Module 2 - Chunking
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Chunking
Forming neural pathways for small bits of information using the focused mode
Creating and connecting smaller bits of information
Stress hinders the octopus’ ability to do this
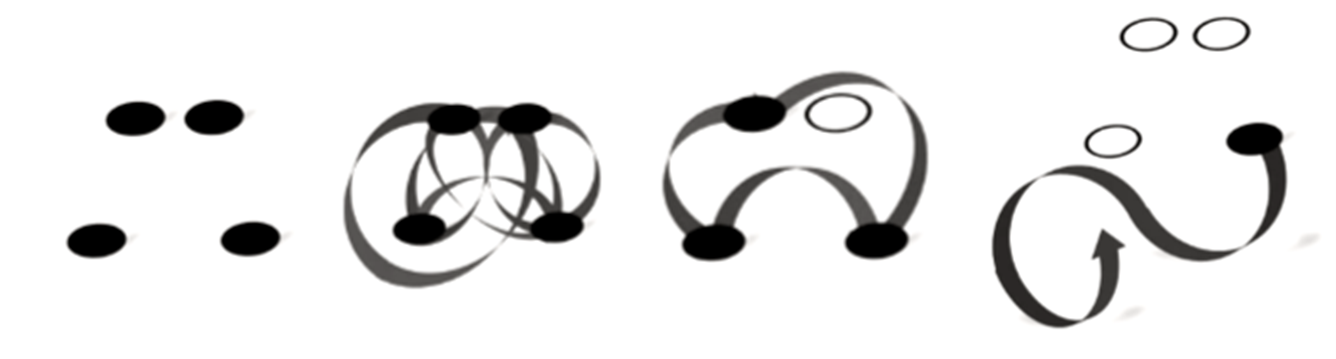
Chunk
Bits of information connected by use or meaning. Form a mental “loop”
Network of neurones/Neural pathway used to firing together to think a thought or perform an action quickly and efficiently/effortlessly
Worked-through example
Typically used in Maths/Science for first problem
Used to help figure out why the steps are taken the way they are
Shows key features and underlying principles
Flaw: can focus on why a step works instead of why this is the next thing you should do
The 3 steps to forming a chunk
Undivided focus and attention - no interruptions
Understand the idea/concept - doesn’t create a chunk
Gain context via practice and repetition - related and unrelated problems
Testing yourself!
This will ensure the concepts are firmly embedded into your mind. Ok to make mistakes
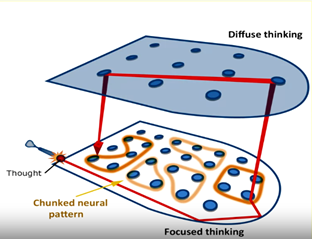
Bottom Up Learning
The learning concept described in module 2 attributed to chunking (directional)
Top Down Learning
The learning concept described in module 2 attributed to thinking about the big picture (directional)
Context
Learning when and when not to use particular techniques or chunks to solve a problem
The middle/meeting of bottom up and top down learning concepts
Illusion of Competence
Thinking you know the material but it is, in fact, not solidified in your mind
Retrieval Process/Recall
Proven to be better than simple re-reading and creation of concept maps for learning
Looking away and trying to remember the key ideas
Helps form chunks
Working memory
Heavily used in the early creation of chunks
Testing in random areas
Recall material when you’re in these areas to avoid association of material with environmental cues/triggers in your learning location
Acetylcholine, Dopamine & Serotonin
Neurotransmitters influencing and controlling concentration/synaptic plasticity, motivation/reward learning and social life/risk-taking behaviour
Transfer
The concept that, understanding a concept/chunk/problem-solving method in a different field can help you understand concepts or form chunks in a different field as they are somewhat similar or related

Diffuse Mode
Can help connect 2 or more chunks together in novel ways to solve new problems
Consistent Practice
Required so that the chunks in your mind do not become weak and faded

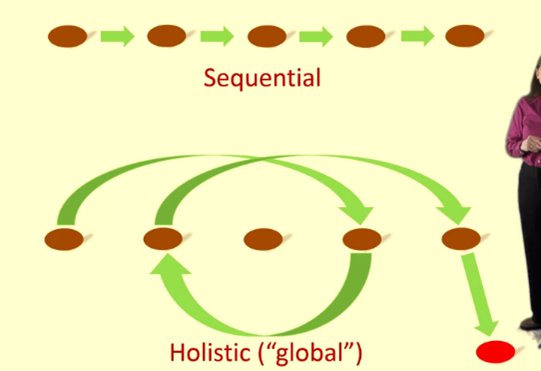
Sequenced Logical Approach
Holistic Intuitive Approach
Methods of approaching a problem/reaching a solution (focused vs diffuse)
Law of Serendipity
TRY TRY TRY

Einstellung
Fill in the blank: The tendency to rely on familiar solutions due to past experiences is known as __________. This hinders the ability to see alternative methods in problem-solving scenarios
Interleaving
Fill in the blank: __________ is a learning strategy that enhances retention by alternating between different subjects or skills during practice.
Deliberate Practice
Fill In the blank: (x) Is a method which emphasises testing areas in which your knowledge is weak in order to avoid the illusion of competence

Transfer
The concept of using one chunk in one area of expertise/knowledge to help you form/create another chunk in a different topical area as they are similar/related