Weed Science Lab Midterm 2023
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
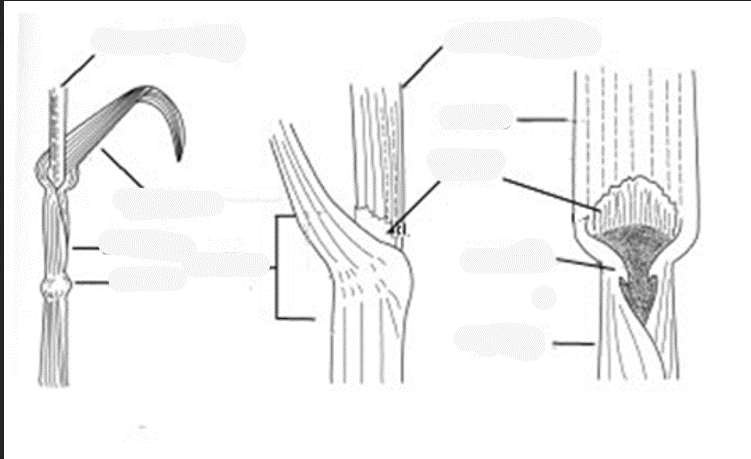
What are all the parts of a grass?
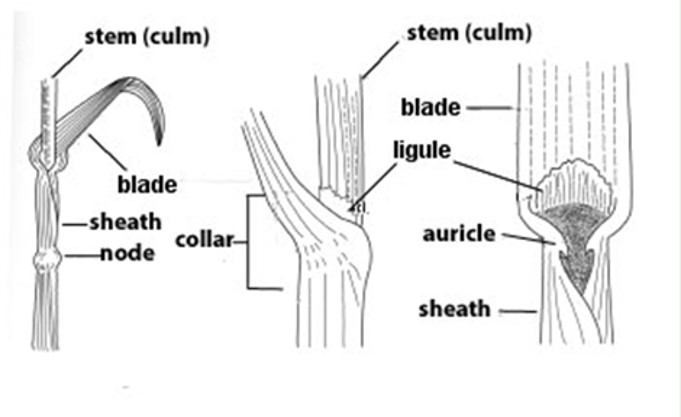
Blade
part of the leaf that doesnt surround the stem
Sheath
portion of the leaf that surrounds stem
Node
joint of stem, point of leaf attachment
Collar
leaf attachment to stem (key to ID grasses)
Ligule
thin projection at the base of sheath
Auricle
appendages at the opening of sheath
What are the two specialized stems for grasses?
Rhizomes: below-ground specialized stems (Johnsongrass)
Stolon: above-ground specialized stems (Bermudagrass)
Types of Ligules: Membranous
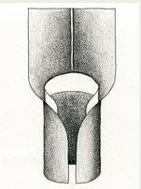
Types of Ligules: Fringe of hairs
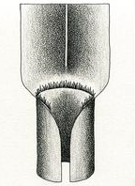
Types of Ligules: Truncate
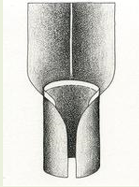
Types of Ligules: Absent
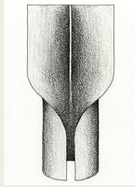
Types of Ligules: Rounded
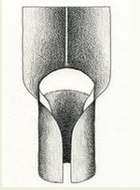
Types of Ligules: Tapered
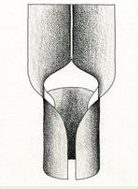
Types of Ligules: Scalloped or toothed
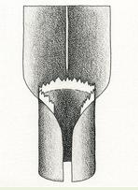
What are the 4 types of auricles?
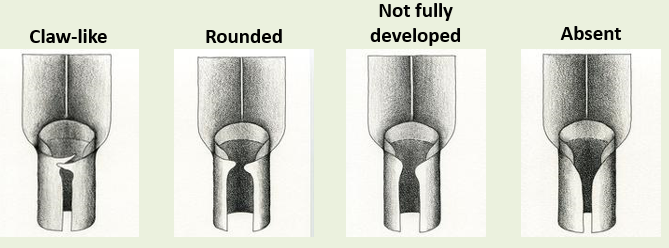
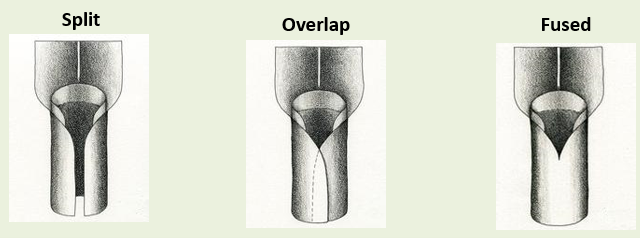
What are the 3 types of sheaths?
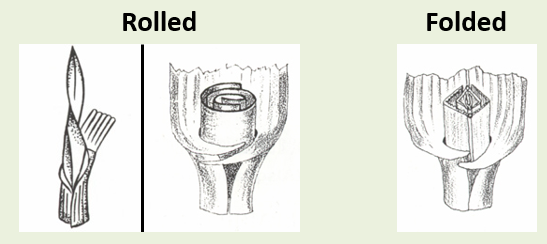
What are the vernation (arrangement of leaf buds) in grasses?
What are the 3 types of stems in grasses?
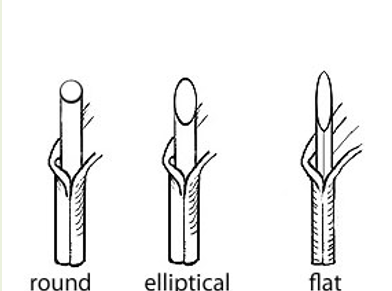
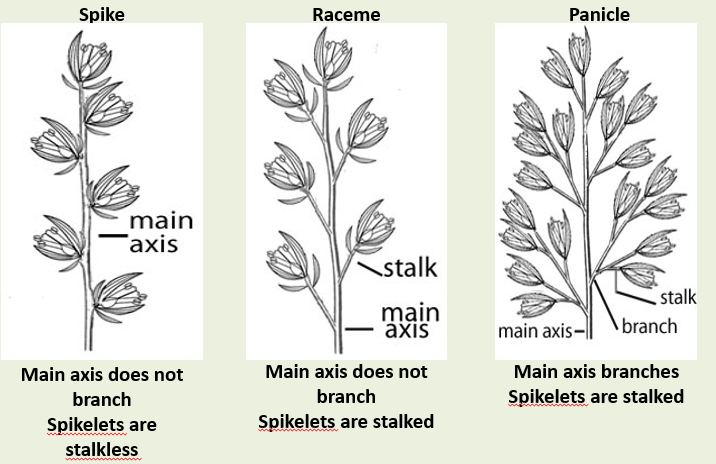
What are the 3 types of seedheads?
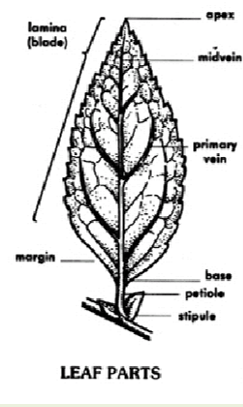
Identifying Dicots: Leaf Parts
Identifying Dicots: What are the 3 types of leaf arrangement?
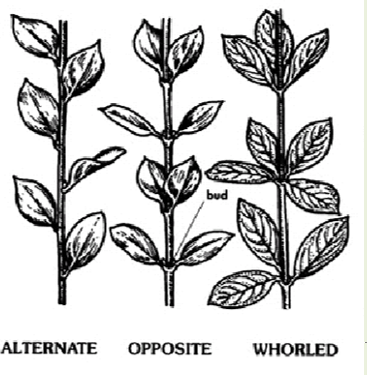
Identifying Dicots: Types of Leaves - Palmately trifoliolate (ternate)

Identifying Dicots: Types of Leaves - Pinnately trifoliolate
Identifying Dicots: Types of Leaves - Biternate

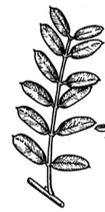
Identifying Dicots: Types of Leaves - Odd-Pinnate
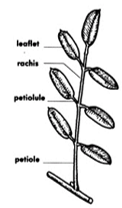
Identifying Dicots: Types of Leaves - Even-Pinnate
Identifying Dicots: Types of Leaves - Bipinnate
Identifying Dicots: Types of Leaves - Tripinnate

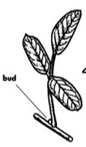
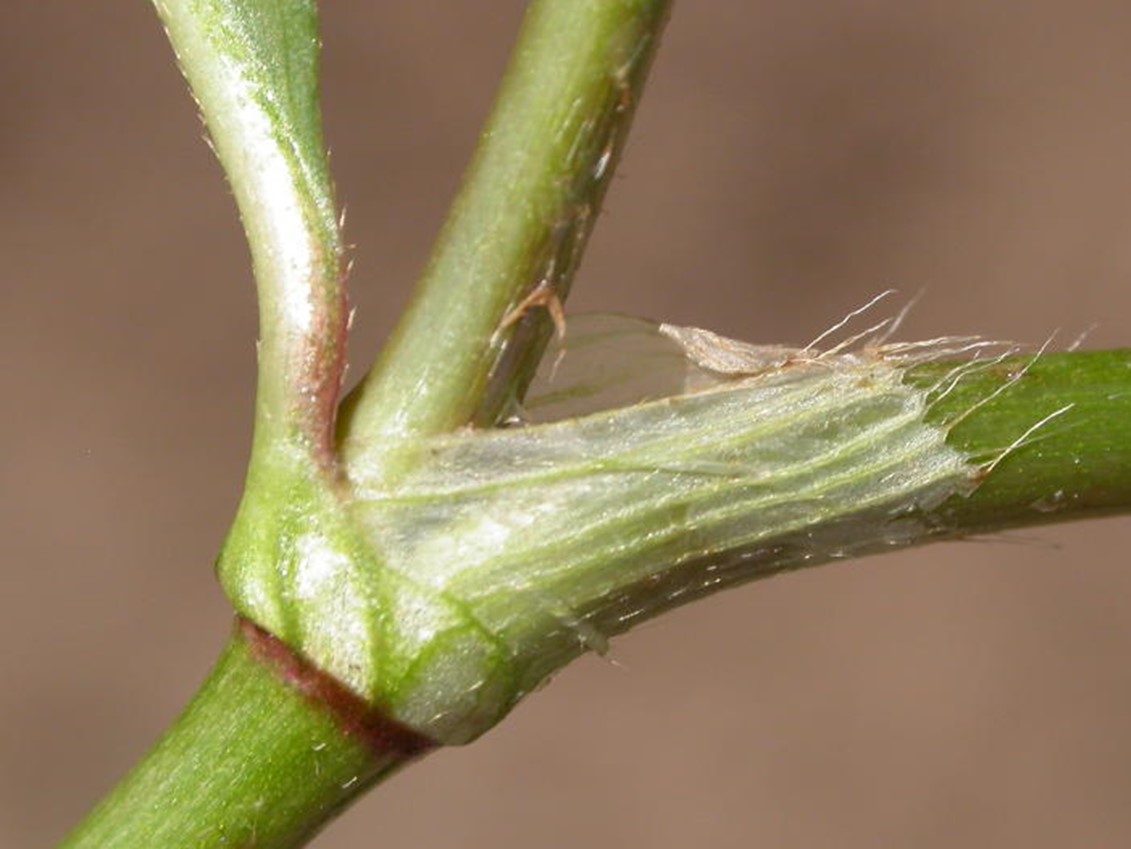
Stipules
Lateral appendages at the base of a leaf (
Examples: Spurred anoda, Prickly sida

Ocrea
Polygonaceae family; a papery sheath that encloses the stem at the nodes, a fusion of 2 stipules
Examples: Pennsylvania smartweed, Ladysthumb

How can the midvein be arranged?
Middle or Offset
Pubescence
presence of hairs (trichomes)
Where can pubescence be found?
All over
Underside of leaf
Around collar region
Seedling only
What is a label?
The information printed on or attached to a pesticide container
What does the label provide the user?
What the product is
What it controls
How it is used
Various precautions
How to mix properly
What it can be used on
Application rate
Where can you find labels?
Who regulates pesticides?
EPA under the authority of the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, Rodenticide Act of 1947
Food Quality Protection Act (more recent)
Worker Protection Standards (more recent)
State government
What is the difference between a label and labeling?
Label: the information printed on or attached to the pesticide container
Labeling: includes the label, plus all other info you receive from the manufacturer about the product
What is a section 3 label?
the regular federally approved label
What does the label mean to different groups?
Manufacturer: “license to sell”
Regulatory groups: a way to control distribution, storage, sale, use, and disposal
User: provides info. on how to use the product, correctly and safely
Physician: a source of info. on the proper treatment for poisoning cases
What is a section 24(c) label?
Special Local Need (SLN): FIFRA specifies a state may provide registration for additional uses of federally registered pesticides to meet a special local need.
What is a section 18 label?
An “emergency condition” that allows someone to use an unregistered pesticide
section 2(ee)
allows a pesticide to be sprayed in conditions not specified on the label
What is the product name of a pesticide?
The trade name (Round-up)
What does the active ingredient include?
Chemical name, CAS #, and concentration
What does the inert ingredients include?
Concentration but not identified
What does KOOROC mean?
Keep out of reach of children (on all lables)
What are the 3 signal words on a label?
Danger: must include poison with a skull and crossbones symbol, Category 1
Warning: moderately toxic, Category 2
Caution: low toxicity, Category 3 and 4
What does PPE mean?
Personal Protection Equipment
What is the purpose of tank mixing two or more pesticides?
Broaden spectrum of control
Save trips across fields
Where can you find the information on what chemicals can be mixed?
any mixtures listed on one or more labels of products under consideration can be mixed
Is it legal to mix two pesticides if neither tank mix partner specifically mentions that mix?
Yes, as long as neither label prohibits that mixture and application rate and timing is within specifications on labels of individual products.
What is SDS?
Safety Data Sheet: provides both workers and emergency personnel with proper safety procedures for handling or working with a particular substance.
What is an Adjuvant?
Any substance in a herbicide formulation or added to the spray tank to modify herbicidal activity or application characteristics
What is the difference between spray and formulation adjuvants?
Formulation: present in the container when purchased by the user; added by the manufacturer for better mixing, handling, shelf-life, formulation stability, efficacy, and drift reduction.
Spray: added to the tank by the user, primarily to improve pesticide performance but also to aid in mixing, reduce drift, and reduce foaming.
What is the difference between activator and utility/spray modifier adjuvants?
Activator: enhance the biological efficacy of the pesticide
Utility/Spray modifier: modify the physical characteristics of the spray mixture.
What is a Surfactant?
WSSA: a material that improves the emulsifying, dispersing, spreading, wetting, or other properties of a liquid by modifying its surface characteristics
ASTM: a material that when added to a liquid medium modifies the properties of the medium at a surface level
How does a surfactant work?
Has a hydrophilic head and lipophilic tail that when mixed reduces the surface tension between the leaf surface and spray droplets and increases the surface area of the droplet across the leaf.
What is crop oil?
A derivative of paraffin-based petroleum oil aka phytobland oil. Consists of oil plus 1-2% surfactant to aid in mixing with water. No longer used in herbicide application.
Are ammonium sulfate (AMS) and urea-ammonium nitrate (UAN) used as adjuvants?
Yes, ammonium ions are thought to be responsible for beneficial effect of herbicide performance.
What do water conditioners and fertilizer adjuvants have in common?
what is a compatibility agent?
a surface-active material that allows simultaneous application of liquid fertilizer and an agrichemical as a uniform tank mix. Basically helps mix two things that otherwise may not mix well.
How do you conduct a compatibility test?
Take 2 jars, put carrier (water or fluid fertilizer) and pesticide in both. If they don’t mix well add a compatibility agent to one of the jars to see if it mixes well. If so tank mix can be used if the compatibility agent is included.
What is a defoaming agent?
a material that eliminates or suppresses foam in the spray tank that occurs from adjuvants in the formulation and agitation of the spray solution.
What is a drift reduction agent?
a material used in a liquid spray mixtures to reduce spray drift
Does a drift reduction agent reduce vapor drift?
No, it only reduces spray drift by increasing the viscosity of the spray solution and increasing droplet size.
What is the difference between spray drift and vapor drift?
Spray: movement of spray droplets off the target site, primarily movement of fine droplets by wind, across a relatively short distance.
Vapor: movement of pesticide off-target site in gaseous form, primarily related to the vapor pressure of herbicide and environmental conditions, can be long distance.
What is the basic purpose of an acidifying and buffering agent?
Acidifying: a material added to spray mixtures to lower pH but will rise if alkaline-based products are added
Buffering: compound or mixture that causes the solution to resist a change in pH, with a characteristic limited range of pH over which it is effective.
Where can you find information on adjuvants?
www.herbicide-adjuvants.com
What is the difference between an adjuvant and a herbicide based on government regulation?
Adjuvants are non-pesticidal and EPA doesn’t regulate
Herbicides are heavily regulated by the EPA and State governments
What is a formulation and what is its purpose?
It is the pesticidal preparation sold by the manufacturer
formulating allows AI to be mixed with a carrier. Aids in mixing with other pesticides and is used to dilute AI due to safety issues. Enhances efficacy
What are the basic types of formulations?
Sprayable formulations
Dry formulations for direct application
Sprayable formulations: Water-soluble liquids, soluble, water-soluble concentrates, or liquid formulation
S, SC, SL, WSC
for water-soluble AI
form true solutions when added to water. Components can’t be separated by physical means, no agitation is required after initial mixing. Transparent but may be colored.
Non-abrasive to nozzles and pumps
Sprayable formulations: Water-soluble powders
SP or WSP
Same as water-soluble sprays but has an inhalation hazard
Sprayable formulations: Emulsifiable concentrates
E or EC
herbicide mixed in with some organic solvent that is soluble, plus an emulsifier to make the formulation with water.
Sprayable formulations: Wettable powders
W or WP
AI combined with finely ground clay carrier and suspension agents
form a suspension (a mixture of finely ground particles dispersed in a liquid) when mixed with water and can be physically separated from liquid
Requires continuous and vigorous agitation
recommended to slurry before adding to the tank
very abrasive
Sprayable formulations: Liquid flowables
F or L
very finely ground solid containing AI suspended in a liquid.
Form suspension in water
Sprayable formulations: Water dispersible granules
DG, WDG, or DF
Basically an WP formulation that has been formed into small granules
Easy pouring and no dust
very abrasive
same agitation as F formulation
Sprayable formulation: Microencapsulated formulations
ME
pesticide particles surrounded by a polymer coating
Dry formulations for direct application: Granules
G
AI impregnated on small dry carrier particles like clay
granule size usually < 10 mm cubed
applied dry with no dilution
rarely used in Ag. crops, common in turf and ornamentals
relatively low % of AI
Dry formulations for direct application: Pellets
P
AI impregnated on dry carrier
Granule size >10 mm cubed
What is a carrier?
the material to which the user adds to the herbicide for application
purpose is dilute the AI to aid in distributing a small amount of AI over a large area
Which form of carrier has the lowest concentrations of AI per unit carrier?
What is the order for mixing tanks?
Follow label directions if given
If no specific label directions
WF → DF → F → EC → SP or SC
Put B for Broadleaf ID, G for Grasses ID, or both
Ligule
Ocrea
Stipule
Pubescence
Leaf shape
Sheath
Pinnate leaves
Collar
Auricle
Lobes
G
B
B
Both
Both
G
B
G
G
B
Give an example of alternate leaf arrangement;
opposite;
whorled;
odd-pinnate;
even-pinnate;
common ragweed
spotted spurge
carpetweed
poison sumac
hemp sesbania
Name a plant with rhizomes;
stolons;
stipules;
ocrea;
Johnsongrass;
Bermuda grass (has both rhizome and stolon)
Cannabis
Lady’s Thumb
Name 3 types of activator adjuvants
surfactant
crop oil
ammonium fertilizers
name 3 utility/spray adjuvants
defoaming agent
compatibility agent
drift reduction agent
What is the calculation for GPM
(GPA)(MPH)(W)
(5940)
Calculation for Speed (MPH)
Distance (ft) * 60
Time (sec) * 88
Calculation for Ounces Per Minute (OPM)
= GPM * 128
For broadcasting how do you find (W)?
For banding?
For Directed crop foliar spray?
nozzle spacing on boom
Band width (in inches)
# of nozzles per band
Row spacing (in inches)
# of nozzels per row
Formula Calibration Method
Select GPA from label
Calculate ground speed by traveling 200 ft (3x average)
Find GPM of each nozzle
select nozzle that delivers that GPM
Convert GPM to OPM
Collect water output from each nozzle in oz, repeat, find the average for each and replace if > 10% above or below
Make adjustments for desired output (Change in pressure = small adjustments)(Change speed or nozzle for large adjustments)
What are the functions of a nozzle?
regulate flow
form droplets
disperse droplets in specific pattern
Factors that affect nozzle flow rate?
orifice size
pressure (more pressure = higher flow rate)
specific gravity of spray solution
viscosity of spray solution
Effects of pressure on nozzle output calculation
GPM1 = Sq root PSI1
GPM2 = Sq root PSI2
Effect of pressure on sprayer output
GPA1 = Sq root PSI1
GPA2 = Sq root PSI2
Effects of Travel Speed Formula (no effect on nozzle output, effects sprayer output GPA)
GPA1 = MPH 2
GPA2 = MPH1