Lecture 41 - Liposomes and Microparticulate Systems
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
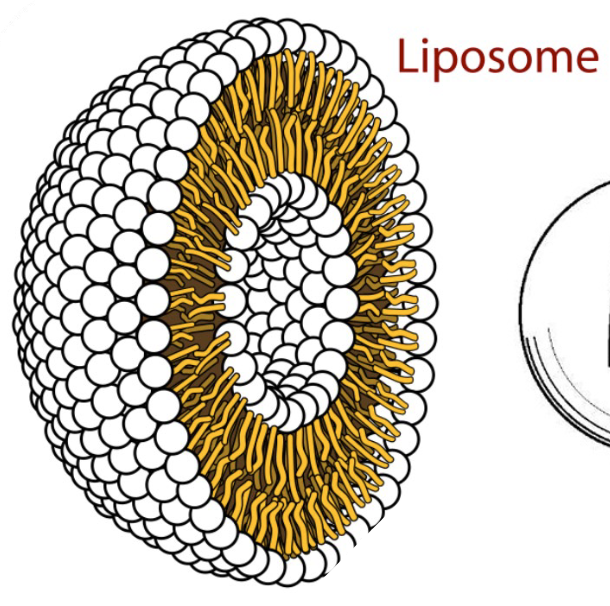
Liposomes?
A spherical vesicle containing one or more lipid bilayers enclosing liquid filled compartments
What is the difference between micelles and liposomes?
The principles of formation are exactly the same
The only difference is liposomes form when the surfactant has two HC chains, while micelles form when the surfactant has one HC chain
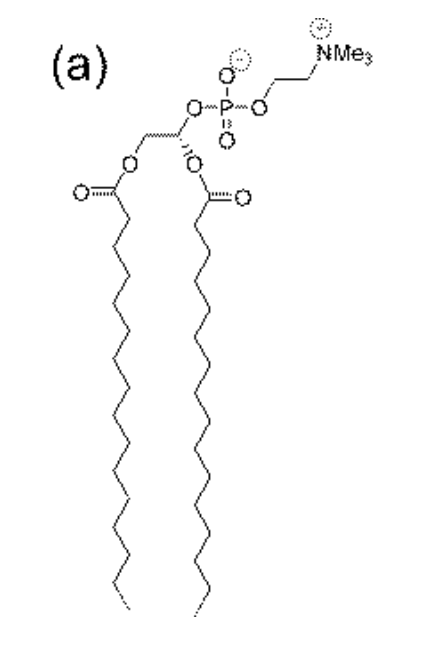
What is DPPC?
An example of a two tailed HC surfactant phospholipid used to make liposomes
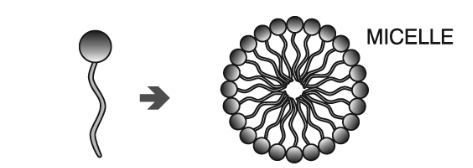
How does a single chain surfactant affect the shape?
The polar head group is equal or larger than the HC chain
This allows it to pack efficiently and form stable micelles
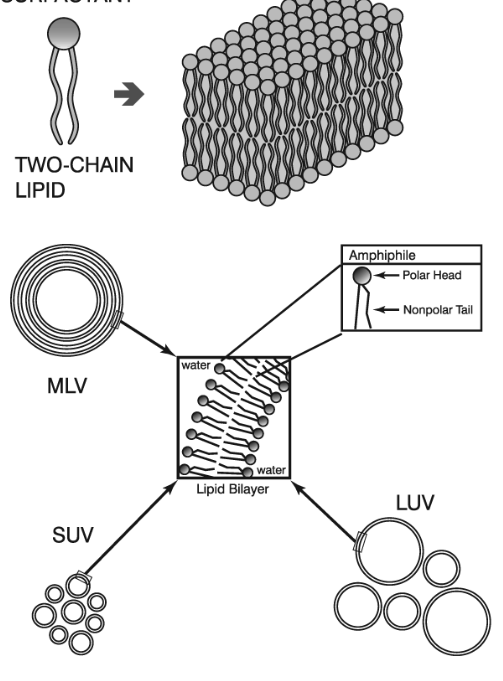
Why do liposomes form?
Because the double HC chains cannot form a micelle → if they did it would allow too much water access
Instead create the lipid bilayers with aqueous core
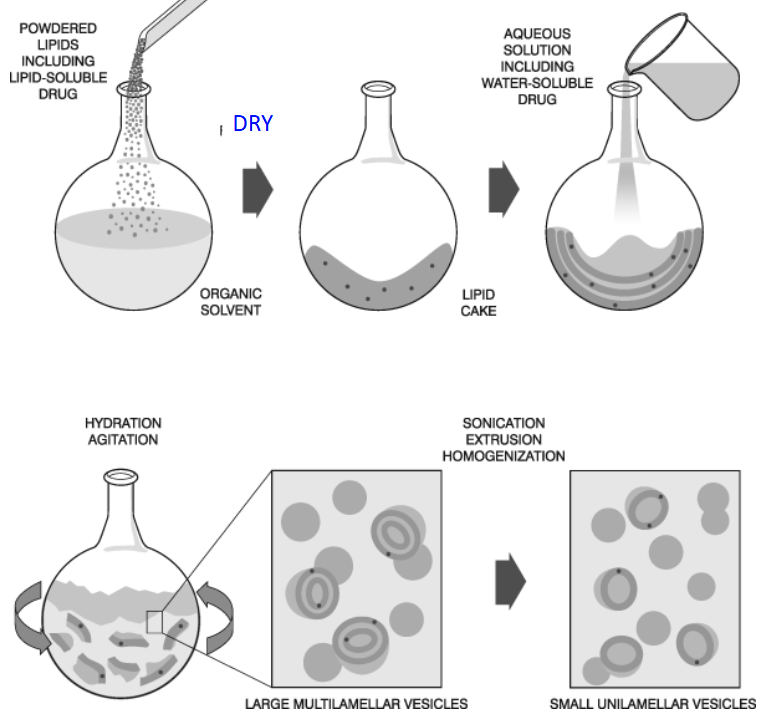
How are liposomes formed in the lab?
Dissolve lipids in a solvent
Remove solvent to form a thin, dry lipid film.
Hydrate the lipid film with aqueous solution to form lipid cake
Size and homogenize vesicles using sonication or extrusion
Sonication/extrusion turns the large multilamellar vesicles into small unilamellar vesicles
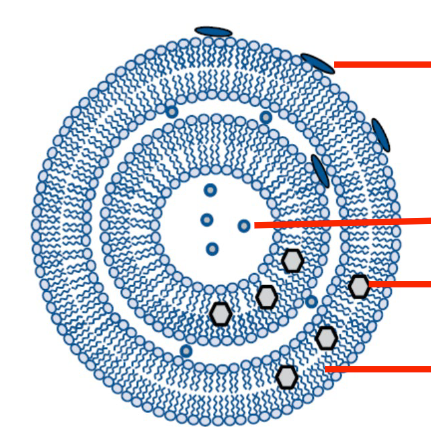
How can drug be incorporated into a liposome?
One the surface
In the aqueous core
Solubilized in the lipid bilayer
In the phospholipid

What is the size of multilamellar vesicle?
MLV
1-5 um
Aqueous fluid volume → 0.5ul/mg of lipid

What is the size of small unilamellar vesicle?
SUV
20-100 nm
Aqueous fluid volume → 4 ul/mg of lipid

What is the size of large unilamellar vesicle?
LUV
100-250 nm
Aqueous fluid volume → 11 ul/mg of lipid
Smallest to larges size liposomes?
MLV < SUV < LUV
What is passive targeting in liposomes?
The liposomes get into the blood stream via IV
Once there they interact and get coated by blood opsonins, marking them for removal by mononuclear phagocytic system
These opsonin coated liposomes accumulate in the MPS and in the liver/spleen
once in the MPS/liver/spleen they get degraded thus releasing drug
What does uptake by MPS allow?
It allows the oponsin coated liposomes to be used for passive targeting of drugs to organs like the liver/spleen
transport of the administered drug to a specific site of action via normal distribution patterns in the body
How is passive targeting used in IM or SQ injections?
The liposomes end up in the lymphatic system/local lymph nodes
Allowing the opportunity for liposomes to be used in delivery of vaccines
can improve antigen specific immune response
What is liposomes surface engineering?
They avoid uptake by MPS by being coated by hydrophilic polymers, like PEG
The PEG increases liposome circulation times and promotes opportunities for the liposomes to interact with target cells rather than those of the MPS
Where can PEGylated surface engineered liposomes accumulate?
In sites with leaky vasculature, like tumor sites or sites of inflammation
Once in those sites the liposomes slowly release the drug resulting in high local concentrations at the site of action
Example of stealth liposomes
Doxil
Uses surface modified PEGylated
90% of the drug is encapsulated in the liposomes
What are the advantages of liposomes?
Biodegradable/inert
Can carry hydrophobic/hydrophilic drug
Reduced drug toxicity
Passive or active targeting
Drugs are more stabilized and less susceptible to degradation
What is particulate delivery of drugs?
Is the delivery of drugs which relies on presenting either the drug, or a formulated composition containing the drug as particles in micrometer/nanometer size range
What are the main ways drug particulates can be used in the body?
Injected directly at site, depot systems for slow release, or systemically injected
How can systemic particulates be targeted to specific sites?
Through active or passive targeting to deliver drug specifically
Microparticles size?
Between 0.1u and 100u
or
100nm-100,000 nm in size
Nanoparticles size?
1-100 nm in size
What happens to microparticles and nanoparticles after being injected into tissues/cavities?
Microparticles remain at the site of injection, while nanoparticles can be transported and cleared from the site of injection
What happens if microparticles are delivered intravenously (IV)?
Can embolize/lodge/obstruct blood vessels with the same diameter
Causes infraction in an organ
What happens if nanoparticles are delivered intravenously (IV)?
Too small to cause embolisms/lodging and are thought to circulate freely throughout vasculature
Similar to liposomes, if they have hydrophobic exteriors will be cleared rapidly by reticuloendothelial system (RES)
Can microparticles cross biological barriers?
Unlikely to cross most biological barrier
Typically must be injected into desired site of action
Can nanoparticles cross biological barriers?
Yes
Tumor blood vessels are leaky, allowing nanoparticles to accumulate passively more in tumors than in normal tissue
Which particles are taken up by which mechanisms?
Microparticles (~10 μm): taken up by specialized phagocytic cells (macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils) via phagocytosis
Nanoparticles: taken up by all cells via pinocytosis
What is Abraxane?
An IV nanosuspension
Accumulation of nanoparticles in the tumor tissue via passive targeting
Also has active targeting on the surface to be transported across blood vesicle walls
What is Lupron depot?
A microspheres IM administration
Supplied in dual compartment syringe, of solid and suspending vehicle
Drug is embedded in microcapsules in biodegradable polymer, released via diffusion and bioerosion
Where in liposomes does it incorporate hydrophilic drugs, lipophilic drugs, and amphiphilic drugs?
Hydrophilic drugs → aqueous core
Lipophilic drugs → lipid bilayer
Amphiphilic drugs → surface