Parasitology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
what is the term for parasites that only infect humans?
Anthroponosis
2
New cards
what is the term for animal parasites that infect humans?
Zoonosis
3
New cards
What is the difference between a parasitic and a symbiotic relationship?
In parasitism, it is only the parasite that gains benefit, but symbyosis is beneficial for both.
4
New cards
What does ectoparasite and endoparasite mean?
ectoparasites are only in the surface but endo- are inside the body of the host.
5
New cards
What are the 4 types of parasitism?
1\.Accidental
2\.Optional
3\.Obligatory (parasitic organism that cannot complete its life-cycle without exploiting a suitable host)
4\.Erratic (wanders in to an organ in which it is not usually found)
2\.Optional
3\.Obligatory (parasitic organism that cannot complete its life-cycle without exploiting a suitable host)
4\.Erratic (wanders in to an organ in which it is not usually found)
6
New cards
What are the two main types of host?
1\.Final host
2\.Intermediate host
\
2\.Intermediate host
\
7
New cards
What is a reservoir?
A place such as an animal, soil, or human where the parasite is able to thrive for a long duration of time.
8
New cards
What is the difference between a monoxenic and heteroxenous life cycle?
Monoxenic=Evolution of parasite during the same host
Heteroxenic= when there is several hosts (e.g plasmodium)
Heteroxenic= when there is several hosts (e.g plasmodium)
9
New cards
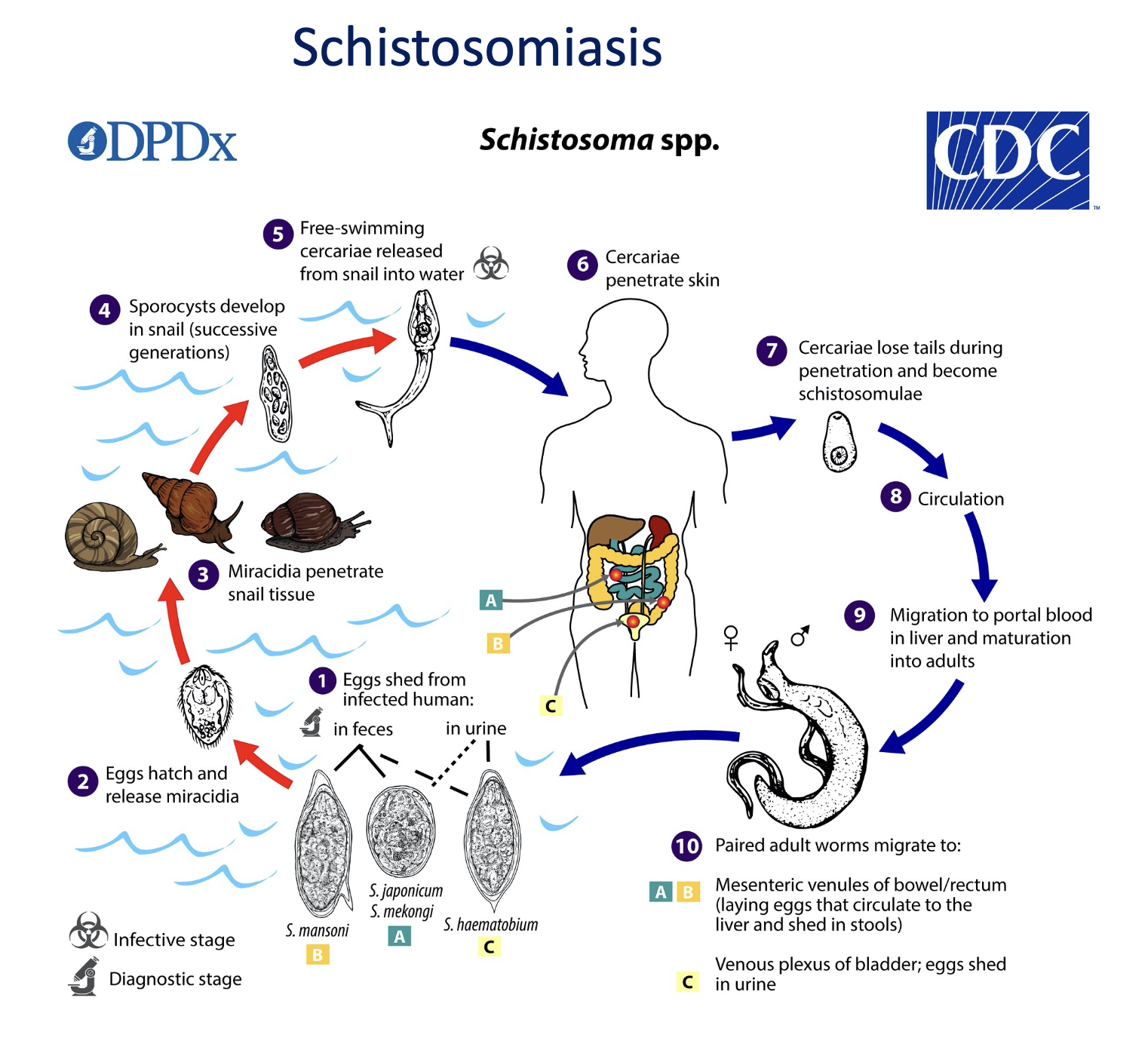
Draw and describe the life cycle of Schistosomiasis:
1\. **cercariae** penetrate the skin of a human that is usually in the aquatic environment like a lake.
2\.The worm then loses its tail inside the host to become **schistosomulae**.
3\. They then migrate to the liver where there is sexual reproduction of the parasite.
4\.The eggs are then shed through the urine or feces and return back to the environment.
5\.The eggs hatch and release the miracidia.
6\.The **miracidia** then penetrate a snail, they then develop into free-swimming cercariae that are released from the snail.
7\.The cercariae can now infect a human to start the life cycle again
2\.The worm then loses its tail inside the host to become **schistosomulae**.
3\. They then migrate to the liver where there is sexual reproduction of the parasite.
4\.The eggs are then shed through the urine or feces and return back to the environment.
5\.The eggs hatch and release the miracidia.
6\.The **miracidia** then penetrate a snail, they then develop into free-swimming cercariae that are released from the snail.
7\.The cercariae can now infect a human to start the life cycle again
10
New cards
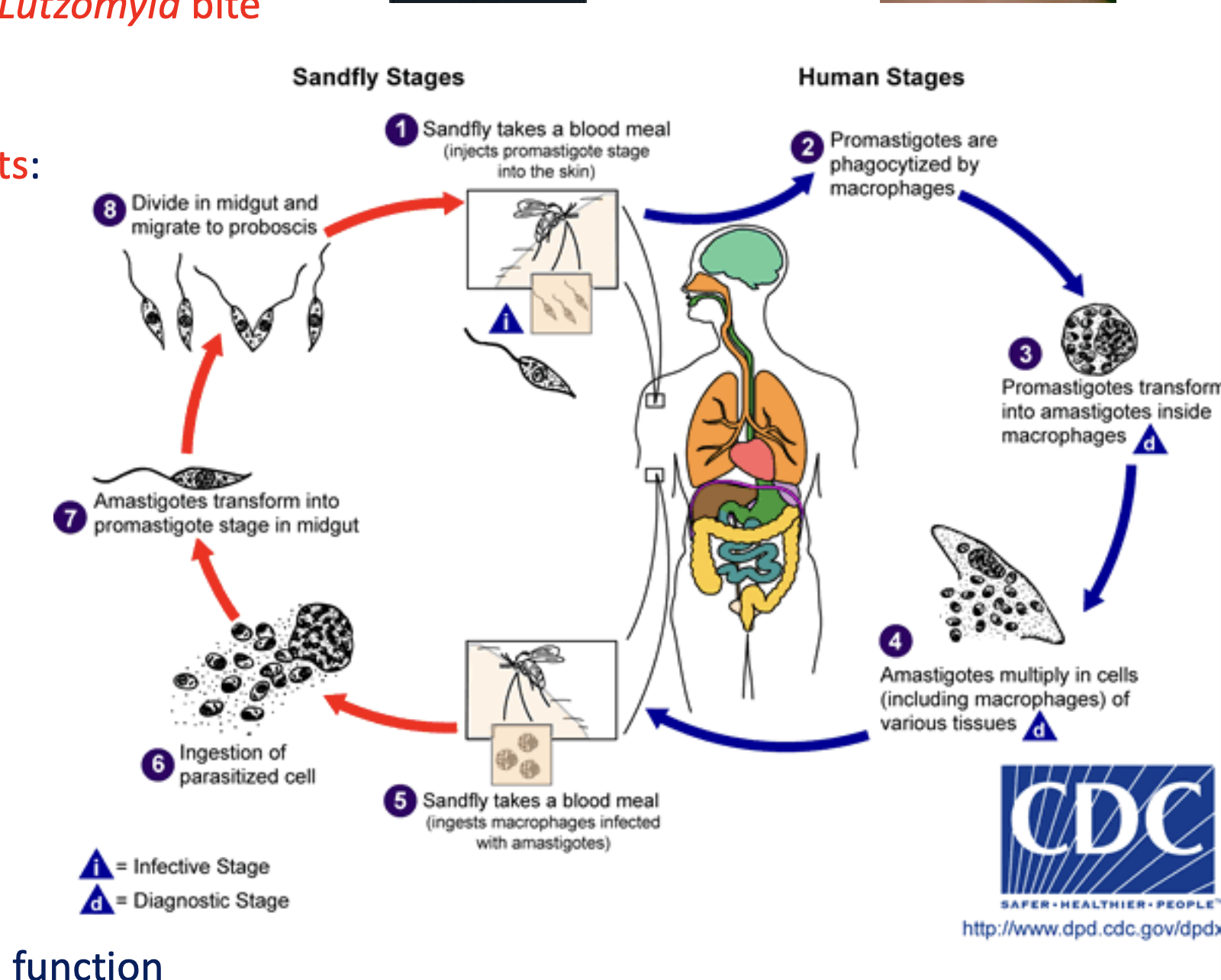
Describe and draw the life cycle of Leishmaniasis:
This is a vector-borne transmission. A sandfly takes a blood meal from a human. **Promastigotes** enter the host through the blood circulation and are phagocytosed by macrophages. Then, the promastigotes transform into **amastigotes** inside the macrophage. The amastigotes multiply. A sandfly takes a blood meal and ingests the macrophages with the amastigotes inside. The amastigotes then become promastigotes again and live inside the sandfly. Next time, the sandly will take a blood meal, it will infect the human again to repeat the cycle.
11
New cards
Name strategies to control parasite infections:
1\.Control of food and water
2\.Control of intermediate hosts
3\.Vector control
4\.Vaccines
2\.Control of intermediate hosts
3\.Vector control
4\.Vaccines
12
New cards
What are vectors?
A vector allows for the active transmission of parasites between humans and or other hosts. BUT snails are not vectors because they do not contribute actively to the transmission.
13
New cards
What type of animals are vectors?
Arthropods
14
New cards
Name 3 vectors of parasites:
1\.Anopheles mosquito
2\.Sandfly
3\.Tse-tse files
2\.Sandfly
3\.Tse-tse files
15
New cards
What are the 5 types of vector control methods
1\.Sanitizing method
2\.Physical methods
3\.Chemical methods
4\.Ecological method
5\.Biological method
2\.Physical methods
3\.Chemical methods
4\.Ecological method
5\.Biological method
16
New cards
Explain the **sanitizing** method for vector control
Use of traps for mosquitoes such as UV and CO2 traps.
Use of a biconical blue and black trap where the colours attract the vectors, and an attractive odour such as acetone is diffused.
Use of a biconical blue and black trap where the colours attract the vectors, and an attractive odour such as acetone is diffused.
17
New cards
Explain the **physical** method for vector control
The aim is to diminish the contact between the host and the vector. For example we can put mosquito nets around the bed or where long sleeves clothes to avoid the mosquito bites.
18
New cards
Explain the **chemical** method for vector control
Use of insecticides in the environment but also on the host, by using mosquito repellant for example
19
New cards
Explain the **ecological** method for vector control
This is related to making the environment of the vector more difficult for its survival. For example it can be to drain swamp areas, to reduce the areas where the mosquito can lay its eggs. This can also be the removal of aquatic plants against flukes as seen in lac d’annecy every year.
20
New cards
What does a Bio-rationale chemical method mean?
Insecticide that is based on the physiology of the vector but that is respectful of the environment.
21
New cards
Explain the **biological** method for vector control
Reducing populations of the vector by using living organisms or their products. For example, the use of some bacteria that produce toxins that lead to the death of the insect larva.
22
New cards
Give 2 examples of biological methods for vector control
1\.The use of some bacteria *(Bacillus thuringiensis)* that produce toxins that lead to the death of the insect larva.
2\.Introduction of sterile males into the enivronment via methods such as irradiation, genetic modifications etc.
2\.Introduction of sterile males into the enivronment via methods such as irradiation, genetic modifications etc.
23
New cards
Explain 2 main ways that invasive species have been introduced:
1\.Intentional→ Pets and crops for medical or aesthetic reasons
2\.Unintentional→Transport of goods where species survive to the transportation.
2\.Unintentional→Transport of goods where species survive to the transportation.
24
New cards
Briefly mention some of the consequences that invasive species can have on the ecosystem.
Some species that are introduced in either an intentional or unintentional way can contribute to the dissapearance of species of plants or animals. An example is the asiatic hornet (frelon asiatique) that has been introduced in a non intentional way and kills bees.
25
New cards
Name some antimalarial drug
Quinoline type (chloroquine, quinine); napthoquinone (atovaquone)
26
New cards
Explain the mechanism of action of quinolines
The drug accumulates in the parasite’s digestive vacuole and inhibits heme biominerilization leading to an accumulation of a cytotoxic complex.
27
New cards
Explain the mechanism of action of napthoquinone
Function as an antimetabolite, it is an analogue of coenzyme Q and inhibits oxidative phosporylation,
28
New cards
What does ACT stand for? what is it for?
Artemisin combination therapy used to treat malaria
29
New cards
what are the 2 drugs in ACT
Pipéraquine and Luméfantrine
30
New cards
Name 3 drugs active against malaria
1\.Luméfantrine
2\.Pipéraquine
3\.atovaquone
2\.Pipéraquine
3\.atovaquone
31
New cards
Name the four things we can inhibit using antimalarial drugs
1\.heme biomineralization
2\.oxidative phosphorylation
3\.trypanothione reductase
4\.polyamine metabolism
2\.oxidative phosphorylation
3\.trypanothione reductase
4\.polyamine metabolism
32
New cards
Name a class of anti amobeic drugs
Nitro-5-imidazole
33
New cards
Name a drug from the Nitro-5-imidazole family
Metronidazole, tinidazole
34
New cards
Explain the mechanism of action of Nitro-5-imidazoles:
Nitro-5-imidazoles interact with pyruvate ferredoxine
oxydoreductase (PFOR) leading to the production of Reactive oxygen species (superoxide anion) leading to DNA fragmentation and inhibtion of nucleic acid synthesis.
oxydoreductase (PFOR) leading to the production of Reactive oxygen species (superoxide anion) leading to DNA fragmentation and inhibtion of nucleic acid synthesis.
35
New cards
Explain why nitro-5-imidazoles are not toxic to the host
The host cells have S**uperOxide Dismutase which is used to convert the ROS into H2O2 which is less toxic, this is then converted by catalases. BUT, parasites dont have these enzymes so the ROS accumulate.**
36
New cards
Name 2 antimonial drugs
1\.Glucantime
2\.Pentostam
2\.Pentostam
37
New cards
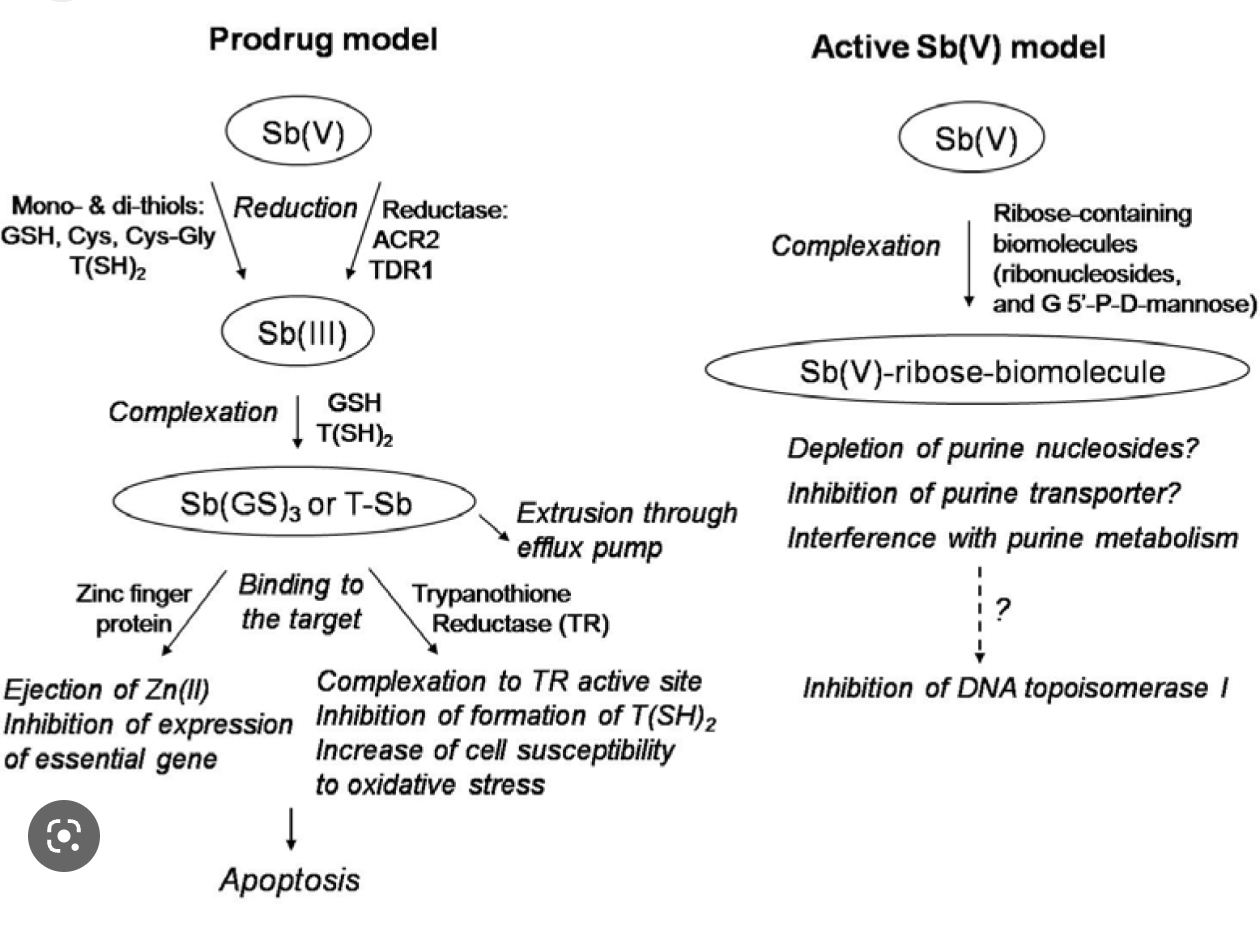
Explain the MOA of antimonials
SbV can transform into SbIII inside the amastigote to inhibit trypanothione reductase. Inhibition leads to an impairment in glycosomal activity, which increases the cell’s suspceptibilty to oxidative stress.
38
New cards
Explain the resistance mechanism of pentavalent antimonials
One mechanism of resistance is the increase in levels of trypanothione reductase in the amastigote, as well as an efflux of SbIII by ABC transporters.
39
New cards
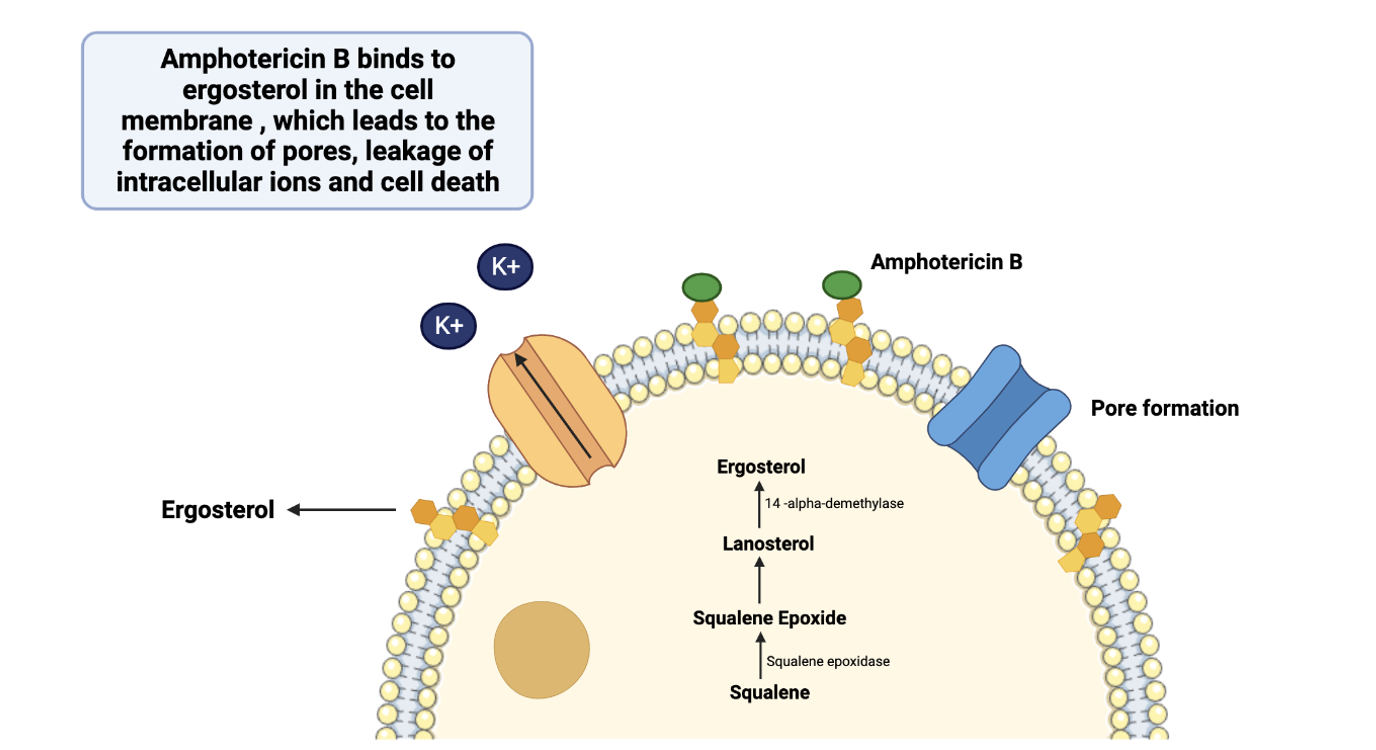
Explain the MOA of amphotericin B (Ambisome)
Amphotercin B binds to ergosterol in the parasite cell membrane, which leads to the formation of pores and leakage of K+ out of the cell, leading to cell death.
40
New cards
Name 2 trypanocidal drugs
1\.Suramine
2\.Nifurtimox
2\.Nifurtimox
41
New cards
What is a combination therapy we can use for trypanosome
**NECT**: Nifurtimox- Eflornithine Combination Therapy
42
New cards
Explain the mechanism of toxicity of Amphotericin B for the host
Ergosterol is structurally very similar to cholesterol, which are found in the membrane of animals and humans. So the drug can sometimes to bind to cholesterol and cause leakage of ions.
43
New cards
Name 3 antihelminthic drugs
1\.Benzimidazole
2\.Avermectines
3\.Pyrazino-isoquinoline
2\.Avermectines
3\.Pyrazino-isoquinoline
44
New cards
What is the target of Benzimidazoles
Inhibition of tubulin polymerization by fixation to beta-tubulin dimers
45
New cards
What is the target of Avermectines
Inhibition of the nerve impulse leading to paralysis of the parasite by mimicking GABA
46
New cards
What is the target of pyrazino-isoquinolone
Impairs membrane permeability and leads to increase in permeability to Ca2+, also leads to paralysis
47
New cards
What can you treat using pyrazino-isoquinolone?
Schistosoma
48
New cards
Give an example of a parasitoses provoked by **protists**
Amoebiasis
49
New cards
Give an example of a parasitoses provoked by **nematodes**
Ascaridosis
50
New cards
Give an example of a parasitoses provoked by **cestodes**
Hydatidosis
51
New cards
Name a parasite where the human is the intermediate host
Echinoccoccus granulosus (sheep)
52
New cards
Name a parasite where the human is the final host
Taenia
53
New cards
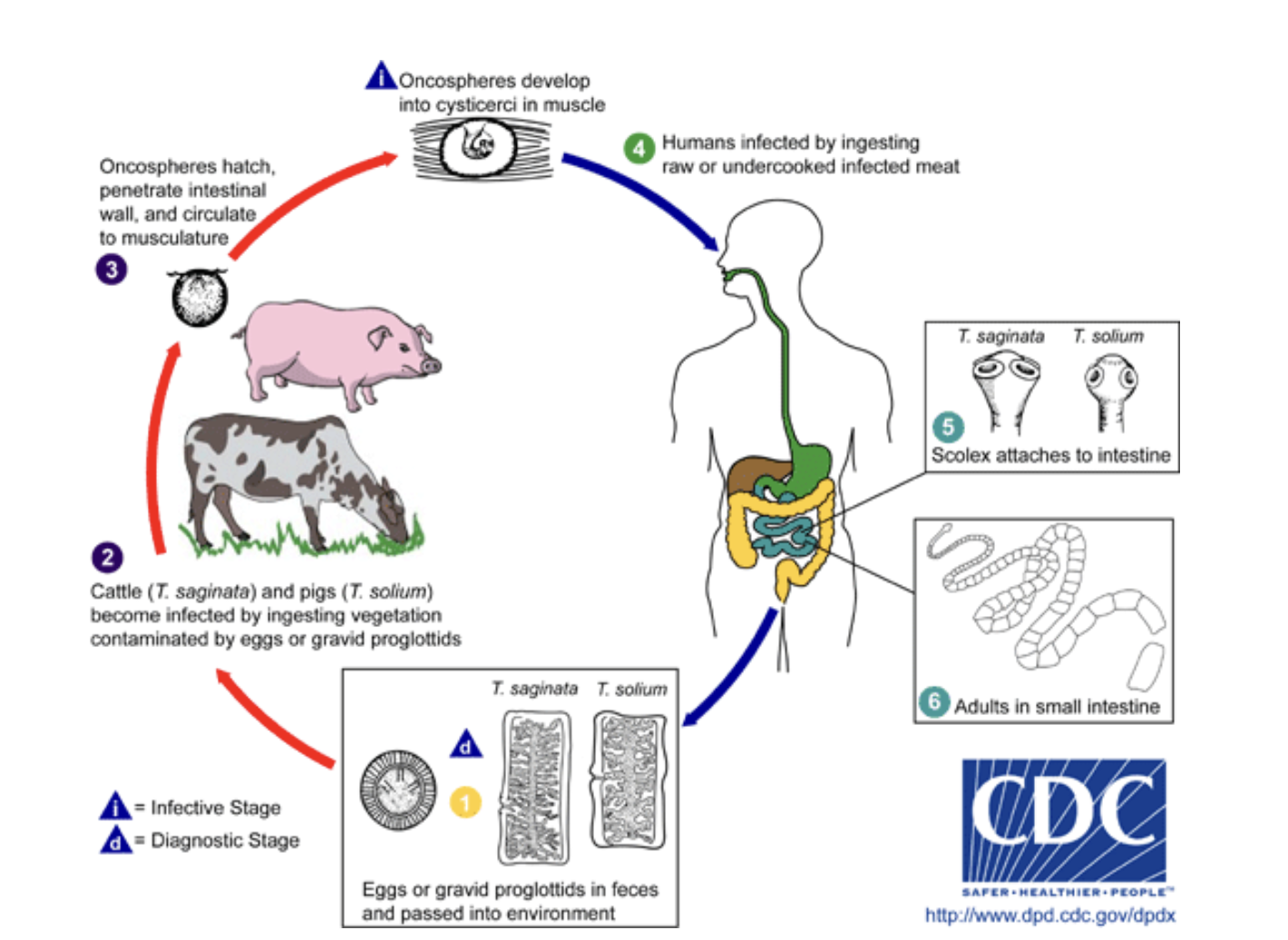
Draw and Describe the life cycle of Taenia
1\.Humans ingest raw or undercooked infected meat
2\.Scolex attach to intestine
3\.Worm grows inside the intestine of the human
4\.Eggs from the adult pass through the human into feces
5\.Eggs are released into the environment
6\.Cows and Pigs can ingest the eggs while grazing
7\.Oncospheres hatch and go into the muscle of the animal
8\.The oncospheres develop into cysticerci
2\.Scolex attach to intestine
3\.Worm grows inside the intestine of the human
4\.Eggs from the adult pass through the human into feces
5\.Eggs are released into the environment
6\.Cows and Pigs can ingest the eggs while grazing
7\.Oncospheres hatch and go into the muscle of the animal
8\.The oncospheres develop into cysticerci
54
New cards
\
\