Organizational Culture
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Class 7-8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is Culture?
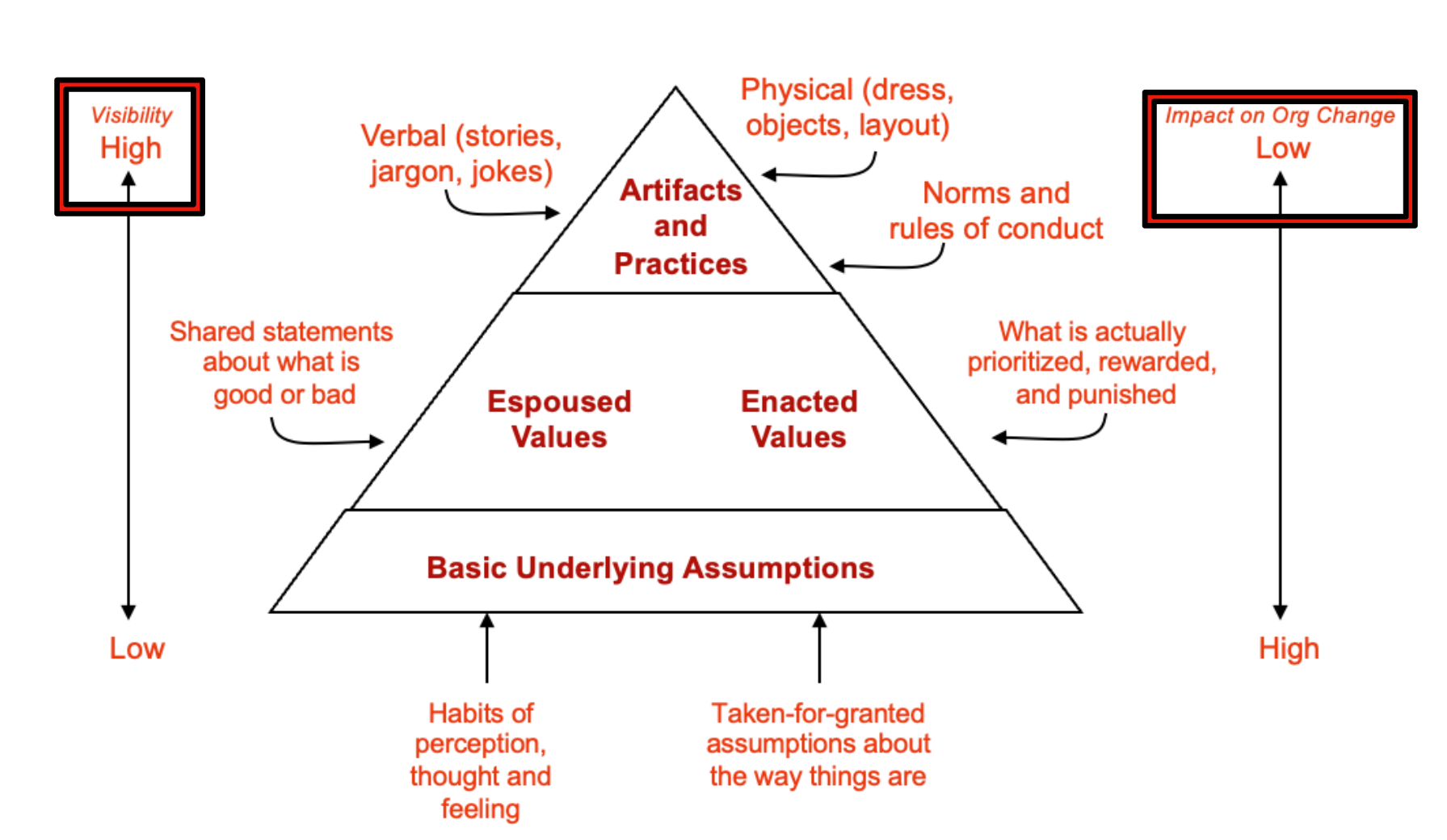
The set of values, attitude, beliefs, and expected behavior shared by members of an organization. “The way things are done around here”
The “personality” of an organization
Method of managerial control counter to formal organization
Part of informal organization of the congruence model
Levels of Culture
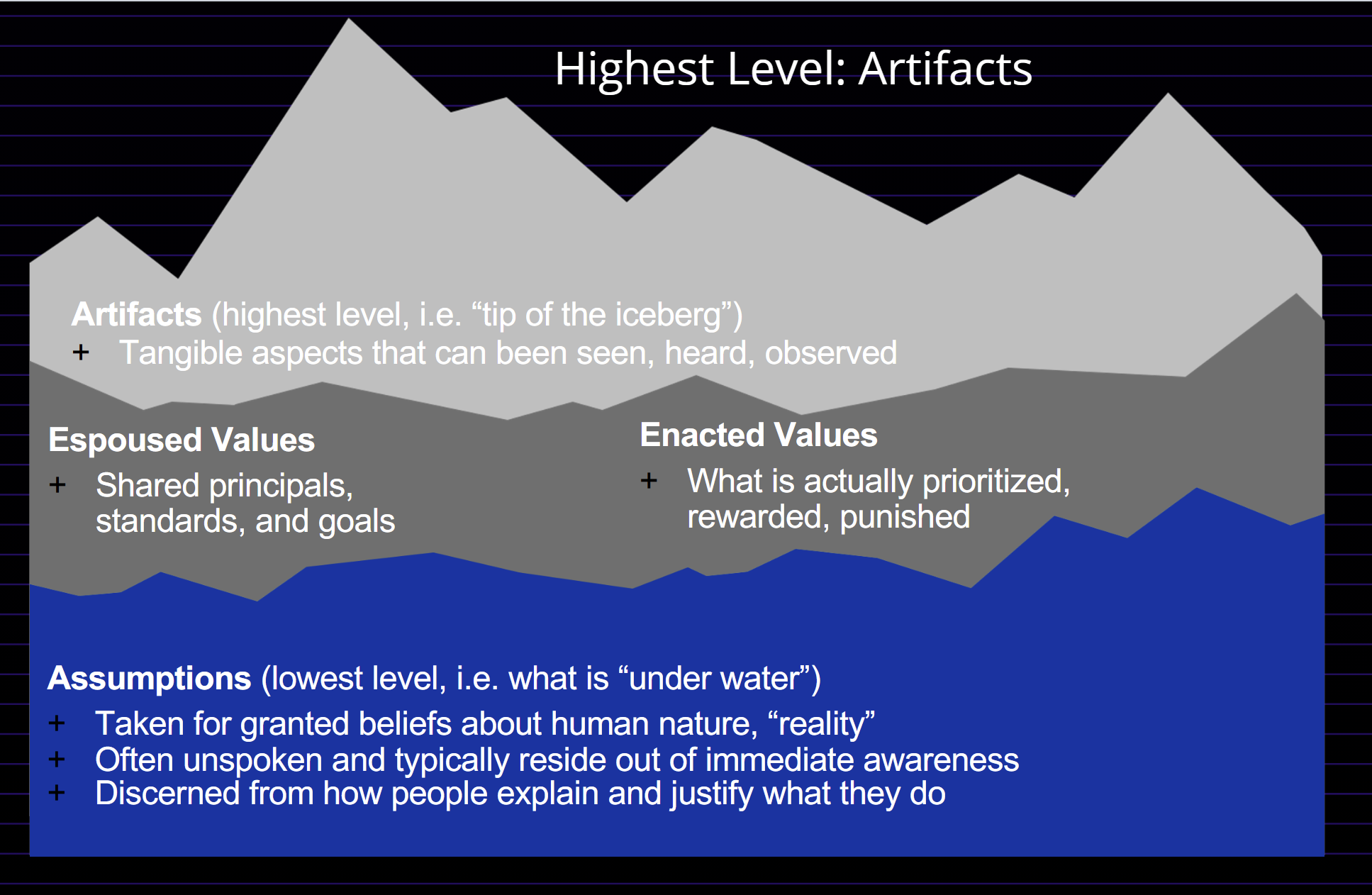
Iceberg Model of Culture
Functions of Organizational Culture?
Control - influences decisions and behaviors
Connect - social glue that bonds people
Comprehend - helps people understand what is happening in the organization, and why
Cultural Strength
Strong culture - values, assumptions, and beliefs are widely held and agreed upon (they exert a strong impact on behavior)
Stronger situations: funerals, ceremonies, libraries, first dates
Weak culture - disagreement or confusion around values, assumptions, beliefs (behavior is influenced through formalized systems, bureaucracy)
Weaker situations: sitting at home, shopping, subway, parties
Benefits of strong cultures
Values that are 1) widely shared and 2) viewed as extremely important.
Benefits
Ability to attract and retain employees
High motivation to achieve the vision
Competitive advantage from employing uniquely skilled and talented individuals
Feelings of “fit”, cohesion, and solidarity
Costs of Strong Cultures
Cult-like features
belief in superiority
unwillingness to question shared values and assumptions
insulation from outside viewpoints
lack of diverse perspectives and opinions
feeling coerced and pressured to comply with norms
How to build culture
Attraction - attracting the right people
Selection - hiring/selecting the right people
Attrition - kicking out the right people
What determines who you go to help?
Competence
Trust
Accessibility
Bad Help Examples
Takeovers
Swoop and Poops