Biology Unit 1 Exam
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotic cells have both a nucleus and organelles, allowing for more complex structures.
Cell size and surface area to volume ratio
Material exchange occurs on the surface.
Effective exchange occurs when the volume is lower than surface. The smaller the cube the greater SA:V ratio.
Small intestines contain villi and microvilli to increase nutrient absorption
Red blood cells are flattened in shape for gas exchange.
Animal Cells
Lysosomes: Contains enzymes that break down waste.
Centrosomes: Involved in cell division and organisation of the cytoskeleton.
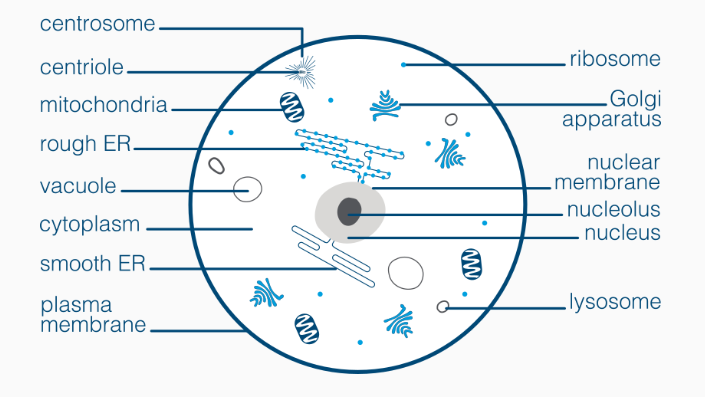
Shared Organelles
Mitochondria
Nucleas
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Ribosomes
Vesicles
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
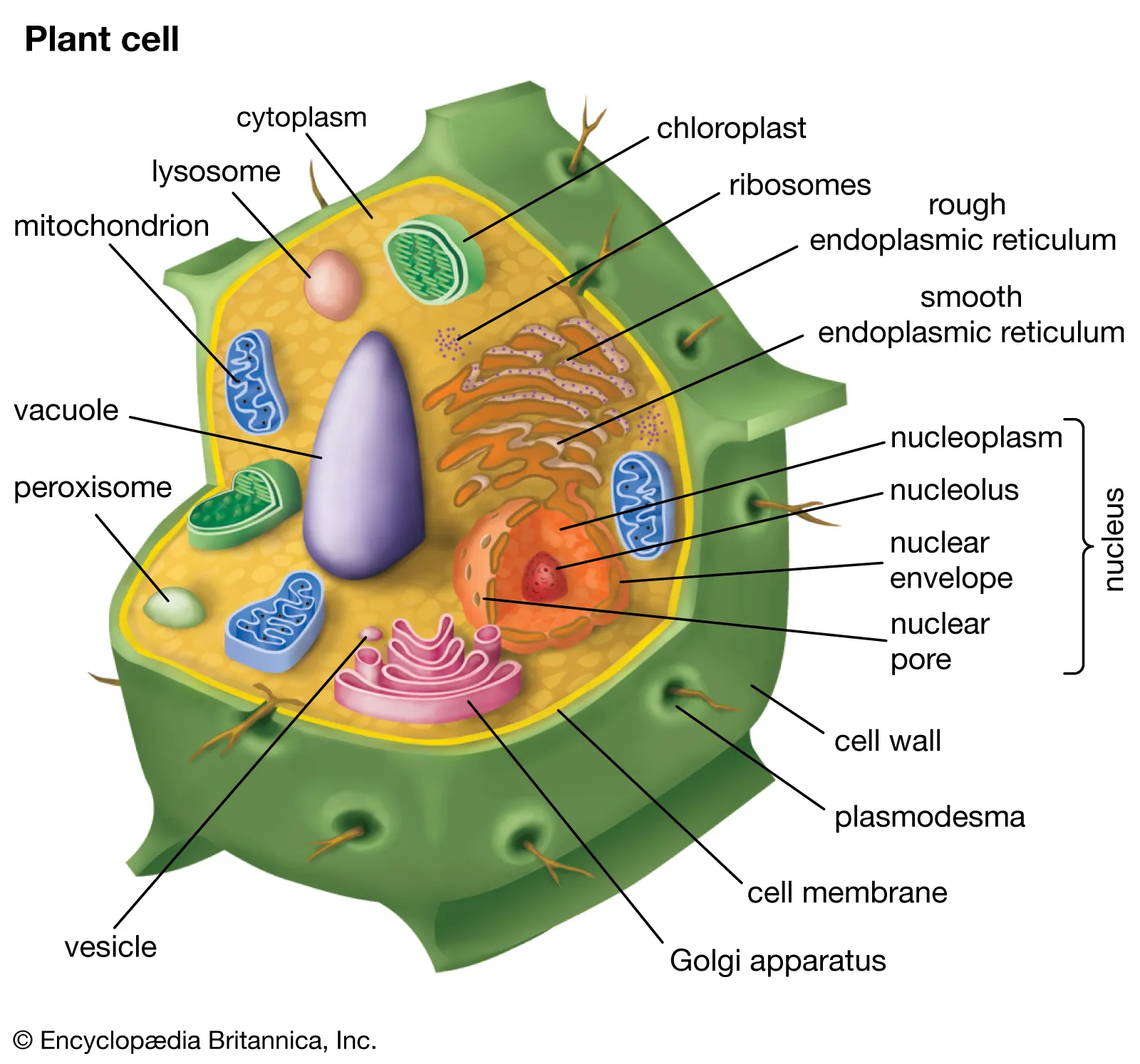
Plant Cells
Chloroplasts: Site for photosynthesis
Cell Wall: Outer layer providing protection and maintaining structure
Large Central Vacuole: storage and help maintaining pressure
The structure and function of the plasma membrane
The plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer, regulates the movement of substances into and out of cells through various transport mechanisms. It's composed of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, which dictate permeability.
Water, hydrophilic molecules, and hydrophobic molecules utilize different pathways, including osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport.
Binary Fission
Binary fission is the primary method of cell division and asexual reproduction in prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria and archea.
DNA replication
Cell elongation
Septum formation
Septum formation
Daughter Cell Separation
The eukaryotic cell cycle, including the characteristics of each of the sub-phases of mitosis and cytokinesis in plant and animal cells
Interphase:
G1: Cell grows
S: Dna replication occurs
G2: Continues growth and prepares for mitosis
Mitosis
Prophase
Pro-metaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a highly regulated process in multicellular organisms where cells are eliminated in a controlled manner. Apoptosis plays crucial roles in development, tissue homeostasis, and immune function.
Disruptions to Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is a carefully controlled process that makes sure cells grow and divide correctly. It has checkpoints to check for problems before moving to the next step.
In cancer, cells often ignore these checkpoints because of mutations in certain genes, like those for cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which help control cell division. This leads to uncontrolled cell growth and the formation of tumors.
Mutations can also damage genes that repair DNA. When this happens, more genetic mistakes build up, making the cancer worse. A common example is a mutation in the p53 gene, which normally helps stop the cell cycle or cause damaged cells to die.
Characteristics of cancer cells
Uncontrolled growth and division
Ability to invade and metasize
Specialization and organization of plant cells into tissues for specific functions in vascular plants, including intake, movement and loss of water.
Xylem: Transport water and minerals from root to rest of the plant
Phloem: Transports sugars and nutrients produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Root hairs: Located on the outer surface of roots, increases surface area
Leaf Tissues: Optimizes light absorption and gas exchange. Waxy cuticle helps regulate water loss through transpiration
Water movement in plants
Water Movement in Vascular Plants:
1. Absorption:
Water is absorbed from the soil by root hair cells, primarily through osmosis.
2. Uptake:
The absorbed water is then transported through the xylem to the rest of the plant.
3. Transpiration:
Water is lost from the leaves through stomata, which are pores regulated by guard cells.
4. Water Circulation:
The movement of water in the xylem is driven by transpiration pull and cohesion-tension forces, which create a continuous column of water from the roots to the leaves
specialisation and organisation of animal cells into tissues, organs and systems with specific functions of the digestive and endocrine system
Animal cells differentiate and organize into tissues, organs, and systems to perform specific functions. The digestive system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients, while the endocrine system uses hormones to regulate bodily functions. These systems work together to maintain homeostasis and ensure the survival of the organism
Regulation of water balance in vascular plants
Vascular plants regulate water balance through stomatal control, transpiration, and water uptake and transport.
Regulation of body temperature and blood glucose in animals by homeostatic mechanisms, including stimulus-response models, feedback loops and associated organ structures.
Stimulus-Response Model
Homeostatic regulation requires systems to detect and respond to internal and external changes via a stimulus-response pathway
A stimulus is a change in the environment (either external or internal) that is detected by a receptor
Negative feedback loops:
Reduce the change or reverse it (blood sugars too high)
Positive feedback loops:
Reinforces the change (contractions strengthening until birth)
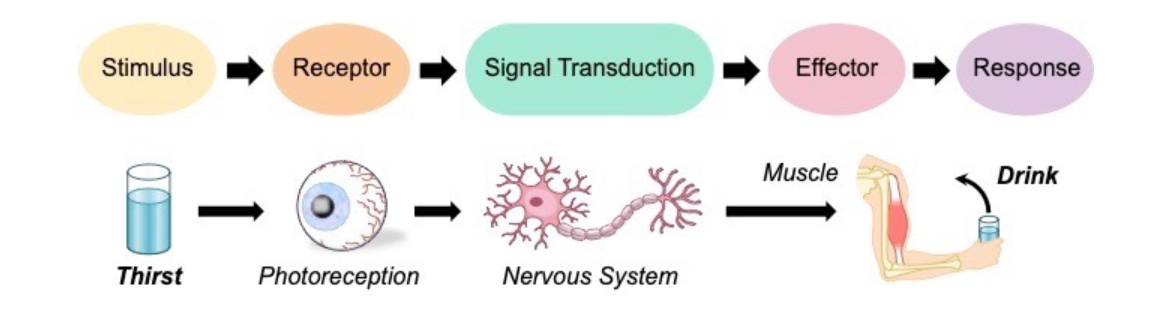
Malfunctions in homeostatic mechanisms: type 1 diabetes, hypoglycaemia, hyperthyroidism.
Type 1 diabetes: is a failure in insulin production, disrupting glucose regulation.
Hypoglycemia: is a state of abnormally low blood sugar, often linked to diabetes but can occur independently.
Hyperthyroidism: involves excessive thyroid hormone production, which can interfere with glucose metabolism and lead to imbalances.
Biological science concepts specific to the selected scientific investigation and their significance, including the definition of key terms
Variables (independent, dependent, controlled)
Hypothesis
Scientific method
Accuracy
Precision
Reliability
Validity
Errors
Techniques of primary qualitative and quantitative data
Qualitative
Interviews
Focus groups
Quantitative
Surveys
Experiments
Primary data characteristics
Primary data is collected directly from the source, making it original and not previously analyzed or interpreted by others.