PE Final Studying
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Agility
Ability to move swiftly & with ease during physical activity
Involves changing direction quickly and effectively
Balance
A skilled-related fitness component
Coordination
Capacity to maintain control over the body’s movements, especially those involved in sports
Power
Ability to apply maximum force as quickly as possible
Reaction time
Amount of time it takes you to react to an impulse or need to move in another direction
Speed
Ability to complete a certain physical activity as fast as possible
5 components of fitness
Cardiovascular Endurance
Muscular Strength
Muscular Endurance
Flexibility
Body Composition
Cardiovascular Endurance
A person’s ability to engage in exercises that raise heart rate for an extended period period of time, anything that forces the cardiovascular system to work for extended periods of time
Muscular Strength
Maximum amount of force your muscles can create, can be improved through resistance training activities
Muscular Endurance
The fatigued resisting ability of skeletal muscles when they are contracted less than maximal force for an extended period of time
Flexibility
The ability of joints to move through their full range of motion
Body Composition
Amount of body fat mass storing compared to fat-free mass
Anatomical Position
Standing upright eyes forward, feet parallel and close together, Arms at side, palms facing out
Transverse Plane
Divides body into upper & lower (rotational)
Sagittal Plane
Divides body from right to left (Flexion, extension, hyperextension)
Frontal Plane
Divides body from front to back (abduction/adduction)
Abduction
Away from midline
Adduction
Toward midline
Circumduction
Circles through two planes
Protraction
Translation of bone away from midline in a plane parallel to the ground
Retraction
Translation of bone toward the midline in a plane parallel to the ground
Flexion
Bending of one bone on another
Extension
Straightening of one bone away from another
Internal Rotation
Moving toward midline
External Rotation
Moving away from midline
Inversion
In
Eversion
Out
Dorsiflexion
Toward body
Planter Flexion
Push out
Radial Deviation
Toward thumb
Ulnar Deviation
Away from thumb
Supination
Palm up
Pronation
Palm down
Frequency
How often you exercise
Intensity
How hard you exercise
Time
How long you exercise
Type
What kind of exercise
Heart Rate
Number of heartbeats per minute
Recovery Heart Rate
Heart rate body decreases to after an activity session
Resting heart rate
Number of bets in one minute while at complete rest, indicates basic fitness level
Maximum heart rate
Highest number of times your heart can contract in one minute
Target Zone
Heart rate range that guides a workout by keeping intensity level between upper and lower heart rate limit
50-60% max heart rate
Light exercise, maintain healthy heart/get fit
60-70% max heart rate
Weight management, lose weight/burn fat
70-680% max heart rate
Aerobic Base building, increase stamina aerobic endurance
80-90% max heart rate
Optimal conditioning maintain excellent fitness condition
90-100% max heart rate
Elite athlete, maintain superb athletic condition
Lifting Rhythm
4 counts with gravity
2 counts against gravity
Extensor
A muscle that extends a jointed body part
Flexion
A movement in which two ends of a jointed body part move closer together
Interval Training
Exercise session in which intensity and duration of exercise are consciously altered between harder and easier work
Metabolism
The total process where the body breaks down substances for energy
1 Rep Max
Maximum resistance a person can execute one repetition of an exercise movement
Muscle Group
Specific muscles that act together at the same joint to produce a movement
Overload
Subjecting a part of the body o efforts greater than accustomed to, in order to elicit a training response
Overuse
Excessive repeated exertion or shock resulting in injuries
Peak Heart Rate
Highest heart rate reached during a workout session
Plyometric
Type of exercise that suddenly preloads and forces the stretching of a muscle an instant prior to concentric action
Prime Mover
The muscle or muscle group that is causing the movement around a joint
Pronation
Face-down position
Radial pulse
Pulse at the wrist
Resistance
Force which a muscle is required to work against
Respiration
Exchange of oxygen & CO2 between atmosphere and cells of the body
Slow-Twitch Fibers
Muscle fiber type that contracts slowly & s used in moderate-intensity, endurance exercises
Specificity
Principle that body adapts specifically to training stimuli required to deal with
Stretching
Lengthening a muscle to its maximum extension
Supination
Horizontal position upward
Phase I
Muscular endurance, 60-65% 1RM, 10-15 Reps, 3-4 sets
Phase II
Muscular Strength, 65-70% 1RM, 8-10 reps, 3-4 sets
Phase III
Muscular Power, 70-95% 1RM, 2-6 reps, 4-5 sets
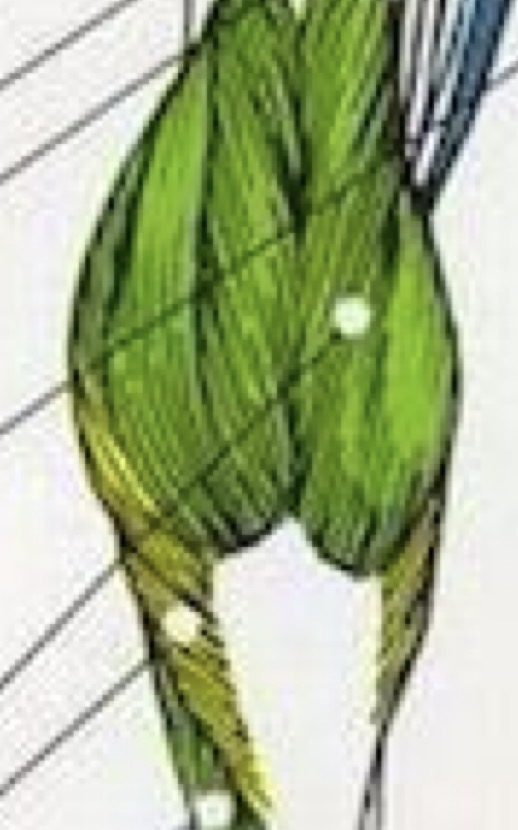
Calf
Hamstring
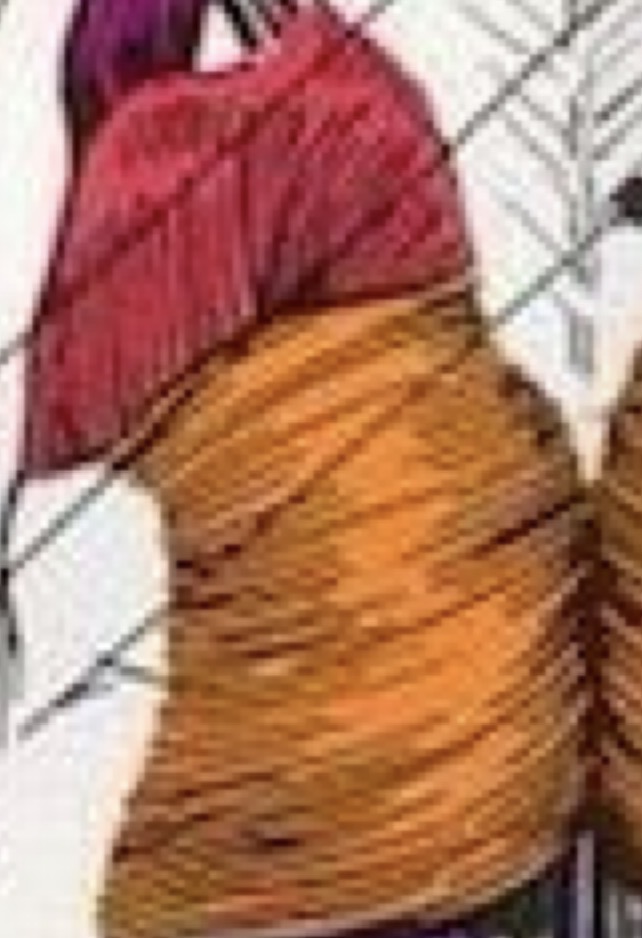

Glute
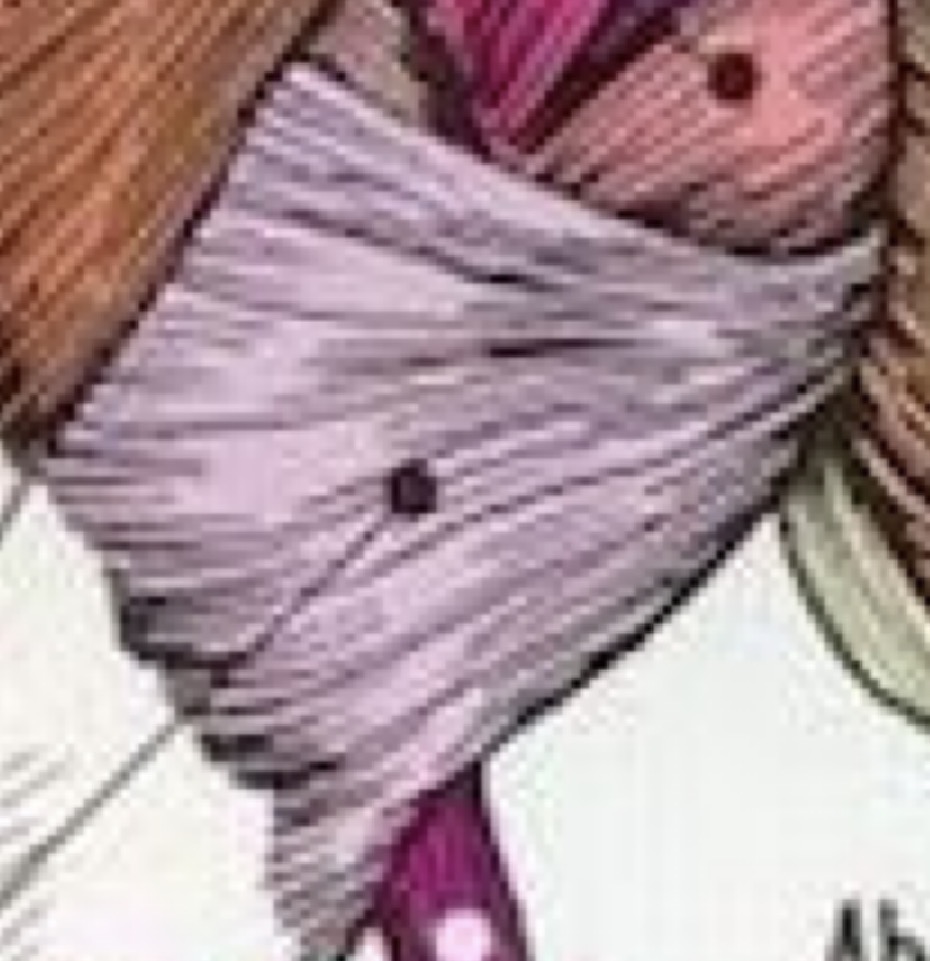

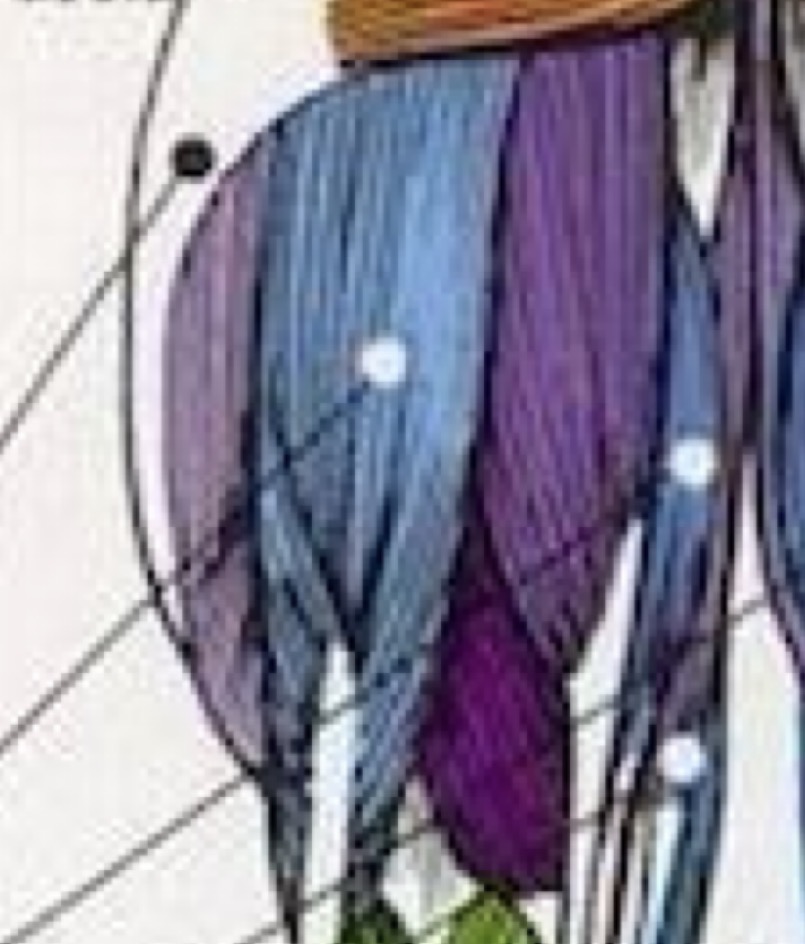
Latissimus Dorsi
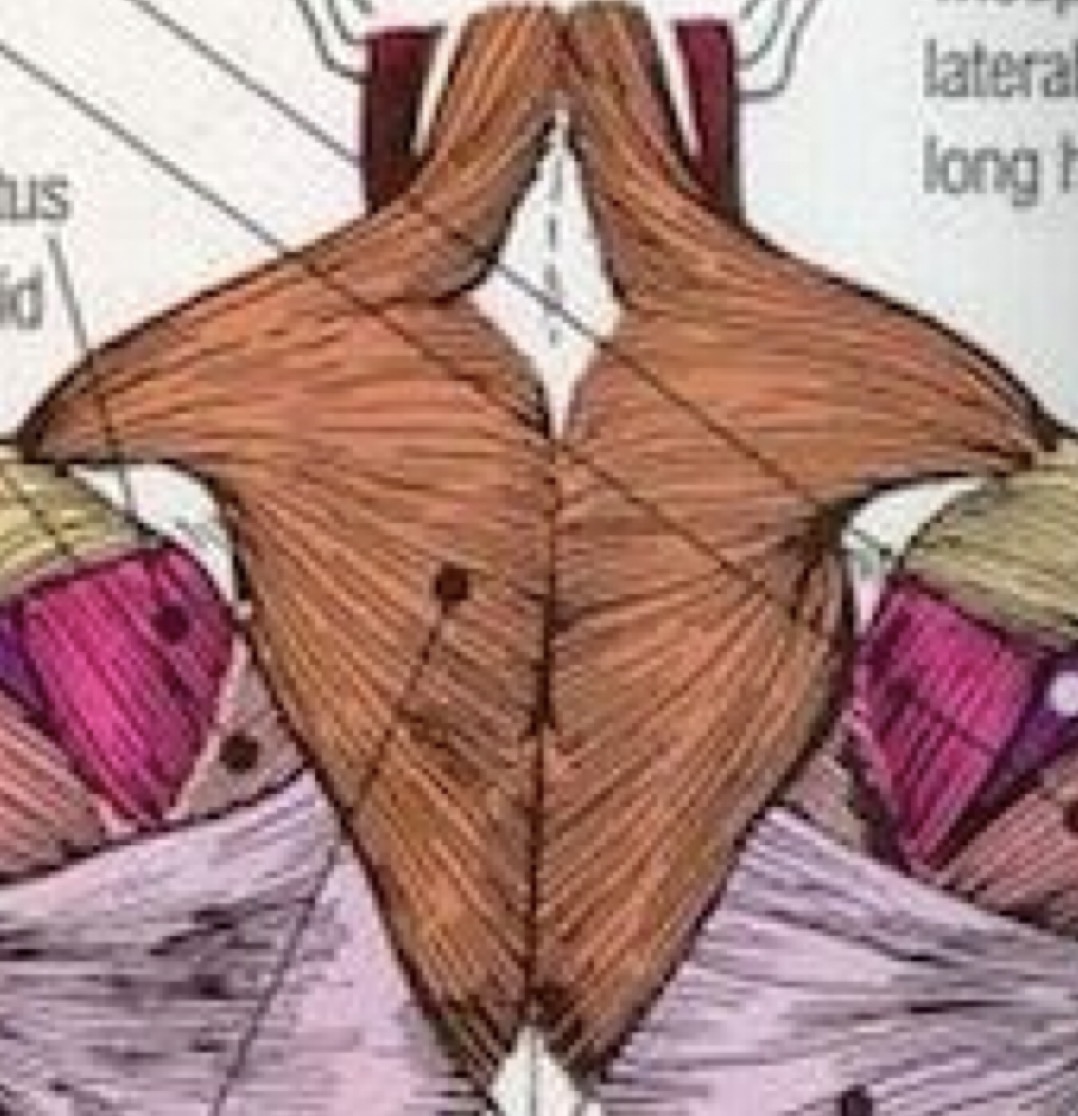
Trapezius
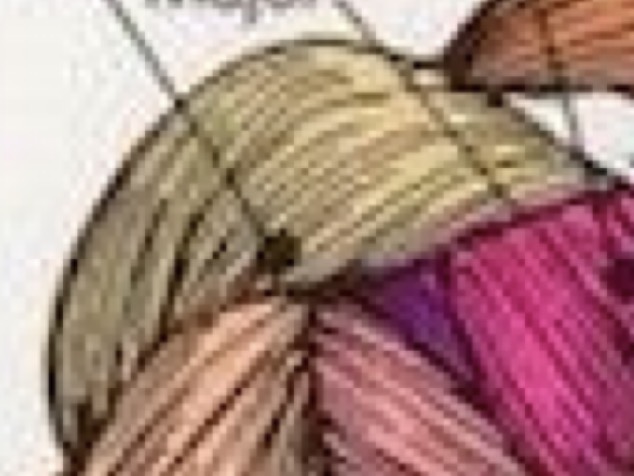

Shoulder
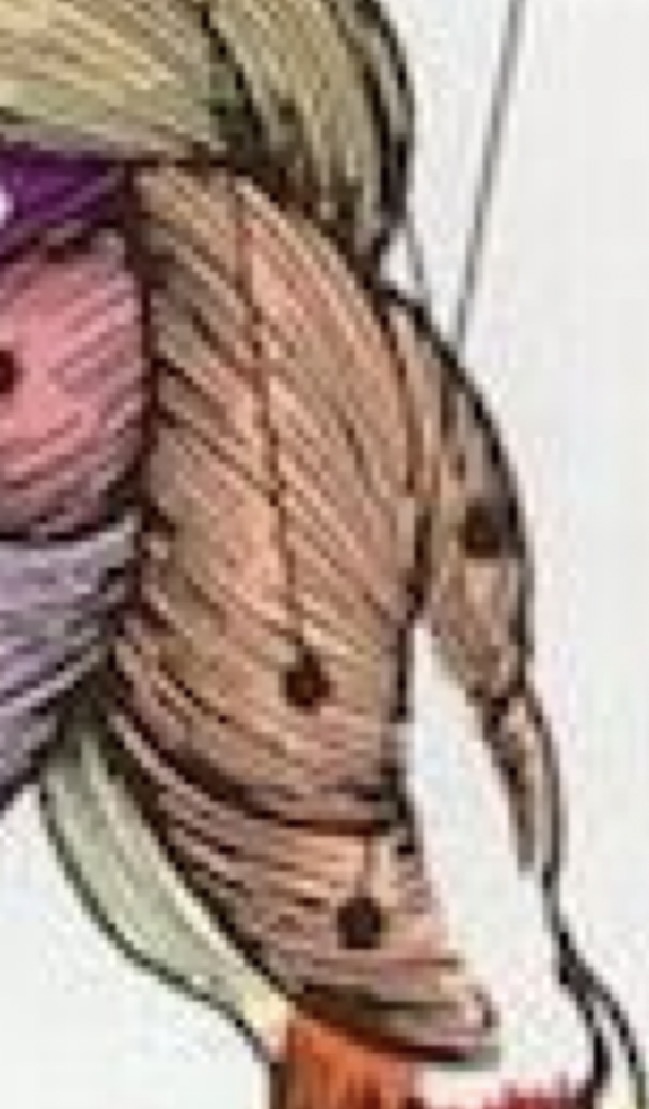

Triceps

Back
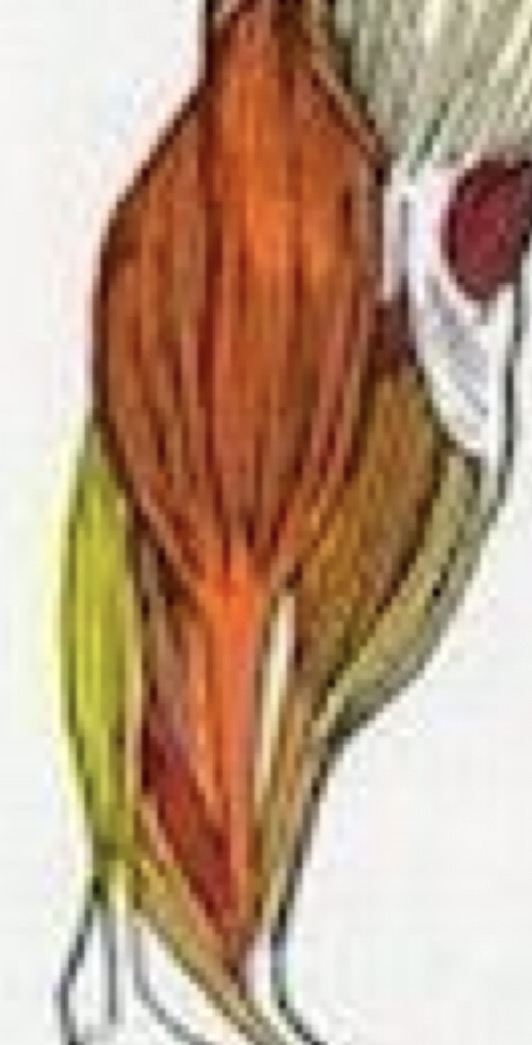
Forearms
Quadriceps
Abs




DB Kickback
Incline Press