ASTRO 101- Exam 4
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Everything around us is made of?
Atoms
Examples of atoms:
H, He, N, O, Fe, Al
How many naturally occuring atoms are there?
92
What are molecules?
Molecules are made up of atoms.
Examples of molecules?
H2o, CO2, O2, O3, N2, CH4
What three particles are atoms made up of?
Protons (positively charged)
Neutrons (neutral- not charged)
Electrons (negatively charged)
An atoms consists of?
A small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
What makes one atoms different than another?
The number of protons in the nucleus.
What is an Ion?
An atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons.
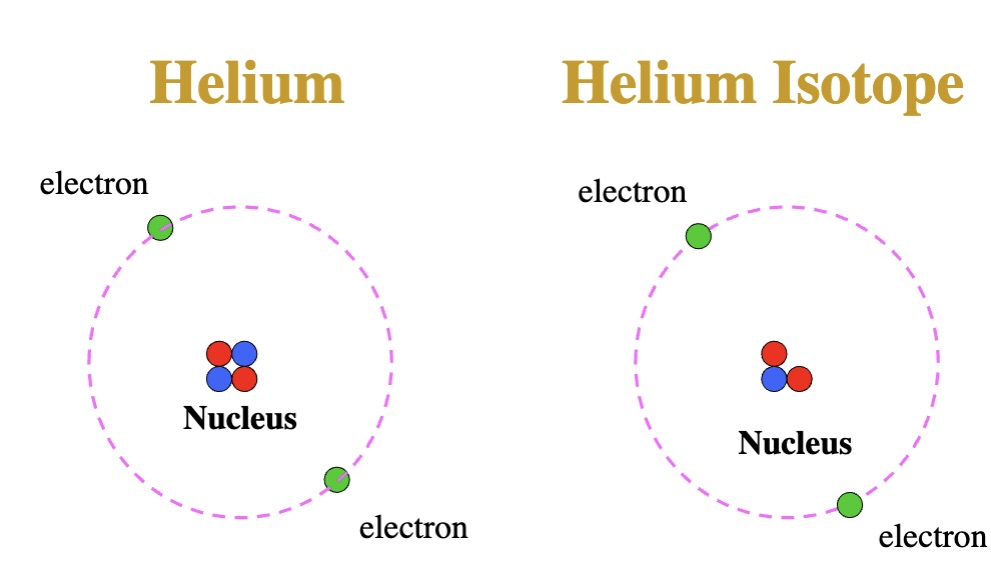
What are isotopes?
Atoms with the same number of protons but having different number of neutrons.
White light can be separated into?
Its component colors.
The sequence of colors is called?
A spectrum.
What color is white light made of?
Visible light
How can white light be separated?
With a prism
What makes each color different?
Each color represents a different wavelength.
What are the wavelengths of visible light?
400nm to 700nm
A wave carried energy from one place to another, but it does not transport _______?
Matter
What type of energy does light carry?
Light carries electromagnetic energy.
Shorter Wavelength=
Higher Energy
Longer Wavelength=
Lower Energy
All types of electromagnetic radiation travel at?
The speed of light.
How fast does light travel?
186,000 miles per second
300,000 kilometers per second
3 × 108 m/s
How are wavelength and frequency related to each other?
Wavelength x frequency= speed of light
λf = c
How are energy and wavelength related?
Energy= 1240 eV nm / Wavelength OR Wavelength= 1240 eV nm / Energy
eV stands for:
Electron Volt
What is a eV?
It is a very very very small unit of energy, like a kilowatt hour (Kwhr) only smaller.
How is light produced in Atoms?
Light comes from the movement of electrons in atoms when the electrons make downward transitions between energy levels.
In the Bohr model, the first and lowest energy level is called?
The ground state.
How do electrons move into higher energy levels?
Usually by collisions with other atoms.
Electrons prefer to orbit in?
The lowest energy level.
When an electron jumps from a higher energy level to a lower energy level?
Light is emitted!
Electrons must _____ energy to move into a higher energy level?
ABSORB
Electrons _____ light when they make downward transitions?
EMIT
The Lyman series lie in:
The U.V.
The Balmer series lie in:
The Visible
Three Basic Types of Spectra:
Continuous Spectrum
Emission line spectrum
Absorption line spectrum
Kirchhoff’s First Rule:
A very hot solid, a very hot liquid, or a very hot dense gas emit a continuous spectrum.

Example of continuous spectrum?
Light bulb filament, molten metal, and hot dense interior of stars.

Kirchhoff’s Second Rule:
A very hot low density gas produces an emission line spectrum.
Each chemical element produces its own?
Unique emission line spectrum.
Kirchhoff’s Third Rule:
If a continuous spectrum passes through a low density gas an absorption line spectrum is produced.
How can we determine a star’s temperature?
Wien’s Law: Temperature = 3,000,000 nm K / Wavelength of peak intensity
The color of a star is an indication of?
Its temperature.
Bluish stars are?
Hotter
Reddish stars are?
Cooler
Peak color shifts to?
Shorter wavelengths as an objects is heated.
Stars are classified according to their?
Temperatures
7 Spectral classes:
O, B, A, F, G, K, M
The sun is a?
G2 main sequence star.
Each spectral is?
Subdivided into 10 subdivisions.
What is Luminosity?
The total energy output of a star.
Luminosity is measured in?
Watts
What is the luminosity of the sun?
3.8 × 1026 W
The luminosity of a star depends on?
Its radius and temperature.
The _______________ gives the relationship between the luminosity of a star and its radius and temperature.
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
The Stefan-Boltzmann Law equation:
𝑳 = 𝟒𝝅𝑹𝟐 ∙ 𝝈𝑻𝟒
The Doppler Effect can be used to?
Determine how fast an object is moving toward or away from the earth.
The Doppler Effect Equation:
v/c = ∆𝝀/ 𝝀
Distances to stars and galaxies are measured in?
Light years or parsecs.
What is a Light Year?
The distance which light travels in one year.
Light Travels at:
186,000 miles/sec or 3×108m/s
1 parsec=
3.26 light years
206, 265 a.u.
In astronomy ANGLES are measured in?
Degrees, or arc minutes or arcseconds.
1 arcminute=
1/60 of a degree
One arc second equals the thickness of a dime from a distance of?
Three football fields!
How can we determine a star’s distance?
Parallax
What is parallax?
The apparent shift in star’s position due to the Earth’s revolutions around the Sun.
Stars masses can be determined by?
Studying and making measurements of the orbits of binary stars.
Monitoring how BINARY STARS move provide?
Information about stellar masses.
Is there a relationship between mass and temperature for main sequence stars?
On the main sequence the most massive stars are also the hottest stars.
Is there a relationship between mass and luminosity for main sequence stars?
On the main sequence the most massive stars have the highest luminosity.
The mass of a star will determine:
How long a star will live
How a star will die
Its final state after death
Which stars on the main sequence have a low mass?
K and M
Which stars on the main sequence have a medium mass?
A,F, & G
Which stars on the main sequence have a high mass?
O & B
Which stars have the shortest lifetimes?
High mass O stars live the shortest only a few million years.
How long do medium mass G stars live?
10 billion years.
How long do low mass M stars live?
100 billion years.
The 3 Final States of Stars:
White Dwarfs
Neutron Stars/ Pulsars
Black Holes
Low to Medium mass stars end up as?
White Dwarfs
High Mass stars end up as?
Neutron stars or Black Holes
Hydrogen Fusion requieres?
15 million K.
Helium fusion requieres?
100 million K.
Low & Medium stars eject their outer layers to produce?
Planetary Nebula
The burned-out core of a low mass star becomes a?
White Dwarf
White Dwarf Characteristics:
Dead Star
Diameter equal to the earth
Supported by the refusal of its electrons to pack themselves into a smaller volume
Density of a White Dwarf?
1 ton/cm3
Maximum mass of a White Dwarf?
1.4 solar masses
What’s a Nova?
A nova is relatively gentle explosion of hydrogen gas on a surface of a white dwarf in a binary star system.
Novas occur when?
The white dwarf steals fuel from its companion and the external layers quickly ignite and shine brightly.
Can the Nova process repeat?
YEEESSSS!!
2 Main Types of Supernovae?
Ia supernova
II supernova
Type Ia supernova occurs when?
A white dwarf in a binary system accumulates matter from its binary companion and it is pushed over the Chandrasekhar limit and the star is completely destroyed in the supernova explosion. No supernova remnant is left behind.
Type II supernova occurs when?
The core of a single massive star collapses suddenly when it runs out of fuel and dies. The most massive stars develop iron cores and the iron core cannot generate energy by nuclear fusion therefore they cannot support there own weight and they collapse. The in-falling matter rebounds off the dense core and the star literally explodes. The supernova explosion leaves a neutron star or black hole.
Evolution of a Small Star:
Small Star, Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, & White Dwarf.
Evolution of a Large Star:
Red supergiant, Supernova, Neutron Star or Black Hole
What are Neutron Stars?
Dead stars produced when high mass stars go through a super nova explosion and are composed entirely of neutrons.
Diameter of Neutron Stars:
less than 20 km (12 miles)
Density of Neutron Stars:
100 million tons/cm3
Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars:
3 solar masses