AP U.S. History - LEP 17 - Reconstruction
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction (1863)
Lincoln offered presidential pardons (except Confederate officials and high-ranking officers) to anyone who took an oath of allegiance to the U.S. and accepted abolition.
If # of white males 21+ taking oath = 10% of voters in 1860, they could reestablish a state government with presidential approval.
Also called for minimal provision for food, shelter, and education of freedmen.
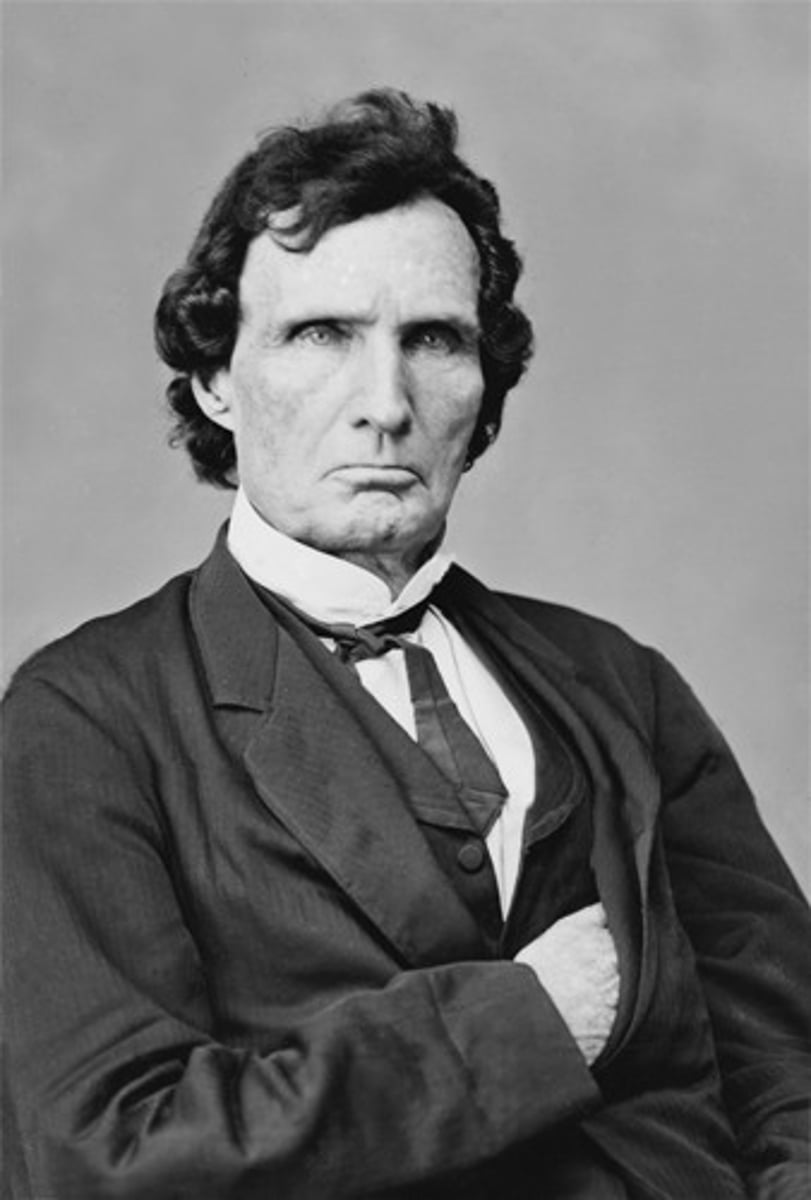
Thaddeus Stevens
Radical Republican leader in the House who believed in harsh punishments for the South. Secretly married to a former slave.

Radical Republicans
These were a small group of people in 1865 who supported black suffrage, redistribution of lands owned by rebelious Confederates, and harsh terms for readmittance to the union. They were led by Senator Charles Sumner and Congressman Thaddeus Stevens. Grew in power in the late 1860s.

Wade-Davis Reconstruction Bill (1864)
It would have required 50% of white males to swear a loyalty oath and the allowance of black male voting to regain admission to the union. Lincoln's pocket veto caused a schism in the Republican Party, which was only healed by Union victories in the fall and the prospects of Democrats winning.
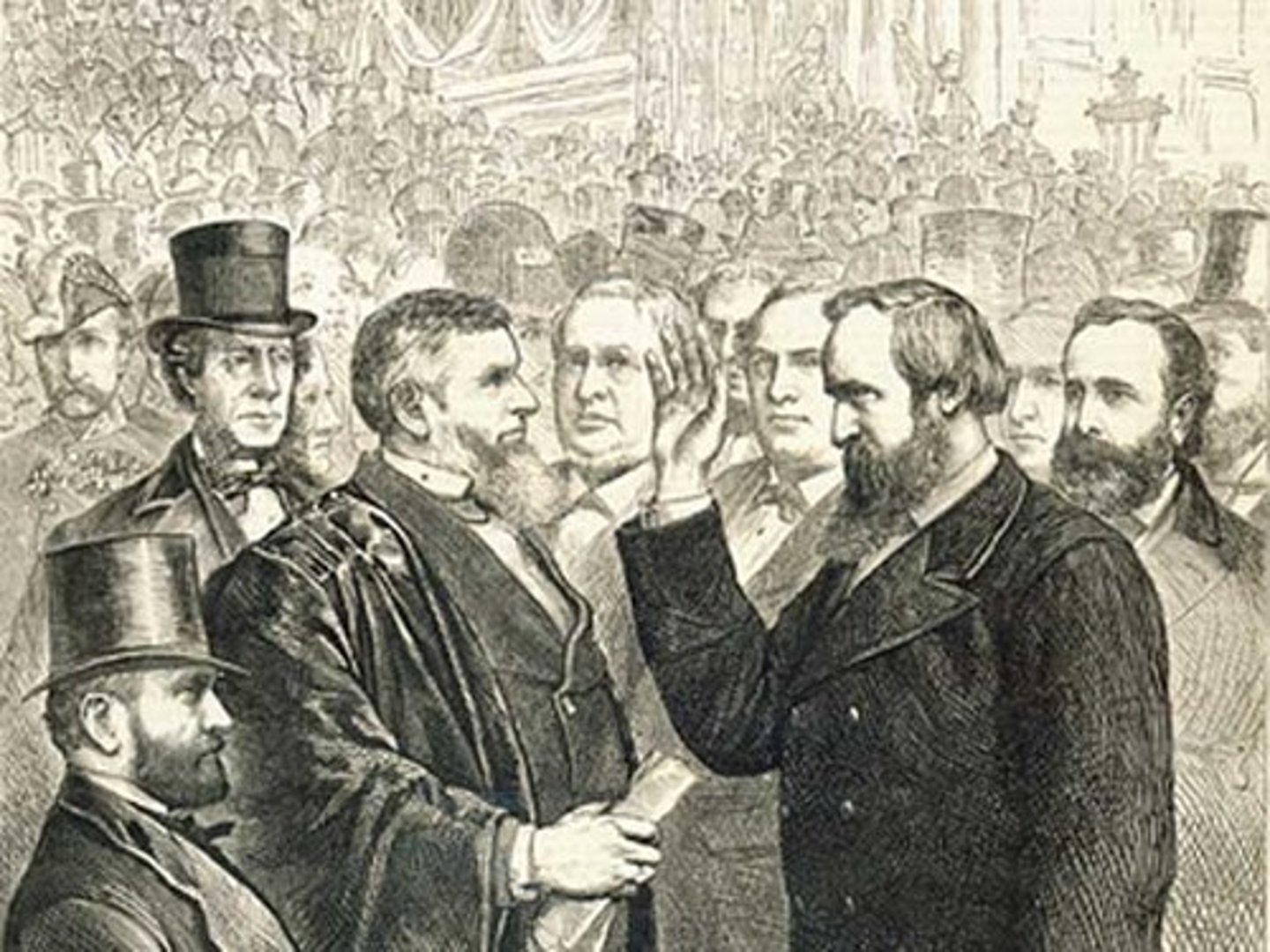
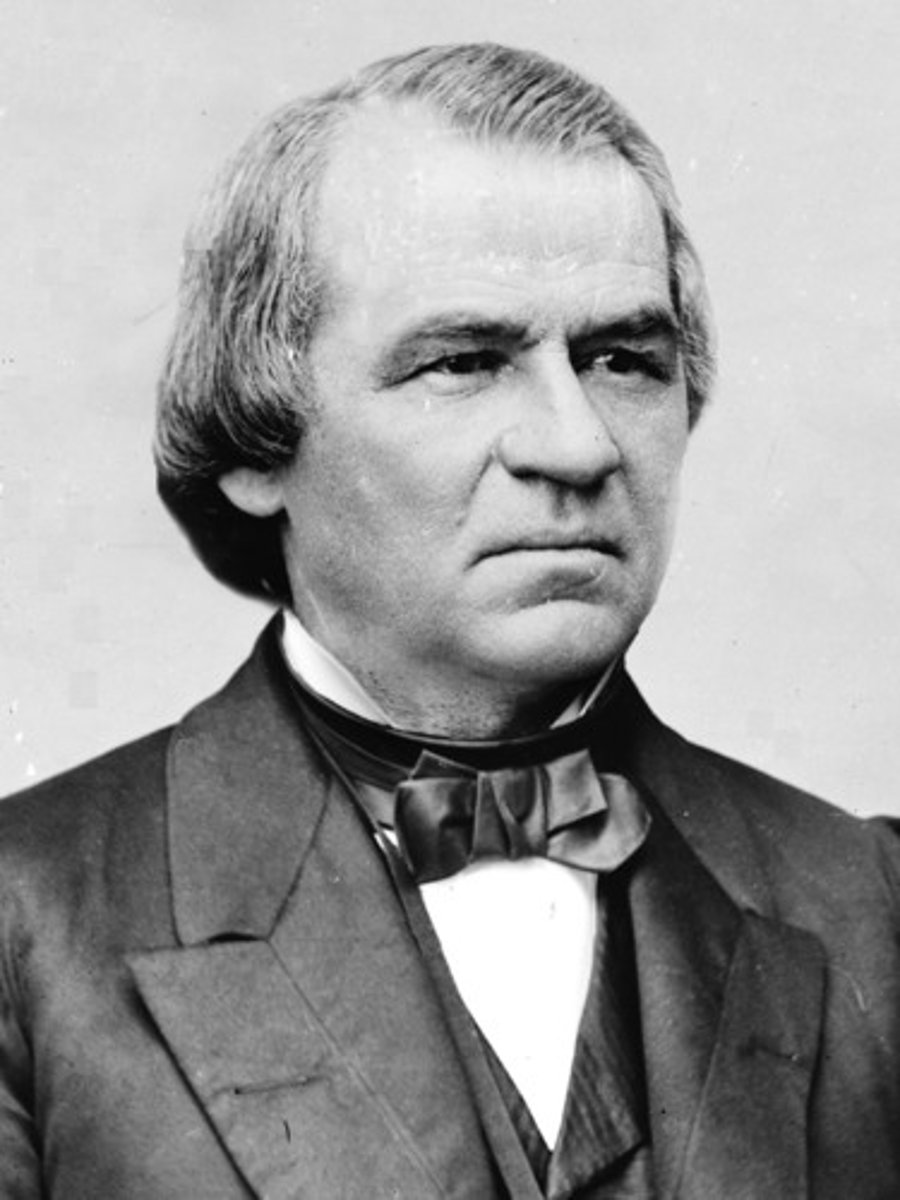
Andrew Johnson
17th president, following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln on April 14/15. He was chosen as the vice presidential candidate in 1864 on the Union Party ticket to attract War Democrats and border-state unionists. He was a senator from TN of poor heritage who learned to read as an adult (from his future wife).
Chastised planters as "stuck up aristocrats" but pardoned almost all of them who applied. Vetoed the renewal of the Freedmen's Bureau and almost every other Radical Republican bill.
Impeached in 1867 (but not convicted).

Black Codes
Laws passed in former confederate states immediately after the end of the Civil War to retain as much of the social order of slavery as possible:
-- forbade vagrancy
-- required year-long work contracts
-- allowed "masters" (land owners) to whip black workers for refusing "lawful orders"
-- punished runaway contract breakers with debtors prison or working it off as a farm hand (while chained)
-- forbade black jurors and voting
-- disallowed blacks to testify against whites in court
-- punished blacks more than whites for some crimes
-- banned interracial marriage
Freedmen's Bureau (1865-1872)
Created to aid newly emancipated slaves (and white refugees) by providing food, clothing, medical care, education, and legal support. Often negotiated work contracts between landowners and black sharecroppers. Its achievements were uneven and depended largely on the quality of local administrators.

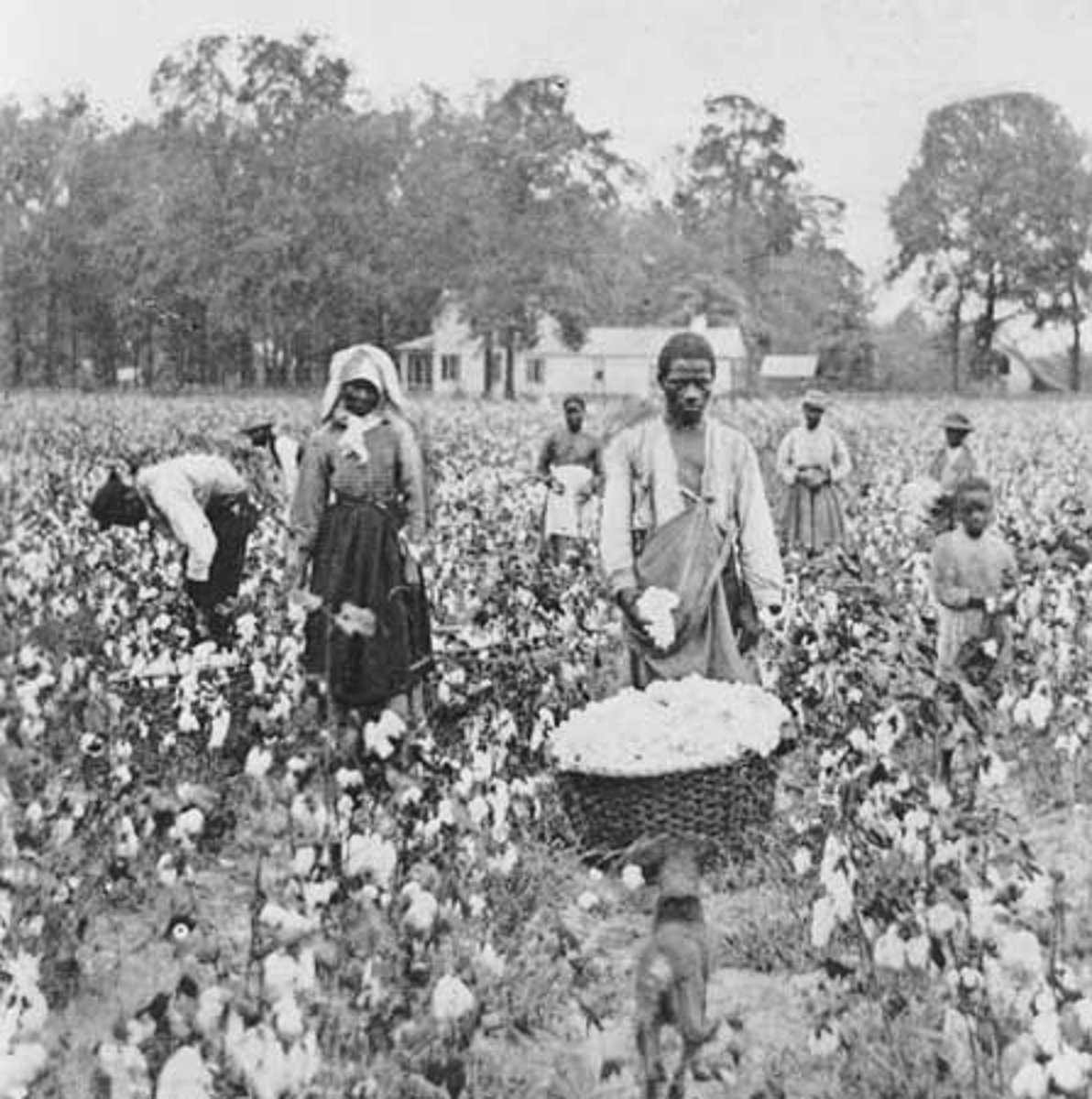
Sharecropping
A system used on southern farms after the Civil War in which landless freedmen and poor whites worked land owned by someone else in return for a portion of the crops (or the proceeds at sale).
-- rolling debt for supplies made it difficult to escape. Lack of gold/silver (and legitimate currency) in the South following the war made regular wages impossible.

40 acres and a mule
1865 as Sherman moved through the south he issues a grant of 40 acres of farmable land (GA + SC) and a surplus mule to freed slaves in an attempt to solve the problems of refugees. But Johnson's Amnesty Proclamation and widespread pardons undid most of this by 1866.

franchise/suffrage
the right to vote

moderate Republicans
Believed that the seceded states should be restored to the Union swiftly and on the terms of Congress, not the President.
Supported some black participation in Reconstruction (possibly limited to union veterans and literate freedmen).
3/5 Clause
The end of slavery meant the end of this, increasing # of southern representatives.

special pardons
Johnson issued many of these to particular ex-Confederates (or their widows) who applied to restore their confiscated property and political rights.
Black schools
Set up by missionary societies and freedmen assistance societies, staffed by some 2000 northerners. Reduced black illiteracy dramatically:
1880: 70% illiteracy
1900: 48% illiteracy
Historically black colleges
Beginning in 1870, many of these were founded during Reconstruction, often by former Union officers, missionaries, and freedmen assistance societies.
Howard University is an example.

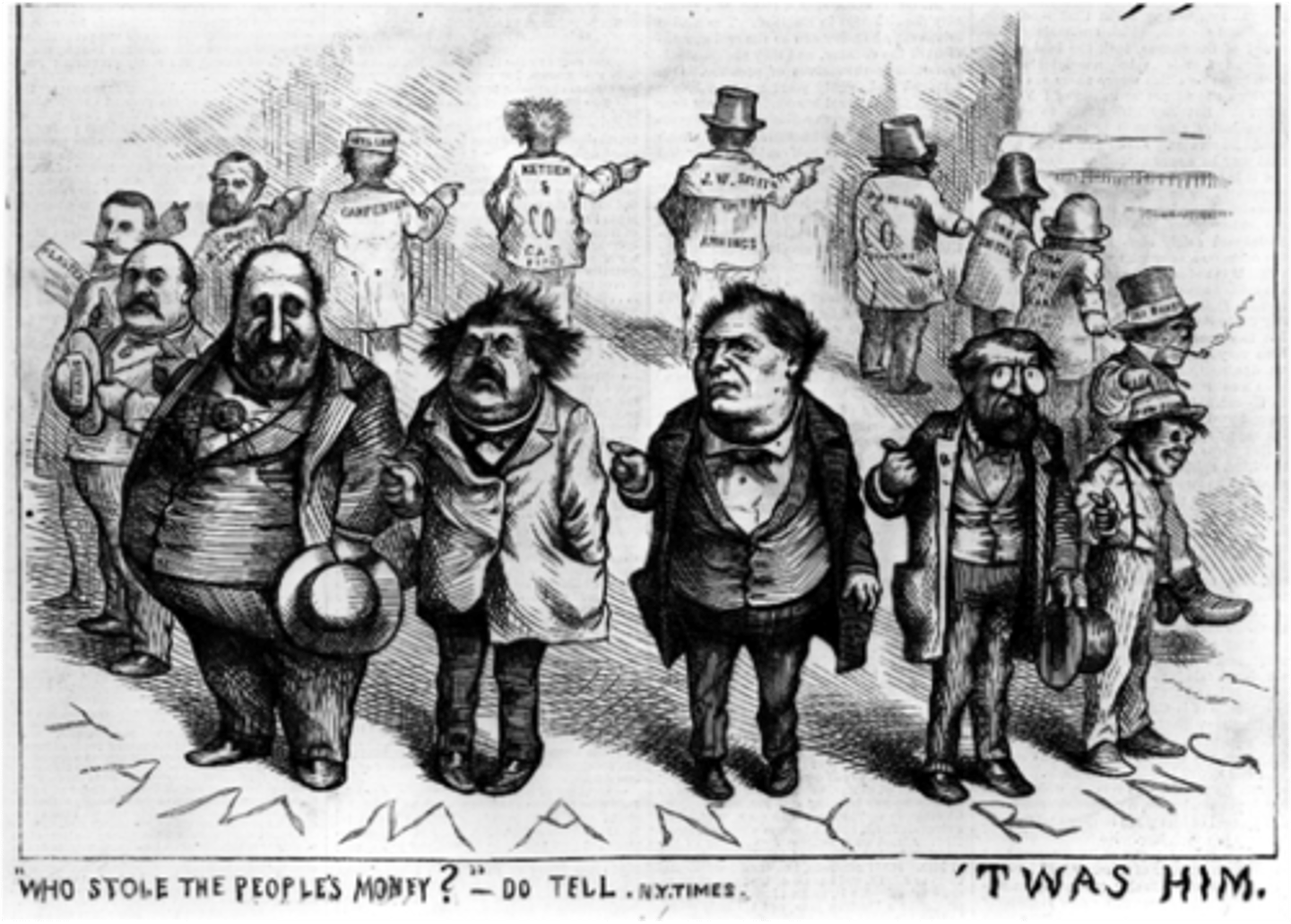
Thomas Nast
Harper's Weekly cartoonist who advocated political rights and protections for freedmen, as well as cutting critiques of political corruption.

Civil Rights Act of 1866
Passed by Congress on 9th April 1866 over the veto of President Andrew Johnson. The act declared that all persons born in the United States were now citizens, without regard to race, color, or previous condition.

14th Amendment (1868)
Congress proposed this in 1866, and made ratification a condition for readmittance to the Union.
Section 1: citizenship, privileges and immunities, due process, equal protection of the law -- by STATE governments.
Section 2 reduced the number of congressmen by the % to which states prohibited black male voting.
Section 3 disqualified ex-Confederates from federal or state office.
Section 4 guaranteed the national debt and repudiated the Confederate debt.
Section 5 empowered Congress to enforce the amendment through "appropriate legislation."
Johnson told southern states to reject it.
Midterm elections of 1866
Johnson tried to rally Democrats and conservative Republicans with the National Union Party, but Republicans swept the election, gaining a veto-proof majority in both houses, bringing in even more Radical Republicans, allowing more aggressive reconstruciton.
Race riots
white mobs in Memphis and New Orleans attacked black neighborhoods, killing 80 African Americans
-- helped contribute to Republican victory in 1866
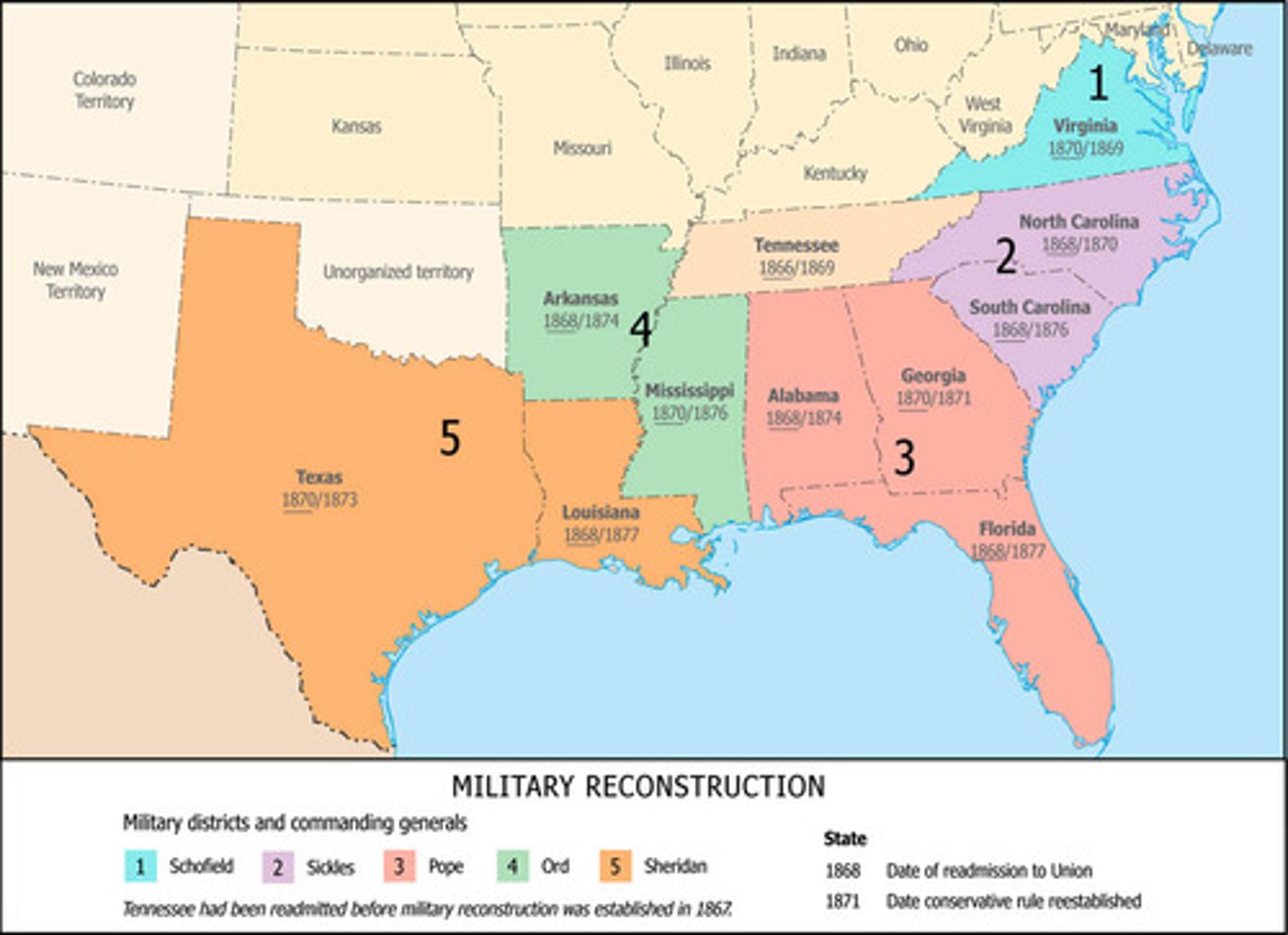
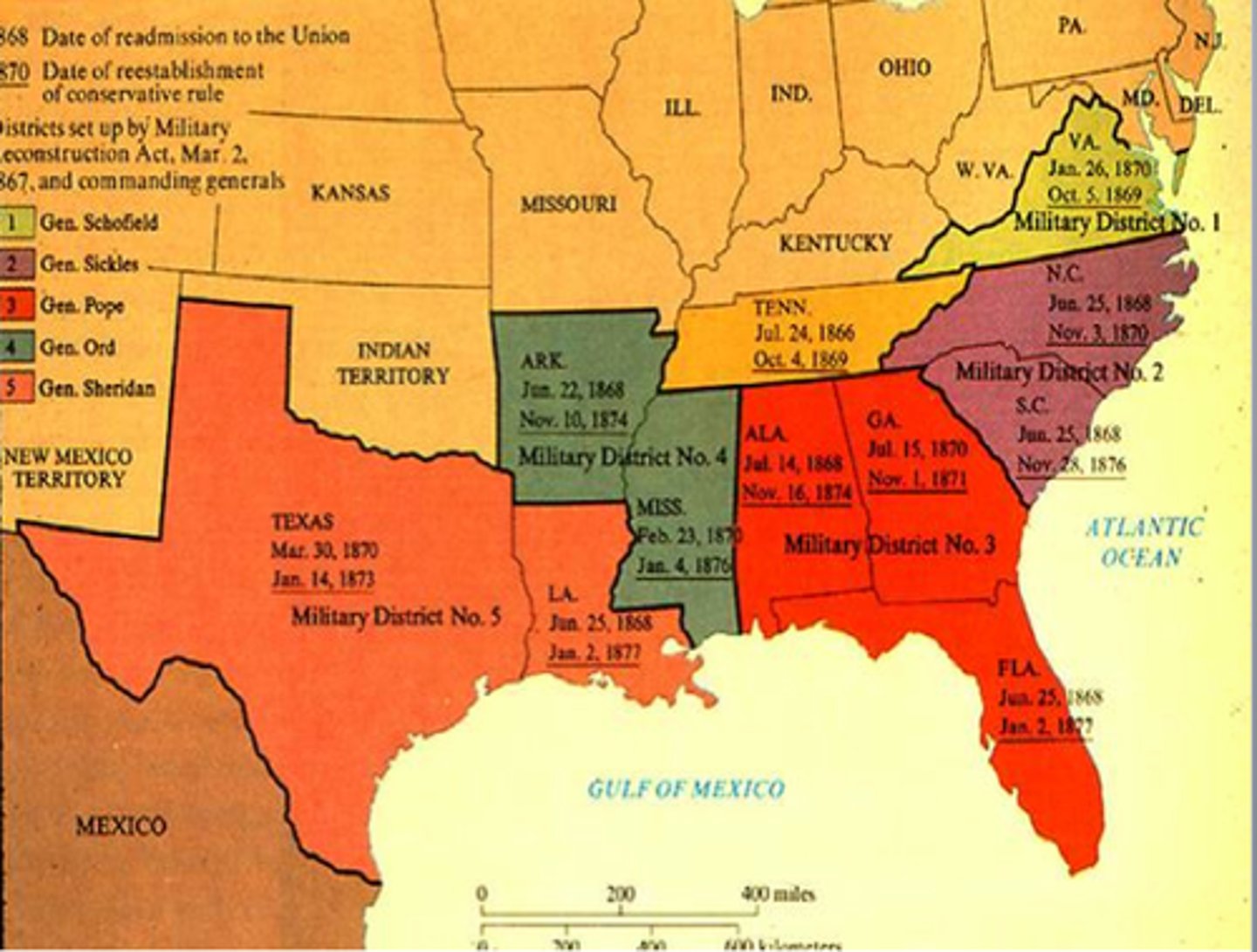
Reconstruction Acts of 1867
Divided the former Confederate states (except TN) into five military districts to be occupied by federal troops who would control violence and register voters (including black males) for the election of delegates to state constitutional conventions.
-- ex-Confederates disqualified under 14th Amd. could not vote in this election.
-- State with constitutions that granted black voting and equal rights would be readmitted.
Union leagues
In the South, a Republican Party organization to mobilize black and sympathetic white voters.

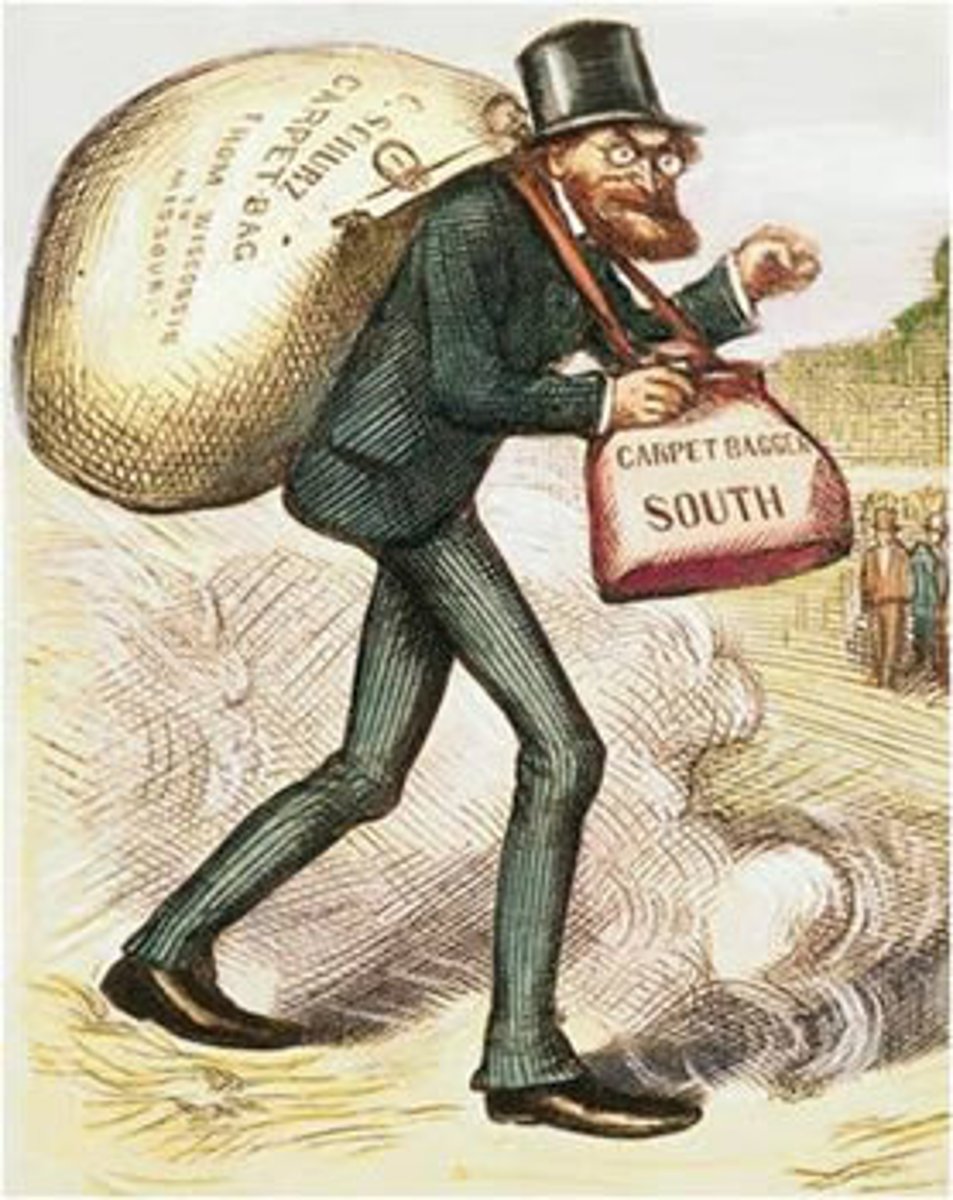
carpetbaggers
Northerners who went south for economic opportunity and political power.
-- Half of the Republican governors, senators, and congressmen were northern whites, many of them former Union officers who worked at the Freedmen's Bureau. Built numerous businesses.

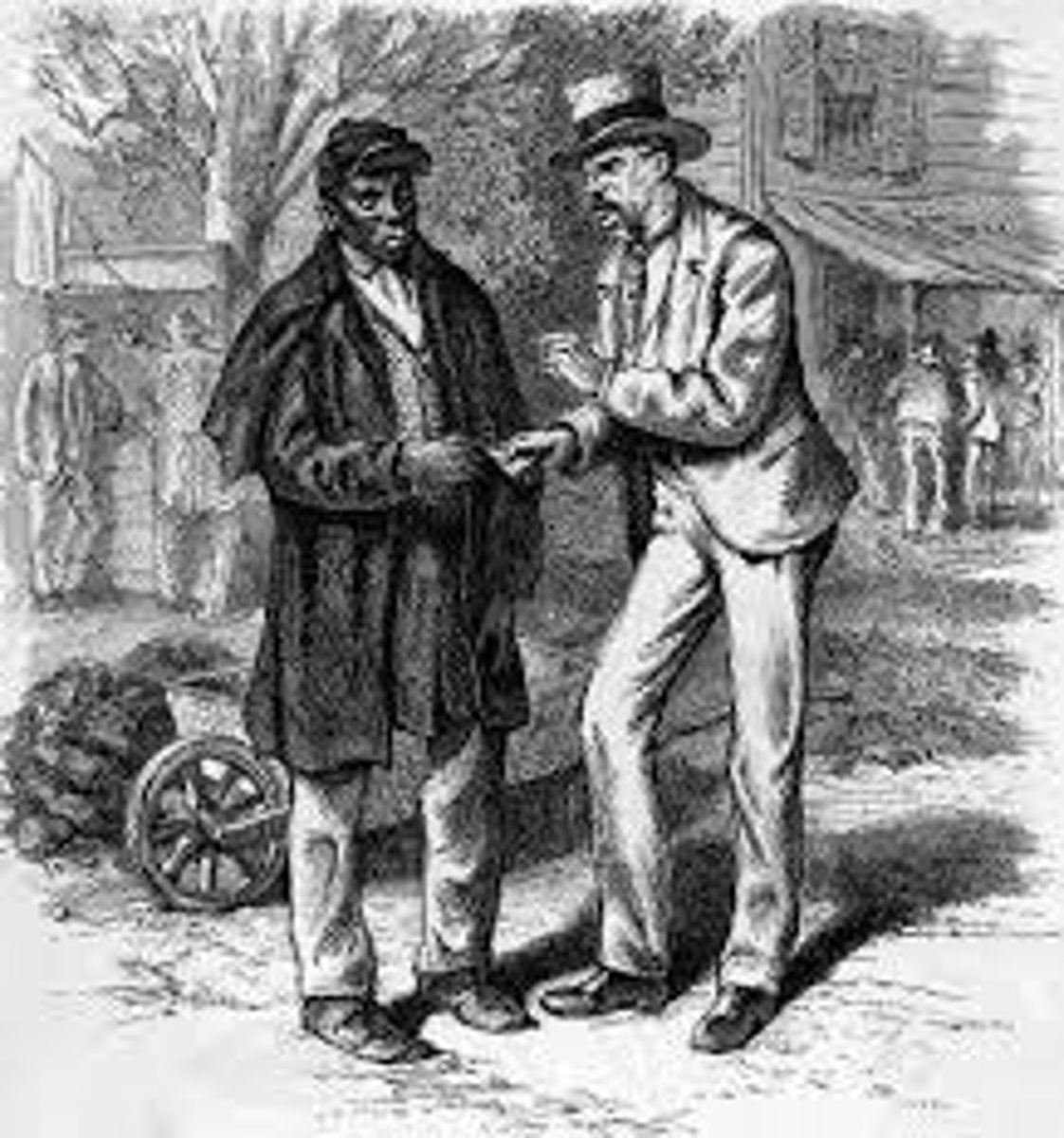
scalawags
A derogatory term for southerners who voted Republican and cooperated with Union occupation; they were often socially and economically ostracized by other white southerners.

state elections of 1867
Republicans lost some seats in the state legislatures as a response to congressional radicalism. Gave hope to Johnson as he geared up for 1868 election.
Tenure of Office Act (1867)
President could not fire cabinet members without approval of Congress.
-- This was the grounds for Johnson's impeachment.

Edwin Stanton
Secretary of War appointed by Lincoln. President Andrew Johnson dismissed him in spite of the Tenure of Office Act. He was a radical. His removal (and the appointment of officers sympathetic to the South) allowed Johnson to undermine the Freedmen's Bureau, military occupation, and black voting.
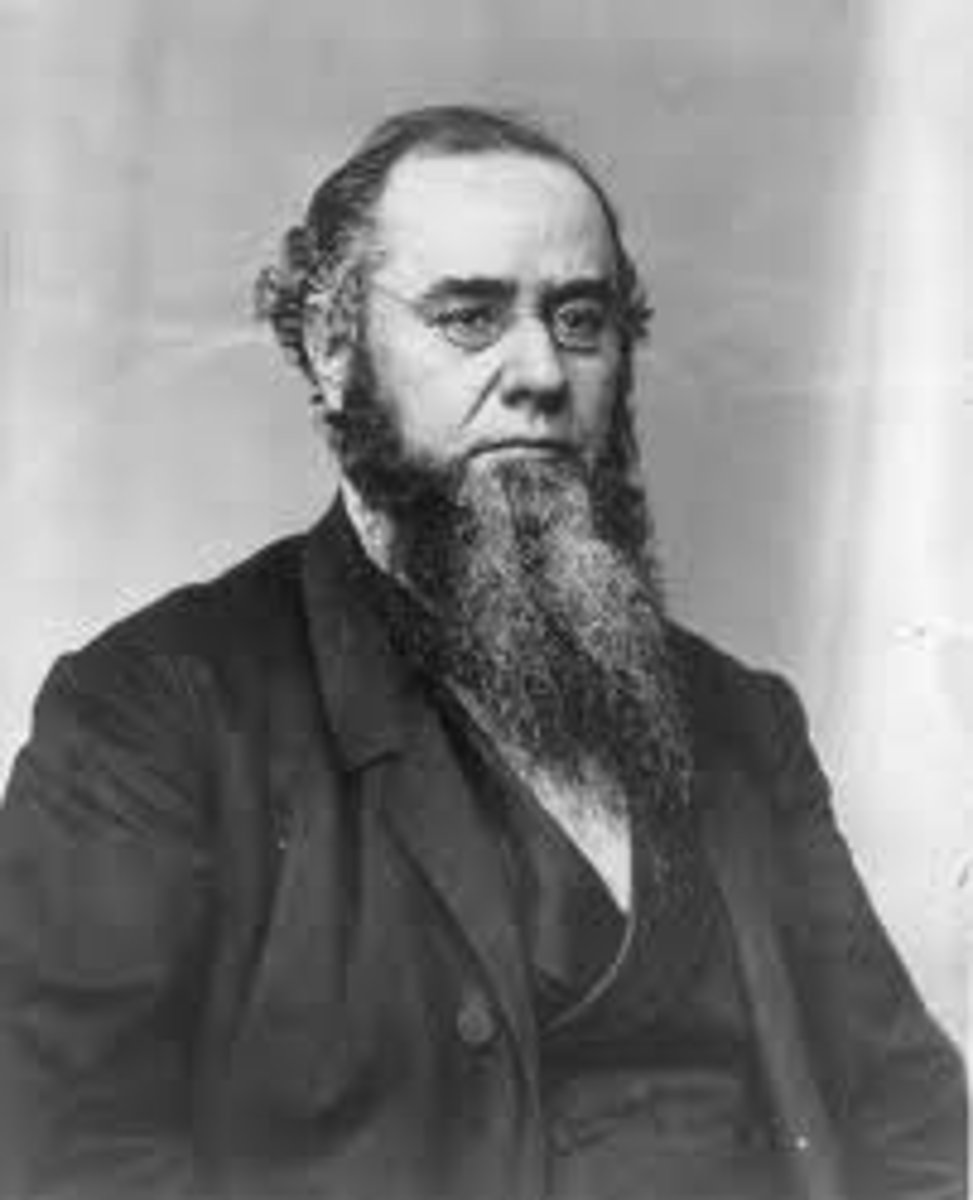

Impeachment of Andrew Johnson (1868)
Eleven articles alleging high crimes and misdemeanors anchored in the Tenure of Office Act. The president was tried in the Senate, but acquitted by a close vote.
-- 7 Republicans voted for acquittal, but there were likely more who would have done so if it was the deciding vote.
-- Johnson agreed behind the scenes to back off his opposition to Radical Reconstruction.

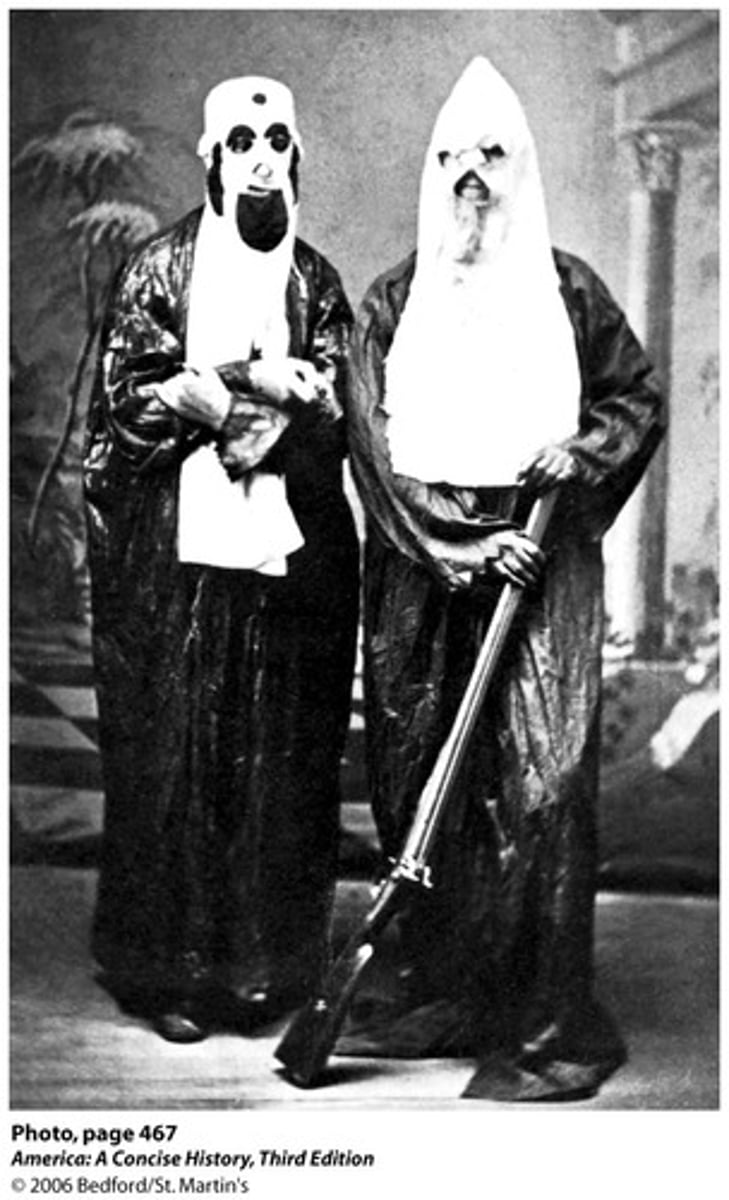
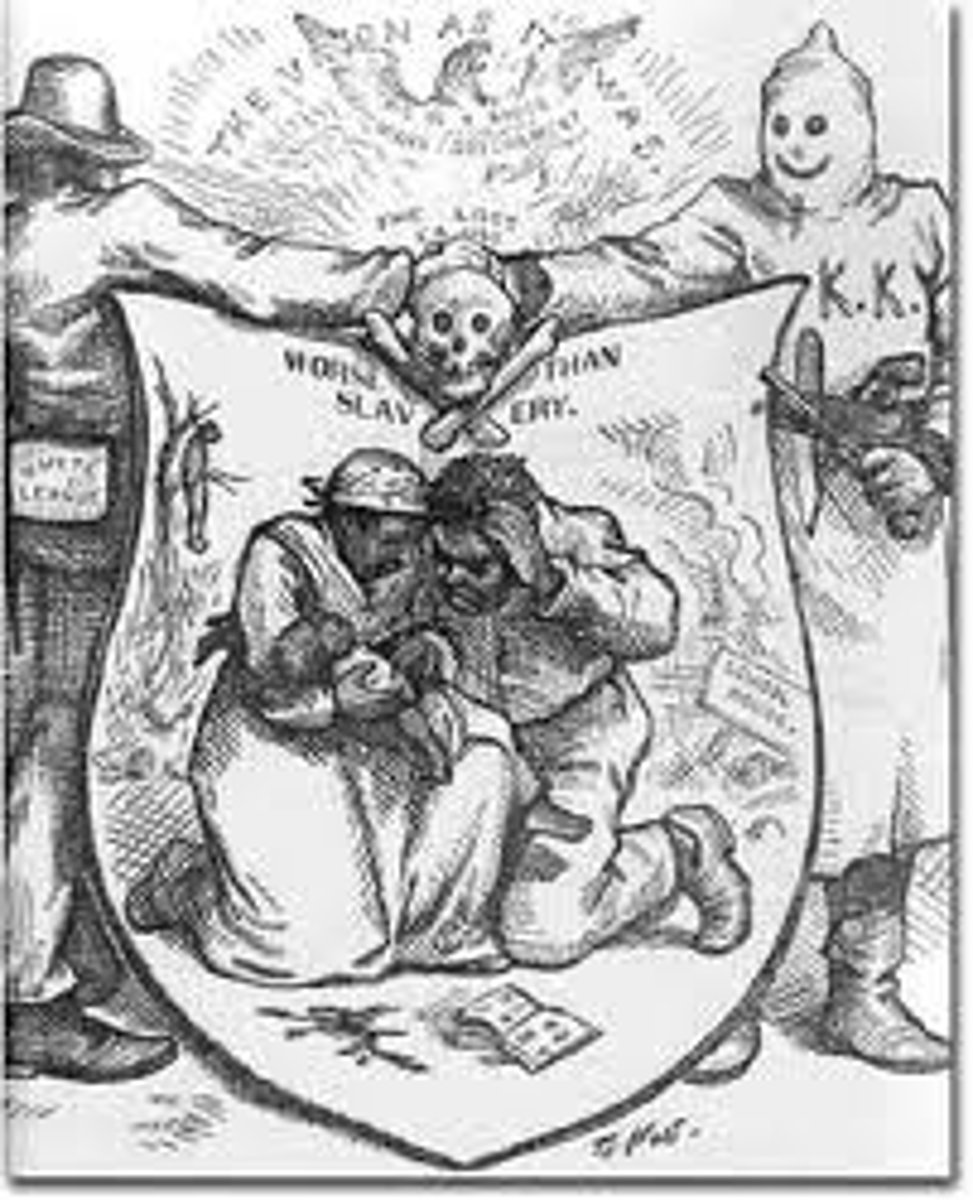
Ku Klux Klan (KKK)
A secret organization founded by Confederate general Nathan Bedford Forest that used terrorist tactics in an attempt to restore white supremacy in Southern states after the Civil War. It was the largest of many such groups.

"Bones and banjoes conventions"
The derogatory term used by white southerners for the state constitutional conventions in 1867/68 that guaranteed universal male suffrage and equality under the law.
-- Bones was a character from minstrel shows, thus representing the large number of African Americans who both voted to appoint delegates and participated in the conventions.
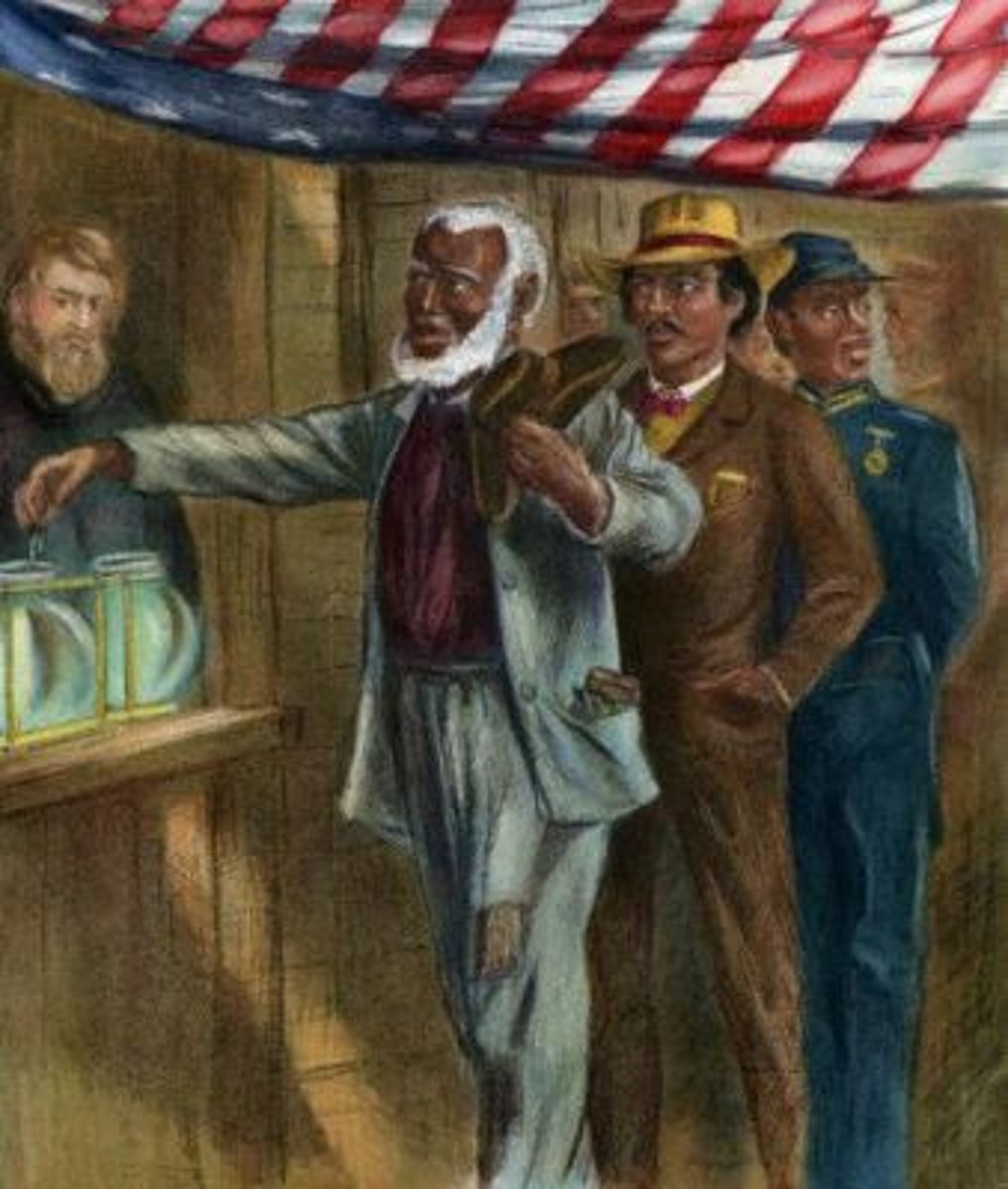
15th Amendment (1870)
Prohibits the denial of voting based on race, color, or previous condition of servitude. Effectively guaranteed black male voting.
-- Congress required the last three unreconstructed states to ratify this and the 14th Amendment.
-- Opposed or criticized by some feminists b/c women should get the vote first: 10M women vs. 1M+ black men.

American Equal Rights Association (AERA)
Founded by male and female abolitionists in 1866, it advocated for suffrage for blacks and women.
-- Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Suzan B. Anthony broke off to form the National Woman Suffrage Association (NWSA) when AERA voted in 1869 to endorse the 15th Amd.
-- Remainder of AERA reformed as the American Woman Suffrage Association (AWSA).

Election of 1868
Grant (R) elected president, defeating Horatio Seymour, Dem. governor of NY.
Army struggled to prevent KKK intimidation in reconstructed states where martial law had been lifted.
Grant depended on black voters in the south to win the electoral college 218-40 (Seymour won majority of white vote nationally).

"Era of Good Stealings"
Post-Civil War period marked by corruption in the railroad industry, stock market, politics, and judicial system.
Civil service reformers tried to end the spoils system/patronage, but didn't pass the Pendleton Civil Service Act until 1883.
Treaty of Washington (1871)
Settled American claims against Britain for building the CSS Alabama and other raiders and set up a tribunal for shipping companies to adjudicate claims.
Some northerners had demanded Britain cede Canada as reparations.
British North American Act (1867)
Parliamentary act joining Canadian provinces into a commonwealth.
-- American demands to annex Canada drove Canadian nationalism, leading to a greater sense of identity and anti-American sentiments.
-- Irish American Fenian Brotherhood - mostly Irish American veterans - tried to raid Canada 1866-1871 to help the Irish independence cause (ineffective).

Santo Domingo affair
Grant's shady personal secretary tried and failed to negotiate a treaty to annex it, but Republicans in the Senate refused to ratify it. Grant, lacking political subtlety, tried to force it through, causing a rift with Republicans.
"Negro Rule" and "Africanization"
Democratic Party talking points during Reconstruction, falsely contending that governments were being taken over by "barbarous Africans". Only 15-20% of public offices were held by black men at the height of Reconstruction, even in places with majority black voters. Democrats also contended that black political power would lead to inter-racial marriage and the disappearance of white skin.
Colfax Massacre (1873)
whites terrorists attacked black officials of a small town in Louisiana; 100 blacks were murdered, half after they surrendered; the few whites who were tried and convicted had their sentences overturned through appeal; this emboldened further violence.
Ku Klux Klan Act (1871)
Empowered president to suspend habeas corpus and send federal troops to suppress political violence.
-- HC only suspended in 9 counties in SC
-- federal marshals and troops arrested thousands of white militia members, indicting 3000, with hundreds pleading guilty to get a lighter sentence. Only 65 of 600 convicted went to prison; most got fines and short jail sentences.

Election of 1872
Grant won reelection against Horace Greeley, whom "Liberal Republicans" had nominated to defeat Grant. Democrats also nominated Greeley.
Greeley said we needed to "clasp hands across the bloody chasm" to end "bayonet rule". Harper's Weekly published Nast cartoons of Greeley shaking the bloody hand of a Klansman who had just killed a black Republican and Greeley as a pirate captain.
-- Grant won every northern state and 10/16 southern & border states.
Panic of 1873 (1873-1879)
A severe international economic depression triggered by the collapse of Jay Cooke's Northern Pacific RR, causing thousands of banks and businesses to fold.
-- 14% unemployment from cutback on industry
-- Led to the *Railroad Strike of 1877

Election of 1874
Democrats took control of House in midterm elections, first time in 18 years.
-- Corruption, northern frustration over southern intransigence, and Democrat takeover of southern states except SC, FL, MS, LA contributed to Republican losses.
-- Dems threatened to cut off funding for army and DOJ related to enforcing "bayonet rule"
Mississippi Plan
Used in the state election of 1875 to block Republican voting, threaten black sharecroppers, and coerce white Republicans. Democrats won the state, with some black majority counties flipping from Republican dominance to just a handful of black votes. Other southern states followed this model.
-- Gov. Ames asked for federal troops, but the Ohio delegation said Reps. would lose Ohio in 1876 if Grant sent them.
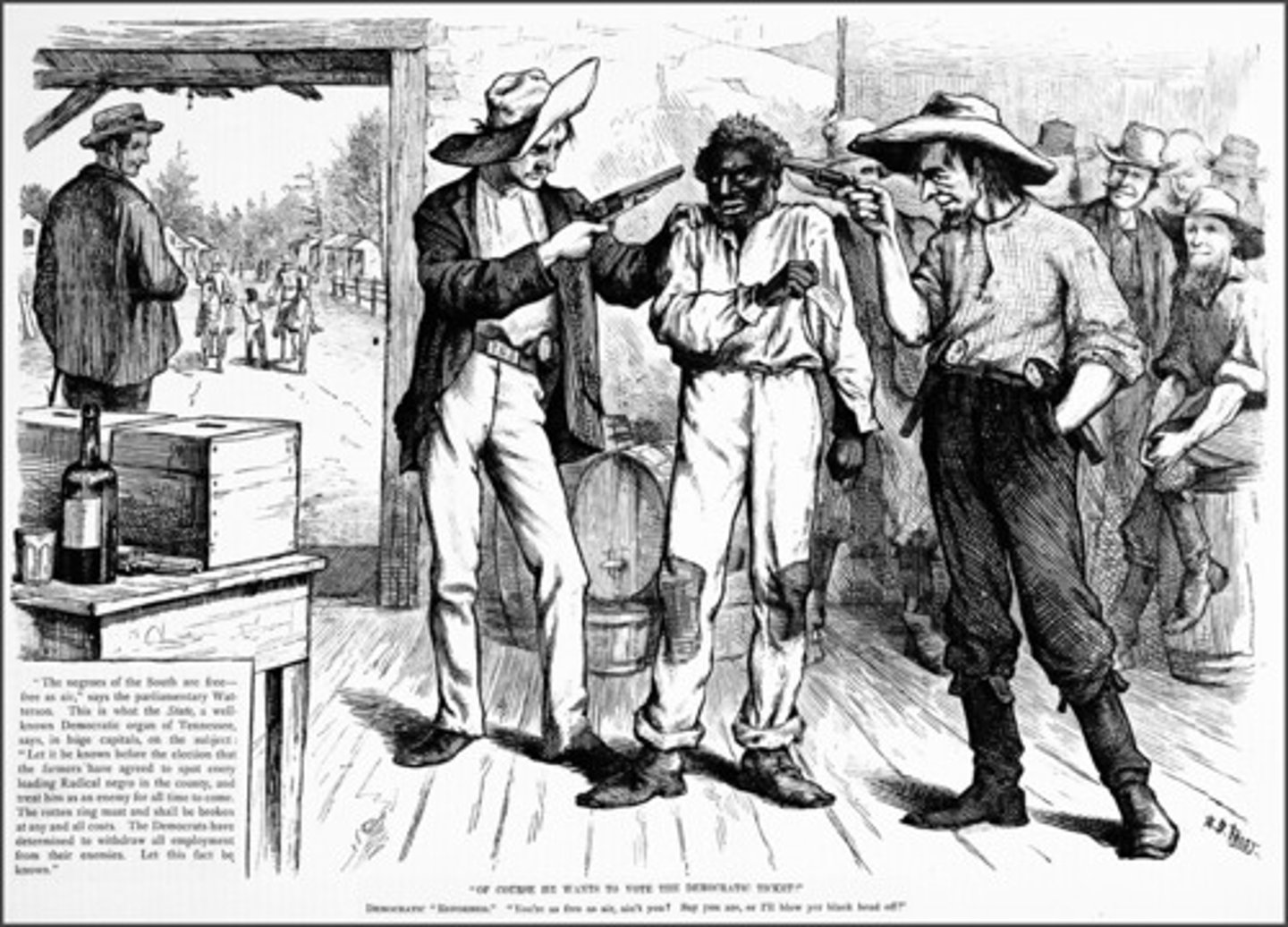

Bulldozing
The use of violence or threat of violence to limit Republican voting in the South during Reconstruction.

"bayonet rule"
Claim made by Democrats and "Liberal Republicans" that the presence of troops in the South was unconstitutional and an abuse of power.
U.S. v. Cruikshank (1876)
The Supreme Court ruled that the 14th Amd. did not apply to individual actions (like the KKK) and that the bill of Rights did not apply to the states. It declared here and in U.S. v. Reese that federal laws punishing individual actions (KKK Act) were unconstitutional.

Civil Rights Cases (1883)
Five cases brought under the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The Supreme Court held discrimination in a variety of public accommodations, including theaters, hotels, and railroads, could not be prohibited b/c no state action.
-- Severan northern states passed civil rights laws.

Election of 1876
Rutherford B. Hayes (R) declared the winner over Samuel Tilden (D) after a bipartisan commission could not come to a conclusion on conflicting electoral college results in SC, OR, LA, FL. Rep. governors sent different results from the Dem. legislatures, because of massive fraud and bulldozing.
-- Republicans and Democrats also elected and seated competing governors and legislatures in several states.
-- Democratic militias threatened a march on Washington.

Compromise of 1877
Compromise that enabled Hayes to take office in return for the end of Reconstruction and
-- a Southern Dem. Postmaster General (for spoils jobs)
-- rebuild MS river levees
-- federal funding for a southern trans-continental RR
