Community Nutrition Exam 3
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10 multiple 5 short answer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
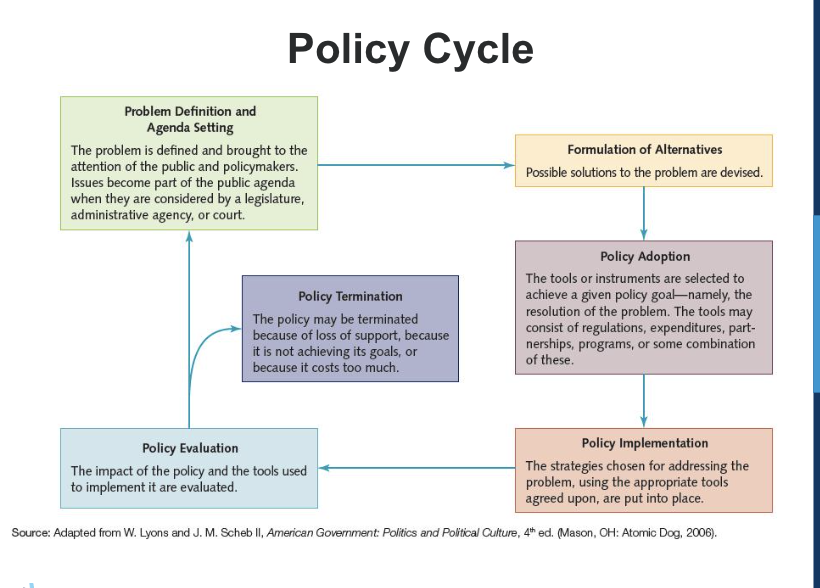
Describe the policy cycle.
Policy adoption is where you put it in a more formal context
Describe the process of a legislative bill becoming law (federal law). (How is a bill made?)
1.Introduction: A bill is introduced in either the House or the Senate.
2. Committee Review: The bill is sent to a committee for discussion, possible changes, and approval. (discussion/hearing& make up. could be in the subcommittee if it was referred to one. → full house committee for vote + debate→ If it is voted yes it moves on to the next step)
3.Floor Debate: The bill is debated and voted on by the full chamber (House or Senate). This is a full house review and debate where they will need to get a majority vote (51%)
4. Other Chamber: If approved, the bill moves to the other chamber for a similar process. (house bills would go to the senate and senate bills would go to the house. the same process that the house went through happens here. people get assignment committees and subcommittees) → if they vote yes it would go to the full chamber this would need to be a majority (51% or more)
5. Conference Committee: If both chambers pass different versions, a committee resolves differences. (this is where both house and senate come together to discuss the changes that was made to see if they can compromise on how the bill is worded)
6. Final Vote: Both chambers vote on the final version. (now it goes back to both chambers to be voted on and need to both pass by the majority)
7. Presidential Decision: The President signs the bill into law or vetoes it. Congress can override a veto with a two-thirds vote. (If it comes from the House the number will start with HR while if it starts in the Senate it will have an S)
outlays are what is going out, revenue is what is going in
receipts or revenue: Amounts that the government expects to raise through taxes and fees.
budget outlays: Amounts actually paid out by government agencies.
Entitlements: Programs that require the payment of benefits to all eligible people as established by law.
The remainder of the federal budget consists of discretionary spending—that is, the budget choices that can be made in such areas as defense, energy assistance, nutrition assistance (e.g., the WIC program and nutrition programs for seniors), and education after the mandatory allocations have been made.
discretionary is money for a population but not everyone in it is going to get that money
The federal FY 2024 begins on __________ and runs through _________.
The federal FY 2024 begins on _Oct 1 2023_________ and runs through __sep 30 2024________.
authorization: A budget authorization provides agencies and departments with the legal ability to operate.
appropriation: A budget appropriation is the authority to spend money.
An authorization defines the scope of a program and sets a ceiling on how much money can be spent on it. Before money can be released to a program, however, an appropriation bill must be passed. The appropriation for a program may cover a single year, several years, or an indefinite period of time.
Defensive – instead Respectful & Open-minded
Complex jargon – instead Simple & Direct Make sure the language you use is understandable (especially to those outside of your field)
Quicksand – instead Brief & Re-focus Make sure to advocate what you are there for (you can quickly answer/acknowlage if they have a question but do not spend the time off of it)
Extra on Amendments (difference between amendments and bills)
Amendments (there is already a law and they want to change part of it) are not the same things as a new bill (new law)
Identify a bill number, sponsor and co-sponsors of a bill, the latest action on a bill, and to whom you would address an email/letter to advocate for or against a bill (e.g., state or federal Senator or Representative).
Copayment: - A fixed amount you pay for a medical service or prescription, usually at the time of the visit. - Example: You might pay $20 for a doctor's visit, while your insurance covers the rest.
Deductible: - The amount you must pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services before your insurance starts covering costs. - Example: If your deductible is $1,000, you'll pay that amount before insurance kicks in.
Premium: - The amount you pay (monthly or annually) to maintain your health insurance coverage. - Example: You might pay $300 per month for your insurance plan, regardless of whether you use services. 2.
End stage renal disease or be 65 and older, citizen (80% is federally funded) Are paying but it is being deducted from social security income
Part A: hospital care (includes hospice care and any inpatient care)
Part B: outpatient care
Part D: prescription drugs
Private insurance company (20%): pay premium → full coverage OR Part C: advantage plan - small or no premium, some deductibles (part A + B + D) 3.
Federally and state funded Eligibility is based on income (for lower-income households) - can vary state to state).
Any age, does not matter what age. Copayment and deductible depends on the state (with the deductible medicaid pays the rest)
Medicare: 80% federally funded (social security) 20% private insurance
Medicaid: federally and state funded
Discuss these questions:
What is the fiscal calendar year?
Starts in the october (1) before that year and ends the september(30) of the year
What is the difference between appropriation and authorization?
Appropriation: the amount that is appropriated of alloted for that program
Authorization: the program has the authority to carry out that program
What is budget revenue, outlays, mandatory spending, and discretionary spending?
Renenue is what is coming in (taxes), outlays (what is going out), mandatory spending (if you are eligable you get the funding as a receiver. must be spent out), discretionary (limited spending, not everyone who is eligable may get benefits)
How do you avoid message pitfalls when meeting with legislators?
be respectful, openminded, simple, direct, focused
Discuss these questions:
What is an insurance premium, co-pay, and deductible?
Premium: monthly, co-pay: pay per visit, Deductible: you pay for part and insurance pays the rest
What are eligibility criteria for Medicaid? Medicare?
Medicaid: low income
Medicare: 65 or older, citizen,
How is Medicaid administered and funded? Medicare? (e.g., State, Federal or both?)
Medicaid: federally and state funded. Medicare: 80% federally funded 20% private insurance
What does Medicare Parts A, B, C and D cover?
Part A: hospital care(inpatient care), Part B: outpatient care, Part C: advantage plan, Part D: prescription drugs