Sleep Hygiene and Complimentary and Alternative Medicine
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Sleep Hygiene
Practices and habits that are necessary to have good nighttime sleep quality and full daytime alertness
What is healthy sleep important for?
Physical and mental health
What can healthy sleep improve?
Productivity and overall quality of life
Who can benefit from practicing good sleep habits?
Everyone
What can sleep issues be caused by?
Any combination of acute or chronic problems
Examples of Sleep Issues
Prolonged sleep onset latency (takes longer to fall asleep)
Excessive wake after sleep onset (wake up and can't fall back)
Short total sleep time (sleeping less than 3 hours a night)
Low sleep efficiency (waking up and feeling tired)
Poor sleep quality (based on subjective and objective data)
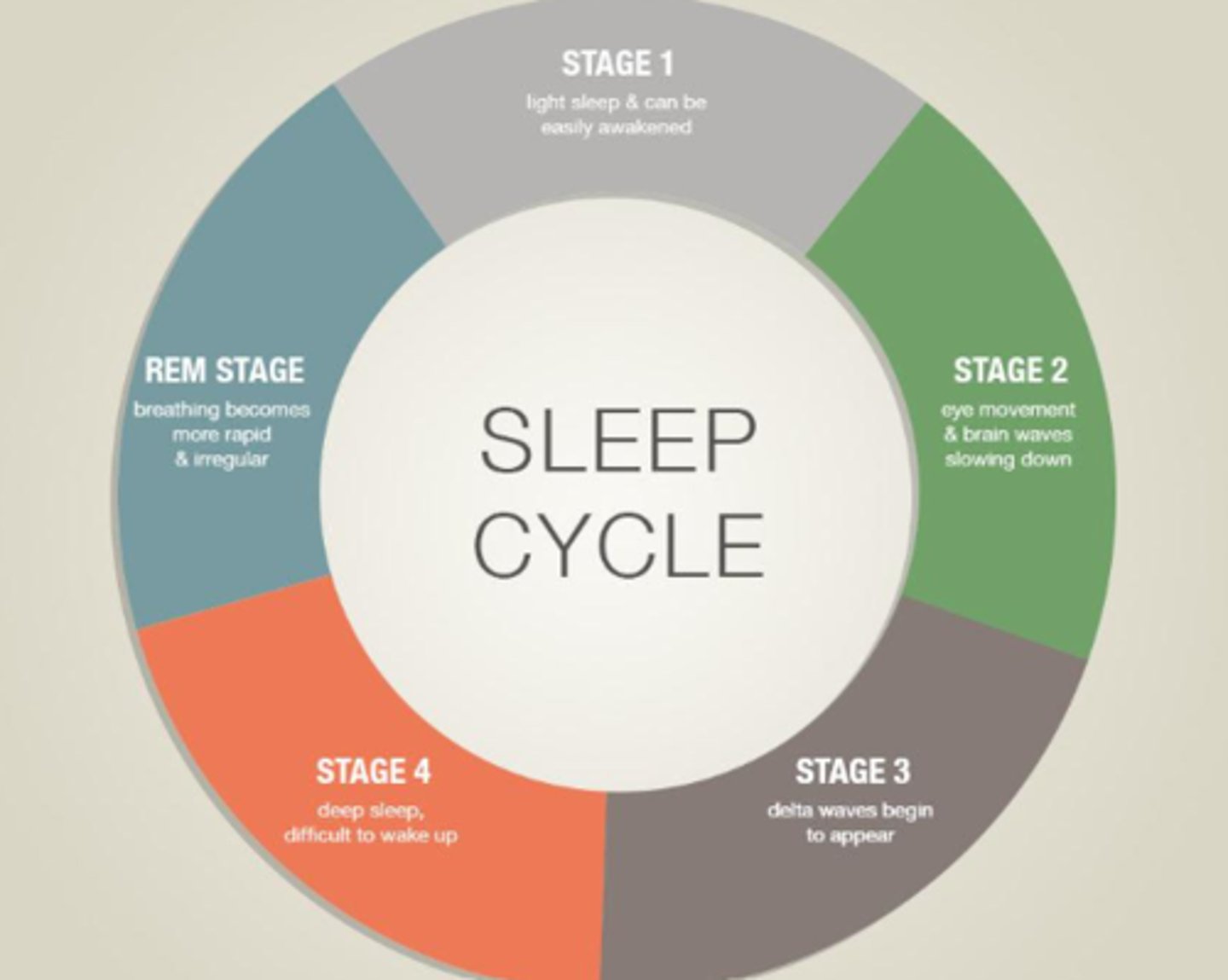
5 Stages of the Sleep Cycle
Stage 1: Light sleep (e.g. can be easily awakened)
Stage 2: Eye movement and brain waves slow down
Stage 3: Delta waves begin to appear
Stage 4: Deep sleep (e.g. difficult to wake up)
Stage 5: Rapid eye movement (e.g. rapid/irregular breathing)
Signs of Poor Sleep Hygiene
Falling asleep at inopportune times
Memory issues
Mood changes
Trouble concentrating
Decreased immune function
Accidents
High blood pressure
Weight gain (e.g. calories are typically loss during sleep)
Lowered libido
How much of the American population has sleep problems as compared to Western Europeans and Japan due to drive to achieve (e.g. hustle culture)?
More than half
Most Americans (61-79%) did not meet clinical diagnostic criteria for what condition based on self-reported symptoms?
Insomnia
Why are sleep problems of growing concern to global public health?
Associated with impairments in motivation, emotion, cognition
Increased risk for serious medical conditions
All-cause of mortality
What is poor sleep associated with?
Impairments in:
Motivation
Emotion
Cognitive functioning
What does poor sleep cause an increased risk for?
Medical conditions (e.g. diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer)
What can poor sleep lead to even when the symptoms are below the threshold for clinical sleep disorders?
Mortality
What can happen after one night of no sleep?
Become more emotional
Decline in hand-eye coordination
Impaired concentration
Equivalent to 0.1% blood alcohol content (e.g. hungover)
What role does sleep play in proper functioning of body systems?
Immune function
Tissue healing
Pain modulation
Cardiovascular health
Cognition (e.g. learning, memory)
What is the recommended amount of sleep per night for individuals 18 years and older?
7 hours

Tips for Getting a Better Night Sleep
Practice a relaxing bedtime ritual
Turn off electronics
Exercise daily
Keep a consistent sleep schedule
Avoid heavy foods, alcohol, and caffeine several hours before
What is the immune system synchronized with?
The body's sleep-wake cycle (e.g. circulation, hormones)
When does the number of immune cells increase in circulation? Why?
During wake hours to combat antigens in a period when the body is more likely to encounter foreign bodies and during sleep
What does the upregulation of immune cells with increased secretions of endocrine hormones (e.g. growth hormone, prolactin, melatonin, leptin) and pro-inflammatory cytokines enable?
Adaptive immune response to be very active during sleep
Sleep regulation is controlled by similar neural mechanisms of what physiological function?
Pain modulation
What neural mechanism controls both sleep regulation and pain modulation?
Central serotoninergic neurotransmission
What does decreased slow-wave sleep lead to in terms of pain?
Increased sensitivity to pain
Increased neuronal sensitivity
When are occupational therapist's supposed to ask about pain?
Throughout the session, making appropriate adjustments or referrals as needed
Regulation of what 2 physiological functions occurs during sleep?
1. Sympathetic nervous system
2. Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis
What does sleep deprivation lead to?
Changes in the immune response
What does sleep deprivation alter?
Body's healing properties
What is too much (>9 hours) or too little (<5 hours) sleep associated with?
Increased mortality due to cardiovascular disease
Cycle of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Sleep onset snoring
Airway collapses
Breathing stops
Sleep disrupted
What conditions does sleep apnea increase the risk of?
Cardiovascular disease
Ischemic heart disease
Arrhythmias
Systolic heart failure
Cerebrovascular accident
What can occupational therapists do to address heart disease from lack of sleep?
Basic screens (e.g. take blood pressure)
What 2 mental health conditions may sleep disturbances contribute to?
1. Depression
2. Anxiety
What percent of people with depression experience insomnia?
75%
What percent of individuals with insomnia have both depression and anxiety?
25%
What can occupational therapists screen patients with depression and anxiety for?
Sleep disturbances
What does sleep enhance the learning of?
Functional gross and fine motor tasks
What ability does a lack of sleep reduce?
Hand-eye coordination tasks
Performance of ADLs and IADLs
Decreased functional mobility
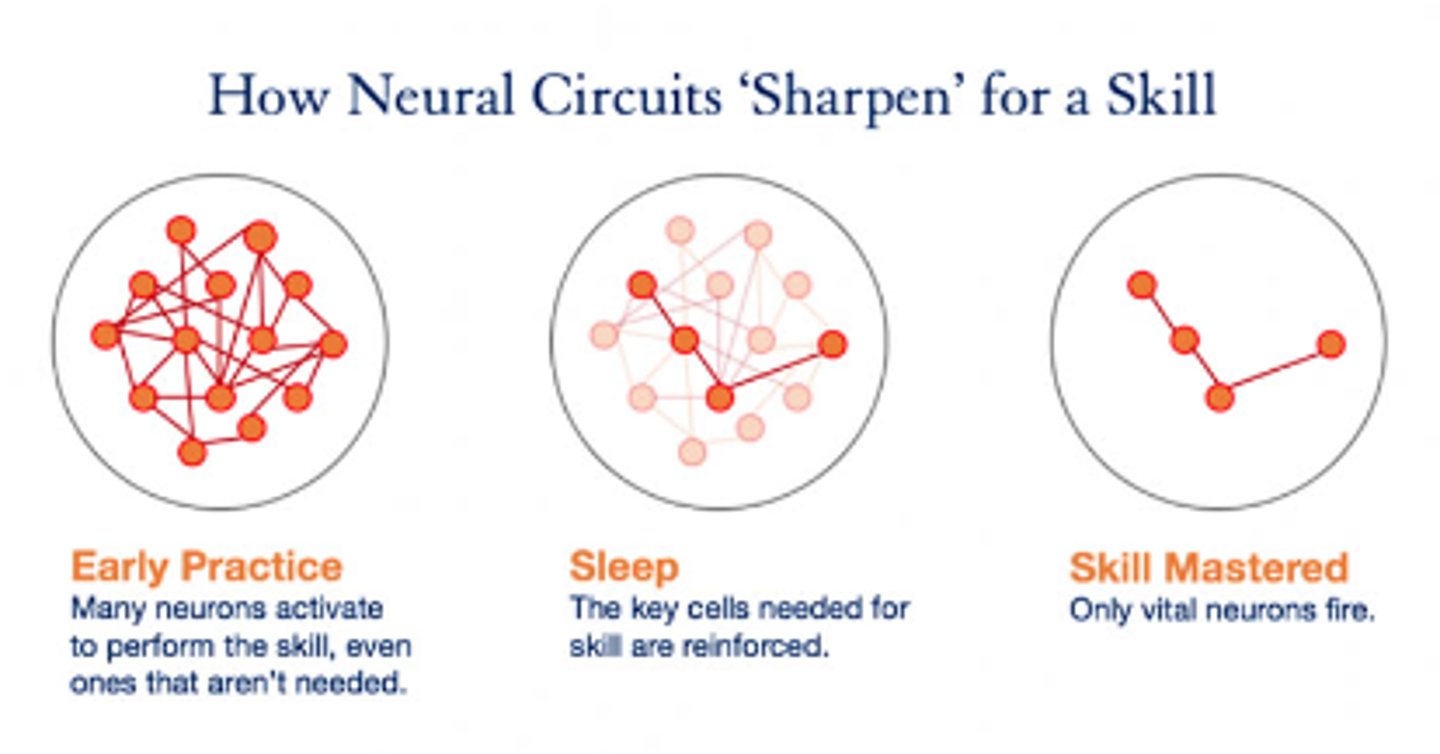
Process of Neuroplasticity
Early practice
Sleep
Skilled practice
What knowledge do occupational therapists have in regards to sleep?
Sleep physiology and disorders
Evidence-based sleep promotion practices
What do occupational therapists evaluate and address in regards to sleep?
The consequences of sleep insufficiency or sleep disorders on occupational performance and participation
How are sleep problems addressed and framed in occupational therapy?
From the perspective of health maintenance and health promotion
What do occupational therapists explore with families who have autistic children?
Impact of sleep deprivation on the family unit and the child's and caregivers' ability to function effectively during the day
What can occupational therapists address in families with autistic children?
Physical environment
Observation skills (e.g. to anticipate emotional reactions)
Calming activities (e.g. easy to facilitate and produce sleep)
How do occupational therapists help families with autistic children?
Bedtime routines
Habits
Patterns
Cognitive-Behavioral Interventions for Autistic Children
Strategies to address sensory avoiding and sensory seeking
Picture poster depicting bedtime routines
Stickers or consistent praise for sleeping through the night
Loose or tight pajamas
Lightweight or weighted blankets
What can occupational therapists working with older adults in long-term care address?
Sleep routine
Lighting (e.g. differentiate between day and night)
Noise level in the environment
Positioning (e.g. turning schedules, privacy needs)
Substance abuse
Mood disorders (e.g. anxiety, depression)
Dietary habits
What type of activities should occupational therapists working with older adults in long-term care encourage?
Daytime activities (e.g. exercise, socialization)
What do occupational therapists working with older adults in long-term care strive to reduce?
Daytime napping
What areas of sleep dysfunction do occupational therapists evaluate?
Sleep preparation and participation
Latency
Duration
Maintenance
Daytime sleepiness
Impact on life, school, work, and caregiving
Pain and fatigue
What should occupational therapists assess in terms of sleep?
Balance
Sensory systems (e.g. vision)
Vision
Strength
Skin integrity
Psycho-emotional status (e.g. depression, anxiety, stress)
Impact of stimulants (e.g. caffeine, nicotine, drugs)
Environment (e.g. acute care hospitals, long-term care, home)
Occupational Therapy Interventions for Sleep Hygiene
Education on cognitive-behavioral therapy
Address co-morbidities (e.g. decreased ROM, anxiety)
Encourage positive health behaviors (e.g. reduce caffeine)
Sleep routine establishment and maintenance
Pain management and fatigue
Target occupational performance deficits
Increase coping skills and stress management
Environmental modifications
Advocate for appropriate work schedules
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
A group of diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not presently considered to be part of conventional medicine
What is complementary medicine?
A type of medicine that is accessed in conjunction with allopathic medical practices
What is alternative medicine?
A type of medicine that is practiced in place of conventional medicine
What is integrated medicine?
A type of medicine that combines treatments from conventional medicine and complementary and alternative medicine for which there is high-quality scientific evidence of safety and effectiveness (e.g. acupuncture)
5 Domains of Complementary and Alternative Medicine
1. Alternative medical systems
2. Mind-body interventions
3. Biologically based treatments
4. Manipulative and body-based methods
5. Energy therapies
Alternative Medical Systems
Entire systems of health theory and practice that developed separately from conventional medicine (e.g. herbal remedies, manipulative practices)
What type of practices does alternative medical systems include?
Traditional Chinese medicine
Ayurvedic medicine
Naturopathy
Homeopathy
Traditional Chinese Medicine
A type of practice that is based on the belief that the uninterrupted flow of energy through 20 meridians is necessary for the maintenance of health (e.g. acupuncture, Qigong)
What does traditional Chinese medicine rely on?
Use of "energy" based practices
What populations has traditional Chinese medicine been utilized for?
Developmental disabilities (e.g. cerebral palsy, intellectual)
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Pain-related conditions (e.g. fibromyalgia)
Psychological disorders (e.g. anxiety, depression, PTSD)
Hormone imbalance
What is one of the oldest holistic healing systems?
Ayurvedic medicine
Ayurvedic Medicine
A type of practice based on Hindu philosophy that health and wellness depend on a delicate balance between mind, body, and spirit, using dietary or herbal remedies and various mind-body therapies
Where did Ayurvedic medicine originate?
India
What have studies of Ayurvedic medicine shown to help osteoarthritis patients with?
Reduce pain
Increase function in osteoarthritis patients
What have studies of Ayurvedic medicine shown to help type II diabetes patients with?
Manage symptoms
Why should patients consult primary care providers prior to using Ayurvedic medicine to treat a medical issue?
Because some treatment techniques may be toxic
What do mind-body interventions focus on?
The relationships among the brain, mind, body, and behavior, and their effect on health and disease
What do mind-body interventions encompass?
Hypnosis
Meditation
Yoga
Biofeedback (e.g. mirror)
Tai-chi
Visual Imagery
What do mind-body interventions integrate well into?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Group therapy
Conventional neurological interventions
What do biologically-based treatments refer to?
Substances found in nature, including herbs, foods, and vitamins otherwise known as dietary supplements
What do biologically-based treatments encompass?
Botox used for spasticity management
Amino acid therapy used in children with cerebral palsy
Red raspberry leaves to relieve menstrual pain
Ginger and turmeric for reducing inflammation
What do manipulative and body-based methods depend on?
Manipulation or movement of a body part
What do manipulative and body-based methods encourage?
Muscle strength and coordination
What manipulative and body-based methods are widely used for children and adults with physical disabilities?
Hippotherapy
Hydrotherapy (e.g. aquatics)
Chiropractic and spinal manipulation
Reflexology
Massage therapy
Tai Chi
Yoga
Energy Therapy
A type of practice based on the belief that energy blockages or imbalances can lead to illness and disease
What do energy therapies aim to create?
A state of balance, health, and peace in a person
What are the most popular forms of energy therapy?
Music therapy
Therapeutic touch
Reiki
Qigong
4 Pillars of Complementary and Alternative Medicine Research
1. Scientific promise
2. Extent and nature of practice and use
3. Amenability to rigorous scientific inquiry
4. Potential to change health practices
What are the key priority areas of complementary and alternative medicine in research currently?
Non-mineral
Non-vitamin
Natural products
Mind-body interventions (e.g. yoga, tai-chi, qigong, imagery)
Deep-breathing exercises
Progressive relaxation
Why are research studies encouraged for complementary and alternative medicine?
Insurance coverage for CAM therapies
Develop practice and referral guidelines
Conduct research about safety and efficacy of CAM practices
What must occupational therapists evaluate in order to determine whether to use complementary and alternative medicine in the delivery of occupational therapy services?
Evaluate the client's strengths and weaknesses in carrying out daily occupations
What must the occupational therapist measure to ensure that the use of complementary and alternative medicine will improve occupational performance?
Whether the use of them will result in positive outcomes
How is complementary and alternative medicine used in occupational therapy?
Address factors that influence occupational performance in daily life occupations, demands, and contexts/environments within which they are performed
How can occupational therapists use complementary and alternative medicine to facilitate the ability of clients to engage in their daily life occupations?
Preparatory method
Purposeful activity
Occupational-Therapy Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Interventions
Sensory Integration (e.g. autism)
Constraint therapy (e.g. stroke)
Prescriptive exercises (e.g. depression)
Tai-chi (e.g. prevention of falling)
Mirror therapy (e.g. stroke)
Mindfulness (e.g. addiction)
Yoga (e.g. autism)
Animal assisted therapy (e.g. post-traumatic stress disorder)
Occupational Therapy Code of Ethics and Ethics Standards
Mandates safe and competent practice, holding occupational therapy practitioners responsible for maintenance of high standards of competence
According to the Occupational Therapy Code of Ethics and Ethics Standards, what may the use of complementary and alternative medicine require?
Training for effective delivery
According to the Occupational Therapy Code of Ethics and Ethics Standards, what must occupational therapy practitioners comply with when using complementary and alternative medicine?
Local, state, and federal laws
Payment for Occupational Therapy Services and Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Insurance coverage (e.g. varies by company)
Cost-effectiveness
Consumer demand
Demonstrated clinical efficacy
State mandate