Neurons and Synaptic `Transmission
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
neuron function
to transmit electrical and chemical signals around the body
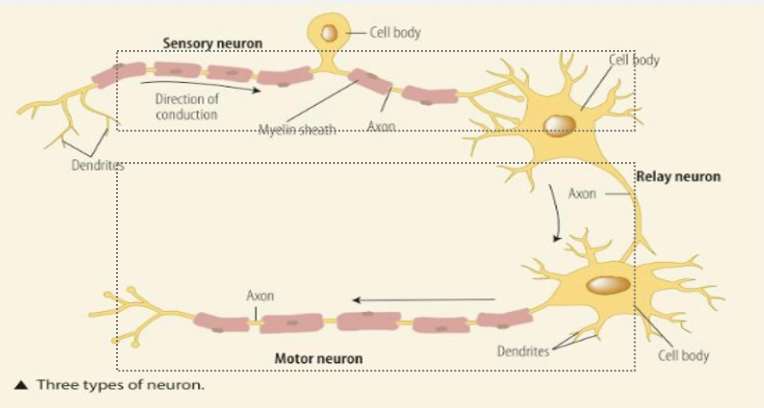
sensory neurones
carry impulses toward the brain
relay neuron
connect sensory and motor neurons
motor neurons
carry impulses away for CNS
Myelin Sheath
fatty layer around the axon
speeds up the rate of transmission
role of nodes of ranvier
gaps between the myelin sheath which allow transmission to be even quicker as electrical impulses jump between them
neuron labelles
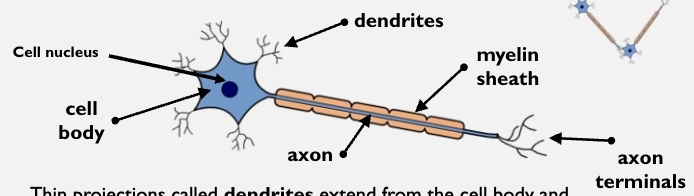
order of neurons
cell body
contains nucleus which holds genetic info of cell
dendrites
carry impulses from neighbouring neurons to cell body
axonq
the stem which carries impulses away from cell body
synaptic terminal
pass impulse to neighbouring neurons across the gap between neurons
synaptic transmission
-an electrical impulse travels down axon of presynaptic neuron
-when impulse reaches axon terminal it triggers vesicles to move toward presynaptic membrane
-synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
-neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft
-they bind to receptors of dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron
-this triggers a new action potential in the postsynaptic neuron
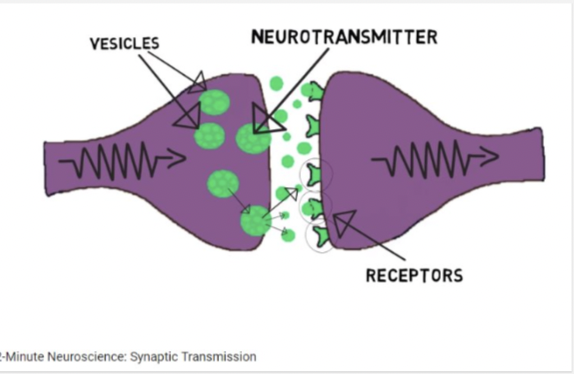
neurotransmitters
molecules that neurons use to communicate
-if enough excitation receptors bind- neuron can fire and action potential is repeated
-if enough inhibition receptors bind- neuron cant fire and action potential isn’t repeated
-excitatory and inhibitory influenced summed together to produce action potential(summation)
adrenaline
hormone and neurotransmitter which is an element in stress response
dopamine
released when we experience reward and pleasurable activities
serotonin
involved with emotion mood and sleeping and regulates sleep cycle
what happens to NT in the synapse
-bind to receptors
-reuptake
-diffusion
-enzymes