13. activation of naive t lymphocytes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
where does T-cell activation occur?
localized infection → draining/local lymph node
systemic infection → spleen (+ lymph nodes)
how is dendritic cell migration directed to the paracortex?
chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 (produced in the paracortex)
CCR7
receptor for chemokines (CCL19 & CCL21) expressed by activated dendritic cells
what 3 things are required for initiation of T-cell responses?
specific antigen recognition
stable adhesion of T cells to APCs
transduction of activation signals
what is the two signal model of naive T-cell activation?
activation of naive T cells requires simultaneous delivery of antigen specific and costimulatory signals
accessory molecules
T cell surface receptors that are not involved in antigen recognition
signal transduction
adhesion
note: T-cell receptor (TCR) is not capable of signal transduction
T-cell co-receptors
CD4/CD8
function with T-cell receptors (TCR) in antigen recognition and signal transduction
what provides the initiating or first signal for T-cell activation?
TCR and CD4/CD8 co-receptor together recognizing peptide-MHC complexes on APCs
what makes up the TCR (T-cell receptor) complex?
TCR, CD3, and ζ (zeta chain)
what is the function of CD3 & ζ (zeta chain)?
signal transduction
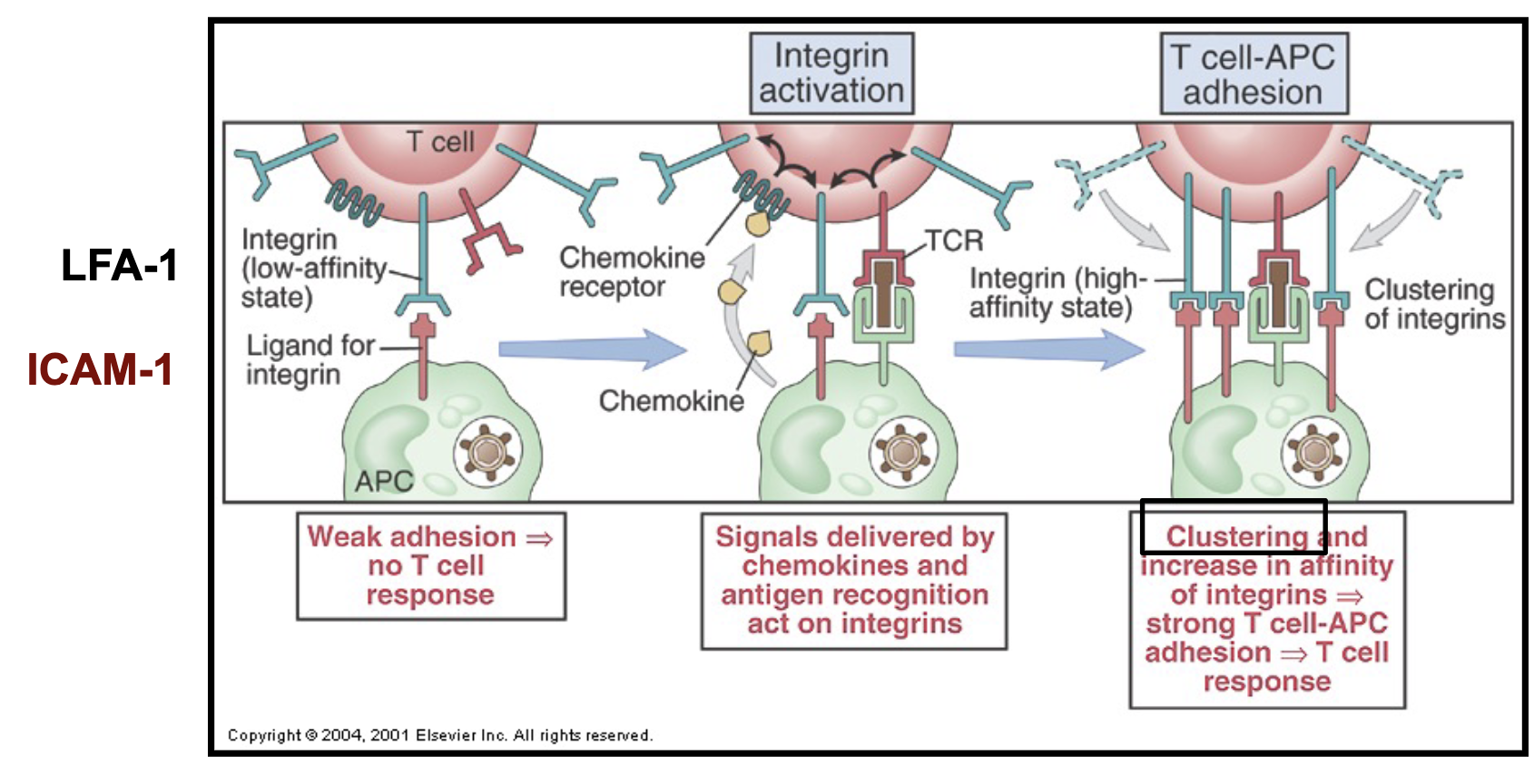
how are integrins involved in T cell activation?
expressed on T cells
mediate stable/strong adhesion between T cells and APCs
switch from low-affinity state to high-affinity state when antigen recognition occurs between APCs and T cells + clustering
how is the co-stimulatory signal produced?
CD28 (on T cells) binds to co-stimulatory B7 molecules expressed on professional APCs
mature DCs initiate activation of naive T cells
activation of APCs by microbes/innate immune response increases expression of costimulators
what happens if there is no co-stimulation signal?
the T cell either has no response or becomes tolerant (self-antigens)
“resting” (co-stimulator deficient) APCs:
presenting self-antigen
immature (not activated)
no inflammation/infection
→ T cell responds to microbial antigens but not self antigens
how does co-stimulation affect T-cells?
necessary for production & secretion of IL2 → autocrine signaling
T cells start expressing high affinity IL2-R (receptor)
(at rest, express low affinity IL2-R)
what is IL2?
a growth factor/cytokine that drives T cell proliferation
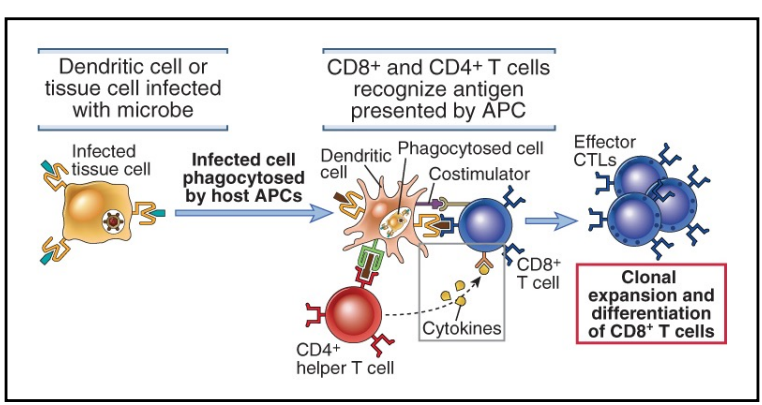
CD4 T-cell independent activation of CD8 T-cells
microbes infect dendritic cells
CD4 T-cell dependent activation of CD8 T-cells
microbes do not infect dendritic cells (ex. viral infection, tumor cells)
cross-presentation → one DC can present to both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
activated CD4+ T cell produces cytokines that act on CD8+ T cells
how do certain adjuvants enhance immunogenicity of antigens?
use innate immunity (PRR signaling and inflammation) to activate APCs → express costimulatory molecules (B7)
what are the T cell co-inhibitory receptors?
CTLA-4
PD-1
when are the inhibitory receptors expressed?
when T cells become activated → function to inhibit activation (brakes)
how does CTLA-4 inhibit activation?
interacts with B7 molecules on APCs
has a higher affinity for B molecules → outcompetes CD28 (activator)
what does PD-1 interact with?
PD-L1/2 on APCs (→ inhibitory signal)
how are co-inhibitory receptors relevant to cancer treatment/treatment of persistent infections?
drugs can have anti PD-1 / anti CTLA-4 effects
remove T cell inhibition → allow T cell to kill tumor cell
controlled autoimmunity
how do superantigens interact with T cells?
cause uncontrolled, nonspecific activation of T cells
↑↑ T cell activation → lethal shock