Orders, rate equations and rate constants
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Define rate of reaction
the change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time
Give the general units for reaction rate
mol dm-3 s-1
What does [A] mean?
Concentration of A
Define the rate constant, k
The constant linking the rate of reaction with the concentration of reactants which are raised to the power of their orders in the rate reaction
Define order
The power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate reaction
Define half-life
The time taken for the concentration of the reactant to reduce by half
Define the rate determining step
The slowest step in the reaction mechanism of a multi-step reaction
Define the initial rate of raection
The change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time at t=0
Define overall order and how it is calculated
The overall effect of the concentrations of all reactants on the rate of reaction
Calculated by the sum of all the individual orders of all of the reactants
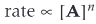
What does this mean?
The rate of reaction is proportional to the concentration of A raised to a power of n
What is a zero order reactant? How is zero order represented?
When the concentration of a reactant has no effect on the rate
Zero order: rate ∝ [A]0
![<p>When the concentration of a reactant has no effect on the rate</p><ul><li><p>Zero order: rate <span>∝ [A]<sup>0</sup></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4464e931-30b4-435e-90b0-d4d57f9da582.png)
Give the 2 rules of a zero order reaction
Any number raised to the power of zero is 1
Concentration does not influence rate
What is a first order reaction?
When the rate depends on its concentration raised to the power of 1
First order: rate ∝ [A]1
![<p>When the rate depends on its concentration raised to the power of 1</p><ul><li><p>First order: rate <span>∝ [A]<sup>1</sup></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/53e55d79-3787-466c-8510-74050fdea778.png)
What happens to the reaction rate when [A] is tripled in a first order reaction?
Reaction rate increases by 3
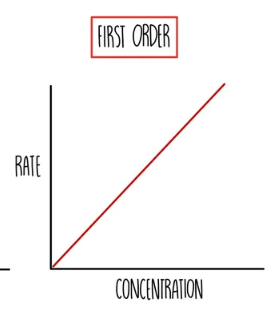
What do you find by calculating the gradient of a first order reactant on a rate-concentration graph?
The rate constant, k
What is a second order reaction?
When the rate depends on a reactant’s concentration raised to the power of 2
Second order: rate ∝ [A]2
![<p>When the rate depends on a reactant’s concentration raised to the power of 2</p><ul><li><p>Second order: rate <span>∝ [A]<sup>2</sup></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/33027b03-56c2-4177-8f6a-76d9a0eb4966.png)
What happens when [A] is tripled in a second order reaction?
The reaction rate increases by 32 = 9
For two reactants, A and B, show the rate equation
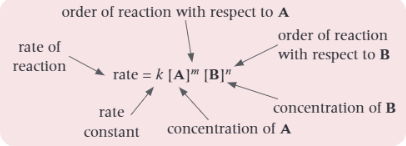

Find the overall order and the rate equation

What are the steps for working out the units of the rate constant, k?
Rearrange the equation to make k the subject
Substitute units into the expression for k
Cancel common units and show the final units on a single line


What must be noted about experimental results when determining orders of a reaction?
The rate should always be measured after the same time, ideally as close to the start of the experiment as possible
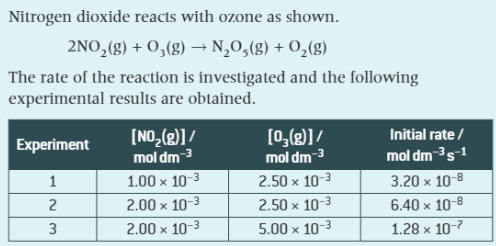
Step 1: Determine the orders, overall order and rate equation by comparing experimental results
