Intro to Psych - Lesson 1 and 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/161
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
1
New cards
Psyche
Greek word meaning ***soul***
2
New cards
Logos
Greek word meaning ***study***
3
New cards
Ancient Greece
Where did the interest in people’s behavior and minds started with?
4
New cards
Plato
* In his ***Theory of Forms***, he introduced the concept of “psyche”, which describes the soul of an individual.
* In ***The Republic***, he proposed a ***Tripartite View of the Soul***.
* In ***The Republic***, he proposed a ***Tripartite View of the Soul***.
5
New cards
Soul
It gives individuals the capacity to think, feel, and have volitions according to Plato.
6
New cards
Logistikon, Thumos, Epithumetikon
According to the Tripartite View of the Soul, the mind is divided into three parts:
7
New cards
Logistikon
Reason and intellect
8
New cards
Thumos
Emotions, feelings, passions, and motivations
9
New cards
Epithumetikon
Desires and appetites
10
New cards
Aristotle
* Was the ***first to acknowledge*** that the ***soul can be a separate entity from the physical body.***
* In his book, ***De Anima***, he provided a rich ***description of the psyche, which gives essence and faculties to living organisms.***
* In his book, ***De Anima***, he provided a rich ***description of the psyche, which gives essence and faculties to living organisms.***
11
New cards
Plant soul
Involves the capacity for ***nourishment and reproduction.***
12
New cards
Animal soul
Have the ***capacity of the plant soul***, and additionally, the capacity for ***sensation and perception.***
13
New cards
Humans
Have ***all the capacities***, with an added element of ***intellect***.
14
New cards
The Dark Ages
Due to the ***decline of the Roman Empire,*** the ***culture and sciences declined*** during this period. The ***Catholic Church was a major catalyst*** in suppressing advances in the scientific field.
15
New cards
Cartesian Dualism
Proposes that the world exists in two entities:
• ***The physical world*** (including our physical bodies)
• ***The mental world***
• ***The physical world*** (including our physical bodies)
• ***The mental world***
16
New cards
Rene Descartes
* Known for his ***Cartesian Dualism***
* ***Revived the idea of the “psyche”*** in his philosophical writings. He would now refer to the ***“soul”***
* ***I think, therefore I am.***
* ***Revived the idea of the “psyche”*** in his philosophical writings. He would now refer to the ***“soul”***
* ***I think, therefore I am.***
17
New cards
Cartesian Dualism
Provided the ***first acknowledgement*** that a ***study of the mind, separate from the study of the physical body, is possible.***
18
New cards
Age of Enlightenment Major Thinkers
* Rene Descartes
* John Locke
* John Locke
19
New cards
British Empiricism (John Locke)
The ***philosophical movement*** that emphasizes that the ***mind is not an innate entity, but something that develops through experiences*** (later called as tabula rasa).
20
New cards
1590
The word “psychology” was first used in?
21
New cards
Christian Wolff
***German philosopher*** who ***popularized the word “psychology***” in his work in ***1732***
22
New cards
During his time, the ***physical sciences*** (biology, chemistry, physics) ***dominated the intellectual culture in Europe.***
Paul Broca
23
New cards
Different parts of the brain had specific mental, emotional, and physiological functions.
Localization of Function (Paul Broca)
24
New cards
Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt
* **Father of [Modern] Psychology** who separated the field of “Psychology” from philosophy and the natural sciences.
* Utilized the ***scientific method in studying the human mind*** called this as ***psychology.***
* Psychology for him was the examination of the ***elements and compounds of consciousness,*** as well as the ***internal mechanisms*** that operate with it such as ***affect (emotion)*** and ***volition (motivation).***
* Utilized the ***scientific method in studying the human mind*** called this as ***psychology.***
* Psychology for him was the examination of the ***elements and compounds of consciousness,*** as well as the ***internal mechanisms*** that operate with it such as ***affect (emotion)*** and ***volition (motivation).***
25
New cards
Why Wundt is the Father of Psychology
* opened psychological lab in 1879 at the University of Leipzig, Germany
* trained scholars
* popularized the use of scientific method in studying the human mind
* first to acknowledge that psychology is a separate entity from neuroscience, psychophysics, and philosophy
* trained scholars
* popularized the use of scientific method in studying the human mind
* first to acknowledge that psychology is a separate entity from neuroscience, psychophysics, and philosophy
26
New cards
Introspection
Coined by ***Edward B. Titchener,*** ***participants*** were required to ***identify their reactions to a stimuli.***
27
New cards
Edward B. Titchener
He referred to the experimental approach in ***psychology popularized by Wundt as structuralism.***
28
New cards
Margaret Floy Washburn
First woman to receive a PhD in psychology.
29
New cards
American Psychology
American scholars, during this time, was ***heavily influenced*** ***by*** ***Charles Darwin and his theory of evolution.***
30
New cards
Characteristics of consciousness according to ***William James***
* dynamic
* ever-flowing
* ever-changing
* cannot be broken down into pieces
* ever-flowing
* ever-changing
* cannot be broken down into pieces
31
New cards
G. Stanley Hall
* He ***founded the American Psychological Association (APA***) in ***1909*** and made the ***first journal of Psychology*** in America, the ***American Journal of Psychology*** in ***1887.***
* He was known for his studies child development and adolescence.
• “Adolescence is a time of storm and stress.”
* He was known for his studies child development and adolescence.
• “Adolescence is a time of storm and stress.”
32
New cards
Francis Cecil Summer
Father of Black Psychology
33
New cards
James McKeen Cattell
***Eugenics:*** a scientific movement in the early 1900s advocating for ***selective breeding of the “intelligent”***.
34
New cards
Gestalt Psychology
A school of thought in psychology that emphasized the ***study of wholes rather than parts (as opposed to structuralism).***
35
New cards
Sigmund Freud
Human mind is made up largely of contents that are inaccessible to us, called as the ***unconscious (hidden desires, wishes, impulses).***
36
New cards
Three personalities of human mind according to Freud
* Id
* Ego
* Superego
* Ego
* Superego
37
New cards
Abraham Maslow
* ***Humanistic Psychology***
* He believed that humans have the autonomous capacity for ***self-actualization.***
* We are motivated and driven to be the best version of ourselves.
* ***People are innately good-natured.***
* He believed that humans have the autonomous capacity for ***self-actualization.***
* We are motivated and driven to be the best version of ourselves.
* ***People are innately good-natured.***
38
New cards
Behaviorism
Psychology must focus on ***behavior*** and reject hypothetical concepts like consciousness and cognition. Coined by ***John B. Watson.***
39
New cards
Cognitive Psychology
The ***study of cognitive processes*** such as attention, memory, and language.
40
New cards
Flashbulb Memory
Is a vivid memory of a shocking and/or surprising event in the past. Coined by ***Roger W. Brown***
41
New cards
George A. Miller
Wrote ***“The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two”*** that claimed that our ***short-term memory can only hold 7 bits*** of information at a time.
42
New cards
Psychology
Is the scientific study of ***human behavior*** and ***mental processes.***
43
New cards
Affect
Emotions, emotional processes, moods, coping, stress
44
New cards
Behavior
Overt and cover behavior, habits, motivation, personality, normal and abnormal behavior
45
New cards
Cognition
Thinking, memory, attention, language, reasoning, decision-making
46
New cards
Positive Psychology
Gives focus to ***character strengths, happiness, and well-being***, not just psychological disorders. Coined by ***Martin Seligman.***
47
New cards
Two Types of Discipline in Psychology
* basic psychology
* applied psychology
* applied psychology
48
New cards
Basic Psychology
Focuses on ***developing concepts***, theories, and methods ***through psychological research.***
49
New cards
Applied Psychology
Concerned with ***applying psychological theories and methods in applied settings*** (e.g., industry, clinics, medicine, education).
50
New cards
Development Psychology
It is concerned with the development of human behavior from infancy to death.
51
New cards
Cognitive Psychology
It is the study of mental processing such as attention, memory, perception, language, decision-making, and thinking
52
New cards
Physiological/Biological Psychology
Investigates the biological basis of behavior, emphasizing the role of the nervous and endocrine system
53
New cards
Abnormal Psychology (Psychopathology)
It is the study of mental illnesses, its causes, etiology, and classification, and treatment
54
New cards
Personality Psychology
It studies the nature of personality: its structure, dynamic processes, and variations
55
New cards
Social Psychology
The study of people’s behaviors, thoughts, and feelings in the context of social groups
56
New cards
Comparative Psychology
The study of behavior and mental processes of non-human animals
57
New cards
Cultural Psychology
The study of how cultural practices, traditions, and norms shape human behavior and cognition.
58
New cards
The study of similarities and differences of cultures in terms of their behavior and thinking
Cross-Cultural Psychology
59
New cards
The study of unique native concepts and beliefs in a culture.
Indegenous Psychology
60
New cards
Sikolohiyang Pilipino
The scientific study of the experience, consciousness, and orientation of the Filipino person
61
New cards
Quantitative Psychology
A field that tackles issues on quantitative methodology, design, and statistical analyses of psychological processes.
62
New cards
Psychological Statistics
The application of the field of statistics in psychological research
63
New cards
Psychometrics
The scientific study of how psychological constructs can be measured
64
New cards
Experimental Psychology
A subdiscipline of psychology that utilizes experiments in testing psychological hypotheses
65
New cards
Phrenology
Involves the measurement of bumps on the skull to predict mental traits. ***Franz Joseph Gall***
66
New cards
Physiognomy
Involves the assessment of a person’s characteristics through facial features
67
New cards
Mesmerism
also called as ***animal magnetism,*** the belief that fluids in our body are influenced by magnetic and gravitational forces in the environment, which in turn, changes our mood, behavior, or thinking. ***Franz Anton Mesmer***
68
New cards
Graphology
the practice of determining one’s personality through handwriting
69
New cards
Astrology
the application of horoscopes to predict one’s life and to describe one’s personality.
70
New cards
Palmistry
refers to the reading of one’s personality as well as one’s destiny through one’s palms.
71
New cards
Neurons (nerve cells)
The building blocks of the nervous system
72
New cards
Central Nervous System
commands and coordinates all human activities in the body. It is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
73
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
these are nerve cells attached from the spinal cord to the different organs in the body
74
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
***Subsystem of peripheral nervous system*** that pertains to ***nerves attached too the muscles.***
75
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
***Subsystem of*** ***peripheral nervous system*** that pertains to ***nerves attached to the organs***. ***Involuntary*** and ***automatic*** movements (heat beat, digestion, etc.)
76
New cards
Sympathetic
Subsystem of Autonomic Nervous System that ***expands energy.***
77
New cards
Parasympathetic
Subsystem of Autonomic Nervous System that conserves energy. Commands organs to rest (homeostasis).
78
New cards
Electro magnetic signals
How do nerve cells communicate with each other?
79
New cards
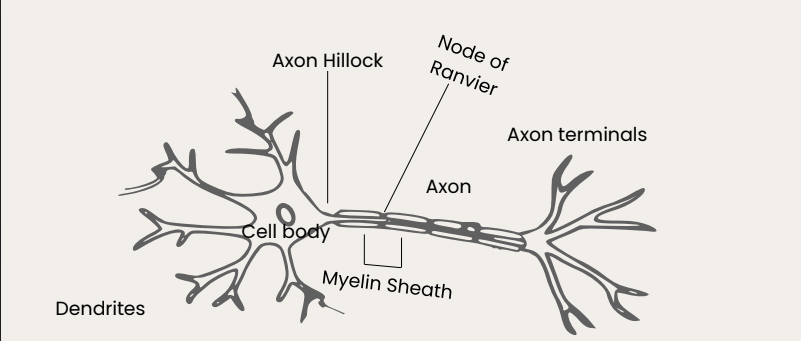
.
80
New cards
Sensory Neurons
A type of neuron also called as ***afferent neurons***, from sense organ to brain.
81
New cards
Motor Neurons
A type of neuron also referred as ***efferent neurons,*** from ***brain to spinal cord.***
82
New cards
Interneurons
A type of neuron that ***connects sensory neuron to motor neurons.***
83
New cards
Node of Ranvier
Part of the nerve cell found in ***between the myelin sheath.***
84
New cards
Glial Cells
The myelin sheath is composed of what?
85
New cards
Dendrites
Part of the nerve cell that receives the signal
86
New cards
Axon
Part of the nerve cell that sends away electricity
87
New cards
Myelin Sheath
Serves as lubricator for faster process of electricity in the axon.
88
New cards
Synapse/ synaptic gap
Space in between every axon and dendrite.
89
New cards
Sodium, potassium, calcium
Three chemical elements involved in neural activity
90
New cards
Neurotransmitters
chemicals at the end of every axon terminal that is transported to the dendrites of another axon to determine if it will fire or not.
91
New cards
Dopamine
Feelings of pleasure and reward, learning, and movement.
92
New cards
Serotonin
Involved with emotions, moods, sleep, dreaming, and arousal.
93
New cards
Norepinephrine
a.k.a adrenaline; involved in alertness, fight-or-flight response, and stress
94
New cards
Acetylcholine
Primarily involved with memory formation and retention
95
New cards
Glutamate
Excitatory neurotransmitter
96
New cards
GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Inhibitory Neurotransmitter associated with anxiety.
97
New cards
Endorphin
Reduces the feelings of pain and stress.
* hugs!!!
* hugs!!!
98
New cards
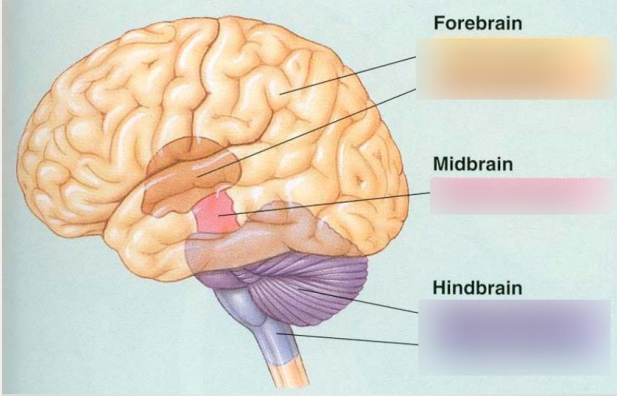
The brain
99
New cards
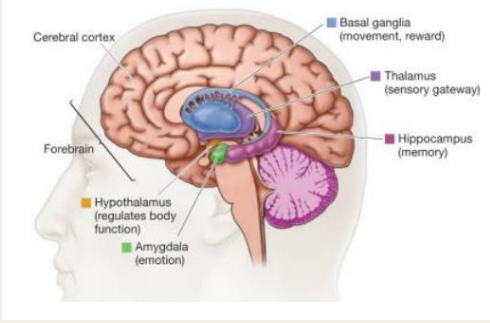
Forebrain
100
New cards
* cerebral cortex
* limbic system
* limbic system
Two main regions of the Forebrain