mocks😭
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
force
push or pull
what can force cause?
change in shape, speed, direction of an object
contact forces
objects must touch
what an example of contant forces?
air resistance, spring force, etc.
non-contant forces
objects are physically separated
what’s an example of non-contact forces?
gravitational force, nuclear, etc.
what’s unit of force?
Newtons
what’s the equation that links mass with weight?
F=ma (F: force in newtons, m: mass in kg, a: acceleration in m/s2 or N/kg)
What’s the gravity on Earth?
9.8 m/s2
mass
a measure of the amount of staff in an object and gives a measure of how difficult it is to get moving or to stop
never changes
vector quantities
a quantity that has both magnitude & direction
can be represented using an arrow
scalar quantity
a quantity that only has magnitude
what happens when a several forces act on an object?
they can be replaced by a single force (resultant force) that has the same effect
how do you calculate the resultant force?
subtract the smaller force from the larger force
constant velocity = terminal velocity
what is a free body diagram?
object shown as a point
forces are drawn as arrows
the length of the arrow indicates the magnitude of the force
the direction of the arrow shows the direction of the force
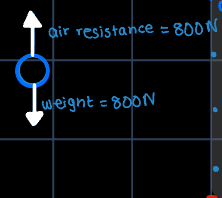
what are the steps of drawing a scale diagram?
1) draw arrows at the correct angles to represent the forces
2) draw lines to make a parallelogram
3) measure the diagonal of a parallelogram (this is your resultant force)
speed
a measure of the distance an object travels in a certain time
what’s the formula of speed?
speed = distance / time
velocity
a vector that tells us how fast an object is moving and its direction
displacement
a vector that tells how far an object has moved and the direction it move in
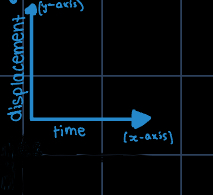
how do you draw a displacement time graph?
acceleration
the rate at which an object changes its speed
what are the 2 factors that affect acceleration?
how the speed changes and how much time the change in speed takes
what’s the formula for acceleration?
acceleration = change in speed (m/s) / time (s) or final velocity - initial velocity / time taken
what’s the unit of acceleration?
m/s2
constant acceleration
speed or velocity is increasing at the same rate over the same time period
how to draw a velocity time graph?
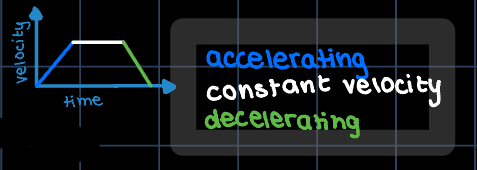
how do you find the area under velocity time graph?
multiply the value on the horizontal axis with the value on the vertical axis
split the area into triangles & rectangles
area of triangle = base x height / 2
what does newton’s second law state?
the acceleration of an object depends on the mass of an object and the force applied
stopping distance
how far a car moves between the driver noticing something in front of them and the car coming to a stop
what is the stopping distance affected by?
thinking and braking distance
braking distance
how far the car travels once you’ve put your foot on the brake
what’s the formula of stopping distance?
stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
how is energy useful?
energy has to be transferred using energy carriers
what unit is energy measured in?
Joules
what is the main property of energy?
energy cannot be created or destroyed
what are some examples of energy sources?
solar, nuclear fusion, tidal, etc.
how are winds caused?
the heating effect of the sun
renewable energy
energy that is being or can as its used
how does geothermal energy work?
heat from the Earth’s core brings water and steam to the Earth’s surface which can be converted to generate electricity
what are the benefits of hydroelectric power?
no waste is produced during energy production
reliable water source for communities
helps with flood control and irrigation support
where can waves transfer energy?
all waves can transfer energy from one to another without transferring matter
Waves can transmit through what?
solid, liquid, gases, and empty spaces
frequency
the number of complete waves passing a fixed point, in a given amount of time
measured in Hertz (Hz)
wavelength
the distance between the point on one wave and the same point on the next wave
measured in metres (m)
amplitude
the distance from the maximum of the disturbance to the initial position
longitudinal waves
the particles vibrate parallel to the direction in which the wave of energy is traveling
places where the particles are bunched together are called compression
where they are furthest apart are called rarefactions
example: sound waves
transverse waves
up and down motion from left to right therefore then particles vibrate at 90 degrees
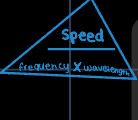
what’s the formula that links speed, wavelength, and frequency?
speed = frequency x wavelength
frequency = speed / wavelength
wavelength = speed / frequency
what are the different types of wave behaviours?
reflection: when waves bounce off an object
transmission: when waves keep traveling in the same direction through an object
refraction: when sound and light waves pass across a boundary between substances (air & glass), they change speed because the substances have different densities
diffraction: when waves meet a gap in a barrier, they pass through the gap, they then spread back out after they pass through the gap
scattering: when waves depart from the expected path and spread out in multiple directions
absorption: when a wave (light or sound) enters a material and loses energy instead of passing through
what affects the speed at sound can travel?
temperature and air pressure
what’s the relationship between the distance the particles and the speed at which sound travels?
the closer the particles lie, the faster sound is able to travel
the more densely the particles are arranged, the faster sound travels
how does temperature affect the speed of sound?
lower temperature = slower speed of sound
higher temperature = faster speed of sound
what’s the formula that links speed, distance and time?
speed = distance / time
electromagnetic spectrum
electromagnetic transverse waves that travel at the speed of light
what are the different types of electromagnetic waves on the spectrum?
radio waves: used for radio/tv, they are reflected off the ionosphere
microwaves: used to heat up, make water molecules vibrate to generate heat
infrared: first part of the spectrum that animals can detect
visible: includes all the parts that make up a rainbow
ultraviolet: exposure can cause cell damage leading to cancers or loss of sight
x-rays and gamma rays: very high energy waves which pentrate matter easily
what are the properties of shorter wavelengths?
higher energy and higher frequency
what are the properties of longer wavelengths?
lower energy and lower frequency
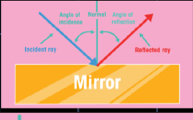
the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
how to draw a ray diagram?
what are the properties of refraction?
if a light wave passes from a medium in which it’s moving faster to a medium in which it’s moving slower, then the light wave will bend towards the normal
when ray passes from a medium where it’s slower to a medium where it’s faster, then the light wave reflects away from the normal
has an angle of incidence and an angle of reflection, but the two angles ARE NOT equal to each other because they travel through different media
no refraction occurs when the waves cross the boundary surface at a 90 degree angle, if this happens the rays continue in the same direction
what are some techniques used in a medical imaging?
Infrared:
passive image technique
camera detects emitted IR
measures body temperature
can locate poor circulation in cooler limbs
can detect raised temperature of a tumours
zero risk to patient or user
X-rays:
can show images of skeletons and soft tissue
images stored on film or digitally
CT scans can show body in 3D
low risk to patient but high risk to radiographers
unsuitable for pregnant females unless baby is shielded
Gamma rays:
patient injected with short half-life radioactive drug
location of radiochemical detected by gamma ray scanner
can target key organs for cleaner imaging
medium risk to patient and higher risk to clinicians
Radio waves(MRI):
high quality 3D images of body
high frequency radio waves
strong magnetic field
low risk to patient and clinician
Ultrasound:
only non electromagnetic imaging method
uses ultrasound which can travel into soft tissue
sound echo at density boundaries shows images of organs
can be done in real time
safe for neonatal scanning
very low risk
low resolution images