Nervous System
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
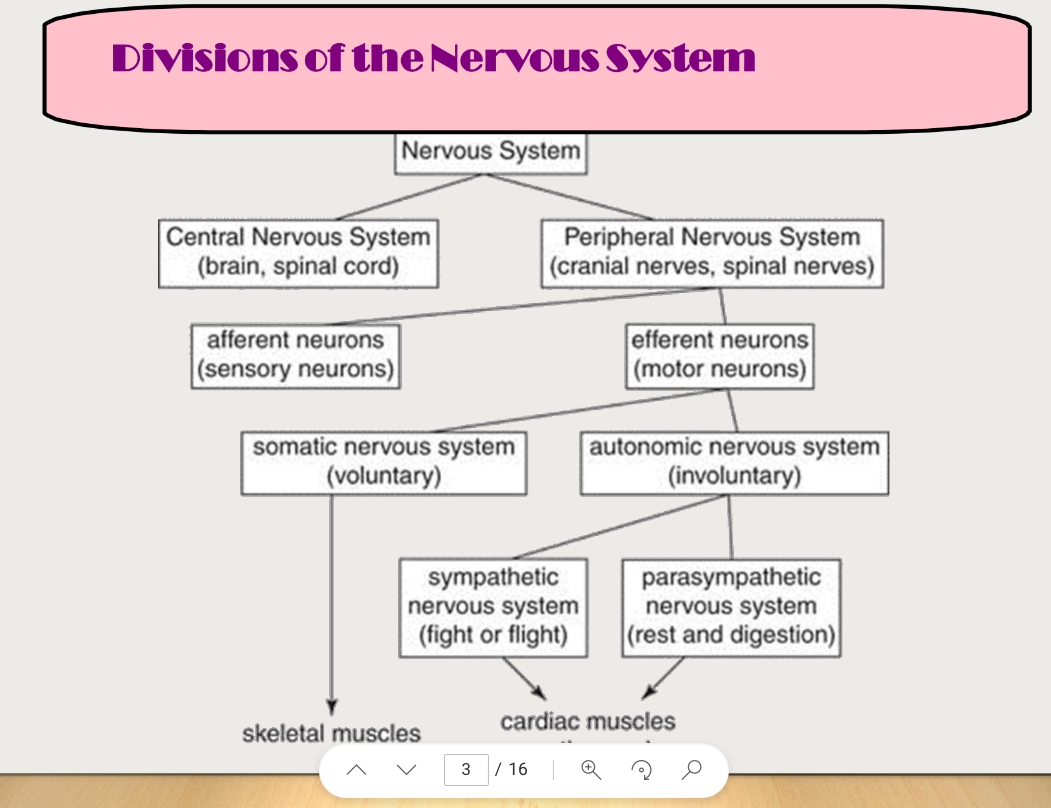
Division of the Nervous system
2
New cards
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
3
New cards
Peripheral nervous System
Crainial nerves and spinal nerves
Are divided into Afferent and Efferent
Are divided into Afferent and Efferent
4
New cards
Afferent Neurons
Made of Sensory Neurons
5
New cards
Efferent Neurons
Made of Motor Neurons
Are divided into somatic and autonomic
Are divided into somatic and autonomic
6
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary Responses
7
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
Involuntary Responses
Are divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic
Are divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic
8
New cards
Sympathetic Nervous System
Fight or Flight Response
Involve skeletal muscles
Involve skeletal muscles
9
New cards
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Involved with rest and digestion
Involve cardiac muscles and glands
Involve cardiac muscles and glands
10
New cards
Neural Cells
Neurons and Glials
11
New cards
Types of Neurons
Inter neuron, Sensory neuron, and Motor neuron
12
New cards
Dendrite
Short-branched fibres that convert chemical information from other neurons or receptor cells into electrical signals
13
New cards
Axon
An elongated fibre that transmits electrical signals to terminal regions for communication with other neurons or effectors
14
New cards
Soma
A cell body containing the nucleus and organelles, where essential metabolic processes occur to maintain cell survival
15
New cards
Inter Neuron
Found in Central Nervous System
The link between sensory and action
^^Short^^ Dendrites
^^Short^^ Axons
The link between sensory and action
^^Short^^ Dendrites
^^Short^^ Axons
16
New cards
Sensonry Neuron
Relay messages from receptors to Central Nervous System
^^Long^^ Dendrites
^^Short^^ Axons
^^Long^^ Dendrites
^^Short^^ Axons
17
New cards
Motor Neuron
Relay messages from the interneuron to the effector (muscle)
^^Short^^ Dendrites
^^Long^^ Axons
^^Short^^ Dendrites
^^Long^^ Axons
18
New cards
Nervous System process
Sensory input, integration, motor output
19
New cards
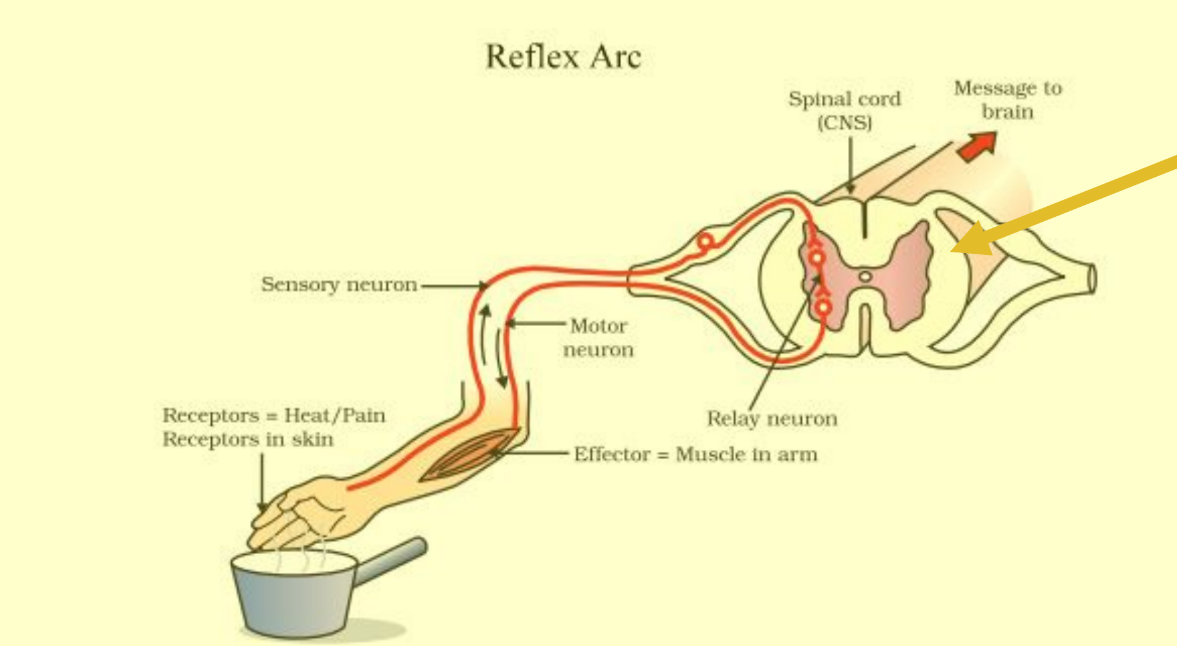
Reflex Arc
Receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector
20
New cards
Cerebrum
Main part of the brain
Associated with thoughts and actions
Made of 4 lobes
Associated with thoughts and actions
Made of 4 lobes
21
New cards
Frontal Lobe
Part of the brain that deals with;
Personality
Emotions
Intelligence
Personality
Emotions
Intelligence
22
New cards
Parietal Lobe
Part of the brain that deals with;
Sensations; pain, touch, temperature
Sensations; pain, touch, temperature
23
New cards
Temporal Lobe
Part of the brain that deals with;
Hearing
language
Hearing
language
24
New cards
Occipital Lobe
Part of the brain that deals with;
Vision
Vision
25
New cards
Brain Stem
Part of the brain that deals with;
Autonomic actions: breathing, heart control, swallowing, blood pressure, sweating, etc.
Autonomic actions: breathing, heart control, swallowing, blood pressure, sweating, etc.
26
New cards
Cerebullum
Part of the brain that deals with;
Balance
Motor Skills
Posture
Is connected to the brain stem
Balance
Motor Skills
Posture
Is connected to the brain stem
27
New cards
Thallamus
At the top of brain stem
two lobes that relay sensory and motor messages to cerebrum
Regulation of sleep and conciousness
two lobes that relay sensory and motor messages to cerebrum
Regulation of sleep and conciousness
28
New cards
Hypothallamus
Below the Thallamus
Involved in homeostasis
regulated blood pressure, body temperature and water balance
Involved in homeostasis
regulated blood pressure, body temperature and water balance
29
New cards
Medulla Oblongata
reflex centre of the brain
swallowing, sneezing, coughing
respiration and circulation
swallowing, sneezing, coughing
respiration and circulation
30
New cards
Spinal Cord
Nerves branch out from main cord to the various parts of the body
Damage to any section will cause problems to lower sections
Damage to any section will cause problems to lower sections
31
New cards
Potential
Difference between +/- ions between two points
32
New cards
Resting Potential
Neuron at rest (not sending a signal!)
More Na+ outside; more K+ inside
Caused by sodium/potassium ATP pump
Overall: mV -65
More Na+ outside; more K+ inside
Caused by sodium/potassium ATP pump
Overall: mV -65
33
New cards
Action Potential (Depolarization)
Depolarization (upswing)
The sodium channel opens and sodium rushes in
Potential changes until the threshold is reached (-40 mV) and an all-or-nothing response occurs
Once it is reached, depolarization goes until 40mV
The sodium channel opens and sodium rushes in
Potential changes until the threshold is reached (-40 mV) and an all-or-nothing response occurs
Once it is reached, depolarization goes until 40mV
34
New cards
Action Potential (Repolarization)
Repolarization (downswing)
Sodium gate closes, Potassium gate opens and it rushes out
Potential changes until it is slightly below resting potential (-65mV)
Inside is negative compared to outside
Sodium gate closes, Potassium gate opens and it rushes out
Potential changes until it is slightly below resting potential (-65mV)
Inside is negative compared to outside
35
New cards
Recovery Phase
Refractory Period
Sodium and Potassium gates close
Na/K Pump pumps K outside and Na inside
Sodium and Potassium gates close
Na/K Pump pumps K outside and Na inside
36
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
Individual sections of the axon
Effeciently and quickly moves signal along
Effeciently and quickly moves signal along
37
New cards
Saltatory Conjunction
The jumping of the action potential from node to node
38
New cards
Myelin Sheath
Insulating layer around the axon
39
New cards
Synaptic Transmission
Changes electrical signal (voltage) to chemical signals (neurotransmitters)
Neurotransmitters bind to dendrites to cause a new action potential
Neurotransmitters bind to dendrites to cause a new action potential
40
New cards
Synaptic Cleft
Between the axon and the dendrite