DISTRIBUTION & IMPACT OF DENTAL CARIES & PERIODONTAL DISEASE
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
define epidemiology
epidemiology: the orderly study of diseases and other conditions in human populations where the group and not the individual is the unit of interest
Mausner & Kramer 1985
what assumptions does epidemiology have about human diseases and conditions
they do not occur at random
they have causal and preventive factors that can be identified through systematic investigation of different subgroups of individuals within a population in different places or at different times (MacMahon & Pugh 1970)
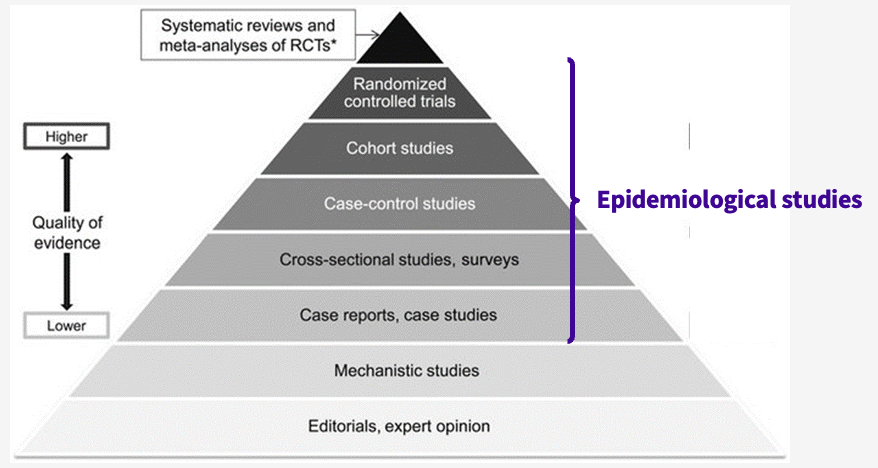
which studies on the hierarchy of evidence are considered epidemiological studies
how many people globally are affected by oral diseases
global burden of oral conditions: 3.9 billion people are affected by oral diseases globally
what is the most common oral disease suffered globally
untreated caries of permanent teeth
what is the second most common oral disease suffered globally
severe periodontitis (people who have 2 or more pockets of 6mm or more)
how is dental caries measured
using the DMF index
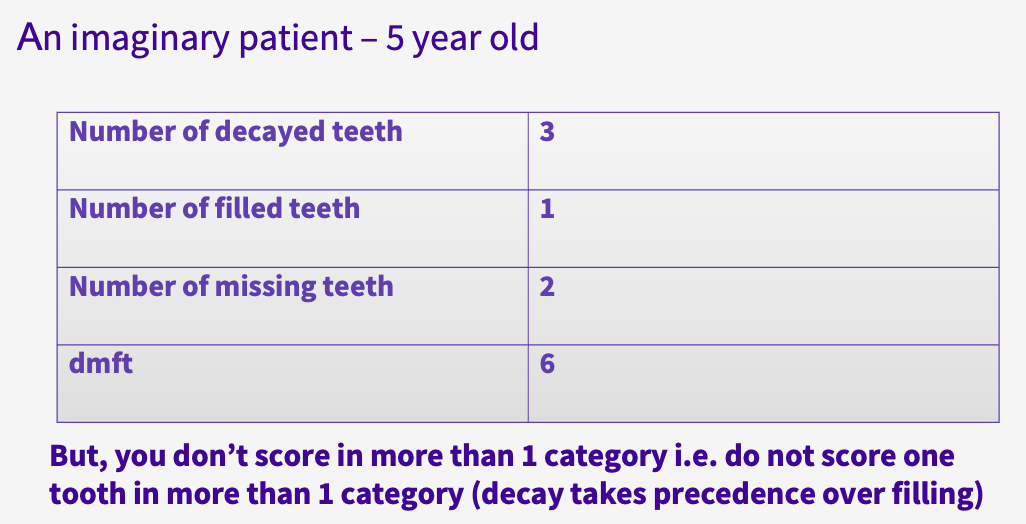
outline the DMF index
DMF index
summarises caries and treatment experience in groups
score of 1 or 0 for each tooth
final DMFT score is the total of decayed, missing and filled teeth
decay takes precedence over filled
example of a DMF index
what is the difference in notation between primary and permanent dentitions when writing DMFT
primary: dmft
permanent: DMFT
what are advantages of the DMFT index
relatively easy to apply
simple to understand
what are disadvantages of DMFT
age specific
cannot compare data from different ages
does not distinguish between treated and untreated decay
no filling, filling in cavity, extracted tooth all score a DMF of 1
cumulative and irreversible
someone with a high DMFT score may have had caries in the past and not currently/ recently
the value will never drop therefore not useful to assess if a person’s oral health is changing
does not distinguish between the severity of disease
less accurate and useful in adults
the status of a tooth reflects dentists’ decisions making rather than indicating disease level
cannot distinguish if teeth are extracted because of caries or due to other reasons
does not tell us about the impact of the disease on a person/ group/ population
____ factors for any disease affect the _____________
risk factors for any disease affect the distribution
what are key risk factors for caries
high carb. diet
availability of fluoride
socioeconomic position (SEP)
genetic susceptibility
how is a disease distributed in the population in terms of trends across…
there are trends across:
age groups
geography
sex
socioeconomic position
time (temporal trends)
when was NHS dentistry introduced
1950
now, approximately 1% of all adults are _________
edentulous
% has decreased massively since mid-late 90s
from 37-6% from 1968 to 2009
how can the impact of caries on individuals be measured
interviews
questionnaires
Oral Health Related Quality of Life (OHRQoL) questionnaire
if caries level is low, what impact does it have on OHRQoL
if caries level is low then there is a low impact of OHRQoL
what impact does caries have on society
children: absenteeism, school performance, some speech and language development
adults: work absenteeism and performance
cost to economy (productivity losses)
costs of dental treatment (> £3.2bn pa in England)
what is a potential consequence of small carious lesions
‘false positive’ diagnoses
is caries equally distributed in the community?
no
how can we tackle the parts of the community that caries is restricted to
these groups appear resistant or unable to change
need to recognise social determinants of health
‘target’ these groups e.g. community programmes like supervised toothbrushing in nurseries
what is the cohort effect regarding fluoride access
people under 50yo have always had F toothpaste
therefore generally have lower disease levels so the treatment they need is simple
—
people over 50yo did not have F when they were younger
therefore generally more caries when younger but keen to keep their teeth
so now they have more complex treatment needs therefore greater need for restorative specialists
what are the two broad types of periodontal disease
gingivitis - reversible inflammation of gingiva
periodontitis - irreversible loss of attachment between tooth and supporting structures
what are key features of periodontitis
recession
pocketing
bleeding
what symptom can sometimes not be present in those with periodontitis
oedema (non-inflamed gums)
how is gingivitis measured in children
by visual signs of redness
how is gingivitis measured in adults
by visual signs of redness
and/ or
bleeding on probing
what is an issue with probing
probing is notoriously unreliable as it depends on the probe force
this becomes a problem in research
how is periodontitis measured
looking for loss of attachment (as pocket depth), recession or both
what is the index for measuring periodontal disease
BPE
outline the basics of the BPE
mouth is divided into six sextants
the worst score for each sextant is recorded
8s are excluded
outline the BPE scoring
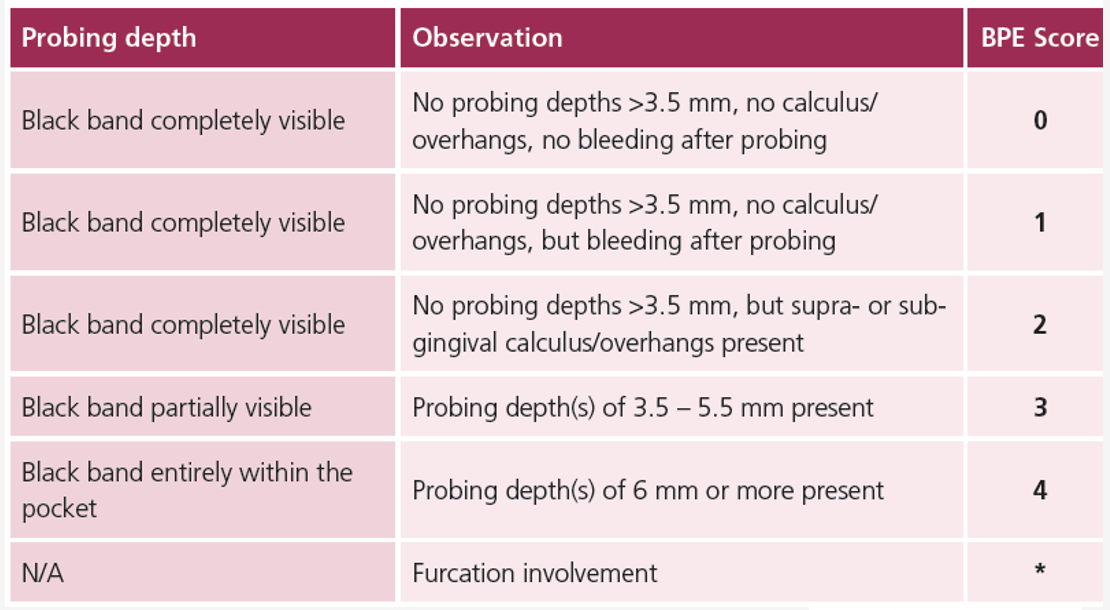
what BPE score constitutes a periodontitis diagnosis
2 sextants with code 4
how prevalent is gingivitis
estimates vary: 50-100% of the population affected at any one time
could be the most common disease in the world
is it a disease? or just inflammation
what is the trend of gingivitis in children
children are brushing their teeth better than they used to
gum inflammation, plaque, calculus have decreased from 2003 to 2013
what is the trend of periodontitis with age
positive correlation with age
risk factors for any disease affect ____________
distribution
what are risk factors for periodontal disease
plaque
tobacco smoking
(inadequate/ poor) restorative dentistry
genetics
immune disorders/ immunity suppression
what other factor shows a relationship with periodontal disease
socioeconomic position
what is the impact of periodontal diseases relative to caries
periodontal disease generally has less of an impact than caries on individuals
what else is periodontal disease associated with
a negative impact on quality of life
based on 25 cross sectional studies (Ferreira et al. 2017)
what is the cost of all dental treatment pa in England
> £3.2 billion
how effective is treatment for periodontal diseases
moderately effective at best
varies greatly between individuals
success is based on control of disease and risk factors
what % of people brush their teeth twice daily
75%