Exam 3 Gen Chem 1 Formulas
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Charle’s Law
V1/T1 = V2/T2
Boyle’s Law
P1V1 = P2V2
Avogadro’s Law
V1/n1 = V2/n2
Dalton’s Law
PT = PA + PB + PC
Rms Formula
Square root of 3RT/M
Ideal gas law
PV = nRT
M (in Rms equation)
kg/mol
R (ideal gas law)
0.08206
R (Rms equation)
8.31
Molarity
n/V
specific heat capacity equation
Q= mcAT
Q
heat
m (for mcAT)
mass
AT
change in temperature
How many mm of Hg are in 1 atm?
760mm
c in Q=mcAT
specific heat
Frequency equation (v)
v= c/lamda
Energy of a photon equation (E)
E= h(v)
Change in Energy (Delta E)
RH = ( 1/ni2 - 1/nf2 )
Lambda =
h/mu
(planks constant) h=
6.626×10-34
(speed of light) c=
3.00×108
(Avogadro’s number) NA
6.022×1023
RH Or EH
-2.18×10-18
molar enthalpy change
Deta H/n
Delta H =
products - reactants
1m3 =
1000L
1000 cm3 =
1L
1in =
2.54 cm
1 kcal =
1000 calories
1 cal =
4.18 J
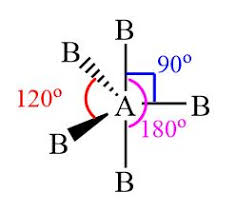
Trigonal bi pyramidal
5 pairs
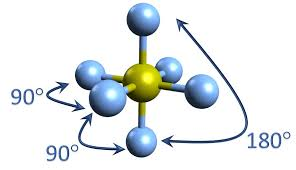
octohedral
6 pairs
moles =
detla H/ Hrxn
Hrxn
heat of reaction or molar enthalpy change
Fahrenheit =
9/5x( c ) + 32
Celcius =
5/9 ( F - 32)
Diamagnetic
all electrons paired
Paramagnetic
unpaired electrons
most strong acids are
soluble
u ( lambda = h/mu)
speed of particle