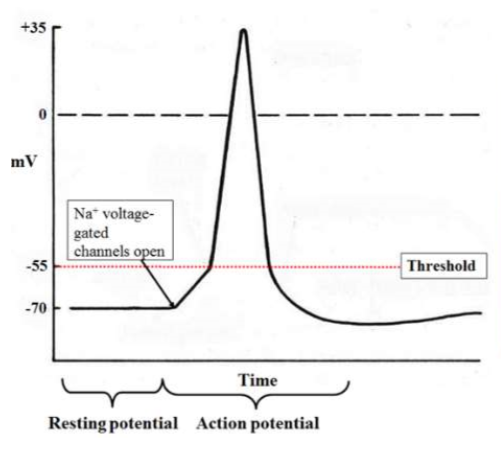
Step 3- Threshold and Depolarization
if signal reaches threshold (-55mV), it triggers action potential.
sodium fated ion channels open= more na+ inside and positive to 35.
DEPOLARISATION- membrane charges reverse
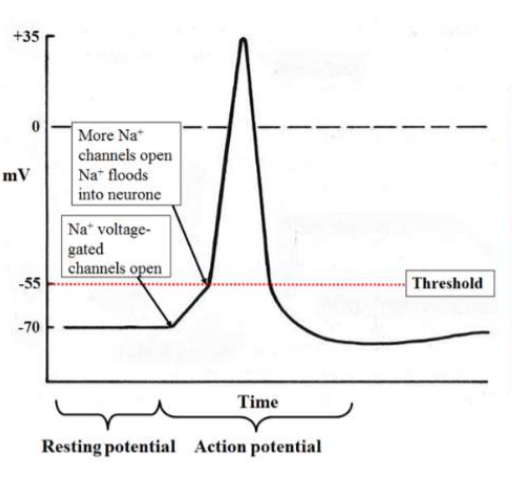
Step 4- Repolarization
Peak voltage +35mV= gated sodium channels to close, and pottasium channels to open.
k+ moves outside and Na+ ions stay inside= repolarization
Step 5- Hyperpolarization
more K+ ions outside than Na+ ions on the inside.
cell membrane potential drops below resting potential
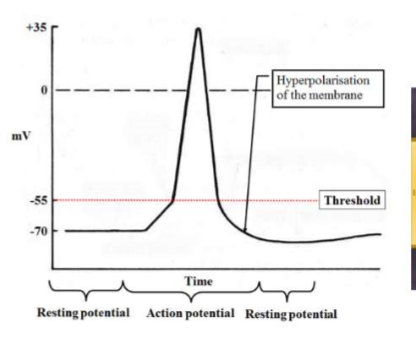
Step 6- Return to resting potential
Sodium pump moves Na+ ions to outside and K+ to inside so cell returns to normal polarized state.
Define refractory period
once sodium channels have opened, they are inactive and unresponsive to no new action potential can be generated during this time.
Define all or nothing law
If cell stimulus exceeds threshole of -55mV, nerve will give a complete response- otherwise there is no response
Myelinated axons
explain how it works
Nerve impulses travel faster along myelinated axons as the myelin sheath insulates axons from extra cellular fluid. Thus action potential must jump from one node of Ranvier to another.
Define Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that allow communication between neurons
Explain the steps of Neurotransmission
Action potential arrives at axon terminal of presynaptic cell
voltage gates calcium channels open
calcium ions enter the cell
calcium ions signal vesicles (containing neurotranmitters) to move to presynaptic membrane
vesicles release neurotransmitters via exocytosis to synaptic cleft
neurotransmitters diffuse across synaptic cleft and bind to receptors of POST SYNAPTIC CELL
If enough bind, stimulates new action potential by opening sodium ion channels
neurotransmitters leave receptors and reuptaken into either vesicles or broken down.
List the effects of chemicals on neurotransmission- and their effects
Stimulants (eg, caffiene)- indicate transmission at synapse
Depressants (weed)- slow/ prevent transmission
Venom- blocks neurotransmission at neuromuscular junction= paralysis
organophosphates- build up of acH NT= muscles of body contract and no breathing.
Define Ganglion
group of cell bodies outside brain and spinal chord
Cranial nerves
how many pairs
what do sensory and motor neurons do?
12
sensory- carry impulses from receptor to brain
motor- carry impulses from brain to muscle
Spinal nerves
how many pairs
where are sensory and motor neurons located?
where are the cell bodies located
31
Motor Neurons in VENTRAL ROOTS- cell bodys in grey matter
Sensory Neurons in DORSAL ROOTS- cell bodies in dorsal ganglion
What are the 2 types of PNS?
Sensory Afferent
Motor Efferent
PNS- Sensory Afferent- what are the 2 types of nerve fibres and their functions?
Somatic sensory- carry signals from bones, skin joints and muscles
Visceral sensory- carry signals from
PNS- Motor Afferent- what are the 2 types of nerve fibres and their functions?
Somatic motor- controls volentary movement of muscles
Autonomic motor- controls automatic functions and has 2 divisions
What are the 2 divisions of the autonomic motor?
and regulated by?
Sympathetic- arouses body for action eg. fight or flight
Parasympathetic- calming effect
Regulated by medulla oblongata, cerebral cortex, and hypothalamus
fight or flight response
controlled by..
explain some eg, of what happens
sympathetic
oxygenated blood to brain and msucles
increased HR
airways open up
Differences between Hormone/Nervous system
Nervous = rapid (miliseconds), Hormone- slow via blood stream
Nervous- stops when stimulus ends, Hormone- slower response
Nervous= electrochemical change, Hormone= chemical hormones
Nervous- specific parts of body, Hormone= multiple parts of body or whole body
Similarities between Nerv/Horm System
some are both NT and hormones eg. dopamine
some have the same effect on target cells eg. noradrenaline and glucagon
some hormones are excreted by neurons
CNS is protected by…
Bone
Meninges
Cerebrospinal fluid
Protection of CNS- Bone
Define
Outermost protective layer of brain that consistents of bone to make up cranium
Protection of CNS- Meninges
list the 3 types and function
Dura Mater (outer)- tough and fibrous tissue to provide protection against forces
Arachnoid mater- loose mesh of fibre to hold cerebrospinal fluid in place
Pia mater (inner)- delicate and sticks closely to surface of brain containing blood vessels
Protection of CNS- Cerebrospinal fluid
define
where is it found?
function
clear watery fluid
found between meningeal layers and circulates the brain cavities and spinal chords
Acts as shock absorber or supports brain inside cranium
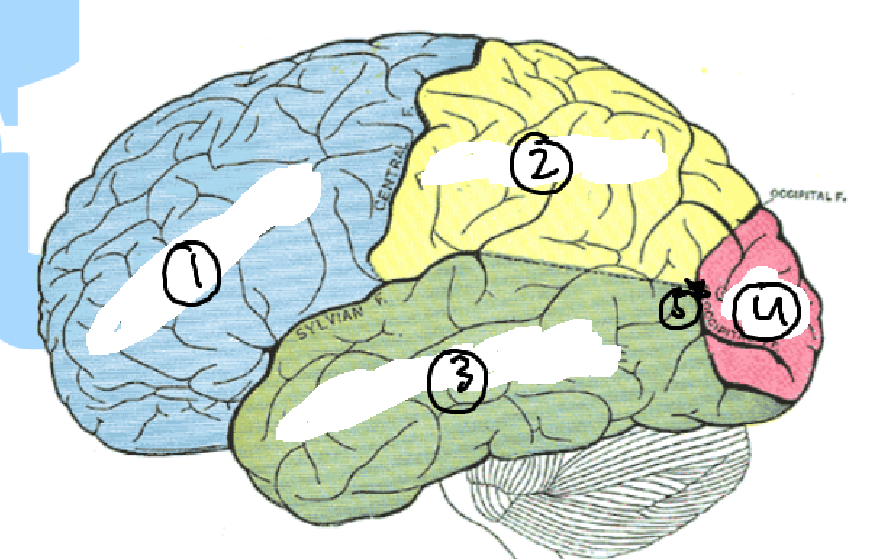
Name the parts of the cranium and their roles
Frontal lobe- cognition, reasoning etc
Parietal- information and senses
Temperal lobe- hearing memory and comprehension
Occipital lobe- vision
Insula lobe- emotions and addiction
Structure of Cranium
longitudinal fissure- deep groove to seperate hemispheres
gyri- thick folds
sulci- shallow grooves
corpus collsum- bundle of nerves that conect the hemispheres
Types of Receptors- list them all, role and where theyre found
pain- trauma to tissue- found everywhere except brain
Touch- close to surface of skin and found everywhere
Thermoreceptors- central and peripheral- detect changes in temp near skin or in blood
Osmoreceptors- detect changes in osmotic pressure in hypothalamus
Chemoreceptors- detect chemicals in mouth nose, and blood.
Define reflexes
rapid automatic response to a change in external or internal environment
Features of reflexes
must be stimulated
rapid
automatic/ involentary
stereotypes- same each time
Steps of a reflex arc
Receptor- sensory neuron detects change and starts nerve impulse
Sensory neuron carries message from PNS to CNS
Synapse- nerve impulse to interneuron or sraight to motor
Motor- carries impulse to effector
Effector- recieves nerve impulse and responds.