market failure
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Market failure
When the free market leads to a misallocation of resources
Types of market failure
Positive and negative externalities, public goods, information gaps
Using an example, explain why the government imposes specific taxes on many gods and services
Specific taxes are a set unit amount on each product sold, one example of this is alcohol and tobacco duty. This is in order to increase the price of the good, so consumers demand for it decreases, which reduces the negative externality and external costs it produces
External benefits
When the social benefits are higher than the private benefits
Marginal private benefit
Benefits gained by producers
Marginal external benefit
Benefit gained by third party
Marginal social benefit
Benefit to society
Marginal private cost
Costs Consumed by seller and buyer
Marginal external cost
Cost incurred by third party
Marginal social cost
Total cots to society
Third arty
People no apart of the transaction
Consumption and production externality
Consumption- benefit or cost third party endures when good is consumed, production opposite
Negative externality
When a god causes external costs to the third party
Negative externality diagram
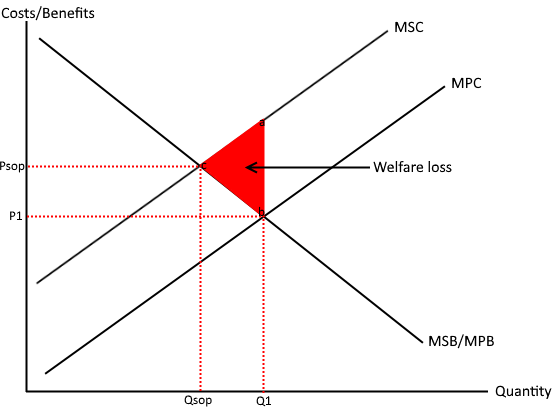
Welfare loss
Output when costs to society are greater than benefits
Positive externality
When a good creates external benefits for the third party
Positive externality diagram
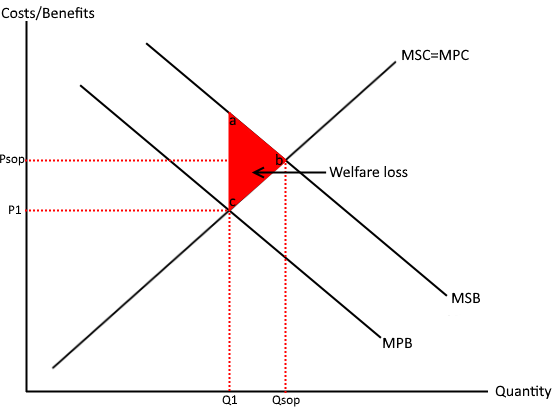
Examples are
Vaccinations, education, public transport
Public goods
Non rival and non excludable- can’t stop someone from using it
Quasi public goods
Aren’t perfectly non rival or rival or non excludable and excludable
Free rider problem
Benefits without paying
Asymmetric information
Where one party has superior knowledge compared to another, sellers take advanategs of buyers lack of knowledge