Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Concepts Chapters 1-4
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Anatomy
Study of the structure of organisms.
Physiology
Study of the functions of living systems.
Principle of Complementarity
Structure determines function in biological systems.
Andreas Vesalius
Pioneering anatomist, dissected criminals for study.
1600 B.C.
Earliest records of anatomical studies date back.
Barber Surgeon
Practitioner combining barbering, dentistry, and medicine.
Father of Modern Anatomy
First accurate book on human anatomy author.
Anatomy
Study of body structures and their locations.
Physiology
Study of functions of anatomical structures.
Gross Anatomy
Examines large, visible structures of the body.
Surface Anatomy
Focuses on exterior features of the body.
Regional Anatomy
Studies specific body areas and their structures.
Systemic Anatomy
Examines groups of organs working together.
Developmental Anatomy
Studies changes from conception to death.
Clinical Anatomy
Focuses on medical specialties and applications.
Microscopic Anatomy
Examines cells and molecules under a microscope.
Cytology
Study of cells and their structures.
Histology
Study of tissues and their structures.
Chemical Level
Atoms and molecules as smallest units of life.
Cellular Level
Cells formed from atoms, molecules, and organelles.
Tissue Level
Tissues consist of similar cells working together.
Organ Level
Organs are different tissues working together.
Organ System Level
Organ systems are groups of organs collaborating.
Organism Level
A human is classified as an organism.
Homeostasis
Stable internal environment maintained by body systems.
Receptor
Component that receives the stimulus in homeostasis.
Control Center
Processes signals and sends instructions in homeostasis.
Effector
Carries out instructions to maintain homeostasis.
Negative Feedback
Response negates stimulus, restoring homeostasis.
Positive Feedback
Response enhances stimulus, moving away from homeostasis.
Anatomical Position
Standard position: standing, palms forward, feet apart.
Dorsal Body Cavity
Contains cranial and vertebral cavities.
Ventral Body Cavity
Divided by diaphragm into thoracic and abdominopelvic.
Pleural Cavities
Contain right and left lungs.
Mediastinum
Region containing heart, blood vessels, and trachea.
Peritoneal Cavity
Chamber within the abdominopelvic cavity.
Parietal Peritoneum
Lines the internal body wall of peritoneal cavity.
Visceral Peritoneum
Covers the organs within the peritoneal cavity.
Atom
Smallest part of an element retaining its properties.
Proton
Positively charged subatomic particle in nucleus.
Neutron
Neutral subatomic particle in nucleus.
Electron
Negatively charged particle in electron cloud.
Atomic number
Number of protons in an element.
Mass number
Total of protons and neutrons in nucleus.
Nucleus
Center of atom containing protons and neutrons.
Electron cloud
Region around nucleus containing electrons.
Valence shell
Outermost electron shell determining bonding.
Ionic bond
Attraction between cations and anions.
Covalent bond
Strong bond formed by shared electrons.
Hydrogen bond
Weak bond based on partial electrical attractions.
Molecular weight
Sum of atomic weights of component atoms.
Exchange reaction
Decomposition followed by synthesis in reactions.
pH
Concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution.
Neutral pH
Balance of H+ and OH-; pure water = 7.0.
Acidic solution
pH lower than 7.0; high H+ concentration.
Basic solution
pH higher than 7.0; low H+ concentration.
Buffer
Weak acid/salt compound that stabilizes pH.
Antacid
Basic compound neutralizing acid, forming salt.
Monosaccharide
Simple sugar with 3 to 7 carbon atoms.
Polysaccharide
Many monosaccharides condensed by dehydration synthesis.
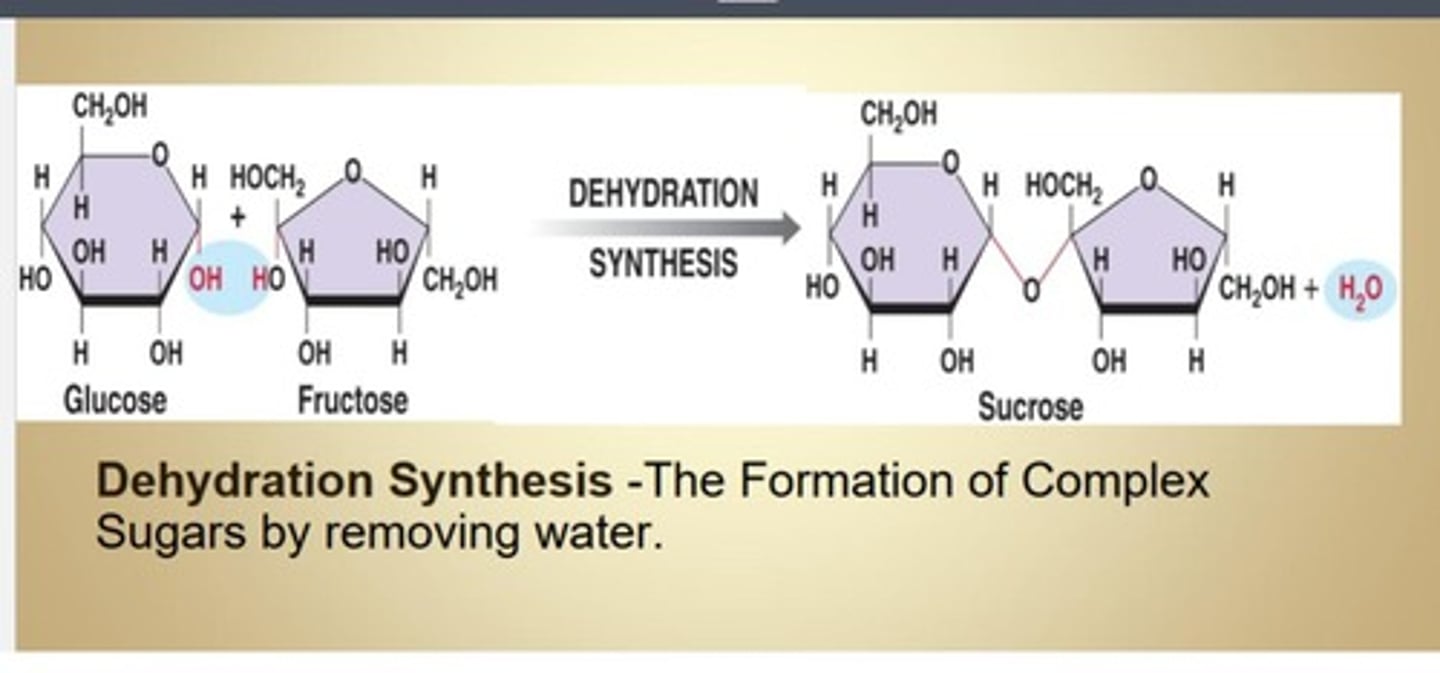
Dehydration synthesis
Formation of complex sugars by removing water.
Lipids
Hydrophobic molecules like fats, oils, and waxes.
Fatty Acids
Building blocks of lipids, long hydrocarbon chains.
Eicosanoids
Signaling molecules derived from fatty acids.
Glycerides
Esters formed from glycerol and fatty acids.
Steroids
Lipids with a four-ring carbon structure.
Phospholipids
Lipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
Glycolipids
Lipids with carbohydrate groups attached.
Proteins
Most abundant organic molecules, made of amino acids.
Amino Acids
20 building blocks of proteins, contain amine group.
Enzymes
Proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions.
Activation Energy
Energy needed to start a chemical reaction.
Substrates
Specific reactants enzymes act upon.
Nucleic Acids
Biomolecules that store and transmit genetic information.
Nucleotides
Building blocks of DNA and RNA.
DNA
Double-stranded nucleic acid with genetic instructions.
RNA
Single-stranded nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis.
Complementary Base Pairs
Specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids.
Purines
Nitrogenous bases adenine and guanine.
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, energy currency of cells.
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, two phosphate groups.
ATPase
Enzyme that catalyzes ATP phosphorylation.
Cell Theory
Fundamental principles about cells and their functions.
Cell
Smallest unit performing physiological functions.
Plasma Membrane
Double layer of phospholipid molecules.
Membrane Lipids
Largest component of plasma membrane.
Hydrophilic Heads
Face watery environment on both sides.
Hydrophobic Tails
Fatty-acid tails inside the membrane.
Integral Proteins
Proteins embedded within the membrane.
Peripheral Proteins
Bound to inner or outer membrane surfaces.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Network involved in synthesis and transport.
Lysosomes
Vesicles containing powerful enzymes for digestion.
Autolysis
Self-destruction of damaged cells.
Mitochondria
Organelles producing ATP through cellular respiration.
Cristae
Folds in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Aerobic Metabolism
Requires oxygen to produce ATP.
Glycolysis
Conversion of glucose to pyruvic acid.
TCA Cycle
Converts pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide.
Electron Transport Chain
Produces ATP in the inner mitochondrial membrane.