The Knee: Bones, Joints, and Movements
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
lateral femoral condyle
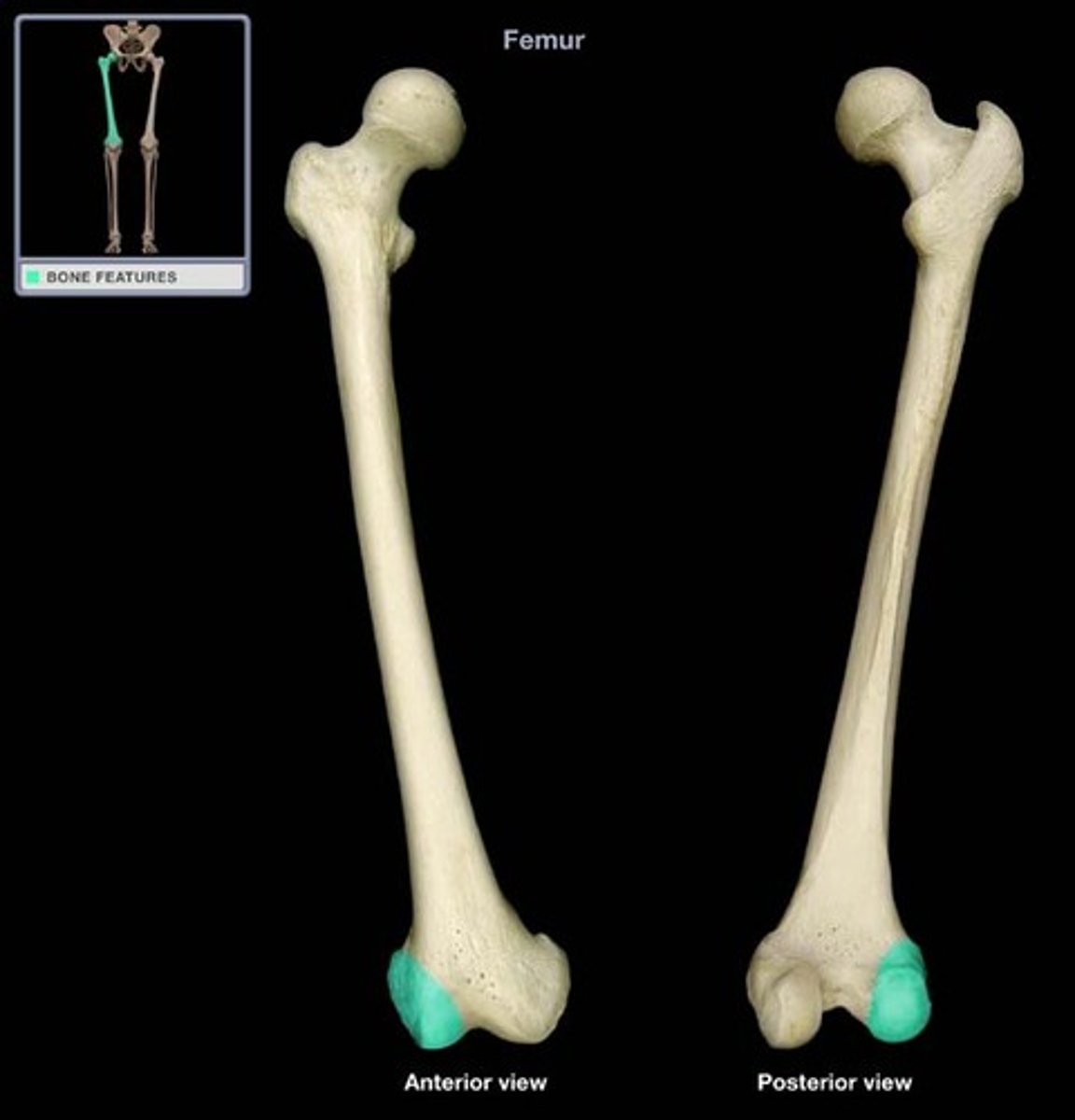
medial femoral condyle
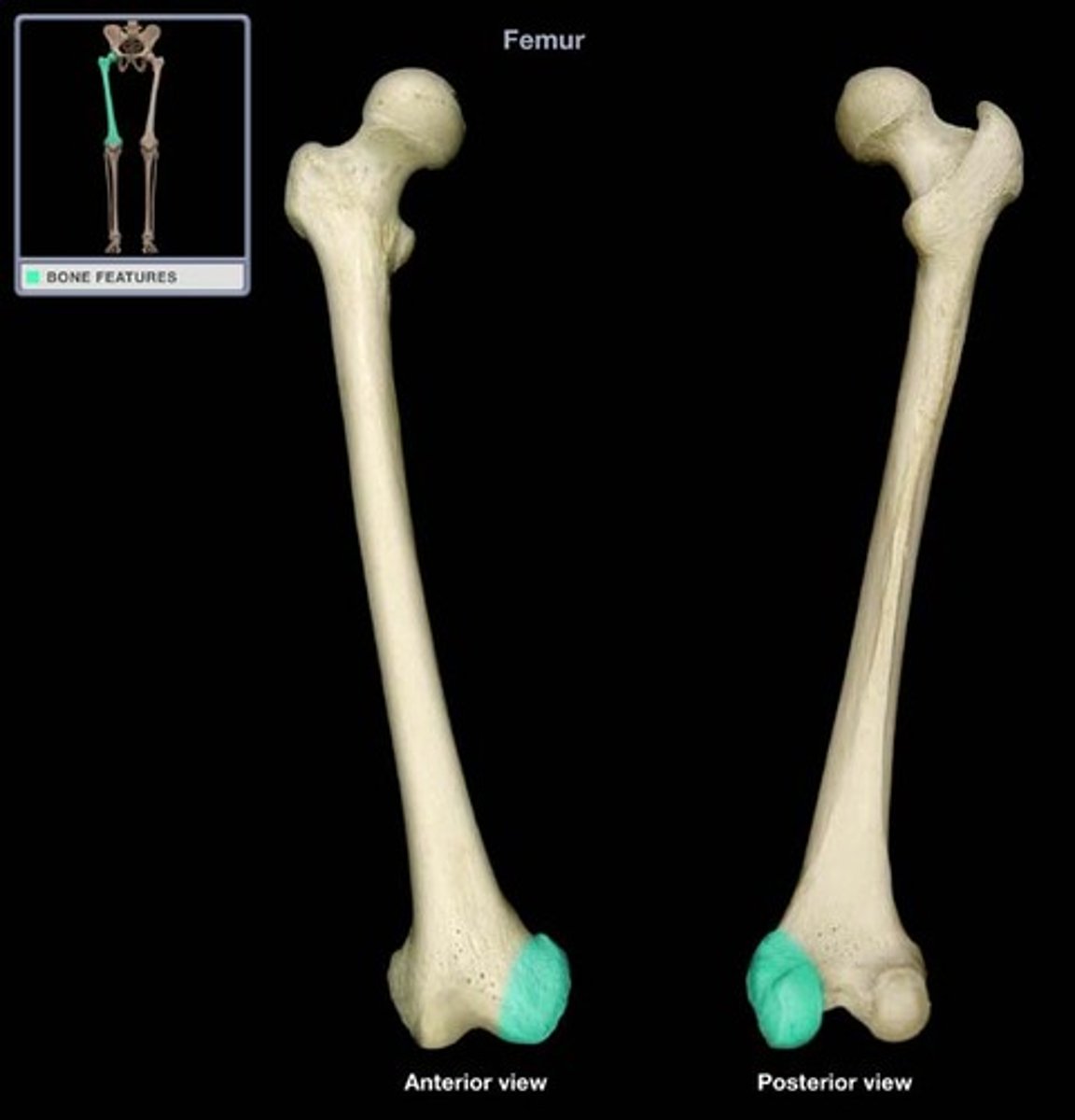
medial condyle
Which femoral condyle is larger and extends further distally?
Laterally
When the femoral condyles lie on the same horizontal plane- which direction is the shaft of the femur angled?
medial and lateral collateral ligaments
Which structures attach at the epicondyles of the femur?
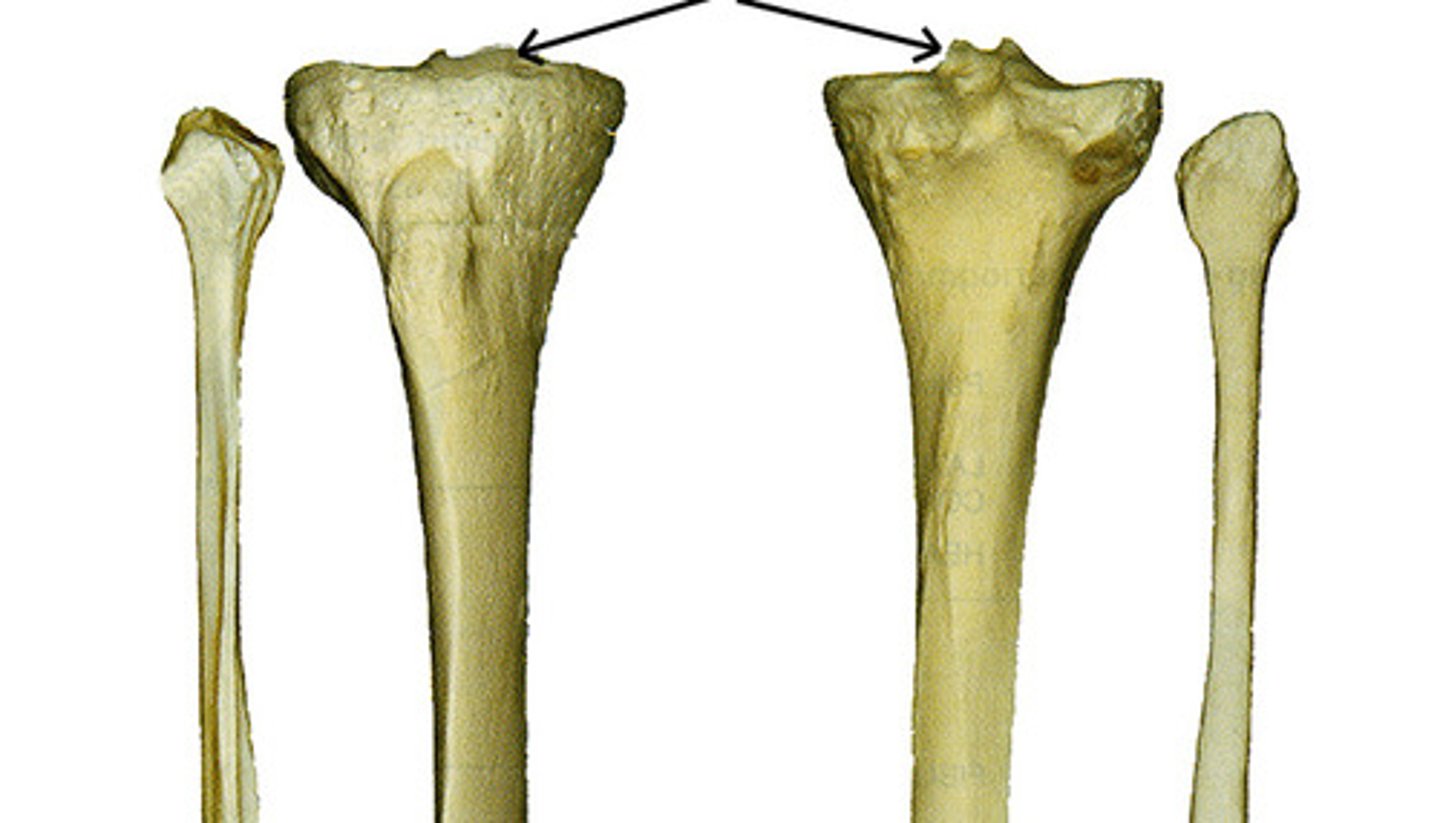
lateral and medial tibial condyles
What are letters B and D?
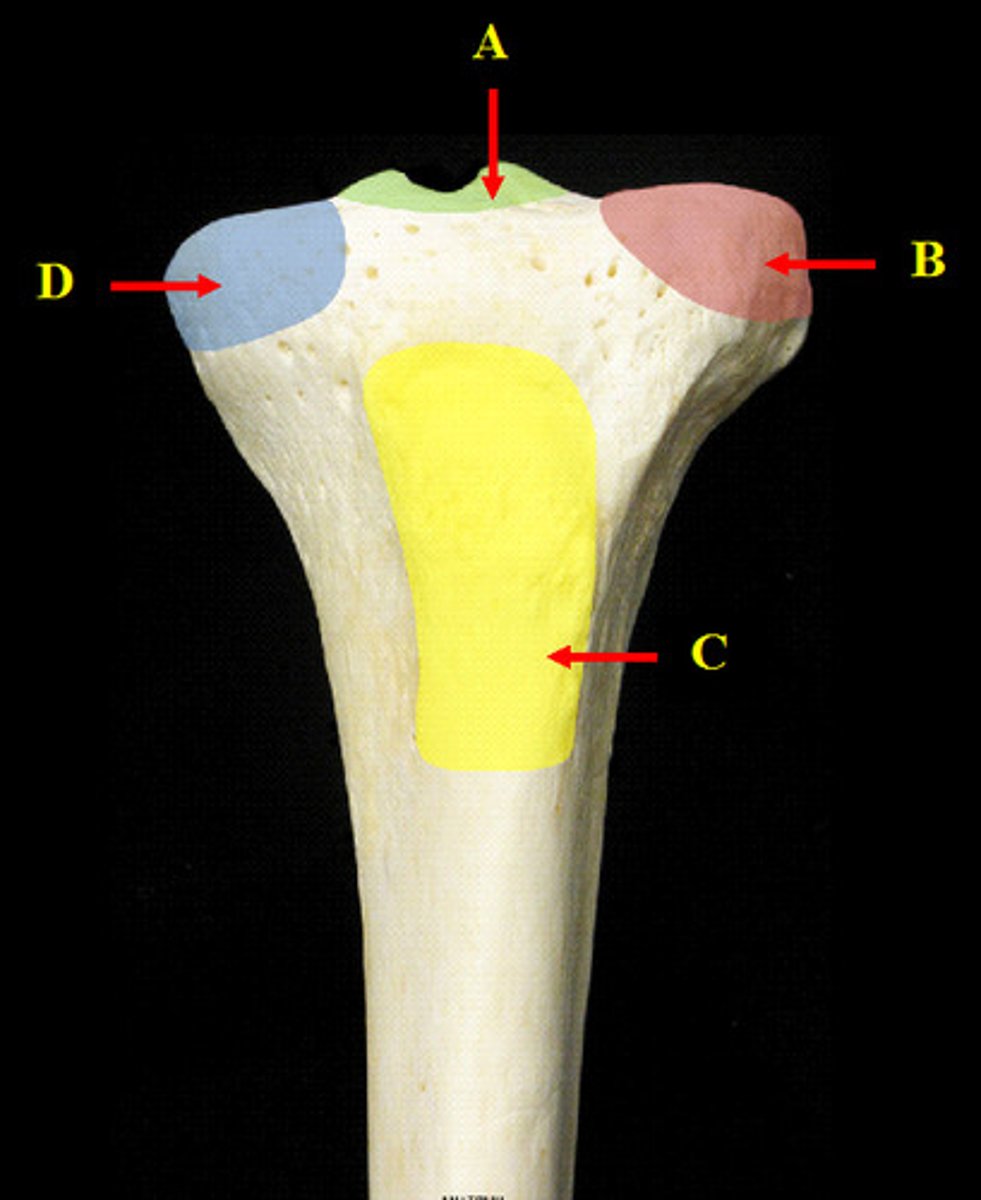
lateral and medial tibial plateaus
intercondylar eminence
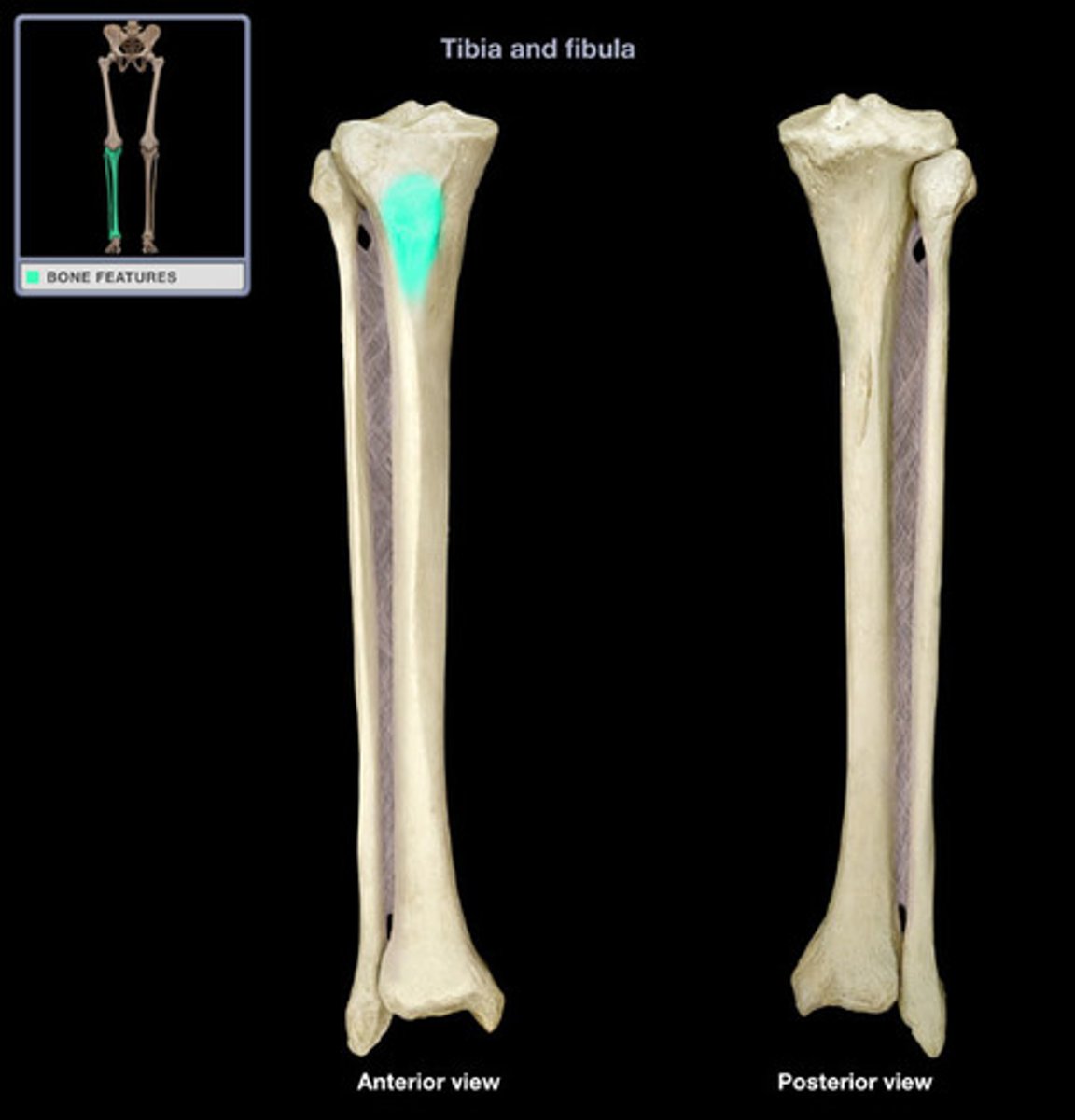
tibial tuberosity
patellar tendon
what structure attaches here?
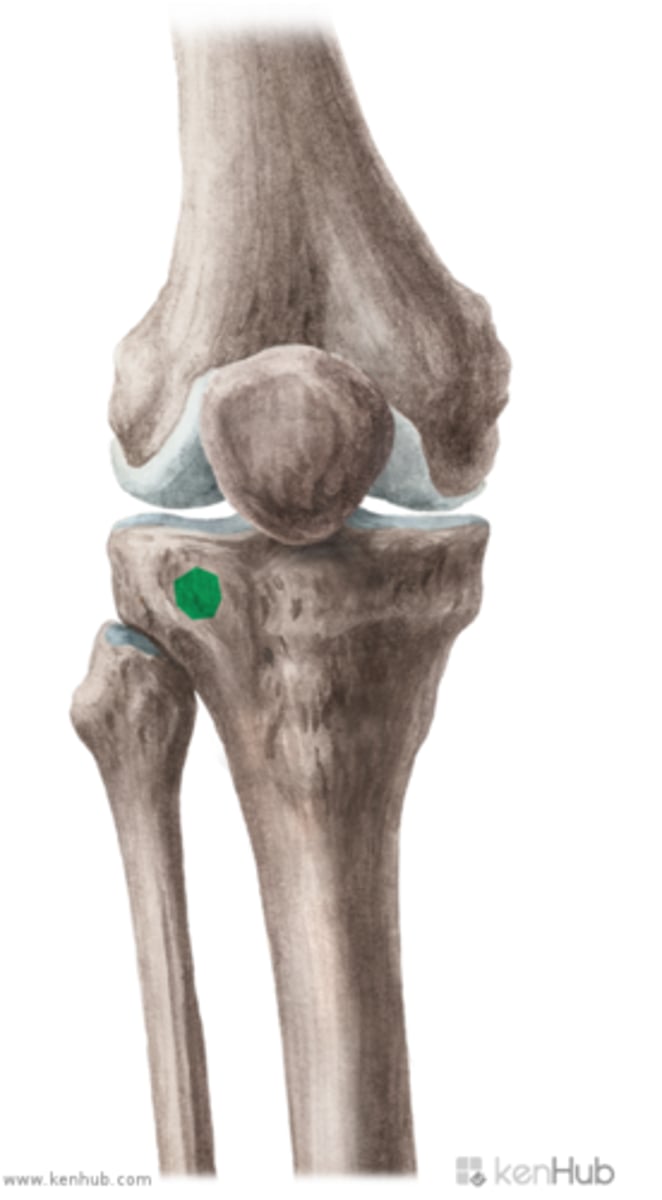
gerdy's tubercle
Iliotibial band/tract
What structure attaches on this?
triangular sesamoid bone that is embedded in the quadraceps muscle group
What is the patella and where is it?
base (superior)
apex (inferior)
articular cartilage
What are the parts of the patella and what lines the posterior surface?
femoral condyles
the medial and lateral facets of the patella articulate with what?
Joint: synvoial modified hinge joint
Surfaces: femoral condyles and tibial plateaus
What is the joint classification and articulating surfaces of the tibiofemoral (knee) joint?
Posterior: attaches to the margins of the femoral and tibial condyles
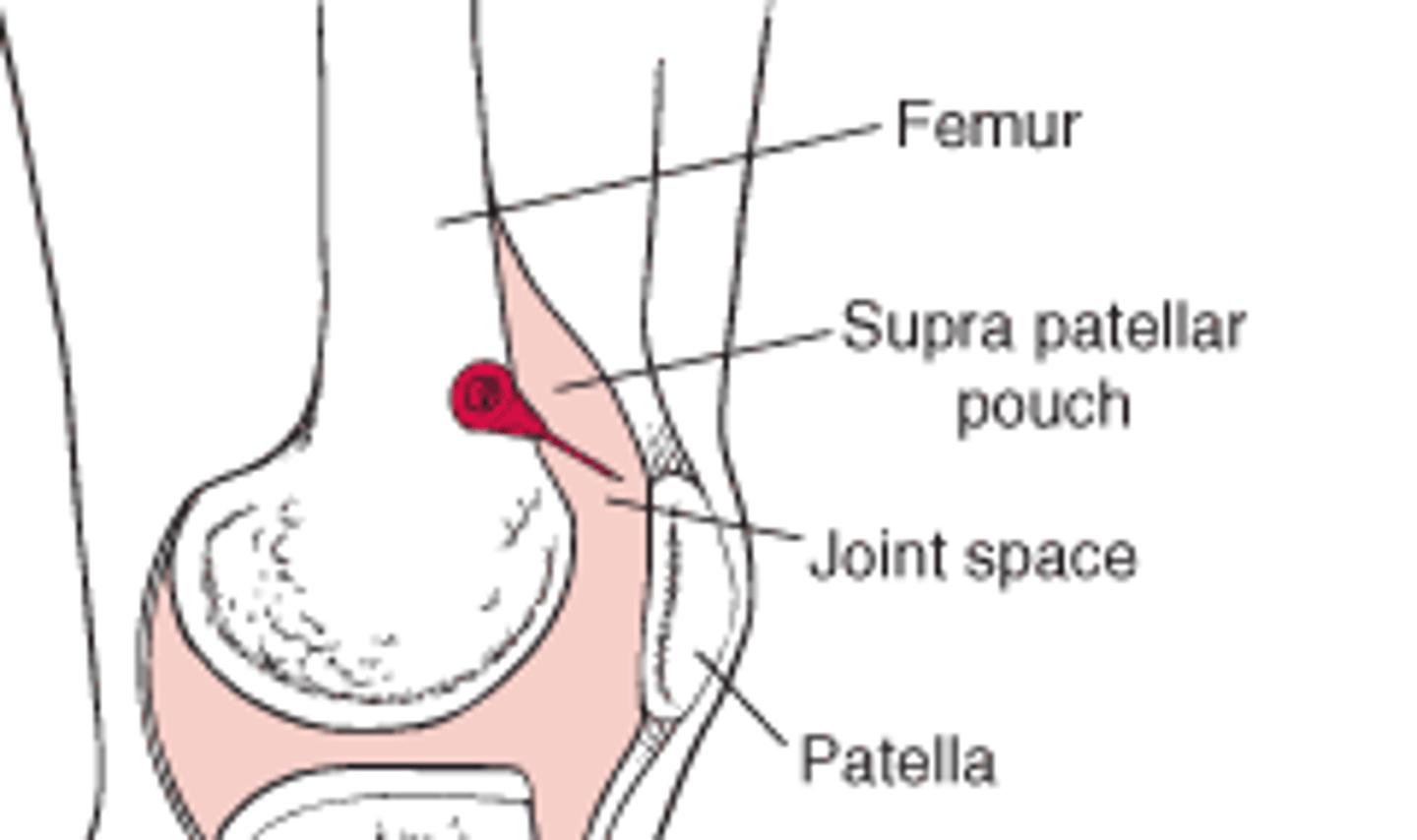
Anterior: attaches to the border of the patella and forms a large pocket (suprapatellar pouch)
Describe the synovial layer of the knee joint capsule posteriorly and anteriorly.
shock absorption
reduces friction
lubricates the joint
nourishes articular cartilage
provides nourishment for the menisci
What are the general functions of the synovial layer of the joint capsule and what is an additional function?
allows for smooth full movement of the patella thus full motion of the knee
What is the suprapatellar pouch important for?
posteriorly to the femoral and tibial condyles and anteriorly to the margins of the patella
Anteriorly to the margins of the patella
Where does the fibrous capsule of the knee attach?
the medial and lateral patellofemoral ligaments (which stabilize the patella)
blends with tendinous expansions of vastus medialis and lateralis to form the medial and lateral patellar retinaculum
What reinforces the fibrous capsule of the knee? What does the capsule blend with and form to support the patella?
suprapatellar bursa
prepatellar bursa
infrapatellar bursa (superficial and deep)
semimembranous bursa
name the different bursa at the knee
when the knee is flexed, it can internally and externaly rotate the lower limb
Why is the knee called a "modified" hinge joint?
when the knee is in full knee extension, the tibia will externally rotate to provide a locking of the knee and this results in the tightening of the cruciate ligaments and it contributes to knee stability
What is the "screw home" mechanism of the knee?
Joint: synvoial plane/gliding joint
Surfaces: medial and lateral patellar facets and femoral condyles
What is the joint classification and articulating surfaces of the patellofemoral joint?
provides protection
provides an attachment site for the quadriceps muscles
reduces friction between the quadratus tendond and femoral condyles
increases the moment arm of the quadriceps tendon (which allows for greater mechanical advantage for knee extension
What are the function of the patella?
glides superiorly on the femur as the knee moves into extension and inferiorly as the knee moves into flexion
describe the movement of the patella
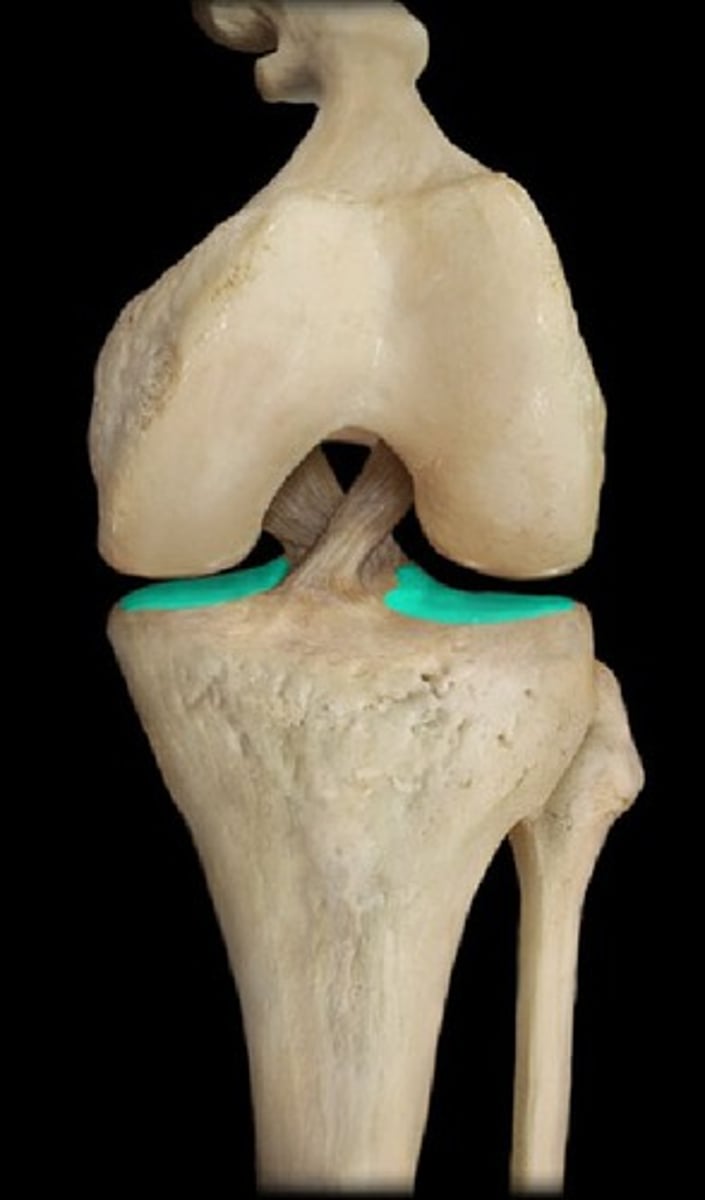
smooth, white, crescent-shaped pads of fibrocartilage that rest on the medial and lateral tibial plateaus
what are menisci and where are they?
increase the congruency between femur and tibia
act as shock absorbers
reduce friction within the joint
*increase the contact area between the femur and tibia and reduce the mechanical stress/loading sustained by underlying cartilage
What are the functions of the menisci?
synovial fluid from the joint capsule
blood supply to peripheral edges of menisci
What supplies nutrition to the medial and lateral menisci?
Medial: open c shape that is broader posteriorly and firmly attached to tibia by coronary ligaments and also to MCL
Lateral: closed c shape that is less firmly attached to tibia wtih no attachment to the LCL, more mobile than the medial meniscus
describe the differences between the medial and lateral menisci
medial meniscus because of the connection to the MCL
which meniscus is more prone to injury?
from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the proximal medial tibia and the deep fibers are attached to the medial meniscus
Where does the MCL attach?
valgus
The MCL maintains medial stability by resisting what forces at the knee?
from the lateral epicondyle to the head of the fibula
where does the LCL attach?
varus
the LCL maintains lateral stability by resisting what forces at the knee?
arises from the intercondylar area of the tibia and passes superior and posterior to the medial aspect of the lateral condyle of the femur
Where does the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) attach?
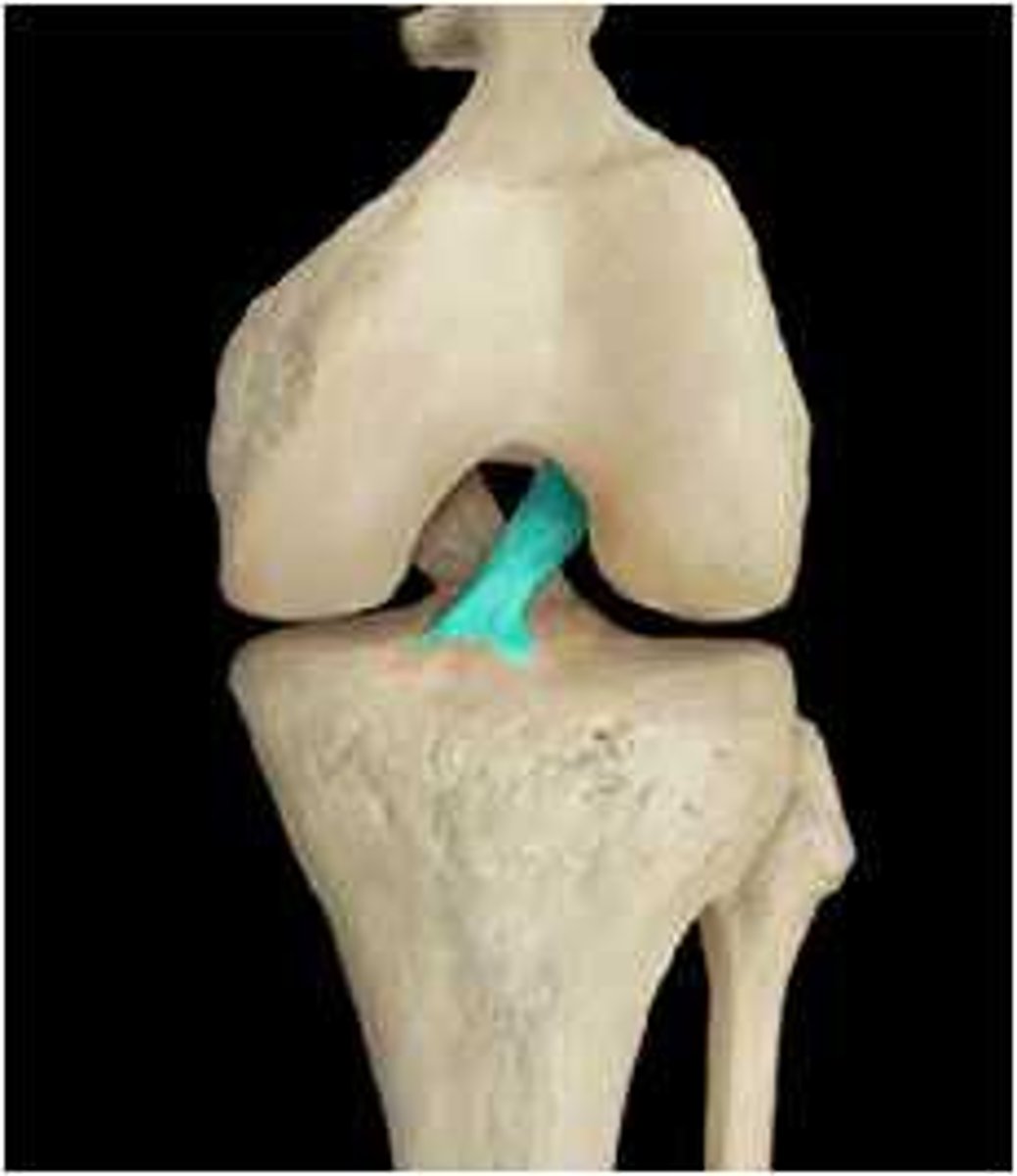
anteromedial- tight in flexion
posteriolateral- tight in extension
what are the two major fiber bundles of the ACL?
Anteromedial fibers
Which bundle of fibers in the ACL prvent against anterior translation of the tibia on the femur?
from the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia and passes superior and anterior to the lateral aspect of the medial condyle of the femur
Where does the PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) attach?
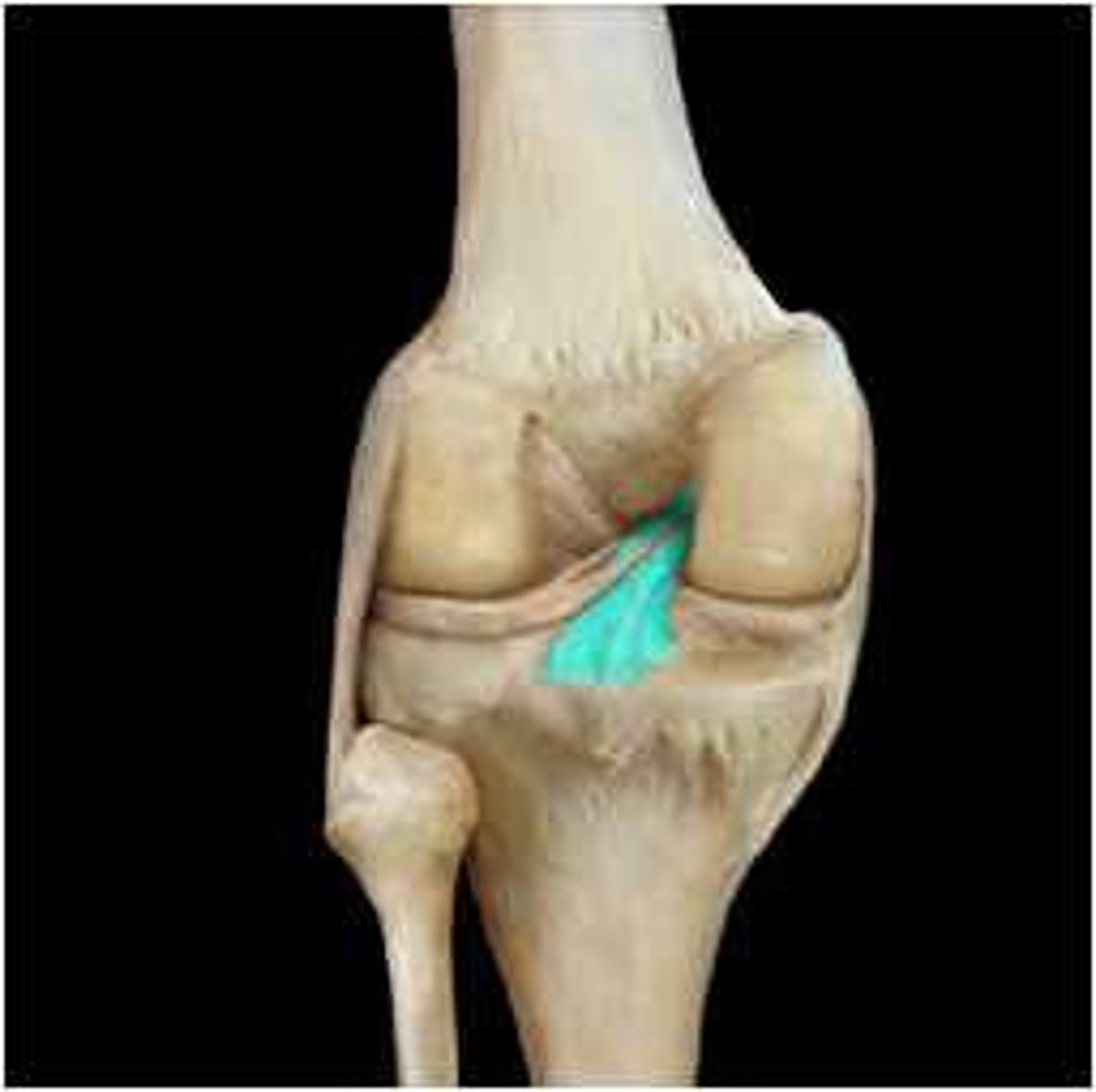
posterior
The PCL protects against which translation?
medial/lateral (valgus/varus) forces and rotational motions
The ACL and PCL stabilize against what?
giving out of the knee, feeling of instability
What are the typical symptoms of an ACL injury?