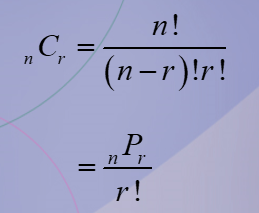Chapter 5: Probability and Counting Rules
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Probability
The chance of an event occurring.
Probability
Can be used to quantify what the “odds” are that a specific event will occur.
Probability Experiment
A chance process that leads to well-defined results called outcomes.
Outcome
The result of a single trial of a probability experiment.
Sample Space
The set of all possible outcomes of a probability experiment
Event
Consists of outcomes
Head, Tail
Provide the sample space for tossing a coin
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Provide the sample space for rolling a die
True, False
Provide the sample space for answering a true/false question
HH, HT, TH, TT
Provide the sample space for tossing two coins

5/36
If two dice are rolled one time, find the probability of getting these results: A sum of 6

6/36 = 1/6
If two dice are rolled one time, find the probability of getting these results: Doubles

8/36 = 2/9
If two dice are rolled one time, find the probability of getting these results: A sum of 7 or 11

6/36 = 1/6
If two dice are rolled one time, find the probability of getting these results: A sum greater than 9
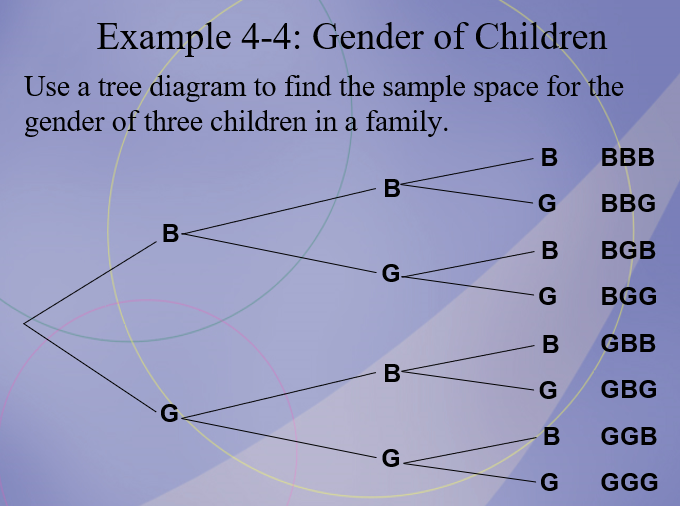
BBB BBG BGB BGG GBB GBG GGB GGG
Find the sample space for the gender of the children if a family has three children. Use B for boy and G for girl.
Tree Diagram
A device consisting of line segments emanating from a starting point and also from the outcome point.
Tree Diagram
It is used to determine all possible outcomes of a probability experiment.
Classical probability
Empirical probability
Subjective probability
There are three basic interpretations of probability:
Classical probability
Uses sample spaces to determine the numerical probability that an event will happen
Classical probability
Assumes that all outcomes in the sample space are equally likely to occur.
Equally likely events
What are events that have the same probability of occurring.

Provide the equation for classical probability
Probabilities should be expressed as BLANK or BLANK
Probabilities should be expressed as reduced fractions or rounded to two or three decimal places. When the probability of an event is an extremely small decimal, it is permissible to round the decimal to the first nonzero digit after the decimal point.

The probability of having two of three children being girls is 3/8.
If a family has three children, find the probability that two of the three children are girls.
Probability Rule 1
The probability of any event E is a number (either a fraction or decimal) between and including 0 and 1.
Probability Rule 1
This is denoted by 0 <= P(E) <= 1.
Probability Rule 1
Rule BLANK states that probabilities cannot be negative or greater than 1.
This is denoted by 0 <= P(E) <= 1.
Probability Rule 1 is denoted by?
This is denoted by 0 <= P(E) <= 1.
The probability of any event E is a number (either a fraction or decimal) between and including 0 and 1. This is denoted by?
Probability Rule 2
If an event E cannot occur (i.e., the event contains no members in the sample space), its probability is 0. What probability rule is this?
Probability Rule 3
If an event E is certain, then the probability of E is 1. What probability rule is this?
Probability Rule 3
In other words, if P(E) = 1, then the event E is certain to occur. What probability rule is this?
Probability Rule 4
The sum of the probabilities of all the outcomes in the sample space is 1. What probability rule is this?
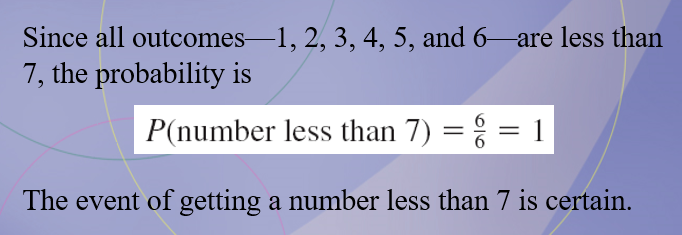
The event of getting a number less than 7 is certain.
When a single die is rolled, what is the probability of getting a number less than 7?

The complement of an event E, denoted by E bar
The set of outcomes in the sample space that are not included in the outcomes of event E. What is this?
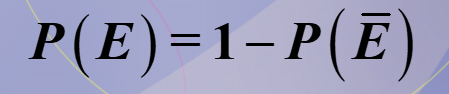
Provide the equation for the complement of an event E, denoted by E bar
The complement of an event E, denoted by E bar
What does this equation represent
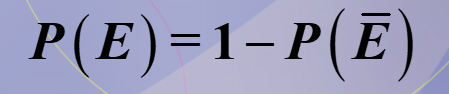
Getting a 1, 2, 3, 5, or 6
What is the complement of the event: Rolling a die and getting a 4
Getting a consonant (assume y is a consonant)
What is the complement of the event: Selecting a letter of the alphabet and getting a vowel
Getting February, March, April, May, August, September, October, November, or December
What is the complement of the event: Selecting a month and getting a month that begins with a J
Getting Saturday or Sunday
What is the complement of the event: Selecting a day of the week and getting a weekday

If the probability that a person lives in an industrialized country of the world is 1/5, find the probability that a person does not live in an industrialized country.
Empirical probability
Relies on actual experience to determine the likelihood of outcomes.

What is the equation for empirical probability?
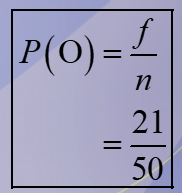
21/50
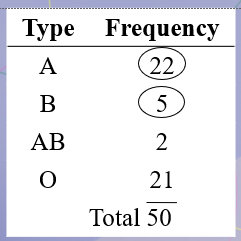
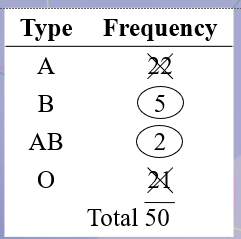
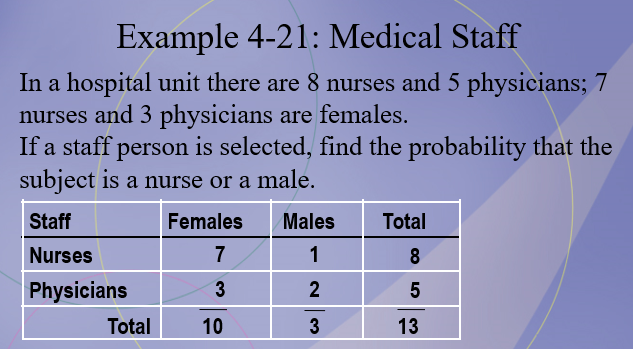
In a sample of 50 people, 21 had type O blood, 22 had type A blood, 5 had type B blood, and 2 had type AB blood. Set up a frequency distribution and find the following probabilities: A person has type O blood.

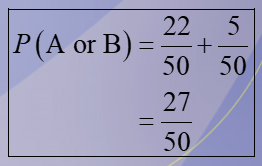
27/50
In a sample of 50 people, 21 had type O blood, 22 had type A blood, 5 had type B blood, and 2 had type AB blood. Set up a frequency distribution and find the following probabilities: A person has type A or type B blood.
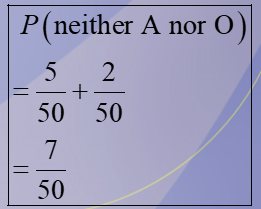
7/50
In a sample of 50 people, 21 had type O blood, 22 had type A blood, 5 had type B blood, and 2 had type AB blood. Set up a frequency distribution and find the following probabilities: A person has neither type A nor type O blood.
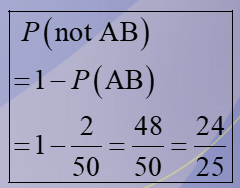
24/25
In a sample of 50 people, 21 had type O blood, 22 had type A blood, 5 had type B blood, and 2 had type AB blood. Set up a frequency distribution and find the following probabilities: A person does not have type AB blood.

Subjective probability
Uses a probability value based on an educated guess or estimate, employing opinions and inexact information
Subjective probability
What type of interpretations of probability is this: weather forecasting, predicting outcomes of sporting events
Mutually Exclusive
Two events are BLANK events if they cannot occur at the same time (i.e., they have no outcomes in common)

What are the addition rules for mutually exclusive and not mutually exclusive events?
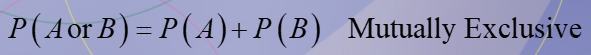
What are the addition rules for mutually exclusive events?
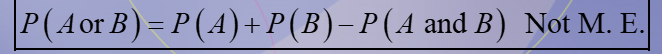
What are the addition rules for not mutually exclusive events?
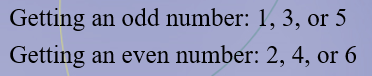
Mutually Exclusive
Determine which events are mutually exclusive and which are not when a single die is rolled: Getting an odd number and getting an even number
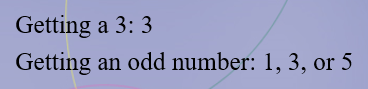
Not Mutually Exclusive
Determine which events are mutually exclusive and which are not when a single die is rolled: Getting a 3 and getting an odd number
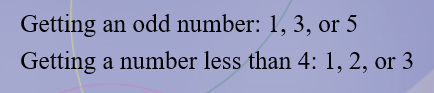
Not Mutually Exclusive
Determine which events are mutually exclusive and which are not when a single die is rolled: Getting an odd number and getting a number less than 4

Mutually Exclusive
Determine which events are mutually exclusive and which are not when a single die is rolled: Getting a number greater than 4 and getting a number less than 4




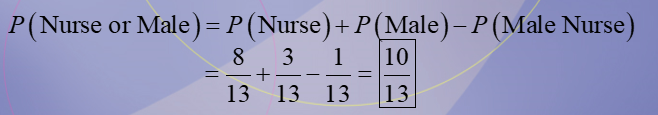
Independent Events
Two events A and B are BLANK events if the fact that A occurs does not affect the probability of B occurring.
Dependent Events
When the outcome or occurrence of the first event affects the outcome
Dependent Events
Occurrence of the second event in such a way that the probability is changed.

What is the equation of an independent event?
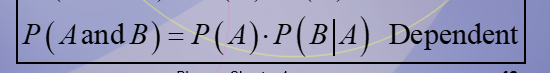
What is the equation of a dependent event?
Independent Events
What event is this: Rolling a die and getting a 6, and then rolling a second die and getting a 3.
Independent Events
What event is this: Drawing a card from a deck and getting a queen, replacing it, and drawing a second card and getting a queen.
Dependent Events
What event is this: Drawing a card from a deck, not replacing it, and then drawing a second card.
Dependent Events
What event is this: Selecting a ball from an urn, not replacing it, and then selecting a second ball.
Dependent Events
What event is this: Being a lifeguard and getting a suntan.
Dependent Events
What event is this: Having high grades and getting a scholarship.
Dependent Events
What event is this: Parking in a no-parking zone and getting a parking ticket.
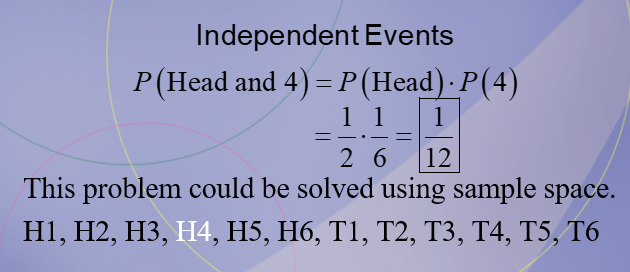
Independent Event: 1/12
A coin is flipped and a die is rolled. Find the probability of getting a head on the coin and a 4 on the die.

Independent Event: 0.097
A Harris poll found that 46% of Americans say they suffer great stress at least once a week. If three people are selected at random, find the probability that all three will say that they suffer great stress at least once a week.
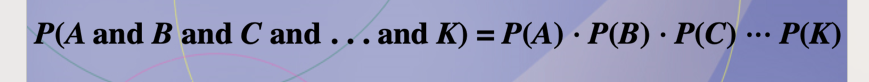
Multiplication rule can be extended to three or more independent events by using the formula:
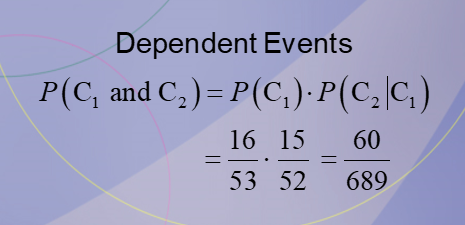
Dependent Events: 60/689
At a university in western Pennsylvania, there were 5 burglaries reported in 2003, 16 in 2004, and 32 in 2005. If a researcher wishes to select at random two burglaries to further investigate, find the probability that both will have occurred in 2004.
Conditional Probability
The probability that the second event B occurs given that the first event A has occurred.
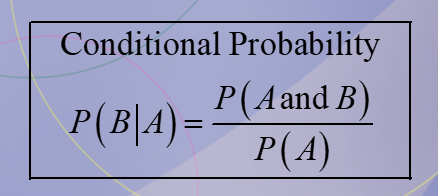
What is the equation for a conditional probability?

The probability that Sam parks in a no-parking zone and gets a parking ticket is 0.06, and the probability that Sam cannot find a legal parking space and has to park in the no-parking zone is 0.20. On Tuesday, Sam arrives at school and has to park in a no-parking zone. Find the probability that he will get a parking ticket.
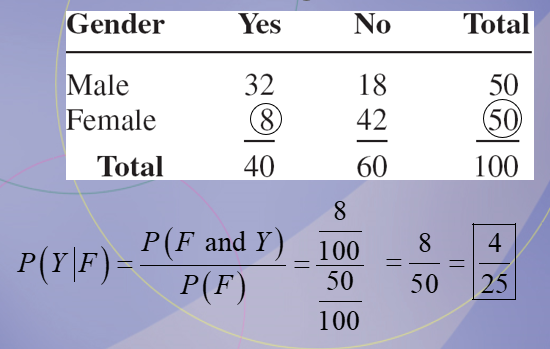
4/25
A recent survey asked 100 people if they thought women in the armed forces should be permitted to participate in combat. The results of the survey are shown. Find the probability that the respondent answered yes (Y), given that the respondent was a female (F).
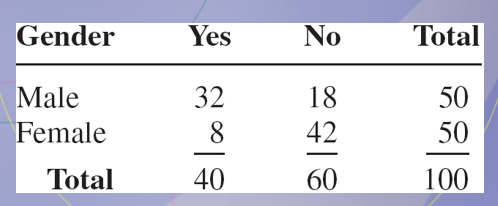
3/10
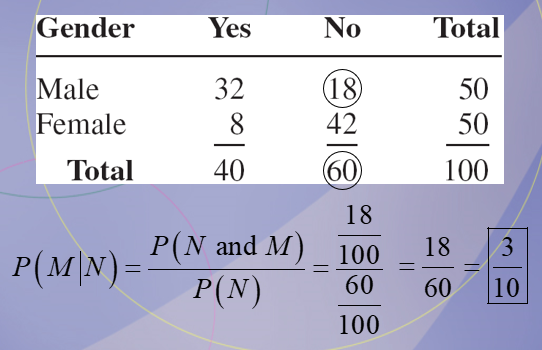
A recent survey asked 100 people if they thought women in the armed forces should be permitted to participate in combat. The results of the survey are shown. Find the probability that the respondent was a male (M), given that the respondent answered no (N).
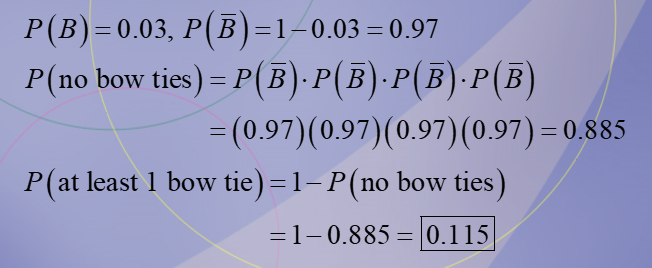
0.115
The Neckware Association of America reported that 3% of ties sold in the United States are bow ties (B). If 4 customers who purchased a tie are randomly selected, find the probability that at least 1 purchased a bow tie.
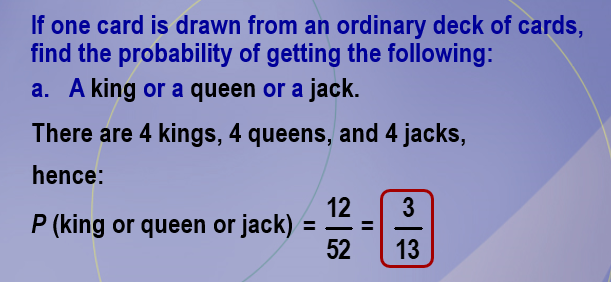
If one card is drawn from an ordinary deck of cards, find the probability of getting the following: A king or a queen or a jack.

3/4
If one card is drawn from an ordinary deck of cards, find the probability of getting the following: A club or a heart or a spade.

19/52
If one card is drawn from an ordinary deck of cards, find the probability of getting the following: A king or a queen or a diamond.

7/13
If one card is drawn from an ordinary deck of cards, find the probability of getting the following: An ace or a diamond or a heart.

15/26
If one card is drawn from an ordinary deck of cards, find the probability of getting the following: A 9 or a 10 or a spade or a club.

0.0954
At a local university 54.3% of incoming first-year students have computers. If three students are selected at random, find the following probabilities: None have computers

0.9046
At a local university 54.3% of incoming first-year students have computers. If three students are selected at random, find the following probabilities: At least one has a computer

0.1601
At a local university 54.3% of incoming first-year students have computers. If three students are selected at random, find the following probabilities: All have computers

0.116


0.7 or 70%
In Rolling Acres Housing Plan, 42% of the houses have a deck and a garage; 60% have a deck. Find the probability that a home has a garage, given that it has a deck.
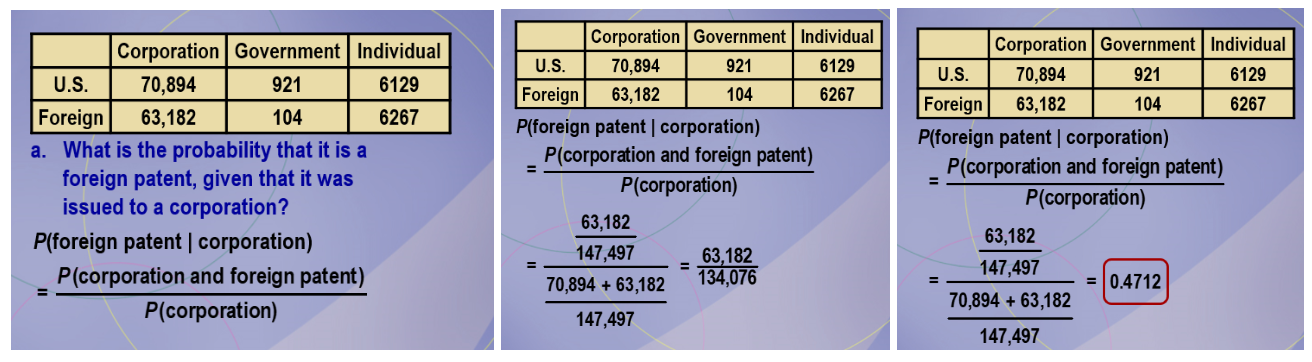
0.4712
Consider this table concerning utility patents granted for a specific year. Select one patent at random. What is the probability that it is a foreign patent, given that it was issued to a corporation?
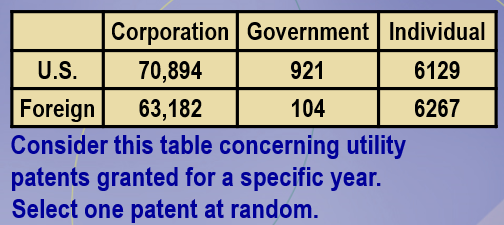
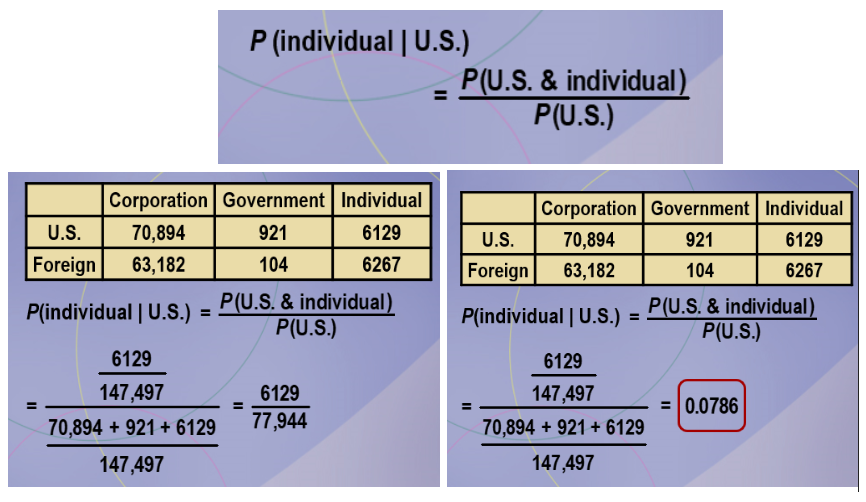
0.0786
Consider this table concerning utility patents granted for a specific year. Select one patent at random. What is the probability that it was issued to an individual, given that it was a U.S. patent?
Multiplication of choices
The fundamental counting rule is also called the BLANK


Factorial
Is the product of all the positive numbers from 1 to a number
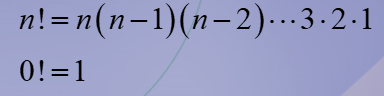
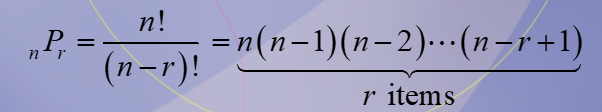
Permutation
Is an arrangement of objects in a specific order. Order matters.
Combination
Is a grouping of objects. Order does not matter.