LESSON 4 WIRED LOCAL AREA NETWORK (LAN) CONNECTION
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Transmission Media
A path that transports data from sender to recipient is known as transmission media. To transport data, we use different type of cable or waves. Electrical or electromagnetic signals are used to transmit data.
Transmission Media
Current is the form of an electrical signal. A series of electromagnetic energy pulses at different frequencies produces an electromagnetic signal. Copper wires, optical fibers, the atmosphere, water, and vacuum can all be used to carry these signals. Bandwidth, delay, cost, and ease of installation and maintenance are all characteristics of different media.
Types of Transmission Media
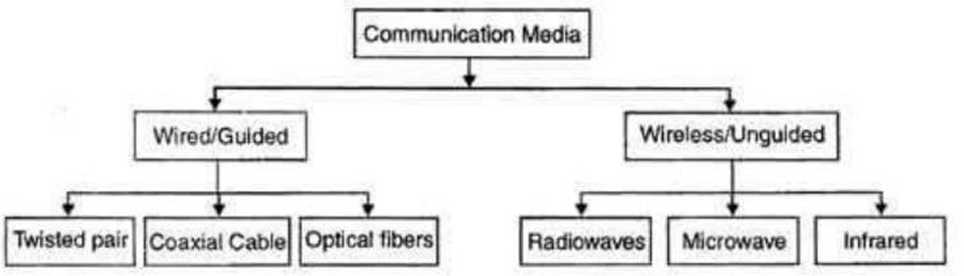
Communications Media Types
Fundamental communication takes place at the OSI Physical layer (also known as Layer 1), which manages communication media and network interfaces.
OSI Layer 1: Media and interface communication
Five basic forms of contact media
Coaxial cable
Twisted-pair cables (UTP and STP)
Fiber optic cable
Hybrid fiber optic cable/ coaxial cable
Wireless technologies
Coaxial
its core is made up of copper
Twisted-pair cables (UTP and STP)
made up of eight insulated coppers.
Fiber optic cable
can be Composed of plastic or fiber glass.
Hybrid fiber optic cable/ coaxial cable
made up of both copper and fiberglass cable.
Wireless technologies
can pertain to a radio wave or a microwave.
Twisted Pair Cables
Contains a set of eight color coded insulators covering the wires inside. The color-coded wires are then coated by another insulating PVC or Teflon jacket.
Twisted Pair Cables
A Registered Jack 45 or RJ-45 is a type of a connector mounted to your devices like routers, modems, etc. while the other end of it is linked to your computer's NIC port. It is also cheaper than T connectors used in coaxial cables.
Configured Twisted pair network media

A twisted pair cable can be divided into two groups, specifically
Shielded Twisted Pair Cable
Unshielded Twisted Pair cable
Shielded Twisted Pair Cable (STP)
Commonly has a woven or corrugated shield that functions a shield for signal interferences (EMI/RFI). An STP cable has a double coating insulation.
Unshielded Twisted-pair (UTP)
has also eight color coded wires with insulation, like any other twisted pair cable type.
Unshielded Twisted-pair (UTP)
It’s only difference with shield twisted pair cables, is that it does not have an additional shielding like STP cables.
Unshielded Twisted-pair (UTP)
This UTP cable is the most widely used twisted pair cable on LAN networks, which also reduces signal interference and features a variety of network cable models that demonstrates how much UTP has evolved over the years since it was launched.
Illustration that shows how the UTP cable wires should be connected to an RJ45
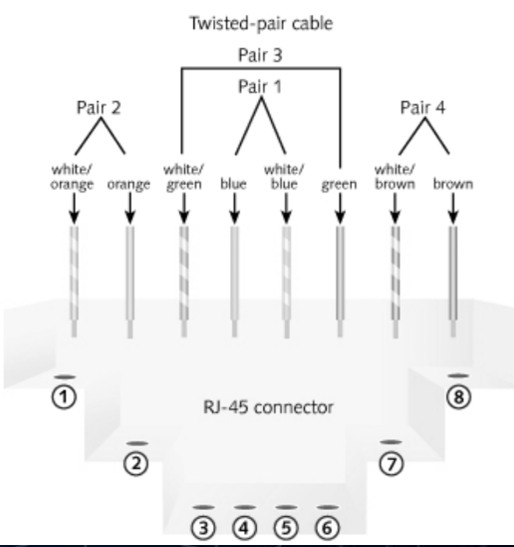
Straight Through Cable
is primarily used for connecting unlike devices.
Crossover Cable
Crossover cable is used for connecting alike devices.
Use straight through cable for the following cabling:
Switch to router
Switch to PC or server
Hub to PC or server
Home Router to PC (a Home Router normally contains a switch and a router)
Use crossover cables for the following cabling
Switch to switch
Switch to hub
Hub to hub (Switch and Hub are alike devices)
Router to router
Router Ethernet port to PC NIC
PC to PC