Week 13: Pharmacotherapy (St. Peter)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
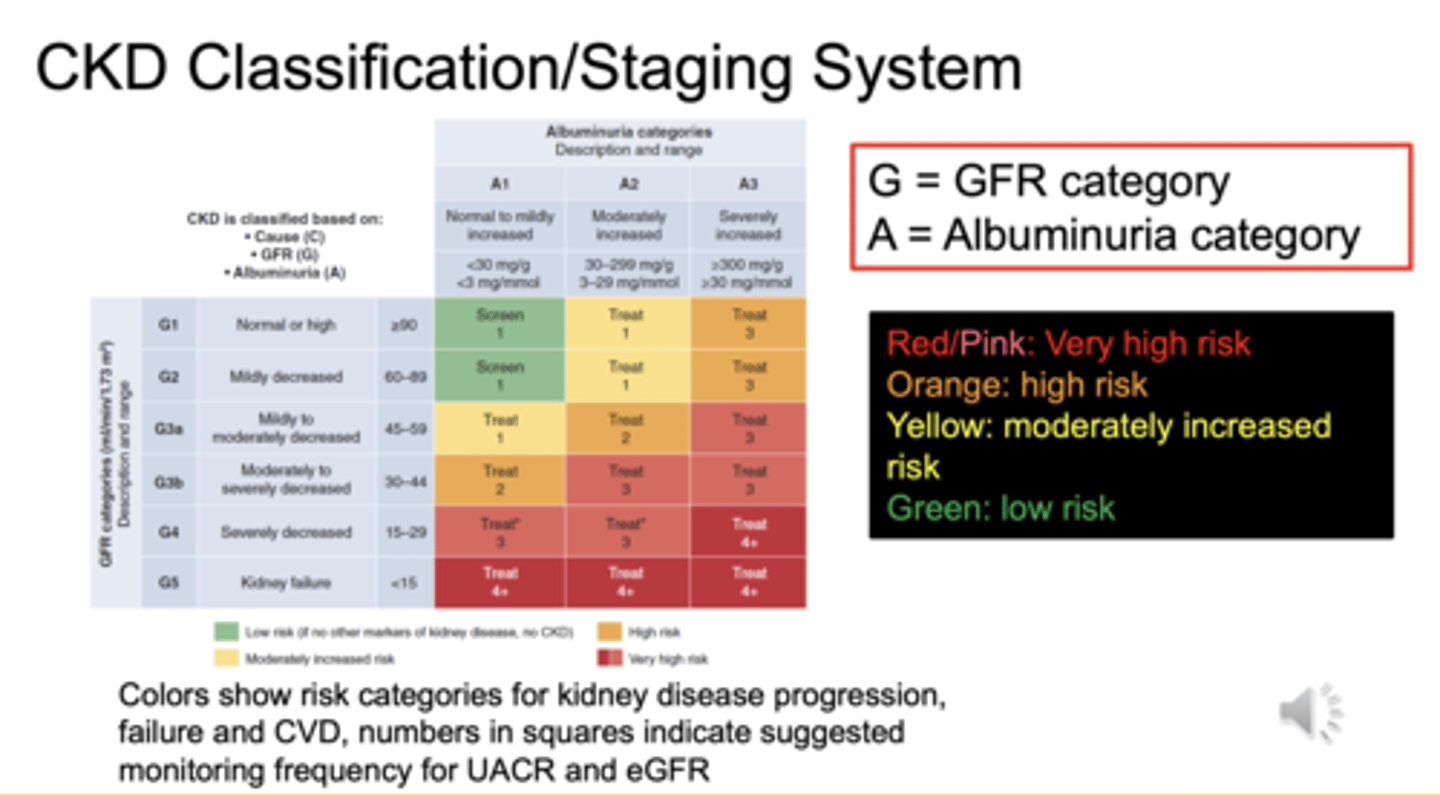
What parameters determine CKD stage and risk category in the KDIGO heat map?
GFR category (G) and albuminuria category (A) determine CKD stage and risk category
What does each color represent in the KDIGO CKD staging heat map?
Green = low risk
Yellow = moderately increased risk
Orange = high risk
Red/Pink = very high risk
What does albuminuria >30 mg/g indicate?
it indicates glomerular damage and increased risk of CKD progression and cardiovascular disease (CVD)
How is CKD linked to the Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome?
progression contributes to higher CKM stages due to increased metabolic dysfunction, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk
What CKM stage is defined by central obesity and impaired glucose tolerance?
Stage 1 is characterized by obesity, dysfunctional adiposity, and metabolic changes like impaired glucose tolerance
How can CKD alone place someone in Stage 2 CKM?
moderate to high CKD risk (yellow/orange on heat map) automatically places a patient in CKM Stage 2, even without metabolic conditions
What CKM stage includes subclinical cardiovascular disease?
CKM Stage 3
- involves asymptomatic cardiovascular changes, such as arterial plaque or left ventricular hypertrophy
What CKD risk category automatically places someone in CKM Stage 3?
very high CKD risk (pink/red on heat map) automatically represents Stage 3 CKM
What defines CKM Stage 4?
includes symptomatic cardiovascular disease such as heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stroke, or myocardial infarction
What are two common causes of albuminuria?
hypertension and diabetes
Why does CKD progression sometimes continue after primary disease is treated?
because remaining nephrons undergo hyperfiltration stress, causing ongoing damage
Which groups have higher risk of kidney failure?
African Americans, Hispanics, American Indians, Pacific Islanders, and Asians
Does normal age-related kidney decline count as CKD progression?
No, it is considered a normal aging process, not CKD progression
What are implications of African American race on CKD outcomes?
higher rates of hypertension, earlier diabetes onset, 3.4x higher risk of ESKD
What are patient engagement strategies sensitive to cultural/race factors?
build trust, avoid assumptions, assess barriers, health literacy, and medication beliefs
What are 3 classes of drugs proven to reduce CKD progression?
ACEI/ARBs, SGLT2 inhibitors, and non-steroidal MRAs (e.g., finerenone)
Do SGLT2 inhibitors reduce CKD progression independently of glucose lowering?
Yes, effects on CKD and CVD protection are independent of blood glucose reduction
What therapy reduces intraglomerular pressure and albuminuria?
ACEi and ARBs
Which agents reduce CKD risk via inflammation reduction?
SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and non-steroidal MRAs
Which blood pressure condition is both a cause and complication of CKD?
hypertension
What BP goal does KDIGO 2021 recommend for CKD patients?
SBP <120 mmHg using standardized office BP measurement
What major study led to the <120 SBP recommendation?
SPRINT trial
What were 2 limitations of SPRINT trial generalizability?
excluded diabetes, few advanced CKD (G4/G5) or elderly patients
What BP goal is used by ADA and ACC/AHA when standardized measurement is not used?
<130/80 mmHg.
Why is standardized BP measurement lower than routine measurement?
it is properly timed, repeated, and controlled, often reading 10-12 mmHg lower
When might SBP <120 not be appropriate?
advanced CKD (G4/G5), dialysis, elderly, or when poorly tolerated
What four conditions represent the CKD risk continuum?
obesity → prediabetes → type 2 diabetes → hypertension
What calculator determines CVD risk in CKD patients without CVD?
PREVENT online risk calculator

According to KDIGO, when are ACE inhibitors and ARBs preferred in CKD?
preferred when UACR is >30 mg/g in CKD patients, with or without hypertension
Why should ACEi and ARBs not be combined with each other or with direct renin inhibitors?
combination increases risk of acute kidney injury (AKI) and significantly lowers GFR compared to monotherapy
Why are ≥3 blood pressure medications often needed in CKD patients?
CKD causes sodium and fluid retention and often requires multiple agents to reach BP targets
What other medication classes are commonly added for BP and CVD risk control in CKD?
diuretics, dihydropyridine CCBs (DHP-CCBs), and beta-blockers (for compelling indications).
What is angiotensin II's predominant effect on kidney arterioles?
vasoconstricts the efferent arteriole, increasing glomerular pressure
How do ACE inhibitors and ARBs protect the glomerulus?
they block angiotensin II, causing efferent arteriole dilation, lowering glomerular pressure and reducing albuminuria
What is the significance of a short-term drop in GFR after starting ACEi/ARB?
it reflects reduced intraglomerular pressure and is expected and beneficial long-term, unless >30% rise in serum creatinine
What is the primary kidney-protective mechanism of ACEi/ARB?
reduction of glomerular pressure, independent of BP-lowering effects
Should ACEi/ARBs be used in African American patients with CKD?
Yes, ACEi/ARBs reduce CKD progression in Black patients, proven by the AASK trial
What did the AASK trial show comparing amlodipine vs ramipril?
Ramipril slowed CKD progression better than amlodipine, even in Black patients
Why are DHP-CCBs less effective than ACEi/ARBs in slowing CKD progression?
they dilate the afferent arteriole, increasing glomerular pressure and albuminuria
When are DHP-CCBs useful in CKD?
only for BP control, not for kidney protection
What are 4 major safety concerns with ACE inhibitors?
hyperkalemia, AKI, cough, and angioedema
What are the ARB safety concerns?
hyperkalemia, AKI, angioedema (but no cough)
Which population has increased risk for ACEi-associated angioedema?
African Americans (4.5× higher risk)
Which population has an increased risk of ACEi cough?
Asians (ACE inhibitors often avoided due to higher cough risk)
Should ACEi/ARB be stopped if hyperkalemia occurs?
No, try diet changes, diuretics, or potassium binders first. Only stop as last resort
What labs should be checked before starting an ACEi/ARB?
baseline serum creatinine, potassium, and blood pressure
When should serum creatinine and potassium be rechecked after starting or increasing ACEi/ARB?
within 2 weeks
hat should be done if serum creatinine rises >30% from baseline?
Reduce dose or stop ACEi/ARB if already at lowest dose
- investigate dehydration, NSAIDs, or diuretics
What is the starting dose and max dose for lisinopril in CKD?
Starting: 5 mg/day
Max: 40 mg/day
What is the starting and max dose for losartan?
Starting: 25 mg/day
Max: 100 mg/day
What is the starting and max dose for telmisartan?
Starting: 20mg/day
Max: 80mg/day
Which ARB has the longest half-life and full 24-hour coverage?
Telmisartan (Micardis)
Why are diuretics commonly used in CKD?
to reduce fluid overload and hyperkalemia risk
Which thiazide-like diuretic is effective even in Stage 4 CKD (GFR 15-30)?
chlorthalidone (CLICK Trial)
What dose of chlorthalidone produced most BP-lowering effects in CKD Stage 4?
12.5 mg/day (lowest dose)
What happens when chlorthalidone is added to a loop diuretic?
high risk of volume depletion, electrolyte loss, and ↑ serum creatinine
*** reduce loop dose first
When should ACEi/ARB be started in the CKD algorithm?
first-line, started alone, titrated slowly every 4 weeks
Why should diuretics not be started at the same time as ACEi/ARBs?
to avoid excessive drop in GFR and difficulty identifying cause of renal function change
At what GFR can thiazides be used?
GFR ≥15 mL/min (Stage 4 or higher)
When should loop diuretics be used instead of thiazides?
GFR <30 mL/min with fluid overload
After ACEi/ARB and diuretics, what is the next BP agent added?
DHP CCBs
What potassium level generally indicates hyperkalemia requiring intervention?
>5.0 mEq/L
What strategies can manage ACEi/ARB-induced hyperkalemia without stopping the drug?
lower dietary K, adjust diuretics, start potassium binders
What are the three major medication classes that reduce CKD progression and CVD risk?
SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and non-steroidal MRAs (finerenone)
What is the leading cause of death in CKD patients?
cardiovascular disease (more likely to die of CVD than reach dialysis)
At what eGFR is metformin contraindicated?
eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m².
What metformin dose is recommended at eGFR 45-59?
1000-1500 mg/day if at high risk for lactic acidosis
What metformin dose is recommended at eGFR 30-44?
Max 1000 mg/day
What lab should be monitored annually in chronic metformin users?
vitamin B12 (risk of deficiency)
What CKM stage includes CKD plus established CVD or high metabolic risk?
CKM Stage 3-4
What are the five pathophysiological drivers of diabetic kidney disease?
hyperglycemia, hyperfiltration, intraglomerular hypertension, inflammation, fibrosis
What happens first in uncontrolled diabetes albuminuria or low GFR?
microalbuminuria appears first; GFR drop occurs later
What is the usual A1c goal for most CKD patients with diabetes?
7%; individualized
When is a less stringent A1c goal (7.5-8%) appropriate?
advanced CKD, frailty, limited life expectancy, high hypoglycemia risk
Where do SGLT2 inhibitors act in the kidney?
proximal tubule; block glucose and sodium reabsorption
How do SGLT2 inhibitors protect kidneys mechanistically?
restore tubuloglomerular feedback → afferent arteriole constriction → ↓ intraglomerular pressure
What are FOUR major clinical benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors?
↓ CKD progression (~30-40%), ↓ HF hospitalization (~30%), ↓ CV death, ↓ MACE
What is the key initial lab effect after starting SGLT2 inhibitors?
temporary eGFR dip of up to 30%; not harmful
What are 3 SGLT2 inhibitor adverse effects?
genital mycotic infections, euglycemic DKA, volume depletion/hypotension
What are 3 "Sick Day Rule" situations where SGLT2 inhibitors should be held
surgery, severe dehydration/vomiting, prolonged fasting, acute illness
What risk increases dramatically when SGLT2i is started in hypovolemia?
AKI and hypotension
Should SGLT2 inhibitors be started while a patient is hypovolemic?
No, correct volume first (risk of AKI and hypotension)
Why should SGLT2i and diuretics not be initiated or up-titrated together?
high risk of volume depletion, hypotension, and AKI
What does weight trending down after starting SGLT2i indicate when patient is on diuretics?
patient may be over-diuresed; reduce or stop diuretic
If a patient is euvolemic and normotensive, what is the action when starting SGLT2i?
continue thiazide diuretics
- if on loop diuretics, reduce dose by 50% and monitor BP and weight
- if stable → continue. If decreasing → stop diuretic
What is recommended if patient is hypertensive when initiating SGLT2i while on diuretics?
continue diuretic therapy and monitor BP, electrolytes, sCr, and weight
How do ACEi/ARBs and SGLT2i complement each other hemodynamically?
ACEi/ARBs: dilate efferent arteriole
SGLT2i: constrict afferent arteriole → Combined ↓ glomerular pressure.
Why should ACEi/ARB and SGLT2i not be initiated at same time as diuretics?
all three lower GFR through pressure reduction → higher risk of AKI
What are two major CV benefits of GLP-1 RAs?
↓ MACE (CV death, MI, stroke) and ↓ albuminuria progression
For what patient type are GLP-1 RAs especially valuable?
CKD + diabetes + obesity or ASCVD risk
In CKM Stage 2 with diabetes, when are GLP-1 RA-based agents preferred over SGLT2 inhibitors?
- BMI ≥35 → use a GLP-1 RA for weight loss
- HbA1c ≥9% or high insulin dose → use GLP-1 RA
- CKD with albuminuria → prioritize SGLT2 inhibitor
- Always keep ACEi/ARB when albuminuria ≥30 mg/g
What defines CKM Stage 3 vs Stage 4?
Stage 3: no symptoms of CVD, but subclinical atherosclerosis or early HF (EF<40)
Stage 4: symptomatic CVD (HF, CKD, obesity complications, HTN, high triglycerides)
What are treatment recommendations for Stage 3 CKM with subclinical atherosclerosis?
statins, PCSK9 inhibitors, ASA, GLP-1 RA
What are treatment recommendations for Stage 3 CKM with heart failure?
SGLT2 inhibitors, ACEi/ARB, β-blockers
What medications are preferred in CKM Stage 4 with symptomatic CVD and obesity?
For HF: ARNI preferred for HFrEF
For obesity: Implement step 1 weight-loss strategies
For CKD: Continue ACEi/ARB, SGLT2i, GLP-1 RA
What makes finerenone different from spironolactone?
it selectively blocks MRA without hormone side effects, reduces inflammation and fibrosis, and causes less hyperkalemia
In which patients is finerenone indicated?
CKD with T2D and albuminuria despite ACEi/ARB therapy
What key labs should be monitored after starting SGLT2i or finerenone?
sCr, eGFR, and K+