A&P - 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
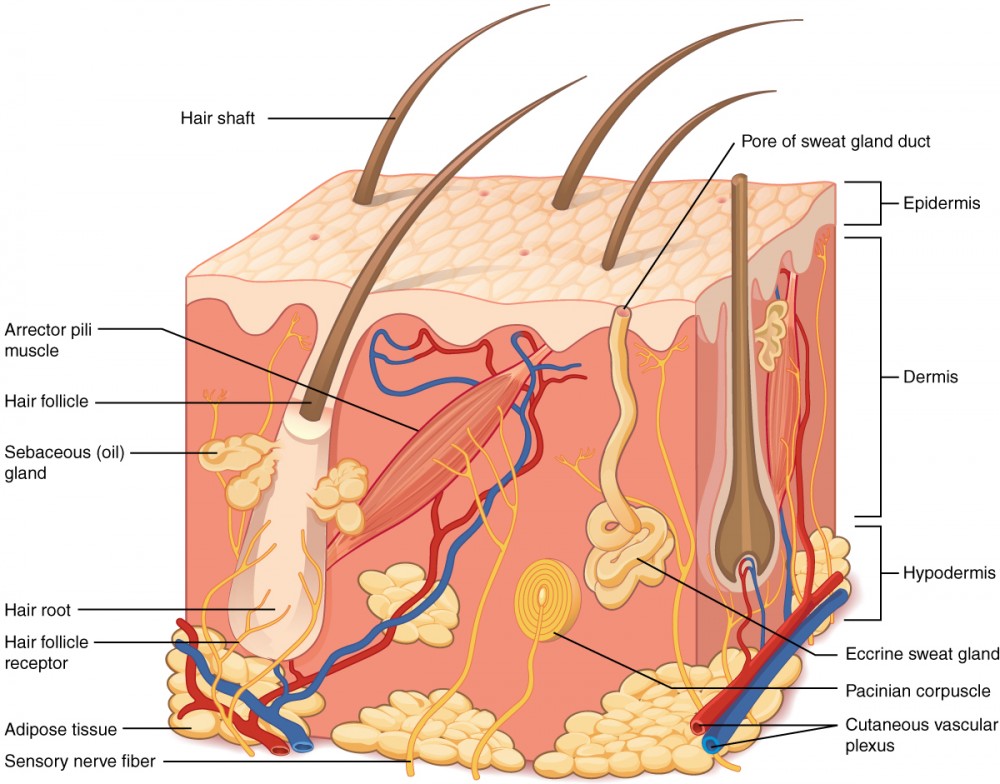
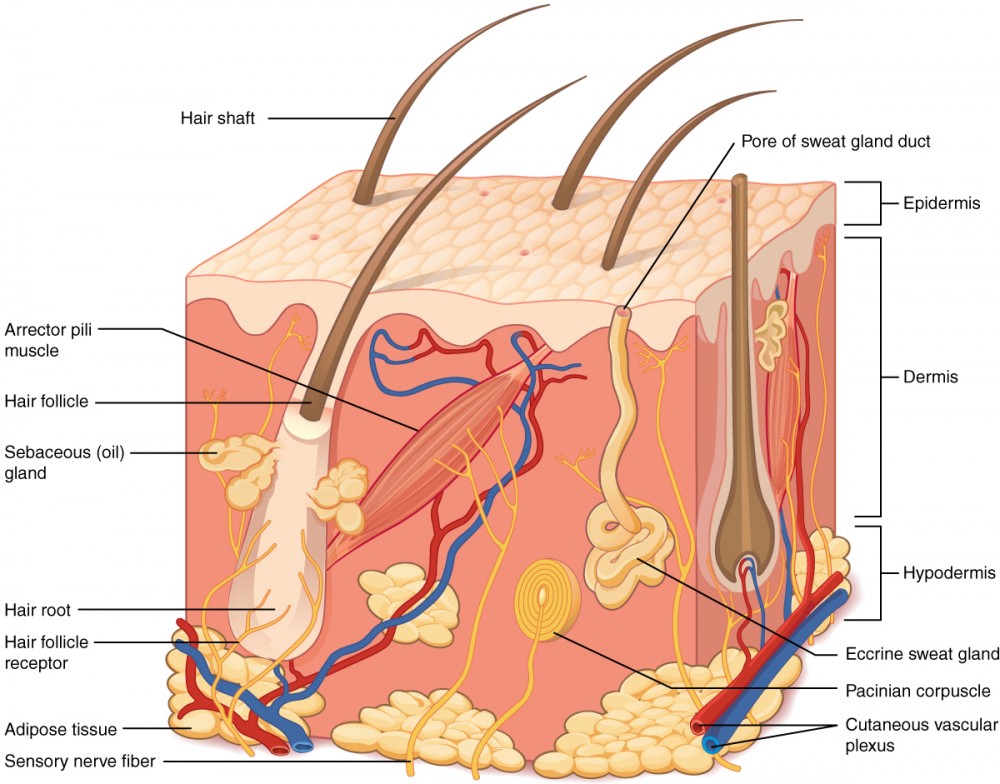
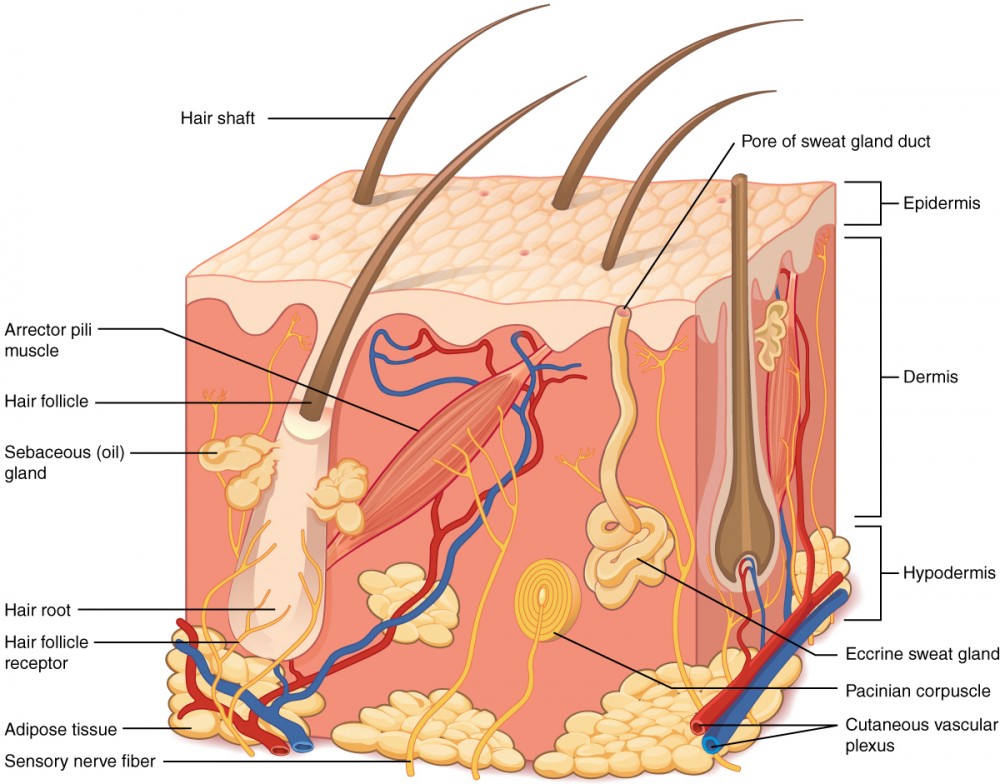
structures of the skin
epidermis
dermis
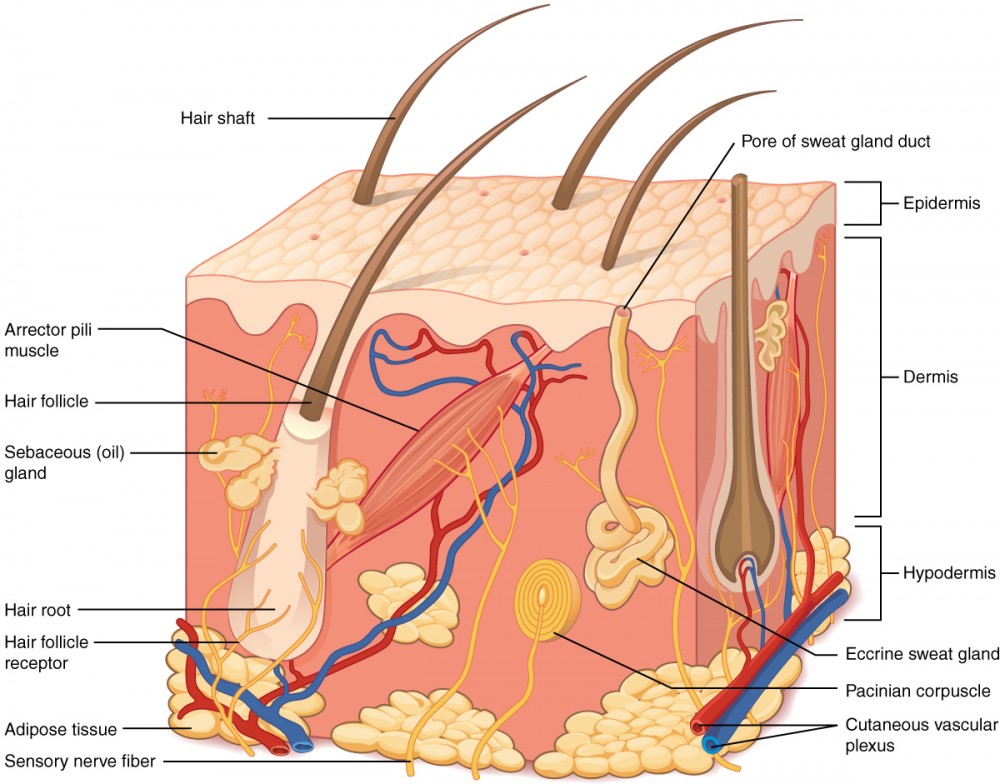
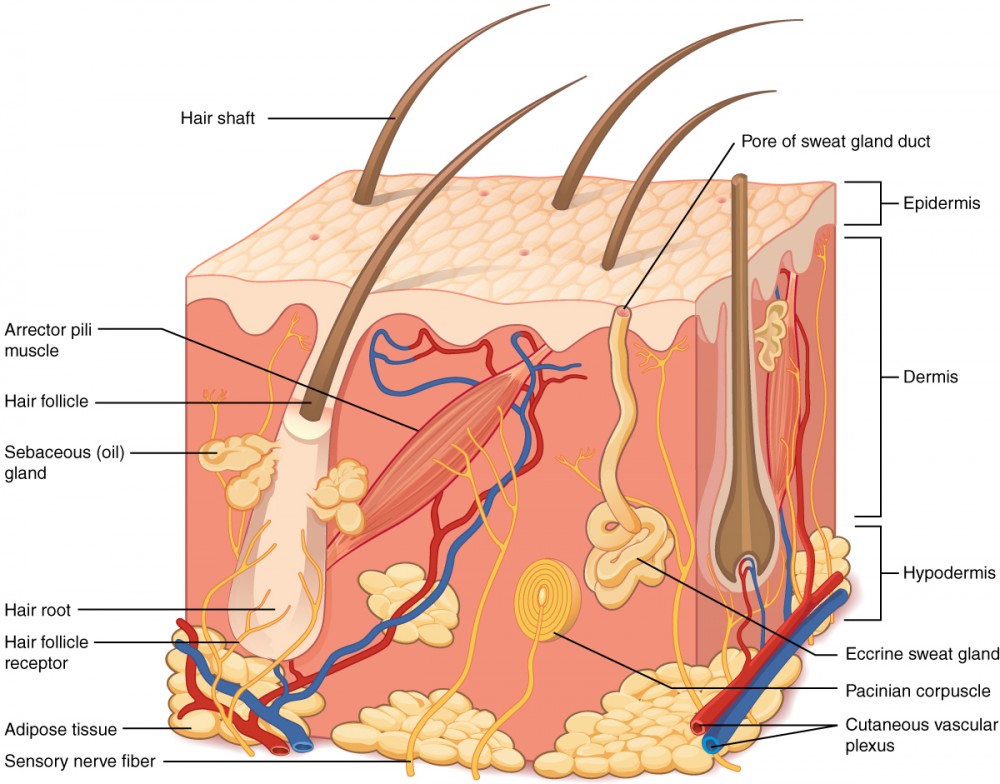
cutaneous vascular plexus
hypodermis
adipose tissue
accessory organs of skin
sensory nerve fiber
pacinian corpuscles
hair follicle
hair root
hair follicle receptor
hair shaft
arrector pili muscle
sebaceous (oil) gland
eccrine sweat gland
pore of sweat gland duct
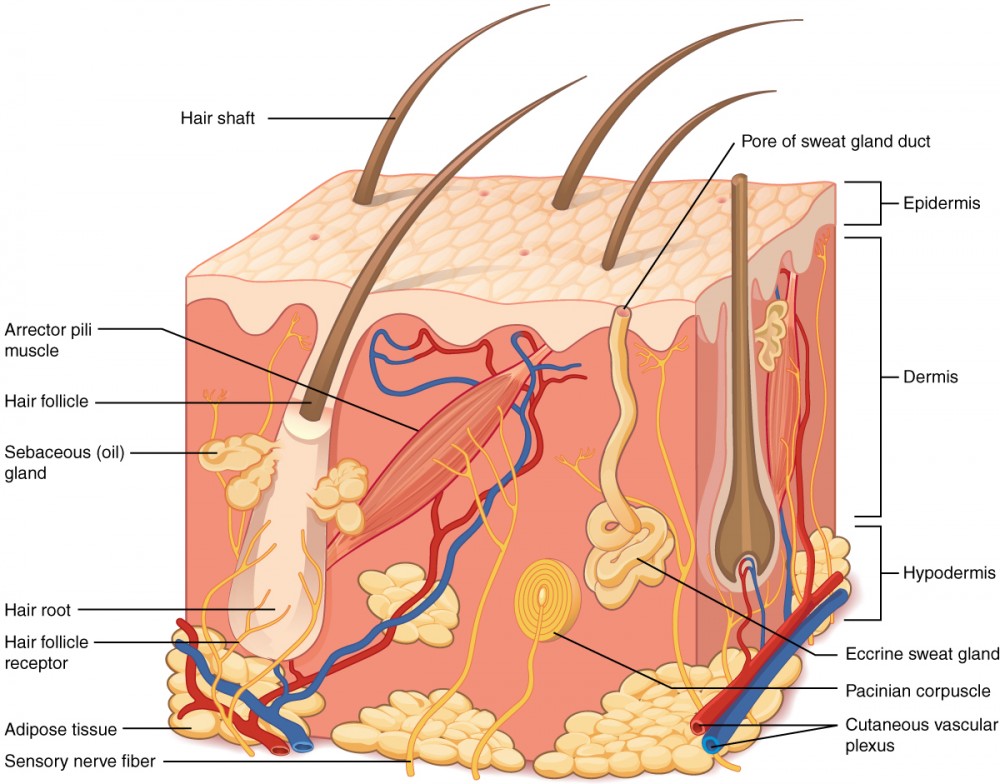
accessory organs of skin
nerve fibers and corpuscles
hair follicles, hair shafts, and arrector pili muscles
glands, arteries, veins, and lymph vessels
nails
cutaneous vascular plexus
network of blood vessels within the skin that nourishes and supports the skin’s layers and structures
hair
keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis
found almost everywhere on the body
except palms of hands, soles of feet, side of fingers, and toes, lips, and parts of external genitalia
body has about 2.5 million hairs
75 percent on general body surface (not on head)
nonliving structures
FUNCTION: sensory input and protection from UV rays
each hair produced by a hair follicle
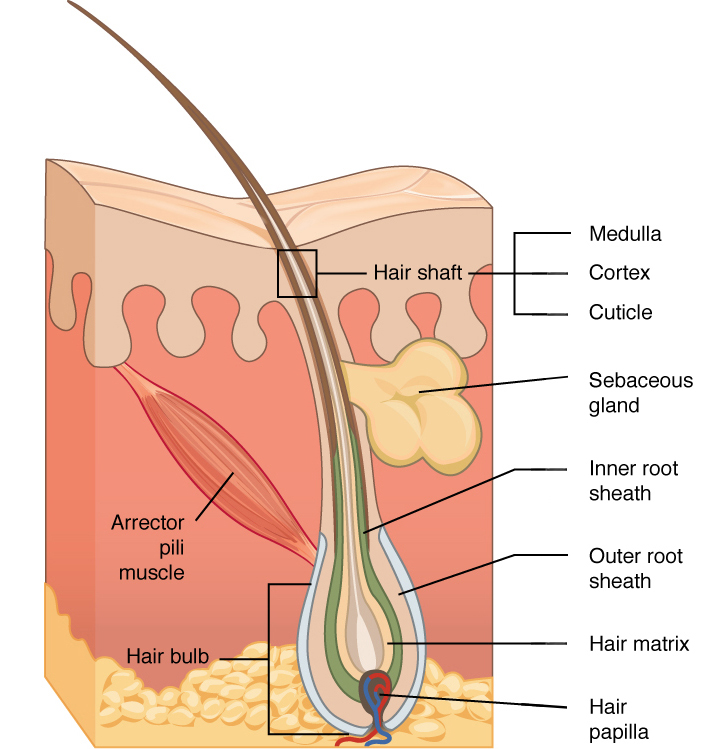
associated structures of hair
hair follicle
hair follicle receptor
hair shaft
hair root
hair follicle
cavity or sac from which hair originates
hair follicle receptor
a sensory nerve ending, called a hair plexus, that wraps around the base of a hair follicle, allowing for the sensation of touch
sensory input; you feel a bug land on you even though its not touching your skin, or you’ll feel a breeze
hair shaft
part of hair that is above the epidermis but is not anchored to the follicle
layers of the hair shaft:
medulla
cortex
cuticle
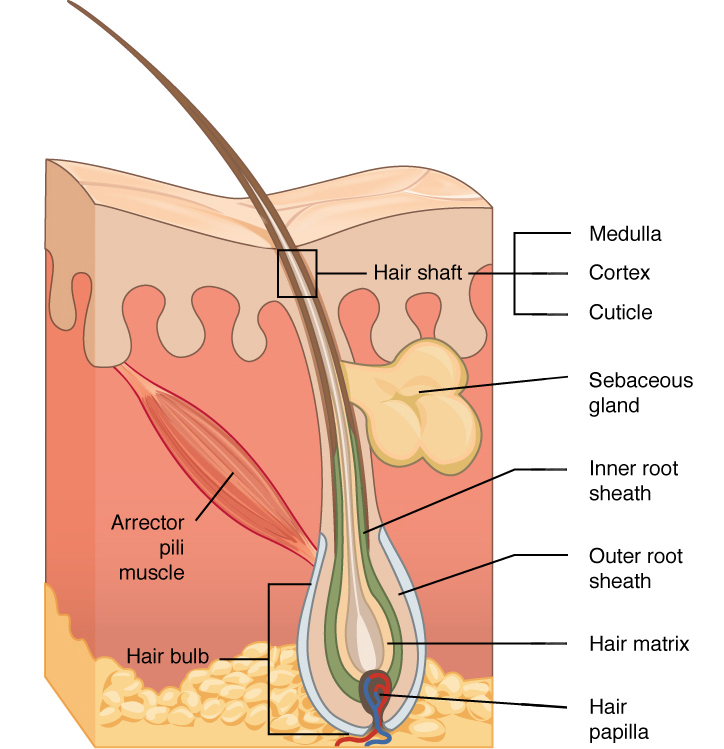
medulla
in hair, the innermost layer of keratinocytes originating from the hair matrix
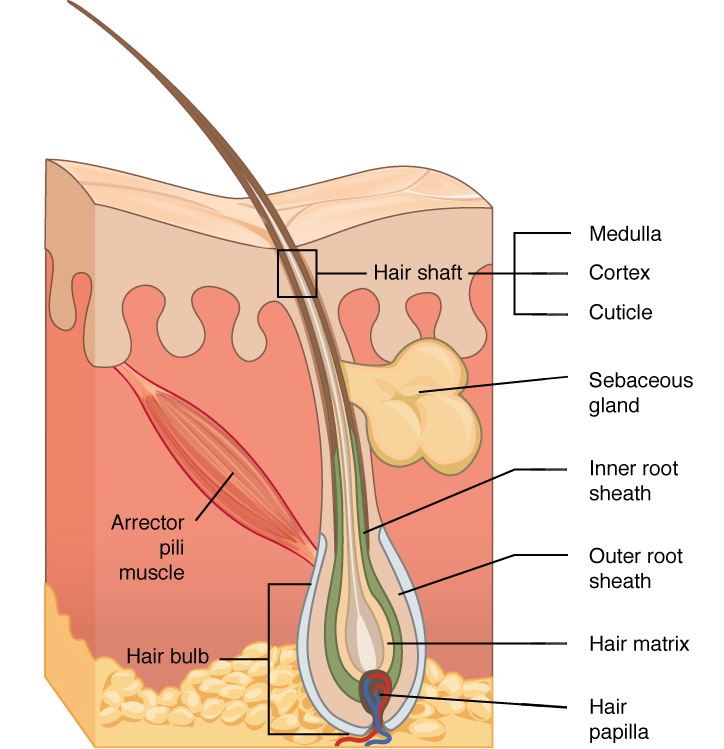
cortex
in hair, the second or middle layer of keratinocytes originating from the hair matrix
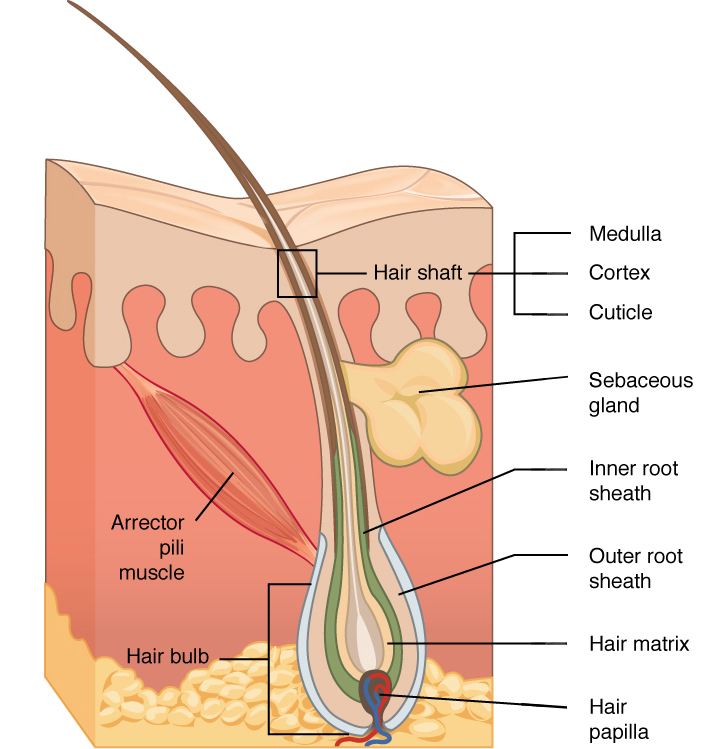
cuticle
in hair, the outermost layer of keratinocytes originating from the hair matrix
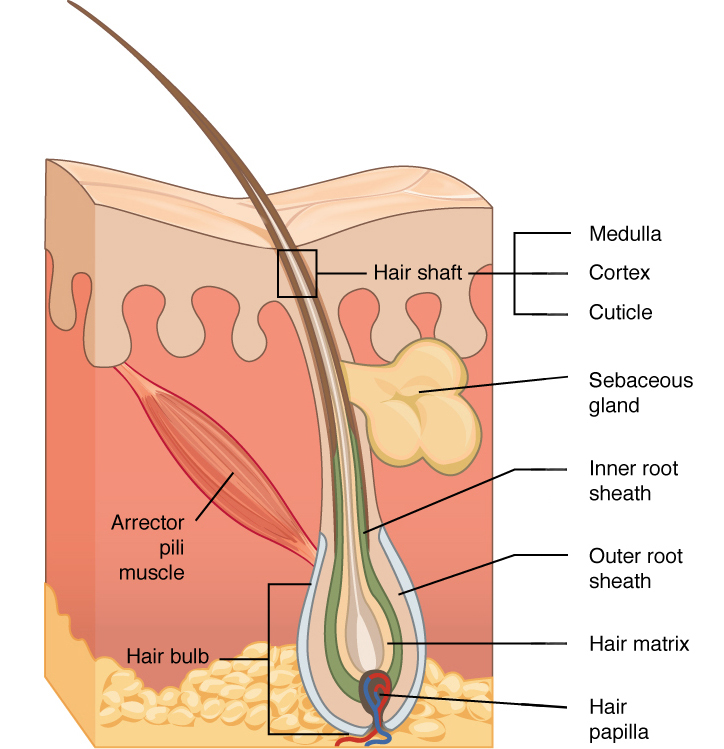
hair root
part of hair that is below the epidermis anchored to the follicle
glassy membrane
layer of connective tissue that surrounds the base of the hair follicle, connecting it to the dermis
types of hair
terminal hairs
vellus hairs
terminal hairs
large, coarse, darkly pigmented
examples: hairs found on scalp or in armpit
vellus hairs
smaller, shorter, delicate
found on general body surface
arrector pili muscle
smooth muscle that is activated in response to external stimuli that pull on hair follicles and make the hair “stand up”
accessory glands
skin has 5 types of glands:
merocrine sweat glands
apocrine sweat glands
sebaceous glands
ceruminous glands
mammary glands
pore of sweat gland duct
small opening on the surface of the skin where sweat, produced by the sweat gland, is released
sudoriferous glands
sweat glands:
eccrine (merocrine)
apocrine
eccrine (merocrine) sweat gland
hypotonic sweat
thermoregulation
all over skins surface
water, salt, antibodies, metabolic waste, dermicidin
apocrine sweat gland
hair follicles in axillary and genital regions
water, salts, organic compounds
waxy sweat
sebaceous gland
oil gland found in the dermis
sebum (oil on skin)
lubrication of skin and hair
antibacterial properties (sweat and oil are antimicrobial)
water retention
keeps skin and hair from becoming dry, brittle, and cracked
lanolin - sheep sebum
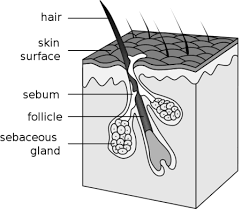
sebum
oily substance that is secreted from sebaceous glands that is composed of a mixture of lipids that lubricates the skin and hair
ceruminous glands
simple, coiled, tubular glands in external ear canal
this secretion combines with sebum and dead epithelial cells to form earwax (cerumen)
keeps eardrum pliable
waterproofs the canal
kills bacteria
makes guard hairs of ear sticky to help block foreign particles from entering auditory canal
mammary glands
milk-producing glands located in the breasts
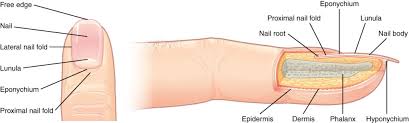
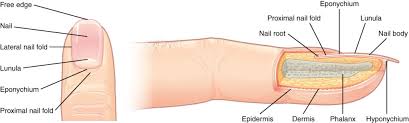
nails
form from thickened epidermal cells nestled into the dermis forming a nail field
FUNCTION: protection and back-support for picking up small objects
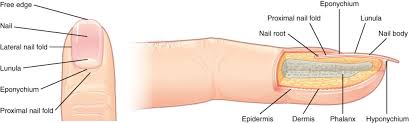
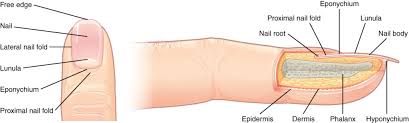
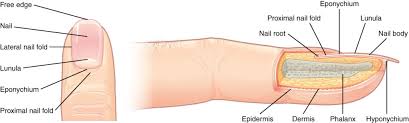
accessory structures of the nails
free edge
nail
lateral nail fold
lunula
eponychium
proximal nail fold
free edge
the hard, white part of the nail that extends beyond the fingertip
nail body (nail)
main keratinous plate that forms the nail
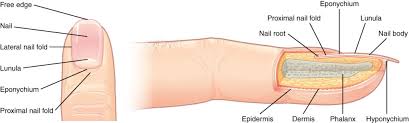
nail fold
fold of the epithelium that extends over the sides of the nail body, holding it in place
lateral nail fold overlaps the nail of the sides, helping to anchor the nail body
proximal nail fold at the end of the nail body form the nail cuticle
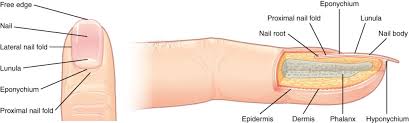
lunula
basal part of the nail body that consists of a crescent-shaped layer of thick epithelium
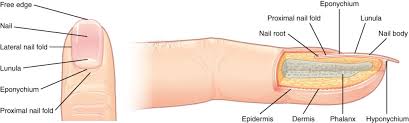
eponychium
nail fold that meets the proximal end of the nail body, also called the cuticle
nail bed
layer of epidermis upon which the nail body forms
nail root
part of the nail that is lodged deep in the epidermis from which the nail grows
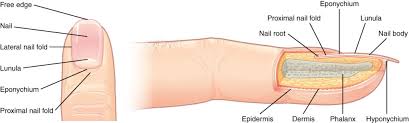
hyponychium
thickened layer of stratum corneum that lies below the free edge of the nail