Updated General Biology 2 Final Exam Reviewer
1/241
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
242 Terms
Gas Exchange
The uptake of oxygen from the environment and the release of CO2 to the environment
External Respiration
Gas exchange between the air of the external environment
Internal Respiration
Gas exchange between the blood and interstitial fluid
Respiratory surfaces
What is the needed requirement to allow gas exchange between living things
invertebrates
The classification of these animals: hydras, earthworms and insects
fish kill
The sudden and unexpected death of aquatic anima;s in a short perido of time, due to the unavailability of oxygen in the stagnant water they inhabit
Respiratory medium
the environmental substance with which an animal exchanges gases, can either be water or air
water is more viscous than air and moving oxygen through a respiratory surface exposed to water requires more effort
water also holds less oxygen than air
changes in water temperature may contain mroe dissolved oxygen while stagnant water contains less
Ventilation
the process of air flowing into the lungs during inspiration and out of the lungs during expiration
Positive pressure breathing
This is done by amphibians; inflation of the lungs with forced air flow. In this process the frog draws air into its nostrils with its mouth shut and forces the air into the lungs and the air is expelled when the body wall contracts and the lungs recoil
One way ventilation
This process is done by birds; occurs in one direction only. Mixing of inhaled and exhaled air is less likely. During the first inhalation it draws air into posterior air sacs and in the first exhalation, this air moves through tiny tubes in the lungs and in the second inhalation the air in the lungs into the anterior air sacs and in the second exhalation air exits the air sacs
Negative pressure breathing
This process is done by mammals which is similar to a syringe, air is pulled rather than pushed into the lungs.
Pulmonary Capillaries
Inside each lung additional branching airways deliver air to the alveoli, where gases are exchanged with ______
alveoli, neighboring capillaries
Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide are diffused through the thin walls of _____ and the _____ _____
Trachea
What is below the larynx
Pharyx and larynx
Air enters through the lungs, then to the _____ then to the _____ to a trachea that branches out into two bronchi, one to each lung
alveolar capillaries
Oxygenated blood from the _____ _____ leaves lungs through pulmonary veins to the heart
right ventricle
which ventricle pumps blood to the lungs where it loads O2 and unloads CO2
left ventricle
Which ventricle pumps the blood to the body tissues
left atrium
which atrium is which where the oxygen rich blood from the lungs enter
Respiratory adaptation
Certain mechanisms developed by organisms that resides in low oxygen environment
one circuitry pathway
has a single atrium and ventricle
Two circuitry pathway
Amphibians that has 2 atriums and 1 ventricle and birds, mammals and humans have 2 atriums and 2 ventricles. What do you call thiese?
complex
The bigger the animal the more ____ the heart
Septum
What separates each side of the heart
Atrium
What receives blood
Ventricles
What pumps the blood
valves
What allows the blood to keep moving in the correct direction
Arteries
What moves the blood away from the heart
Veins
What moves the blood towards the heart
Pulmonary circuits
What carries the oxygen poor blood to the lungs via pulmonary veins
systematic circuits
What carries the oxygenated blood to the body systems then returns the oxygen poor blood to the heart via veins
Georges-Louis Leclerc
🇫🇷 French nationalist
Proposed various causes of evolution with evidence
Wrote a 44-volume natural history series
Histoire Naturelle
George-Louis Leclerc wrote this 44-volume natural history series to describe plants and animals
Carolus Linnaeus
🇸🇪 Swedish botanist
Developed binomial nomenclature and classification
Father of taxonomy
Taxonomy
Carolus Linnaeus proposed this as a way to organize biotic life into a hierarchical structure in which a scientific name was assigned to each organism (Binomial Nomenclature)
Binomial Nomenclature
Classification system in which each species is assigned a two-part scientific name
[ Genus ] [ Species ]
Erasmus Darwin
🇬🇧 British physician and naturalist
First to formally theorize about evolution in Zoonomia
Based his conclusions on development changes in animals, artificial animal breeding, and vestigial structures
Vestigial Structures
Present body parts that lack function
Georges Cuvier
🇫🇷 French Zoologist
Established comparative anatomy and paleontology
Developed Catastrophism
Catastrophism
Developed by Georges Cuvier
Organisms are destroyed by natural catastrophes repeatedly, causing evolution and the creation of new species
James Hutton & Charles Lyell
Proposed Uniformitarianism
Uniformitarianism
Hutton and Lyell's principle that geologic processes that occurred in the past can be explained by current geologic processes
The same things that have happened before will play the same way in the future
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Developed Lamarckism
Proposed two principles: "The Law of Use and Disuse", "The Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics"
Lamarck's hypothesis: The environment can produce physical changes in an organism which can be inherited by the next generation
Lamarckism
An evolutionary theory by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck stating that species change over time by the use and disuse of structures and the inheritance of acquired traits
Opposes Darwinism
The Law of Use and Disuse
A principle which states that parts of the body that are used extensively develop whilst those that are not used deteriorate
The Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
A principle which states that an organism could pass its modifications to its offspring
Thomas Malthus
🏴 English economist
Published "An Essay on the Principle of Population" which stated that the human population's size is limited by the availability of necessary resources
Malthus' principle was the basis for Darwin's natural selection
Charles Darwin
🏴 English naturalist
Proposed his theory of evolution by natural selection
Formulated his theory after his voyage, and wrote the book, "On The Origin of Species"
Defined evolution using his idea of “Descent With Modification"
Natural Selection
A natural process resulting in the evolution and survival of organisms best adapted to the environment
The Voyage of the Beagle
Charles Darwin's famous global voyage, where he found his first evidence of evolution
Galápagos Islands
The place where Charles Darwin made his observations during his voyage
Darwin's Study of Geology and Fossils
Earth must be old
Darwin observed geological changes that were the result of slow processes
Darwin collected fossils that differed from modern species
Observations of Nature
Genetic Variation: Genetic variation is inheritable
Limited Resources: Essential resources (e.g. food, space) are limited in every habitat
Overproduction of Offspring: More offspring are born than can survive. The capacity to overproduce was a characteristic shared by all species
Inferences from Observations
Struggle For Existence: Individuals compete for limited resources that enable them to survive
Unequal Reproductive Success: The inherited characteristics of some individuals make them more likely to survive (natural selection)
Descent With Modification: A population’s characteristics can change by natural selection, giving rise to new species
Modern Evolutionary Synthesis
Genes are responsible for hereditary characteristics
Population, not individuals, that evolve
Speciation occurs due to the accumulation of small genetic changes
Gene Pool
Collection of all genes in a certain population
Gene or Allele Frequency
The relative frequency of an allele at a particular locus of a population
Genotype Frequency
How many genotypes there are
Phenotype Frequency
How many manifestations of a genotype there are
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
A population’s allele frequencies are constant unless there is an evolutionary force acting upon them
Assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
No natural selection
No mutation
No genetic drift
No gene flow
No non-random mating
Systematics
It is the classification and study of biodiversity
Include
Taxonomy - Classification of organisms
Phylogenetics - Evolutionary relationships between species
Linnaean Taxonomy
Devised by Carolus Linnaeus to organize life into a hierarchy of inclusive categories
Binomial Nomenclature
Two-part format of the scientific name (Binomial)
Avoids ambiguity when communicating about research
Linnaean System of Classification
Linnaeus grouped organisms into a hierarchy of increasingly inclusive categories
Taxonomic Levels
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Taxon
A group at any level of the hierarchy
The more features two organisms share, the more taxonomic levels they share
The Flaw of the Hierarchy
The hierarchy does not disclose the evolutionary relationships between species
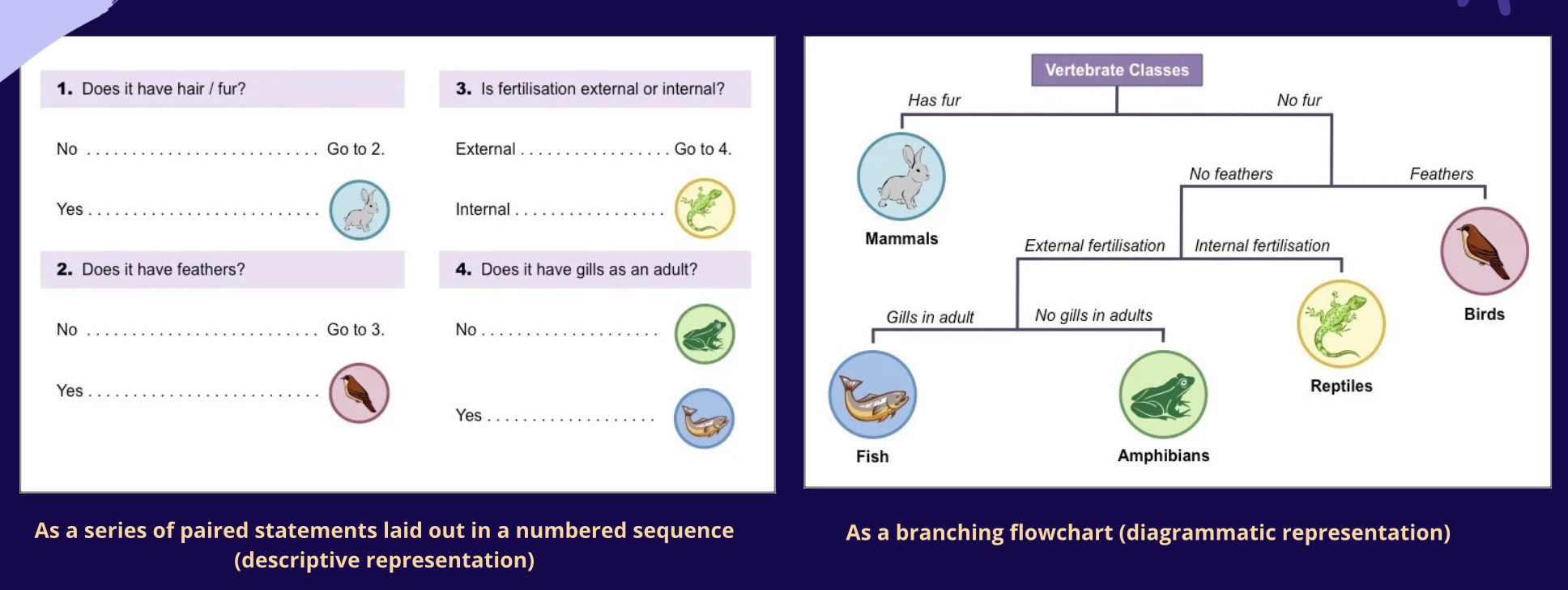
Dichotomous Key
A method of identification wherein groups of organisms are divided into two categories repeatedly
Usually represented in two ways
Descriptive Representation
Diagrammatic Representation
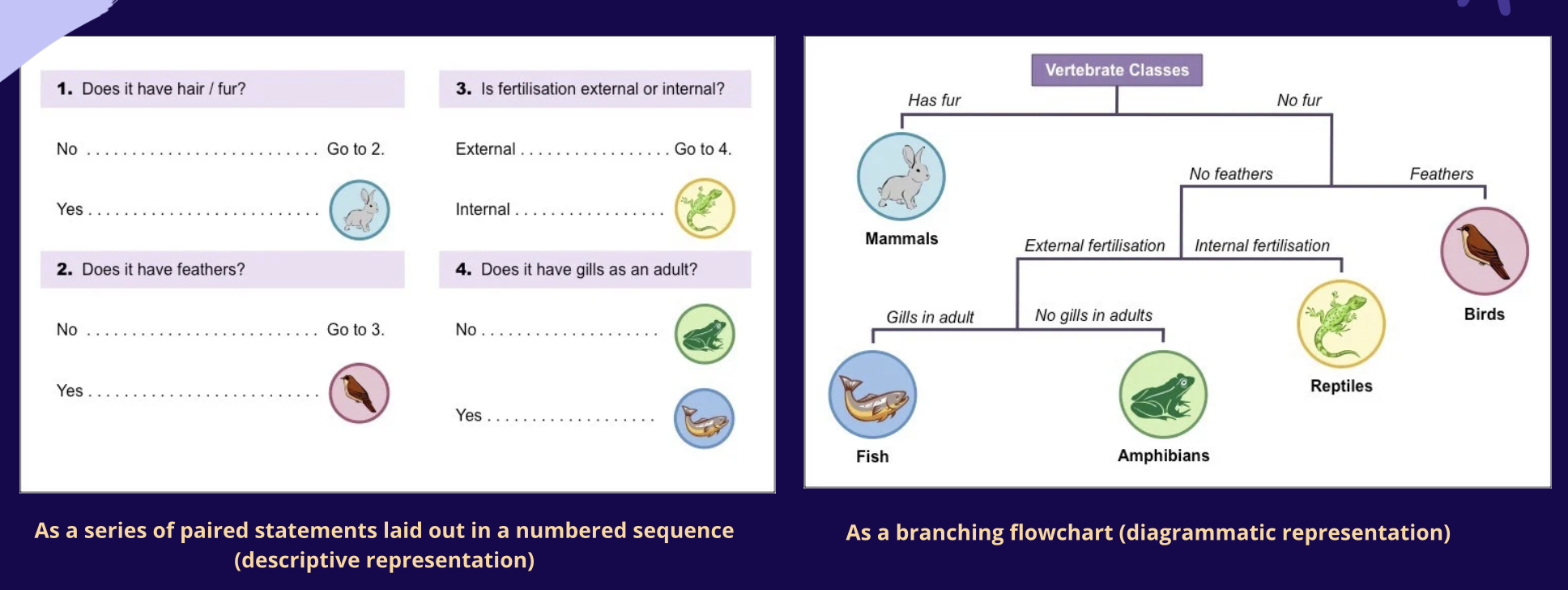
Descriptive Representation
A series of paired statements laid out in numbered sequences
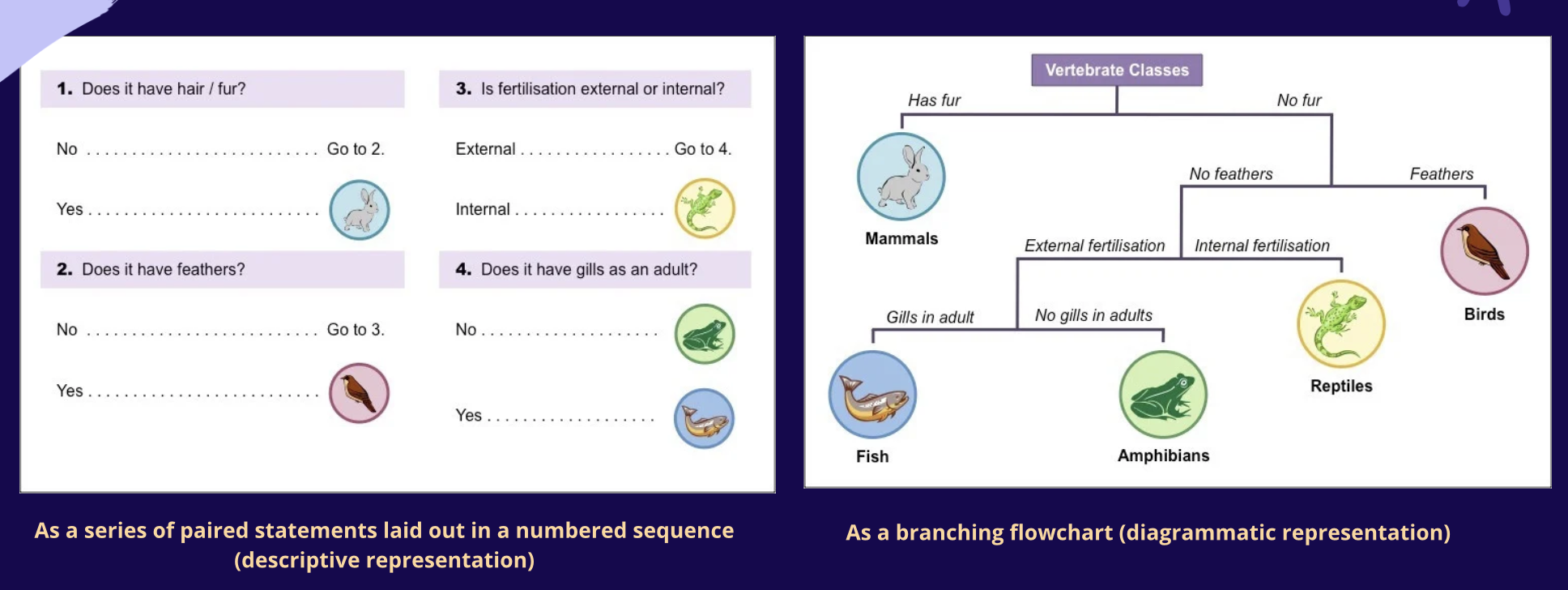
Diagrammatic Representation
A branching flowchart
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species or a group of species
Cladistics
A phylogenic system that categorizes groups into ancestral and derived characters
A phylogenic system that categorizes groups into clades
Ancestral Characters
Inherited traits that resemble the ancestor’s
Derived Characters
Features that differ from the ancestor’s
Cladogram
A treelike diagram built using shared derived characteristics
Features of a Cladogram
Clade
Outgroup
Root
Node
Clade
Includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants
Is monophyletic
Outgroup
The most distantly related species and functions as a reference group
Root
An initial ancestor common to all organisms
Node
A common ancestor tied to two or more taxa
Monophyletic
“Single tribe”
A single common ancestor and all of its descendants
Paraphyletic
“Beside the tribe”
A common ancestor and some of its descendants
Polyphyletic
“Many tribes”
A group with no recent common ancestor
Phylogeny Based On Molecular Data
DNA Sequence Comparisons
Protein Sequence Comparisons
DNA Sequence Comparisons
The DNA sequences of a gene are aligned to determine the evolutionary relationships among some mammals
Protein Sequence Comparisons
The number of differences on the amino acid sequences of different species are used to measure relatedness
Fossil Records
Support evolutionary theory
Fossils are remains or traces of past organisms that are mostly found in sedimentary rocks
Display the evolution of organisms
Fossil Formations
Compression
Petrifaction
Impression
Cast
Intact Preservation
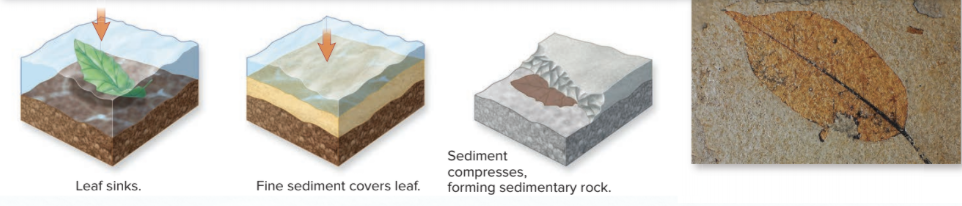
Compression
Sediments accumulate on top of organic material and compress it

Petrifaction
A decaying organism gradually turns into stone

Impression
An organism leaves imprints in mud that harden to rock

Cast
An organism is covered by mud and rots away, leaving a hollow interior once the mud has hardened

Intact Preservation
A whole organism is preserved in material (e.g. tree resin)
Transitional Fossils
Fossils that resemble two groups that are classified separately in the present-day
No Fossil Traces
A reason for incomplete fossil records
Most organisms never leave a fossil trace
Plates Are Constantly Moving
A reason from incomplete fossil records
Decomposing organisms are usually destroyed by plate motions
Hard To Discover
A reason for incomplete fossil records
Scientists will never find fossils buried deep in the Earth or the ocean
Biogeographical Evidence
Supports evolutionary theory
The study of the geographic distribution of fossils and species
Wallace’s Line
Patterns of organic life on either side of an imaginary boundary