Gene Expression Notes
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Gene expression
the process where DNA directs protein synthesis involving transcription and translation
Synthesis
the process of combining different components or elements to form a coherent whole or a new entity.
Protein synthesis
the process where cells generate new proteins, involving the translation of genetic information contained in mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids to form a protein.
Central dogma of molecular biology
describes the flow of information from DNA —> mRNA —> protein
Genes specify the sequence of mRNA which then specify the sequence of proteins and explains how genetic information is transferred within biological systems.
Transcription
DNA being copied into mRNA serving as a bridge between genetic information and the synthesis of proteins
Transcription and translation is coupled
in prokaryotes, meaning they can occur simultaneously, allowing for rapid protein synthesis.
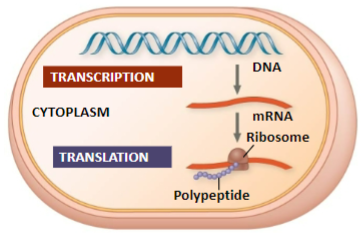
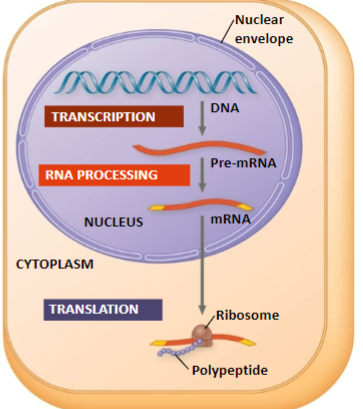
Transcription and translation is not coupled
in eukaryotes, where transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation occurs in the cytoplasm, requiring additional processing steps.
Codons
are sequences of three nucleotides (tri-nucleotide) in mRNA that correspond to specific amino acids during protein synthesis.
Stop codons
UAA, UGA, UAG
AUG
Start codon, also codes for Methonine, the first amino acid in protein synthesis.
Genetic code is redundant
multiple codons can code for the same amino acid
Non-Univeral genetic code
Mitochondria and Protists (paramecium)
Three main stages of initiation
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation stage
The promotor region: increases in TATA boxes critical for RNA polymerase attachment.
Forms transcription factors and RNA polymerase
TATA box
A promoter that states the initiation complex in eukaryotic DNA
Binds to TATA binding protein, causing a bend in the DNA molecule
Determines the start point transcription
5’ → TATAAA→ 3’
Not in bacteria DNA
Transcription factors
Mediates the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription
RNA polymerase
Catalyzes RNA synthesis, pulls DNA strands apart, and joins them together with RNA nucleotides
does not require a promoter and synthesizes RNA in the 5' to 3' direction.
Elongation stage
RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA by unwinding the DNA helix (10-20 bases at a time).
Continues until it encounters a termination signal.
Elongation of the RNA strand
the process during transcription where RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing RNA molecule, extending it 5' to 3' until a termination signal is reached.
Termination stage in bacteria
Polymerase stopes transcription at the end of the terminator and the mRNA can be translated without further modification
Termination stage in eukaryotes
Transcription stops after transcribing a poly A signal releasing mRNA that requires modification before translation.
RNA polymerase 2 transcribes the polyadenylation signal sequence; the RNA transcript is released 10-35 nucleotides past the is polyadenylation (poly A) sequence
Translation
mRNA being read and amino acids are assembled into polypeptides to form proteins. (happens on ribosomes during protein synthesis)
pre-mRNA
initial transcript of a gene that undergoes processing to become mature mRNA (including splicing, capping, and polyadenylation). It includes both exons and introns.
5’ Methel Cap
added to the 5’ endof the pre-mRNA molecule to protect it from degradation and assist in ribosome binding during translation.
Capping
the addition of a modified guanine nucleotide to the 5' end of the primary transcript, which protects the RNA from degradation and facilitates ribosome binding during translation.
3’ Poly A tail
added to the 3’ end of the pre-mRNA to enhance stability and promote export from the nucleus, as well as assist in translation.
Polyadenylation (poly A tail)
a long stretch of adenine nucleotides, to the 3' end of the transcript, enhancing its stability and aiding in its export from the nucleus.
Introns
non-coding regions of a gene that are transcribed into pre-mRNA but is cut out during RNA splicing.
Exons
coding regions of a gene that are joined together in the final mRNA after RNA splicing.
Function of RNA modification
Facilitate mRNA export to the cytoplasm
Protects mRNA from enzymatic degradation
Helps ribosomes attach to the 5’ end of mRNA
Splicing
removing non-coding regions (introns) from the primary transcript and joining the coding regions (exons) together, forming the mature mRNA that can be translated into proteins.
Ribozymes
RNA molecule that acts like an enzyme→ RNA splicing and the separation of RNA chains.
Properties allowing RNA to function as an enzyme
Can form a 3D structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself
contains functional groups that participate in catalysis
Hydrogen bonds with other nucleic acid molecules
Function of introns
gene regulation: Introns may contain regulatory sequences that influence gene expression.
Alternative splicing: A single gene can lead to multiple proteins depending on which exons are included in the final mRNA
Exon shuffling: Introns promote genetic diversity and evolution of proteins by allowing different combinations of exons.
Examples of alternative RNA splicing
Protein with all three exons.
Protein with exons one and two.
Protein with exons two and three.
tRNA
A type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis, ensuring the correct sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
tRNA characteristics
single-stranded RNA molecule composed of approximately 80 nucleotides, which allows for unique structural conformations.
has a specific amino acid attachment site at one end, allowing it to bind the corresponding amino acid, while the anticodon at the other end is crucial for recognition of the matched codon on the mRNA. has a specific amino acid attachment site at one end, allowing it to bind the corresponding amino acid, while the anticodon at the other end is crucial for recognition of the matched codon on the mRNA.
The flattened 3D structure that resembles a cloverleaf due to its specific folding, which is essential for its function in translation.
tRNA amino acid attachment site
specifically binds to the amino acid corresponding to the tRNA, ensuring the correct amino acid is added during protein synthesis.
(structure)
tRNA anticodon
This three-nucleotide sequence is complementary to the mRNA codon, facilitating accurate pairing and ensuring that the correct amino acid is incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain.
Matching tRNA with amino acids
Correct match between tRNA and amino acid: This critical pairing is catalyzed by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, which ensures specificity in the translation process.
Correct pairing of the tRNA anticodon with mRNA codon: This ensures the fidelity of protein synthesis, as any mismatch could lead to incorrect amino acid incorporation.
Amnio acid - tRNA bonding process
The amino acid and tRNA are brought into the active site of the relevant enzyme (e.g., tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase), which recognizes both the tRNA and its corresponding amino acid.
The hydrolysis of ATP provides energy required to catalyze the accurate formation of the ester bond between the amino acid and the tRNA.
Once the amino acid is covalently attached to the tRNA, the aminoacyl-tRNA is released, ready for delivery to the ribosome for polypeptide synthesis.
Ribosome function
essential for protein synthesis as it facilitates the coupling of tRNA anticodons with their corresponding mRNA codons, enabling the translation of genetic information into functional proteins.
Eukaryotic ribosomes
The two ribosomal subunits (large and small) are made of ribosomal proteins (~ 80) & ribosomal RNAs (18S, 5S, 5.8S, 28S)
procaryotic v eukaryotic ribosomes
Bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes are somewhat similar but have significant differences: some antibiotic drugs specifically target bacterial ribosomes without harming eukaryotic ribosomes.
Ribosome large subunit
Comprised of 50 ribosomal proteins along with 3 rRNAs (28S, 5S, and 5.8S), which play crucial roles in the structure and function of the ribosome.
Ribosome small subunit
Small subunit: Contains 30-40 ribosomal proteins and one rRNA (18S).
Ribosome Aminoacyl (A) site
Binding site where incoming aminoacyl-tRNA binds, adding its amino acid to the growing peptide chain.
Ribosome Peptidyl (P) site
Holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain.
Ribosome exit (E)
Where discharged tRNA exits the ribosome after delivering its amino acid.
Translation initiation
imitation complex is at the P site and it starts protein synthesis. The complex is made of small and large ribosomal subunits, mRNA, and initiator tRNA.
This process involves the assembly of the ribosome at the start codon of mRNA, preparing for translation.
Elongation of Translation
The stage where amino acids are sequentially added to the growing polypeptide chain, driven by the movement of the ribosome along the mRNA.
Termination of Translation
Triggered by the stop codons.
A release factor enters the A site leading to water being added instead of an amino acid which makes the polypeptide chain detach from the tRNA, concluding protein synthesis.
the ribosomal subunits dissociate and the mRNA is released allowing the subunit to be recycled
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence that can alter the function of a gene, potentially leading to changes in the protein product or regulatory elements.
Missense mutation
incorrect codon pairing that leads to the incorporation of a different amino acid in the protein, potentially affecting its function. (sickle cell)
Silent mutation
The mutation has no effects
Nonsense mutation
change an amino acid codon into a stop codon, nearly always leading to a non-functional protein and results in premature termination of protein synthesis.
Ribosome RNA
Ribosomal protein
Part of the ribosome helps with its structure (does not make protein)
pre-mRNA
genetic code → affects proteins
mRNA
a single-stranded molecule that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis. (no introns, they were spliced!)
tRNA
a type of RNA that transports amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis, matching the amino acid to the corresponding codon on the mRNA.
RNA primer
a short segment of RNA that serves as a starting point for DNA synthesis during replication.
snRNP
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins that are involved in the splicing of introns from pre-mRNA transcripts.
spliceosome
a complex of snRNPs and other proteins that facilitates the splicing of introns from pre-mRNA.