[PT13] Knee, Leg, Ankle, and Foot
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
1
New cards
The branch of the femoral nerve that supply the anteromedial surface of the leg:
a. Saphenous nerve
b. Lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf
c. Superficial peroneal nerve
d. Sural nerve
a. Saphenous nerve
b. Lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf
c. Superficial peroneal nerve
d. Sural nerve
Saphenous N.
2
New cards
The mid-anterior thigh is a dermatomal representation of nerve root:
a. L2
b. L3
c. L4
d. L5
a. L2
b. L3
c. L4
d. L5
L2
3
New cards
Which of the following structures prevents anterior translation of the femur against the tibia?
a. Medial meniscus
b. lateral collateral ligament
c. anterior cruciate ligament
d. posterior cruciate ligament
a. Medial meniscus
b. lateral collateral ligament
c. anterior cruciate ligament
d. posterior cruciate ligament
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
4
New cards
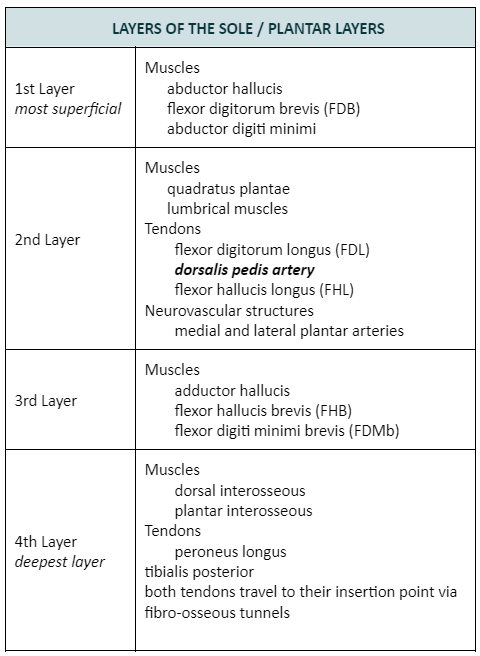
The following are muscles located in the first layer of the sole of the foot, EXCEPT:
a. Abductor hallucis
b. Flexor digitorum brevis
c. Abductor digiti minimi
d. Adductor hallucis
a. Abductor hallucis
b. Flexor digitorum brevis
c. Abductor digiti minimi
d. Adductor hallucis
Adductor Hallucis
5
New cards
The following muscles are located in the anterior fascial compartment of the leg, EXCEPT:
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Extensor digitorum longus
c. Peroneus tertius
d. Flexor hallucis longus
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Extensor digitorum longus
c. Peroneus tertius
d. Flexor hallucis longus
Flexor Hallucis Longus
6
New cards
The structure that binds the tibia and fibula together and provides attachment for neighboring muscles is the:
a. Retinacula
b. Interosseous membrane
c. Aponeurosis
d. Deep fascia
a. Retinacula
b. Interosseous membrane
c. Aponeurosis
d. Deep fascia
Interosseous Membrane
7
New cards
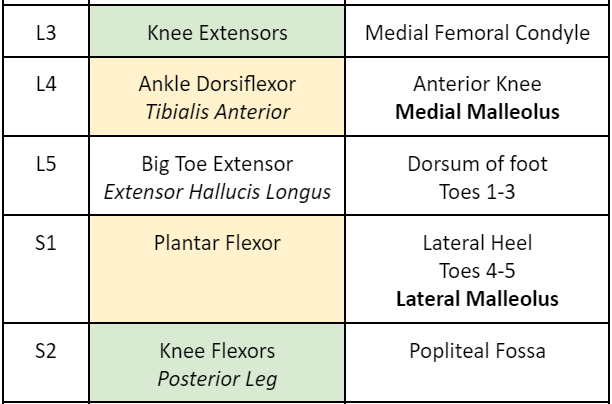
The medial malleolus area is a dermatomal representation of nerve root:
a. L3
b. L4
c. L5
d. S1
a. L3
b. L4
c. L5
d. S1
L4
8
New cards
Which of the following nerve is involved if there is an increased pressure in the anterior compartment of the leg?
a. Tibial nerve
b. Sural nerve
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
a. Tibial nerve
b. Sural nerve
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
Deep peroneal
9
New cards
Which of the following muscles dorsiflexes the foot at the ankle joint?
a. Extensor digitorum brevis
b. Peroneus brevis
c. Tibialis posterior
d. Extensor hallucis longus
a. Extensor digitorum brevis
b. Peroneus brevis
c. Tibialis posterior
d. Extensor hallucis longus
Extensor Hallucis Longus.
\
It’s an anterior leg compartment muscles so by virtue of its position it dorsiflexes the ankle.
\
It’s an anterior leg compartment muscles so by virtue of its position it dorsiflexes the ankle.
10
New cards
The following are structures in the knee involved in the “unhappy triad of O’Donoghue”, EXCEPT:
a. Medial meniscus
b. Anterior cruciate ligament
c. Medial collateral ligament
d. Lateral collateral ligament
a. Medial meniscus
b. Anterior cruciate ligament
c. Medial collateral ligament
d. Lateral collateral ligament
Lateral Collateral Ligament
\
The “Unhappy Triad of O’Donoghue” is a knee injury wherein there is a blow to your lower leg while your foot is in the ground. This pushes your knee inward and femur & tibia to twist in opposite directions. It causes damage to the:
Anterior cruciate Ligament
Medial Collateral Ligament
Medial Meniscus
\
The “Unhappy Triad of O’Donoghue” is a knee injury wherein there is a blow to your lower leg while your foot is in the ground. This pushes your knee inward and femur & tibia to twist in opposite directions. It causes damage to the:
Anterior cruciate Ligament
Medial Collateral Ligament
Medial Meniscus
11
New cards
The tibialis anterior represents myotome level:
a. L3
b. L4
c. L5
d. S1
a. L3
b. L4
c. L5
d. S1
L4
\
Anterior compartment muscles are innervated by Deep Peroneal N. whose roots are L4-S1. Since Tibialis Anterior is the most medial it represents L4.
\
Anterior compartment muscles are innervated by Deep Peroneal N. whose roots are L4-S1. Since Tibialis Anterior is the most medial it represents L4.
12
New cards
Which of the following structures checks valgus stress in the knee joint?
a. Medial collateral ligament
b. Lateral collateral ligament
c. Anterior cruciate ligament
d. Posterior cruciate ligament
a. Medial collateral ligament
b. Lateral collateral ligament
c. Anterior cruciate ligament
d. Posterior cruciate ligament
Medial collateral ligament
13
New cards
The plantarflexors represent myotomal level
a. L4
b. L5
c. S1
d. S2
a. L4
b. L5
c. S1
d. S2
S2
14
New cards
The predominant nerve root supply of the muscles of the sole of the foot is
a. L5
b. S1
c. S2
d. S3
a. L5
b. S1
c. S2
d. S3
S3
\
Tibial N. has roots in L4-S3. The Posterior Tibial N. passes through the Tarsal Tunnel and divides into the Medial & Lateral Plantar Nerves which are the primary nerves that supply the sole of the foot.
\
Tibial N. has roots in L4-S3. The Posterior Tibial N. passes through the Tarsal Tunnel and divides into the Medial & Lateral Plantar Nerves which are the primary nerves that supply the sole of the foot.
15
New cards
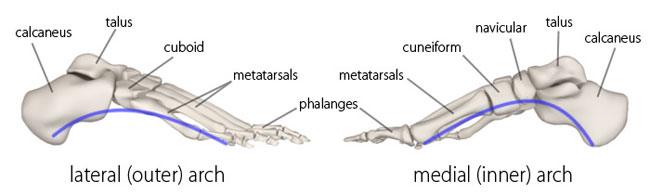
The keystone of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot is the:
a. Talus
b. Navicular
c. Cuboid
d. Cuneiforms
a. Talus
b. Navicular
c. Cuboid
d. Cuneiforms
Talus
16
New cards
The following muscles are located in the posterior compartment of the leg, EXCEPT:
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Flexor digitorum longus
c. Flexor hallucis longus
d. Plantaris
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Flexor digitorum longus
c. Flexor hallucis longus
d. Plantaris
Tibialis anterior
17
New cards
Muscles in the anterior fascial compartment is innervated by:
a. Deep peroneal nerve
b. Superficial peroneal nerve
c. Tibial nerve
d. Sural nerve
a. Deep peroneal nerve
b. Superficial peroneal nerve
c. Tibial nerve
d. Sural nerve
Deep peroneal nerve
18
New cards
Which retinaculum forms the tarsal tunnel?
a. Superior extensor retinaculum
b. Flexor retinaculum
c. Superior peroneal retinaculum
d. Inferior peroneal retinaculum
a. Superior extensor retinaculum
b. Flexor retinaculum
c. Superior peroneal retinaculum
d. Inferior peroneal retinaculum
Flexor retinaculum
19
New cards
The pulsations of this artery can be felt between the tendons of extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus:
a. Anterior tibial
b. Posterior tibial
c. Popliteal
d. Dorsalis pedis
a. Anterior tibial
b. Posterior tibial
c. Popliteal
d. Dorsalis pedis
Dorsalis pedis
20
New cards
The following muscles of the sole of the foot are innervated by the medial plantar nerve, EXCEPT:
a. Flexor digitorum brevis
b. Quadratus plantae
c. Abductor hallucis
d. 1st lumbrical
a. Flexor digitorum brevis
b. Quadratus plantae
c. Abductor hallucis
d. 1st lumbrical
Quadratus plantae.
\
Lateral Plantar N. is an intrinsic foot nerve that supplies the AbDM, FDMb, Quadratus Plantae, Adductor Hallucis, and Lumbricals 2-4.
\
The rest of the intrinsic muscles are innervated by the Medial Plantar N.
\
Lateral Plantar N. is an intrinsic foot nerve that supplies the AbDM, FDMb, Quadratus Plantae, Adductor Hallucis, and Lumbricals 2-4.
\
The rest of the intrinsic muscles are innervated by the Medial Plantar N.
21
New cards
This structure can be palpated an inch below the medial malleolus:
a. Peroneal tubercle
b. Navicular tuberosity
c. Sustentaculum tali
d. Tendon of peroneus brevis
a. Peroneal tubercle
b. Navicular tuberosity
c. Sustentaculum tali
d. Tendon of peroneus brevis
Sustentaculum tali.
\
A shelf-like, medial projection of the calcaneus, which supports the talus
\
A shelf-like, medial projection of the calcaneus, which supports the talus
22
New cards
The extensor digitorum brevis is innervated by:
a. Medial plantar
b. Lateral plantar
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
a. Medial plantar
b. Lateral plantar
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
Deep peroneal
23
New cards
The following are structures that pass behind the medial malleolus beneath the flexor retinaculum,
EXCEPT:
a. Flexor hallucis longus
b. Tibial nerve
c. Flexor digitorum longus
d. Tibialis anterior
EXCEPT:
a. Flexor hallucis longus
b. Tibial nerve
c. Flexor digitorum longus
d. Tibialis anterior
Tibialis anterior. It passes beneath the extensor retinaculum.
24
New cards
The tendons of the flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus can be located in which layer of the sole?
a. 1st layer
b. 2nd layer
c. 3rd layer
d. 4th layer
a. 1st layer
b. 2nd layer
c. 3rd layer
d. 4th layer
2nd layer
25
New cards
Unlocking the knee joint to facilitate knee flexion is the primary action of:
a. Popliteus
b. Plantaris
c. Articularis genu
d. gastrocnemius
a. Popliteus
b. Plantaris
c. Articularis genu
d. gastrocnemius
Popliteus.
\
It unlocks the knee during flexion conversely, Plantaris locks the knee in extension.
\
It unlocks the knee during flexion conversely, Plantaris locks the knee in extension.
26
New cards
The following are muscles located in the third layer of the sole of the foot, EXCEPT:
a. Flexor hallucis brevis
b. Adductor hallucis
c. Flexor digiti minimi brevis
d. Abductor hallucis
a. Flexor hallucis brevis
b. Adductor hallucis
c. Flexor digiti minimi brevis
d. Abductor hallucis
Abductor hallucis
27
New cards
The following are components of the deltoid ligament of the ankle, EXCEPT:
a. Anterior talotibial
b. Posterior talotibial
c. Calcaneofibular
d. Tibionavicular
a. Anterior talotibial
b. Posterior talotibial
c. Calcaneofibular
d. Tibionavicular
Calcaneofibular

28
New cards
The gastrocnemius muscle is innervated by:
a. Tibial nerve
b. Common peroneal
c. Deep peroneal
d. Superficial peroneal
a. Tibial nerve
b. Common peroneal
c. Deep peroneal
d. Superficial peroneal
Tibial nerve
29
New cards
Which of the following muscles can dorsiflex and evert the ankle?
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Peroneus longus
d. Peroneus tertius
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Peroneus longus
d. Peroneus tertius
Peroneus Tertius
30
New cards
Which of the following structure DOES NOT participate in the formation of the medial longitudinal arch?
a. Calcaneum
b. Cuboid
c. Talus
d. Navicular
a. Calcaneum
b. Cuboid
c. Talus
d. Navicular
Cuboid
31
New cards
The condition in which the medial longitudinal arch of the foot is collapsed is known as:
a. Pes planus
b. Pes cavus
c. Equinovarus
d. Calcaneovalgus
a. Pes planus
b. Pes cavus
c. Equinovarus
d. Calcaneovalgus
Pes planus
32
New cards
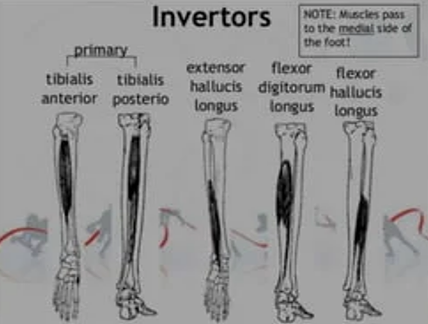
The foot is inverted by the following muscles, EXCEPT:
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Extensor hallucis longus
d. Peroneus tertius
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Extensor hallucis longus
d. Peroneus tertius
Peroneus Tertius.
\
It is located laterally so it everts the foot instead.
\
It is located laterally so it everts the foot instead.
33
New cards
Which of the following muscles can plantarflex and invert the foot
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Extensor hallucis longus
d. Peroneus tertius
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Extensor hallucis longus
d. Peroneus tertius
Tibialis posterior
34
New cards
The extensor hallucis longus is a myotomal representative of nerve root:
a. L4
b. L5
c. S1
d. S2
a. L4
b. L5
c. S1
d. S2
L5
35
New cards
The lateral heel is a dermatomal representation of nerve root:
a. L4
b. L5
c. S1
d. S2
a. L4
b. L5
c. S1
d. S2
S1
36
New cards
Which ligament of the knee prevents posterior translation of the tibia against the femur?
a. Lateral meniscus
b. Lateral collateral ligament
c. Anterior cruciate ligament
d. Posterior cruciate ligament
a. Lateral meniscus
b. Lateral collateral ligament
c. Anterior cruciate ligament
d. Posterior cruciate ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
37
New cards
The subtalar joint of the ankle is otherwise known as:
a. Talotibial joint
b. Talocalcaneal joint
c. Calcaneonavicular
d. Calcaneocuboid
a. Talotibial joint
b. Talocalcaneal joint
c. Calcaneonavicular
d. Calcaneocuboid
Talocalcaneal joint
38
New cards
The Common Peroneal N. is most often injured in:
a. Neck of the fibula
b. Posterior mid-thigh area
c. Popliteal fossa
d. Extensor retinaculum
a. Neck of the fibula
b. Posterior mid-thigh area
c. Popliteal fossa
d. Extensor retinaculum
Neck of fibula
39
New cards
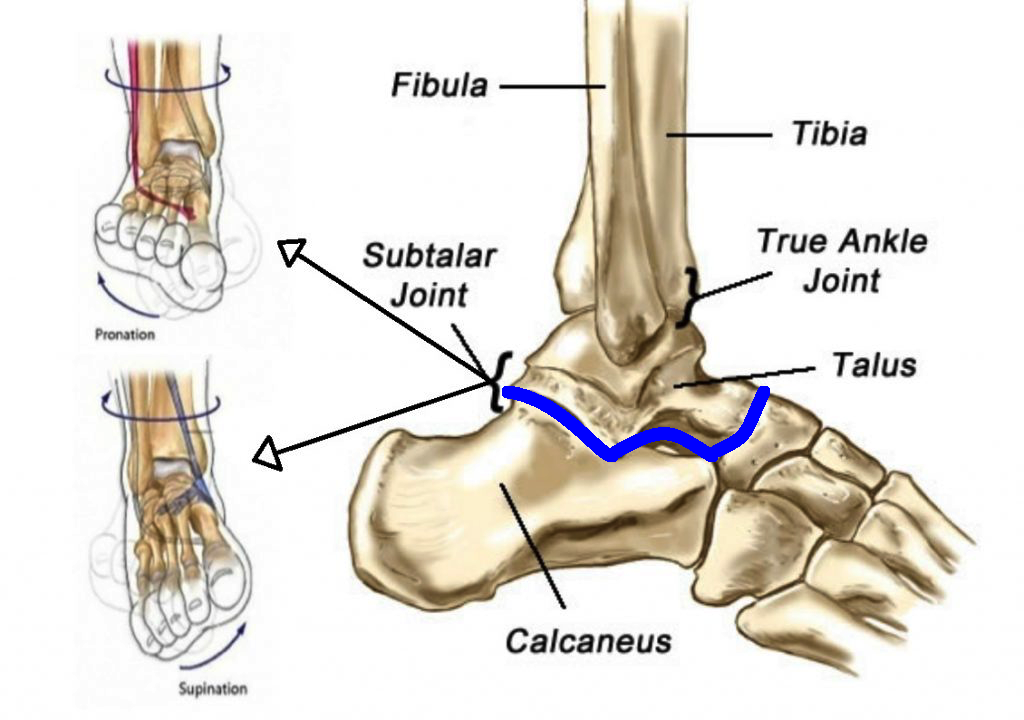
In which joint of the ankle complex does foot inversion and eversion occur?
a. Tarsometatarsal joint
b. Subtalar joint
c. Metatarsophalangeal joint
d. Talocrural joint
a. Tarsometatarsal joint
b. Subtalar joint
c. Metatarsophalangeal joint
d. Talocrural joint
Subtalar joint
40
New cards
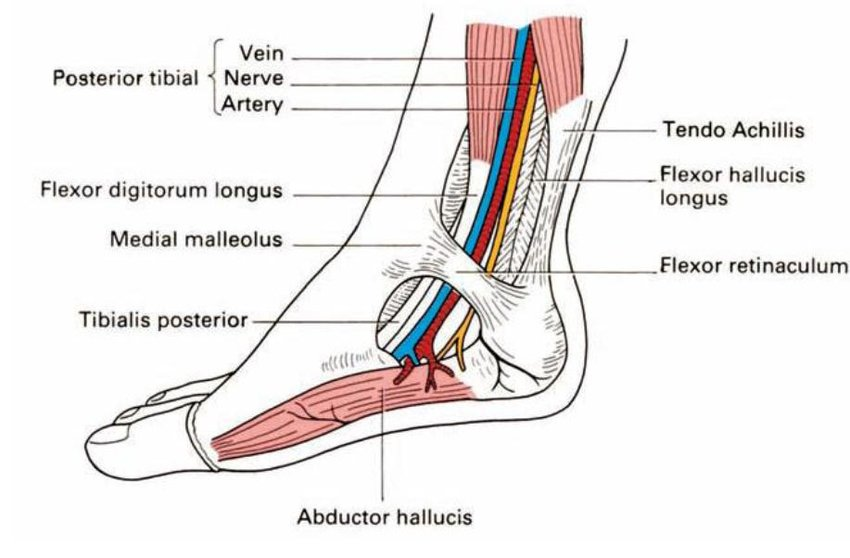
Pulsations of this artery is palpable between the heel and medial malleoulus:
a. Anterior tibial
b. Posterior tibial
c. Popliteal
d. Dorsalis pedis
a. Anterior tibial
b. Posterior tibial
c. Popliteal
d. Dorsalis pedis
Posterior Tibial Artery
41
New cards
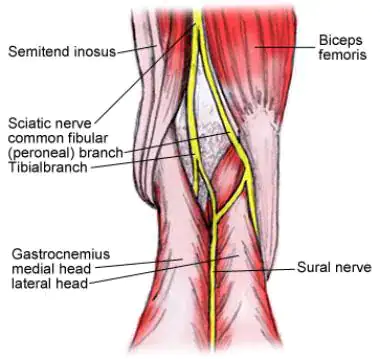
Which nerve is palpable on the medial side of the tendon of the biceps femoris?
a. Sciatic nerve
b. Tibial nerve
c. Common peroneal
d. Superficial peroneal
a. Sciatic nerve
b. Tibial nerve
c. Common peroneal
d. Superficial peroneal
Common peroneal
42
New cards
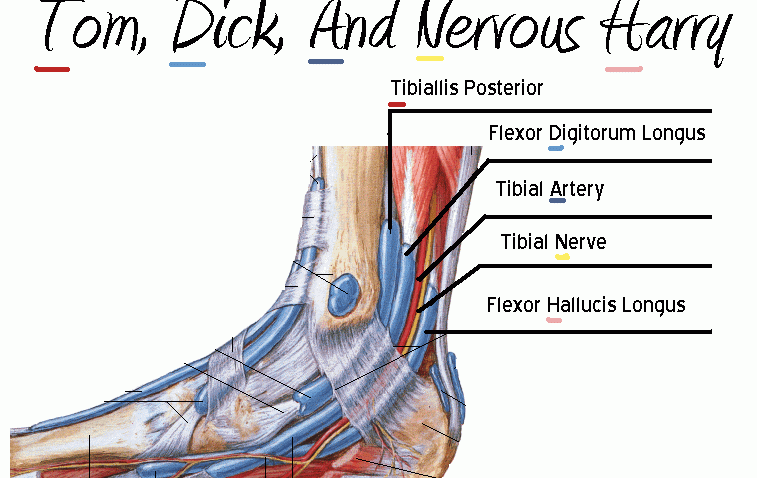
The following are structures that lie behind the medial malleolus, EXCEPT:
a. Flexor hallucis longus
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Flexor digitorum longus
d. Tibialis anterior
a. Flexor hallucis longus
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Flexor digitorum longus
d. Tibialis anterior
Tibialis anterior
43
New cards
Unopposed plantarflexion and inversion is secondary to damage or injury to this nerve:
a. Common peroneal
b. Tibial
c. Sciatic
d. Femoral
a. Common peroneal
b. Tibial
c. Sciatic
d. Femoral
Common peroneal
44
New cards
Unopposed dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot is an attitudinal condition known as:
a. Calcaneovalgus
b. Talipes Equinovalgus
c. Calcaneovarus
d. Talipes Equinovarus
a. Calcaneovalgus
b. Talipes Equinovalgus
c. Calcaneovarus
d. Talipes Equinovarus
Calcaneovalgus.
\
The heel (calcaneus) is positioned downward (that is, the ankle is flexed upward), and the heel is turned outward (valgus).
\
The heel (calcaneus) is positioned downward (that is, the ankle is flexed upward), and the heel is turned outward (valgus).
45
New cards
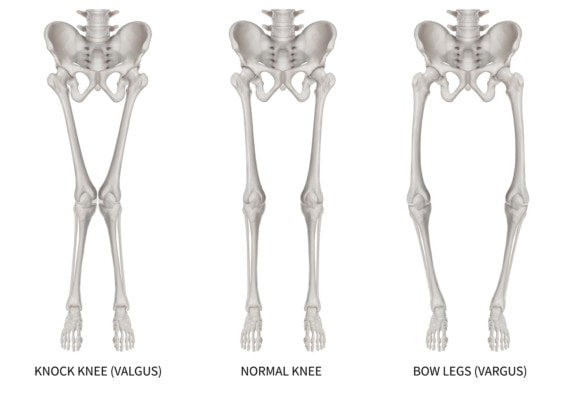
The ligament of the knee that checks on the varus stresses imposed in it is:
a. Oblique popliteal
b. Lateral collateral
c. Medial collateral
d. Patellar
a. Oblique popliteal
b. Lateral collateral
c. Medial collateral
d. Patellar
Lateral collateral.
\
LR = Lahi Ra = Lateral collateral : checks on vaRus stresses
MG = MiGa = Medial collateral : checks on valGus stresses
\
LR = Lahi Ra = Lateral collateral : checks on vaRus stresses
MG = MiGa = Medial collateral : checks on valGus stresses
46
New cards
Which bone of the ankle and foot DOES NOT have any muscle attached to it?
a. Calcaneus
b. Cuboid
c. Navicular
d. Talus
a. Calcaneus
b. Cuboid
c. Navicular
d. Talus
Talus
47
New cards
The following muscles dorsiflexes the foot, EXCEPT:
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Extensor hallucis longus
c. Peroneus tertius
d. Peroneus longus
a. Tibialis anterior
b. Extensor hallucis longus
c. Peroneus tertius
d. Peroneus longus
Peroneus longus.
\
Its actions are to plantarflex and evert the foot.
\
Its actions are to plantarflex and evert the foot.
48
New cards
The nerve that supplies the muscle that plantarflexes and everts the foot is the:
a. Tibial nerve
b. Common peroneal
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
a. Tibial nerve
b. Common peroneal
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
Superficial peroneal
\
Peroneus Longus both everts and plantarflexes the foot.
\
Peroneus Longus both everts and plantarflexes the foot.
49
New cards
To stretch the gastrocnemius, you need to perform:
a. Knee flexion and ankle plantarflexion
b. Knee extension and ankle dorsiflexion
c. Knee flexion and ankle dorsiflexion
d. Knee extension and ankle plantarflexion
a. Knee flexion and ankle plantarflexion
b. Knee extension and ankle dorsiflexion
c. Knee flexion and ankle dorsiflexion
d. Knee extension and ankle plantarflexion
Knee extension and ankle dorsiflexion
50
New cards
The nerve that supplies the muscle that plantarflexes and inverts the foot is the:
a. Tibial nerve
b. Common peroneal
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
a. Tibial nerve
b. Common peroneal
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
Tibial N. innervates Tibialis Posterior
51
New cards
What is the Lateral Plantar Nerve homologous to in the hand?
a. Tibial Nerve
b. Musculocutaneous Nerve
c. Median Nerve
d. Ulnar Nerve
a. Tibial Nerve
b. Musculocutaneous Nerve
c. Median Nerve
d. Ulnar Nerve
Ulnar N.
\
The Lateral Plantar N. innervates all the intrinsic muscles in the sole, except for the muscles supplied by the Medial Plantar N. (abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, flexor hallucis brevis, and 1st lumbrical)
\
The Lateral Plantar N. innervates all the intrinsic muscles in the sole, except for the muscles supplied by the Medial Plantar N. (abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, flexor hallucis brevis, and 1st lumbrical)
52
New cards
What is the Medial Plantar Nerve homologous to in the hand?
a. Tibial Nerve
b. Musculocutaneous Nerve
c. Median Nerve
d. Ulnar Nerve
a. Tibial Nerve
b. Musculocutaneous Nerve
c. Median Nerve
d. Ulnar Nerve
Median Nerve
53
New cards
What innervates posterolateral skin of the lower leg
A. Tibial nerve
B. Sural nerve
C. Common peroneal nerve
D. Obturator nerve
A. Tibial nerve
B. Sural nerve
C. Common peroneal nerve
D. Obturator nerve
Sural nerve
54
New cards
Which of the following nerves of the lower extremity tightens when you perform hip flexion, knee extension, and ankle dorsiflexion with eversion?
a. Tibial nerve
b. Saphenous
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
a. Tibial nerve
b. Saphenous
c. Superficial peroneal
d. Deep peroneal
Tibial nerve
55
New cards
The following are muscles located in the first layer of the sole of the foot, EXCEPT:
a. Abductor digiti minimi
b. Flexor digiti minimi brevis
c. Abductor hallucis
d. Flexor digitorum brevis
a. Abductor digiti minimi
b. Flexor digiti minimi brevis
c. Abductor hallucis
d. Flexor digitorum brevis
Flexor digiti minimi brevis
56
New cards
The following are components of the deltoid ligament of the ankle, EXCEPT:
a. Anterior tibiotalar
b. Posterior tibiofibular
c. Tibionavicular
d. Calcaneotibial
a. Anterior tibiotalar
b. Posterior tibiofibular
c. Tibionavicular
d. Calcaneotibial
Posterior tibiofibular
57
New cards
The pulsations of this artery can be felt between the medial malleolus and Achilles tendon insertion:
a. Anterior tibial
b. Posterior tibial
c. Popliteal
d. Dorsalis pedis
a. Anterior tibial
b. Posterior tibial
c. Popliteal
d. Dorsalis pedis
Posterior tibial
58
New cards
The Flexor Digitorum Brevis is innervated by:
a. Sural nerve
b. Tibial nerve
c. Medial plantar
d. Lateral plantar
a. Sural nerve
b. Tibial nerve
c. Medial plantar
d. Lateral plantar
Medial plantar
59
New cards
The foot is everted by the following muscles, EXCEPT:
a. Peroneus longus
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Extensor digitorum longus
d. Peroneus tertius
a. Peroneus longus
b. Tibialis posterior
c. Extensor digitorum longus
d. Peroneus tertius
Tibialis posterior.
\
Both Tibialis muscles are located medially (as in near the Tibia) so it inverts the foot!
\
Both Tibialis muscles are located medially (as in near the Tibia) so it inverts the foot!
60
New cards
The condition in which the medial longitudinal arch of the foot is high-arched is known as:
a. Pes equinus
b. Pes planus
c. Calcaneovalgus
d. Pes cavus
a. Pes equinus
b. Pes planus
c. Calcaneovalgus
d. Pes cavus
Pes cavus