Distal Humerus and Elbow
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What is the condyle of the humerus?
the expanded distal end
What are the sharp edges of the humerus above the condyle called?
supracondylar ridges
What are the epicondyles?
rough projections on either side of the distal end of the humerus for forearm muscle attachments
What is the difference between the medial and lateral epicondyles?
medial is larger and more easily palpated
What is the capitulum?
rounded knob on the lateral aspect of the humerus that articulates with the head of the radius
forms the humeroradial joint
What is the humeroradial joint?
diarthrodial, synovial, hinge joint made up of the capitulum and radial head
What is the trochlea?
spool-like surface on the medial aspect of the humerus that articulates with the ulna
forms the humeroulnar joint
What is the humeroulnar joint?
diarthrodial, synovial, hinge joint made up of the trochlea and ulna
What is the trochlear sulcus?
the central concave depression on the articular surface of the distal humerus where the ulna articulates
What is the coronoid fossa?
anterior depression on the humerus (receives the coronoid process of the ulna when the arm is flexed)
What is the radial fossa?
depression in the humerus lateral to the coronoid fossa (receives the radius when the arm is flexed)
What is the olecranon fossa?
depression on the posterior distal humerus, triangular in shape, receives the olecranon when the arm is extended
What are the Joints that make up the Elbow Joint Proper
made up of 3 joints
Humeroulnar Joint
Synovial, Diarthrodial, Hinge/Ginglymus
Humeroradial Joint
Synovial, Diarthrodial, Hinge/Ginglymus
Proximal Radioulnar Joint
Synovial, Diarthrodial, Pivot/Trochoid
When are the fat pads of the elbow visualized?
in a true lateral view of the elbow
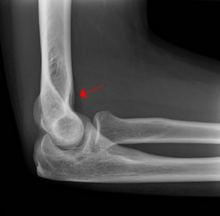
What is shown by the arrow?
anterior fat pad
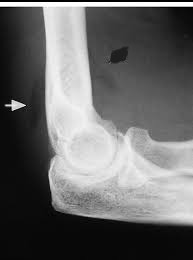
What is shown by the arrow?
posterior fat pad
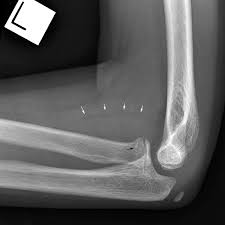
What is shown by the arrows?
supinator fat stripe
Which fat pad is only seen when there is an injury?
posterior
What is a routine elbow?
AP, internal/medial oblique, external/lateral oblique, lateral
Explain the AP elbow image
arm extended with hand supinated
epicondyles parallel to IR
slight superimposition of proximal radius and ulna
How are elbow images sent?
as if someone is standing in front of you in anatomical position
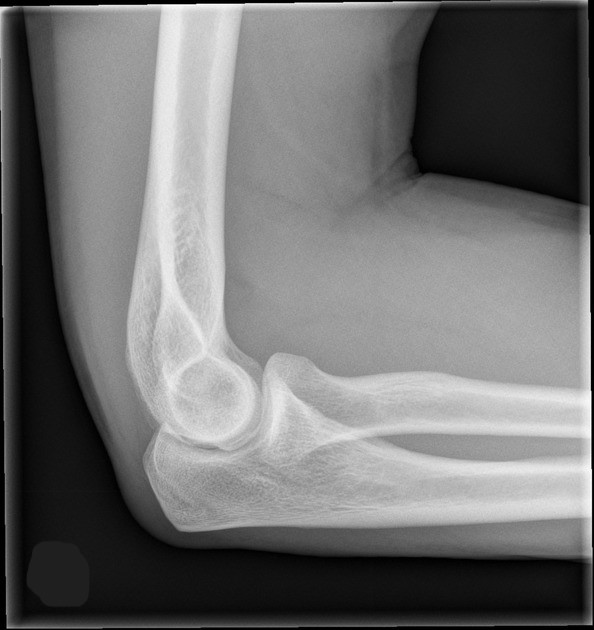
Based solely on how the image was oriented when sent, is this a right or a left elbow?
right
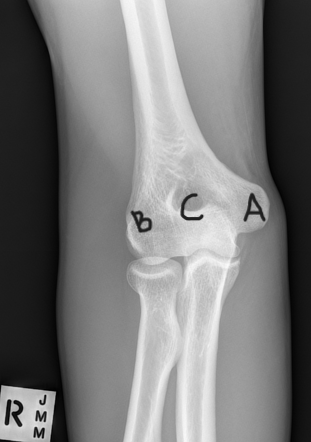
What are A, B, and C in this image?
A: medial epicondyle
B: lateral epicondyle
C: olecranon
Explain the internal AP oblique image
arm rotated medially with hand pronated
medial epicondyle in contact with IR, lateral epicondyle 45o up
coronoid process in profile
superimposition of the proximal radius and ulna
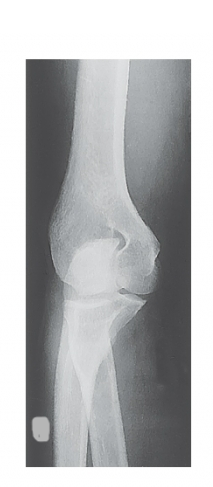
What projection was taken to obtain this image? R or L?
right elbow, internal AP oblique
Explain the external AP oblique image
arm rotated laterally
lateral epicondyle in contact with IR, medial epicondyle 45o up
radial head free of superimposition
radial tuberosity free of superimposition
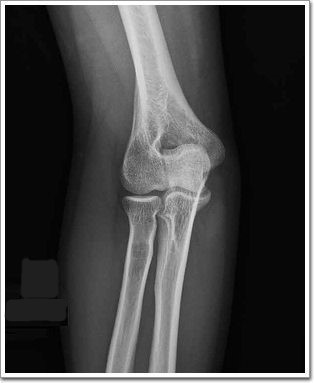
What projection was taken to obtain this image? R or L?
right elbow, external AP oblique
Explain the lateral elbow image
90o flexion, true lateral
lateromedial projection
superimposed epicondyles (perpendicular to IR)
hand in lateral position
this places radial tuberosity anterior
List the 3 concentric arcs visible on a lateral elbow image (in order from middle circle to outermost circle)
trochlear sulcus
superimposed capitulum and trochlea
trochlear notch
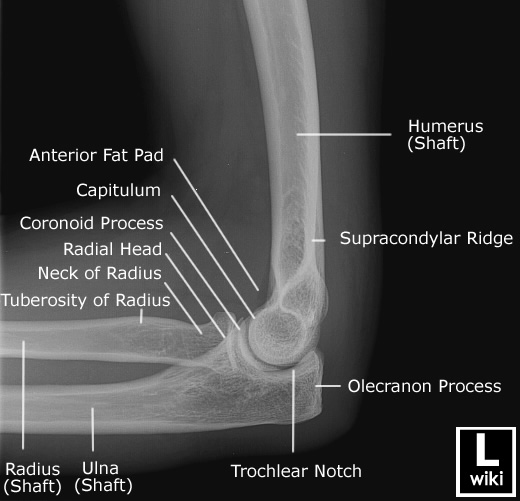
Explain the supracondylar fracture
most common fracture in children
occurs through the growth plate of the humerus
caused by falling on an outstretched arm
Explain the olecranon fracture
a fracture of the olecranon; makes up 10% of elbow fractures
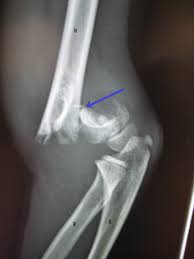
What kind of pathology is shown in the image?
supracondylar fracture
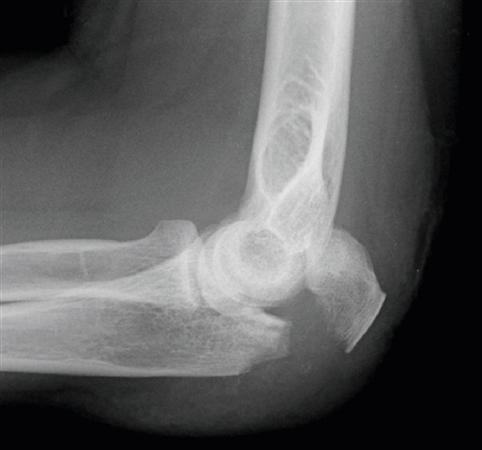
What kind of pathology is shown in the image?
olecranon fracture
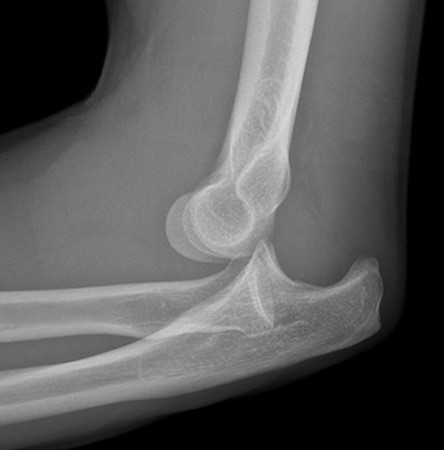
What kind of pathology is shown in the image?
complete dislocation
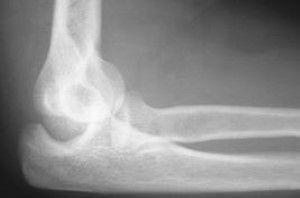
What kind of pathology is shown in the image?
partial dislocation
Explain the radial head fracture
caused by a fall on an outstretched arm
most common elbow fracture in adults (30%)
can be subtle and hard to see on an x-ray
best demonstrated on external oblique