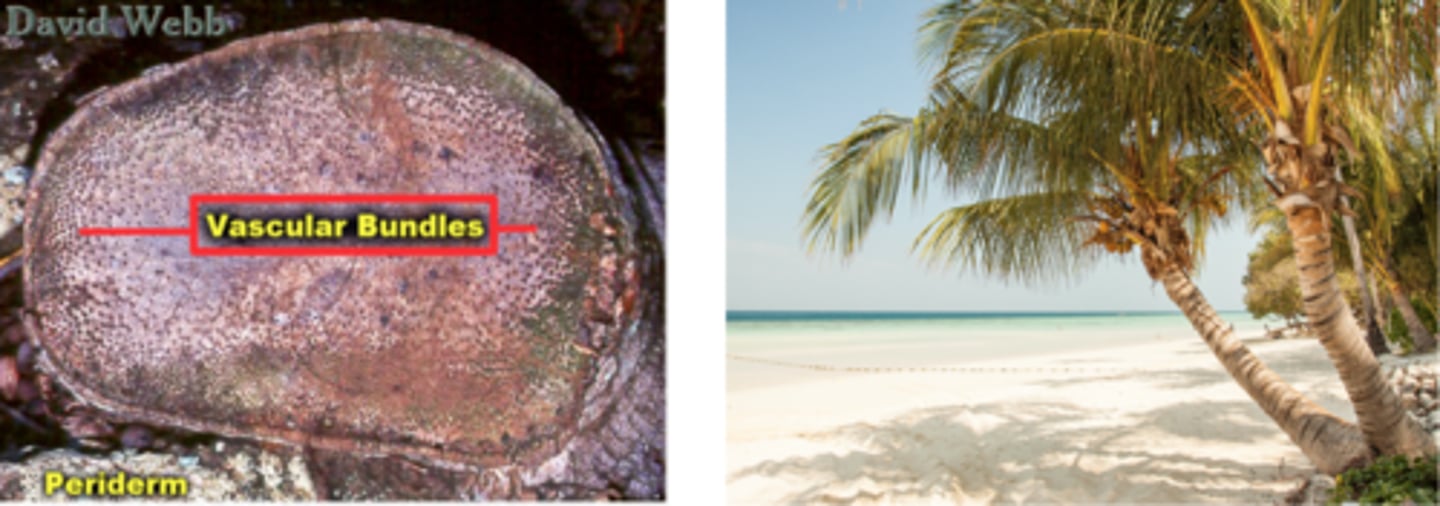
9: Stem (k)
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
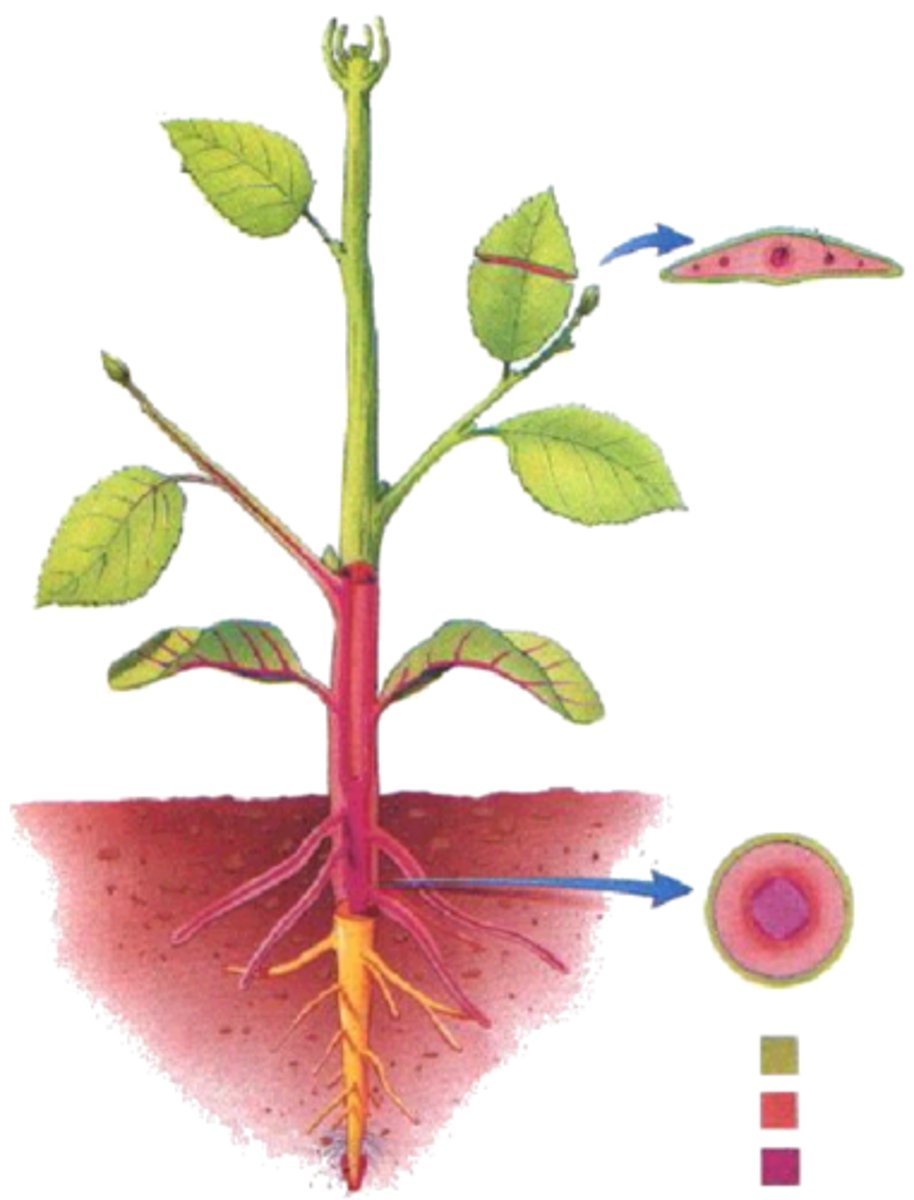
shoot
- the above ground portion of the plant
- Includes stems, leaves, buds, flowers and fruits
Leaves
are sites of food production and stems function in conduction and support
epicotyl
Shoot growth is initiated in the embryo from the _______, which may or may not have one or more leaf primordia
epicotyl
segment of a seedling; pt where cotyledon is attached and becomes upper part of stem and leaves
hypocotyl
segment of a seedling; pt where cotyledon is attached and becomes lower part of stem and leaves
nodes
areas where leaves arise
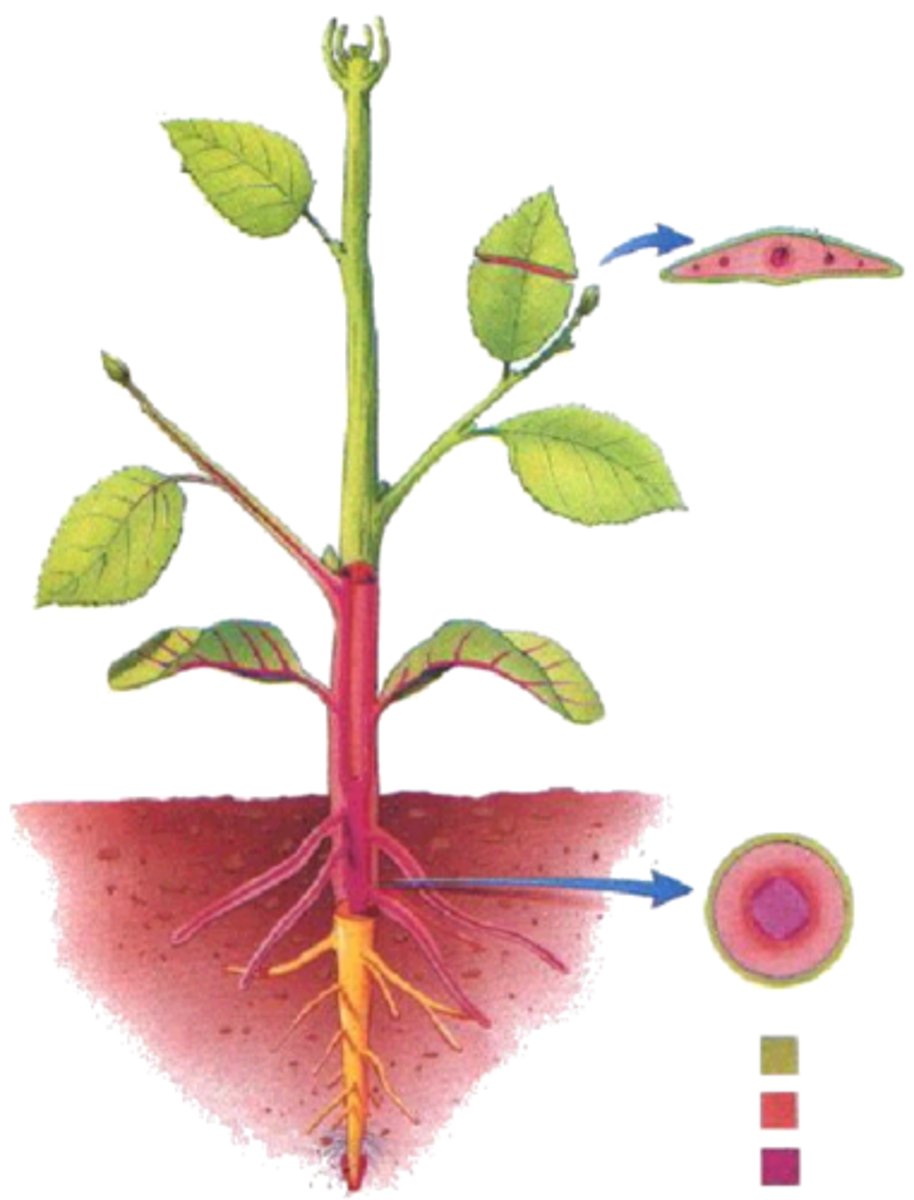
internodes
the intervals between the nodes
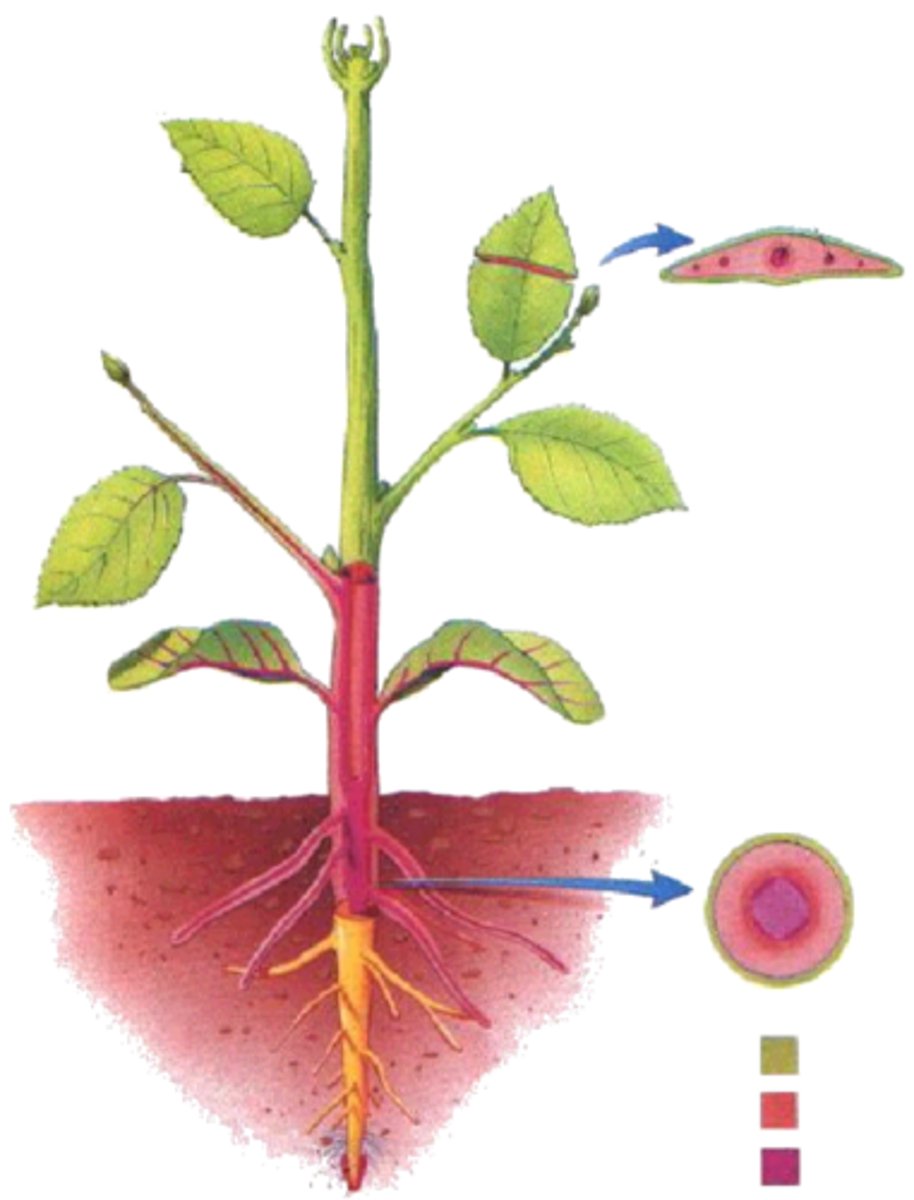
Axil
upper angle between a leaf stalk (or any lateral structure) and the stem
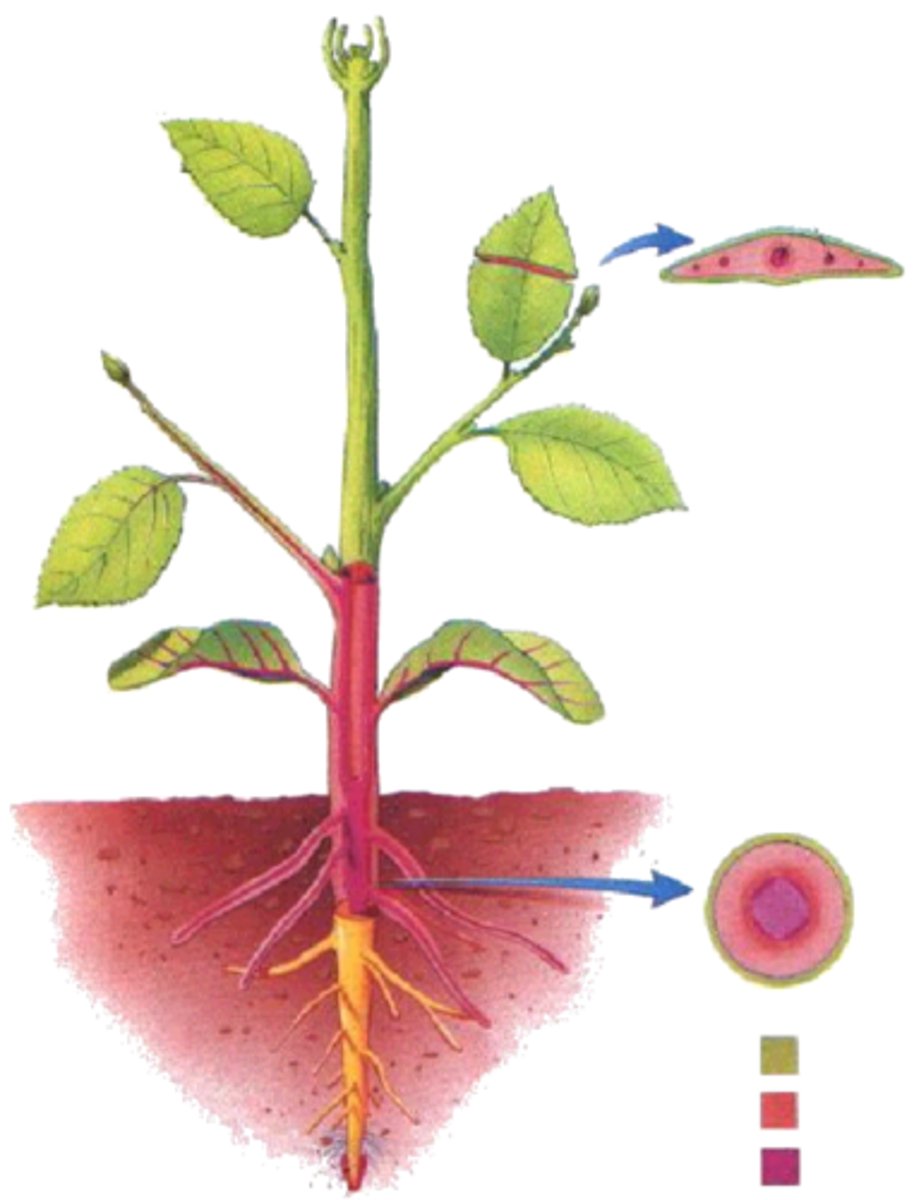
axillary structure
anything that arises from axil
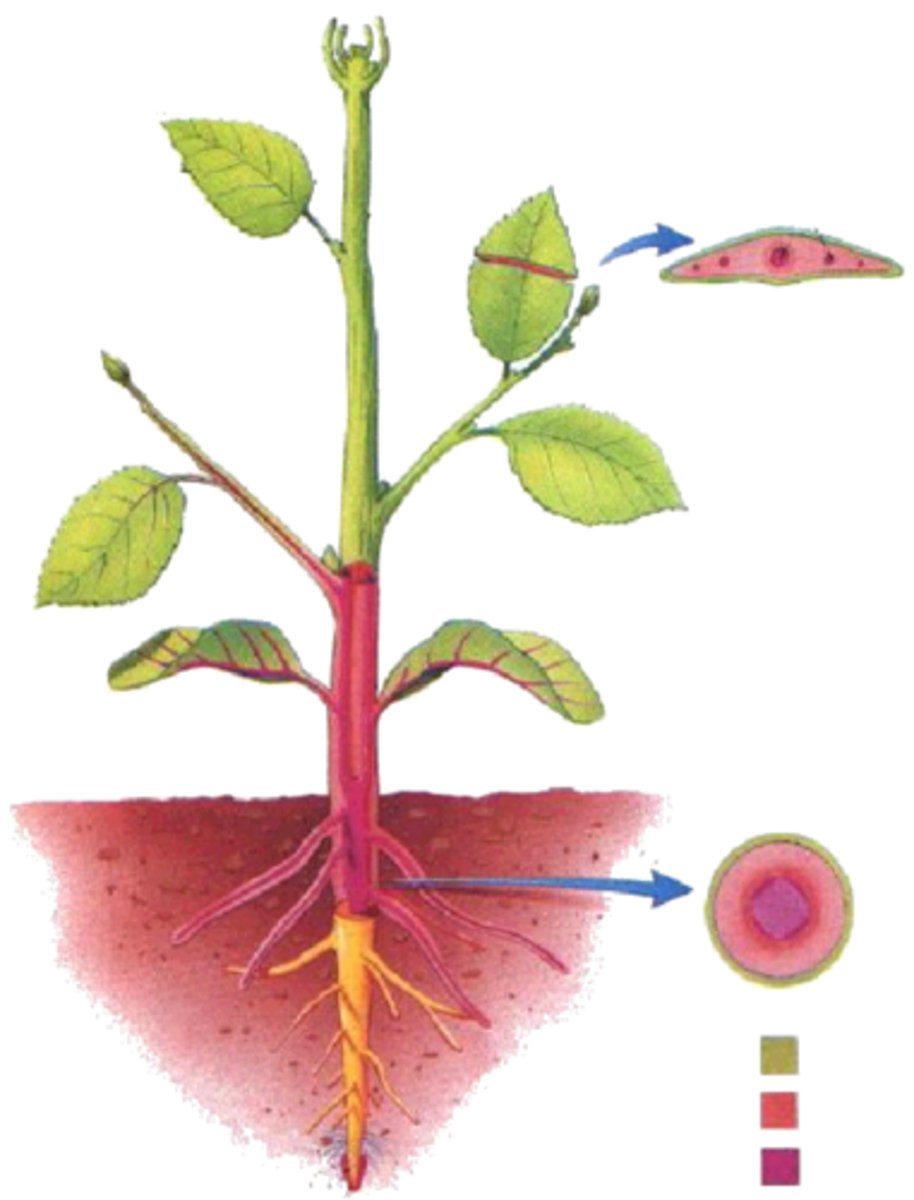
buds
an external meristem; can be protected by a bud scale; could become branch or flowers
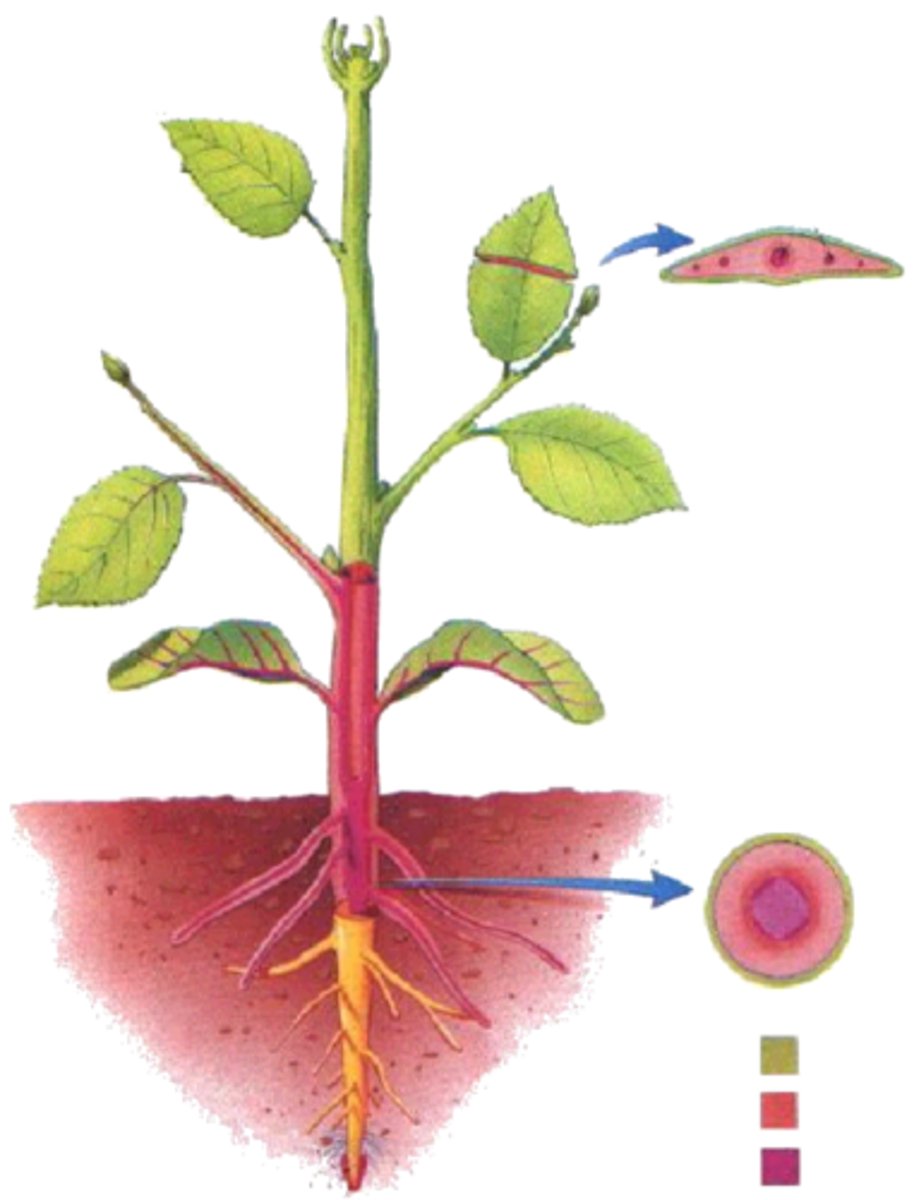
Lateral buds
buds along the side of the twig; may be for new leaves, flowers or branches
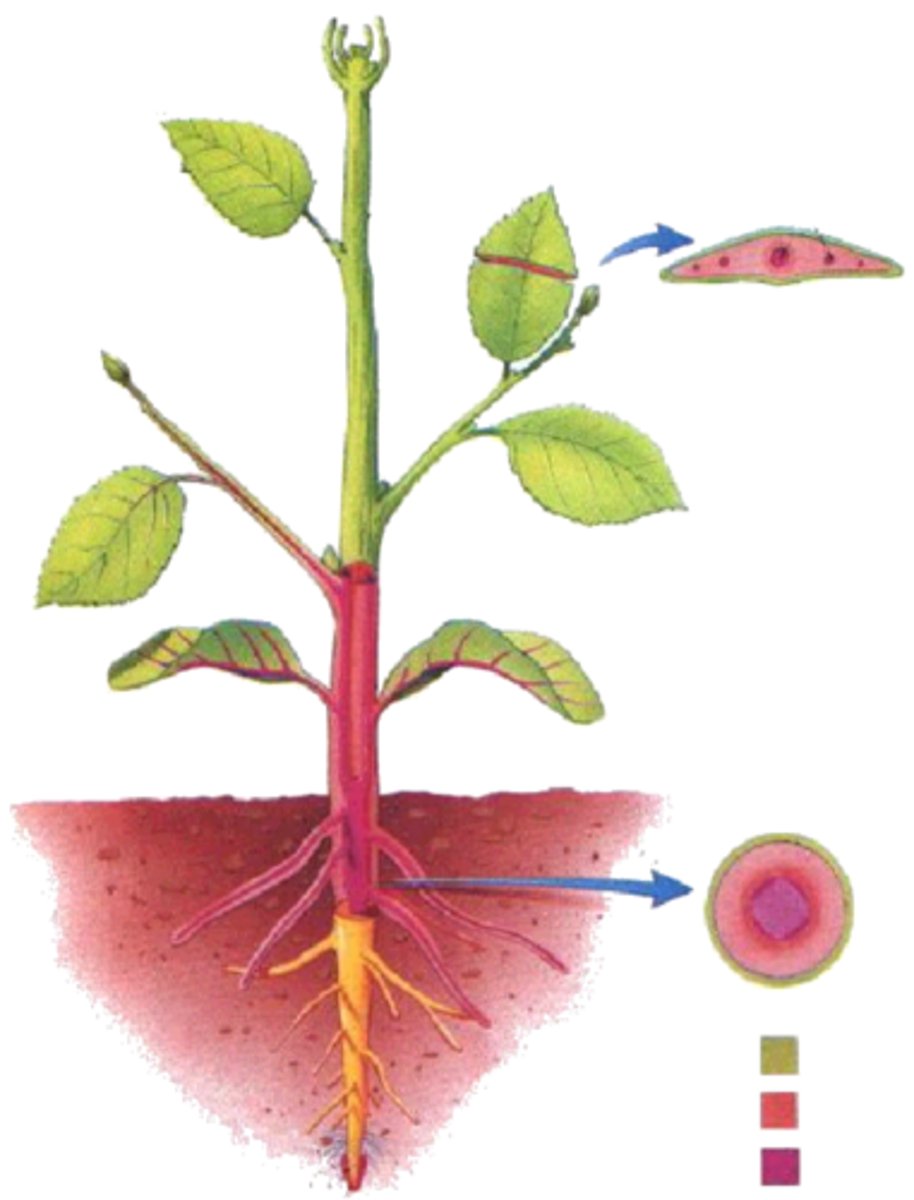
Terminal buds
buds at the end of the twig; only for extending length of stem
- Support leaves and reproductive structures
- Produce carbohydrates
- Store materials
- Transport water and solutes between roots and leaves
functions of stems
Herbaceous stem
soft, green & short- lived stem

Woody stem
hard, brown & long-lived stem

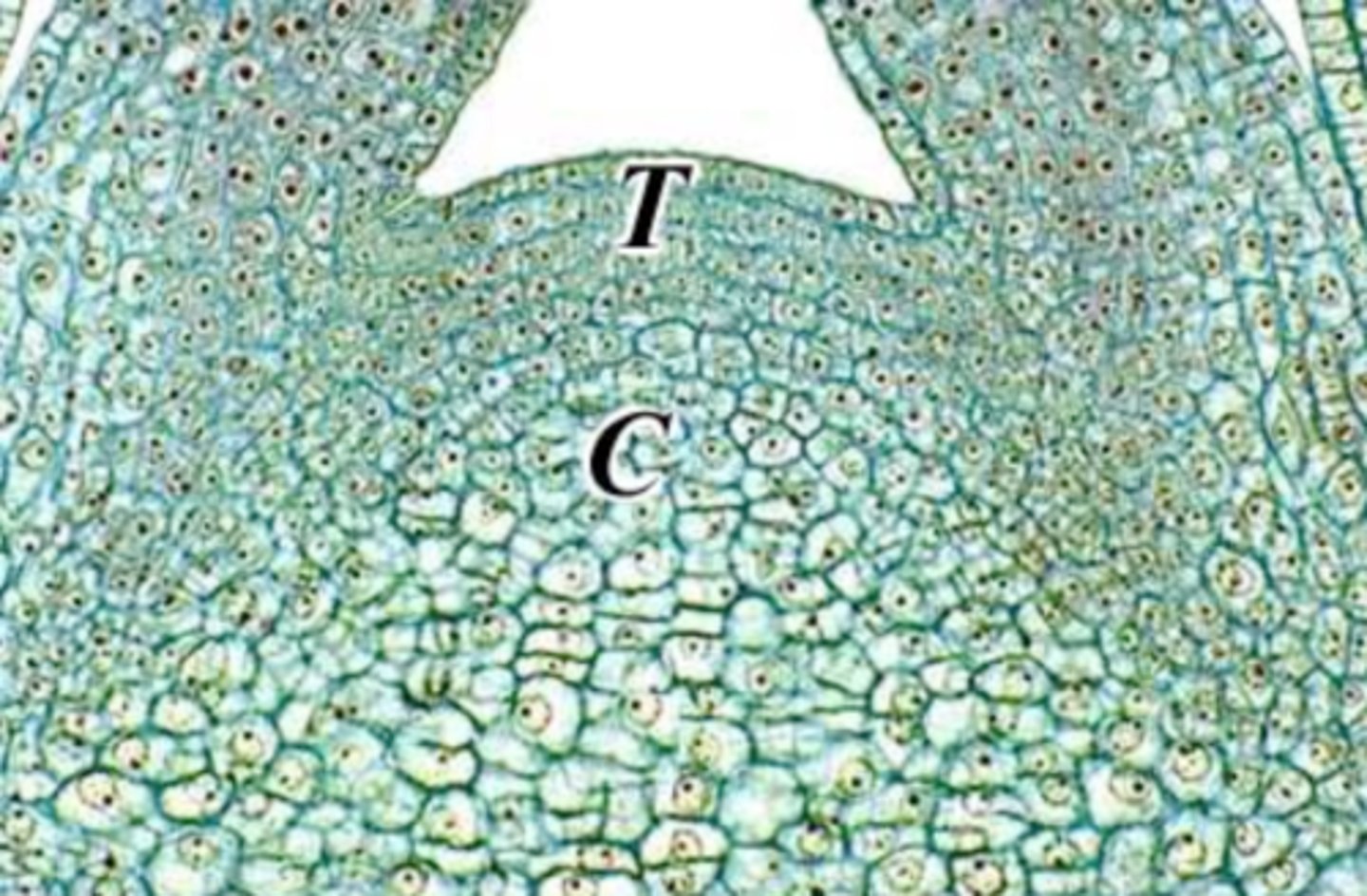
Corpus
adds bulk to the apical meristem by increase in volume (anti + peri)
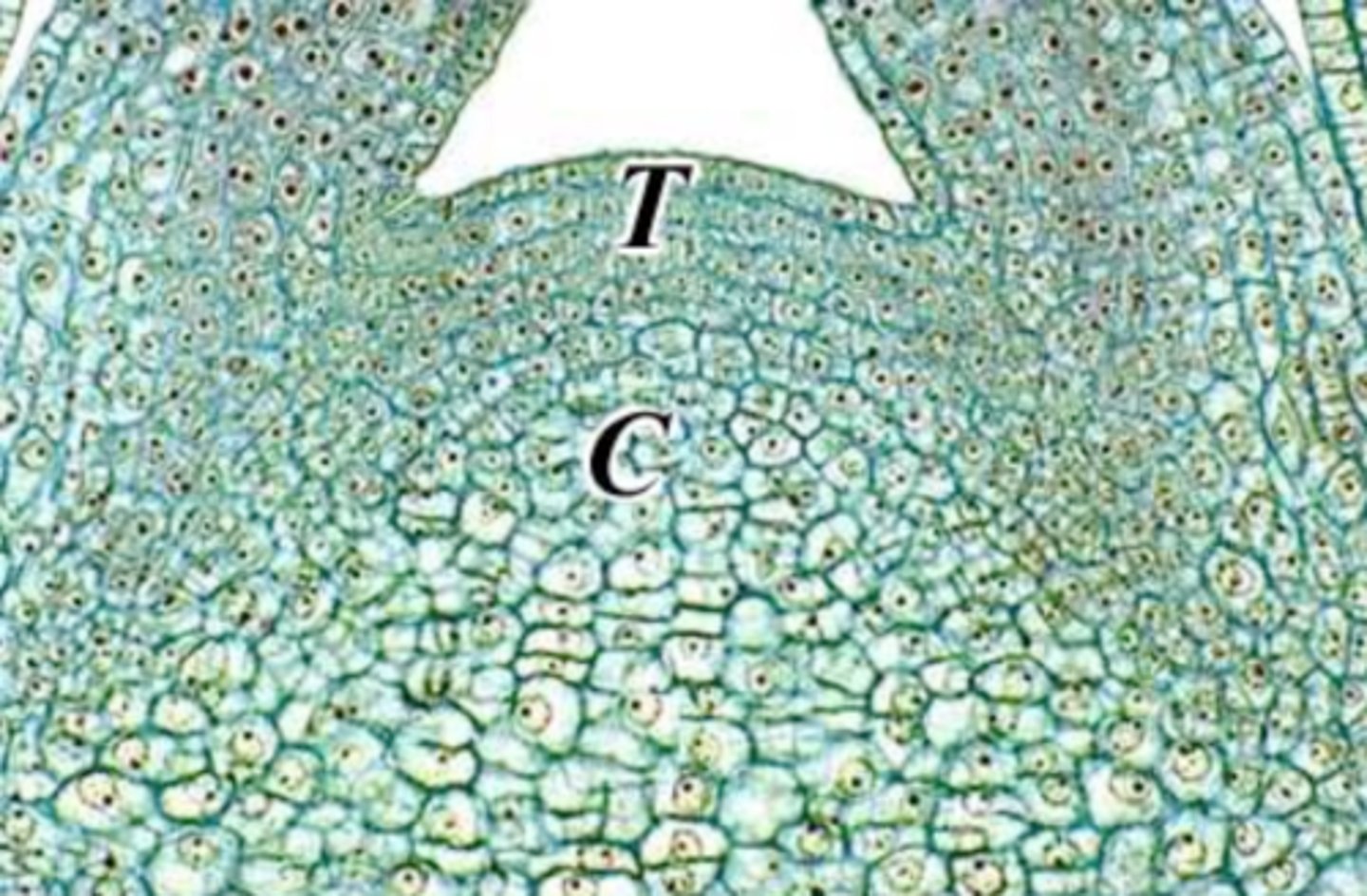
Tunica
surface growth to maintain their continuity over corpus (anticlinal growth)
primordia
develop into all the above ground organs of a plant from shoot apex
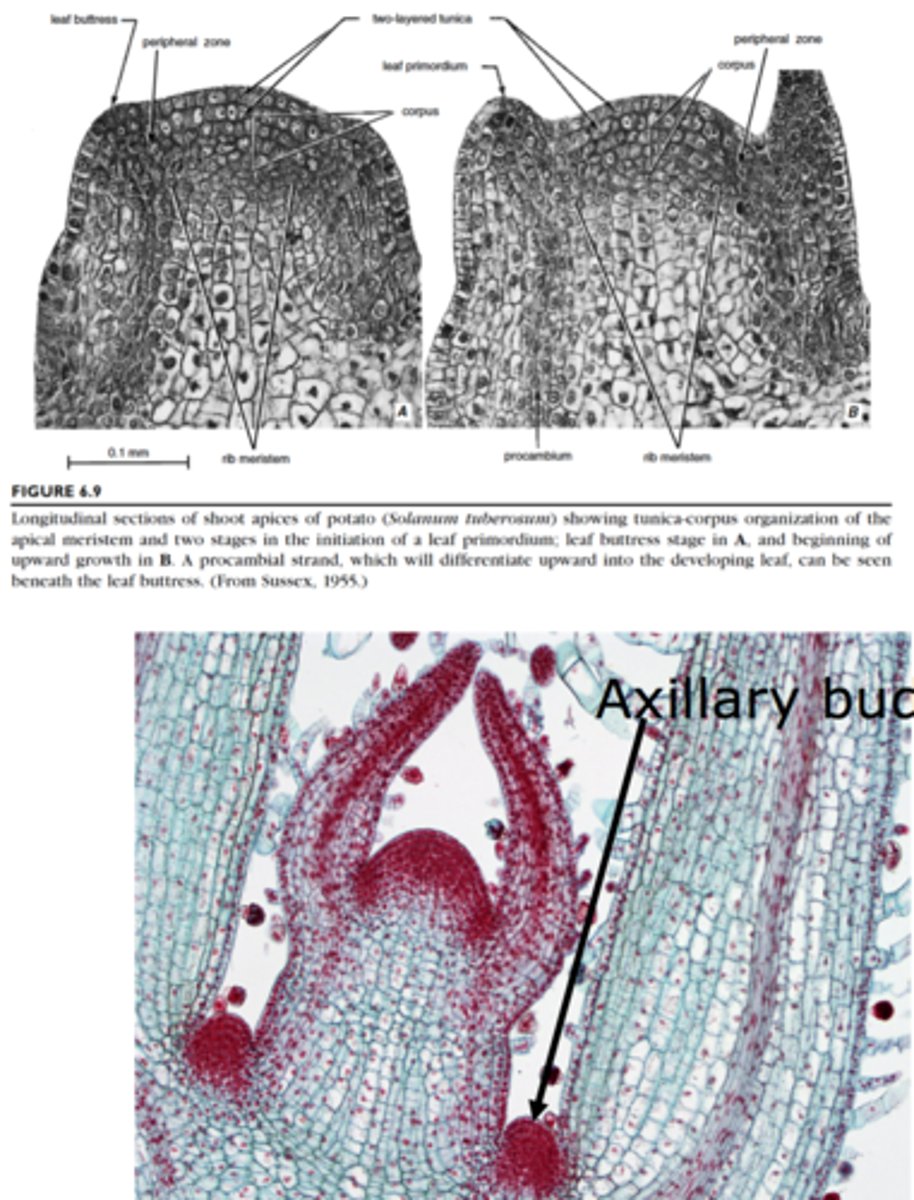
leaf primordia and axillary buds
lateral appendages from shoot apex
primary stem
- Product of the apical meristem
- Tissues include dermal, ground (cortical) and vascular
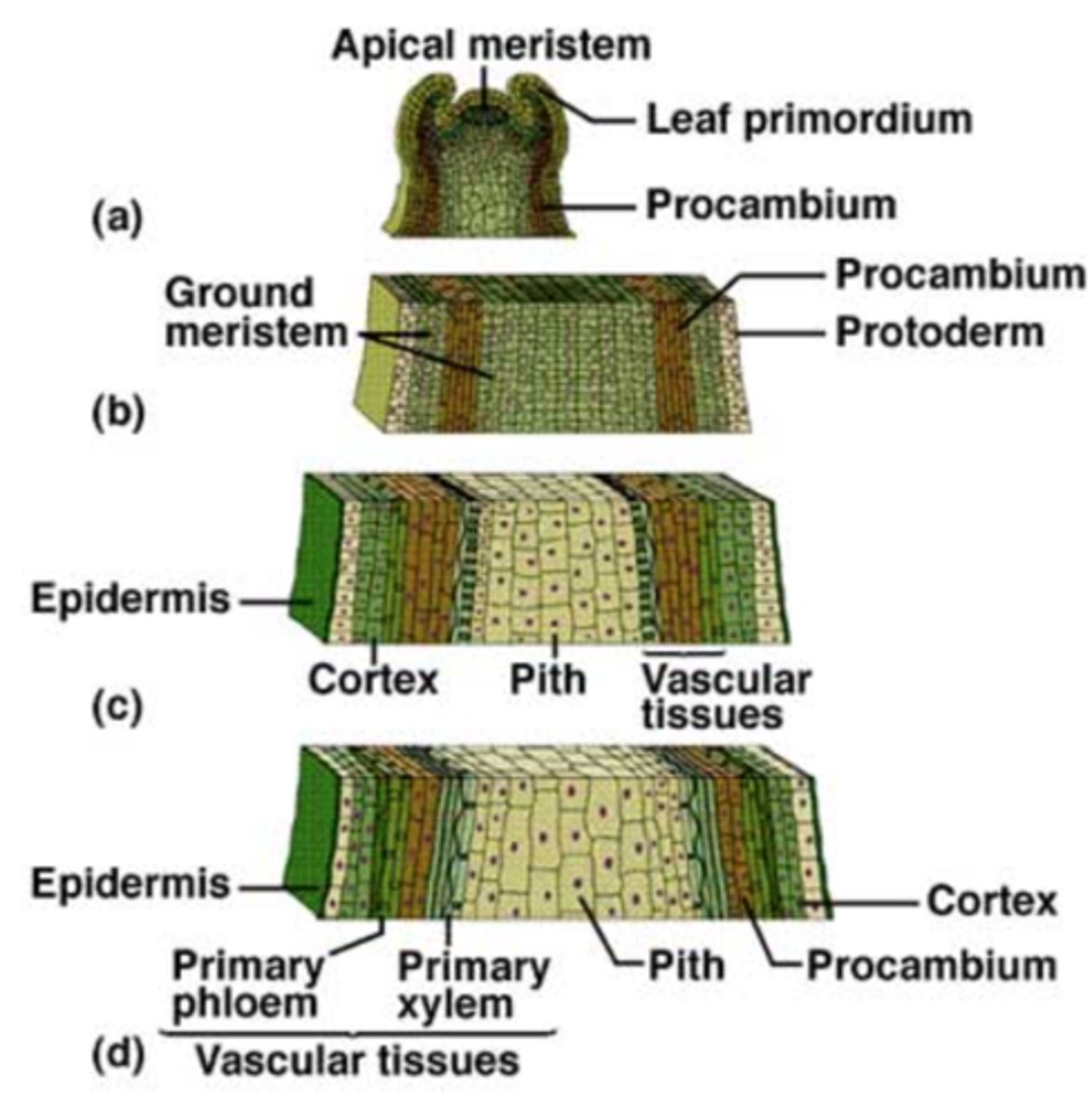
- Epidermis from protoderm via tunica
- Ground tissues: cortex and pith
- Vascular bundles
3 main tissues primary stem
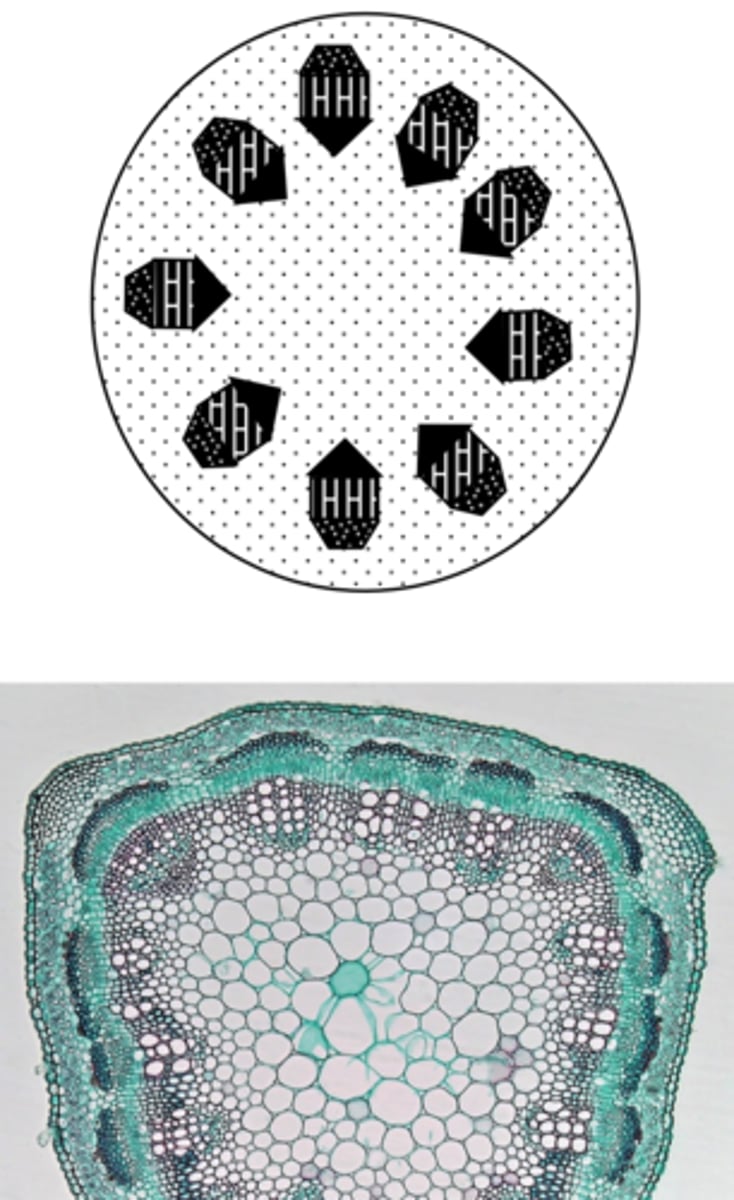
stele
- Primary vascular tissues + associated ground tissues (e.g. pith)
- Central cylinder
protostele
The simplest type of stele, consisting of a solid column of vascular tissue.
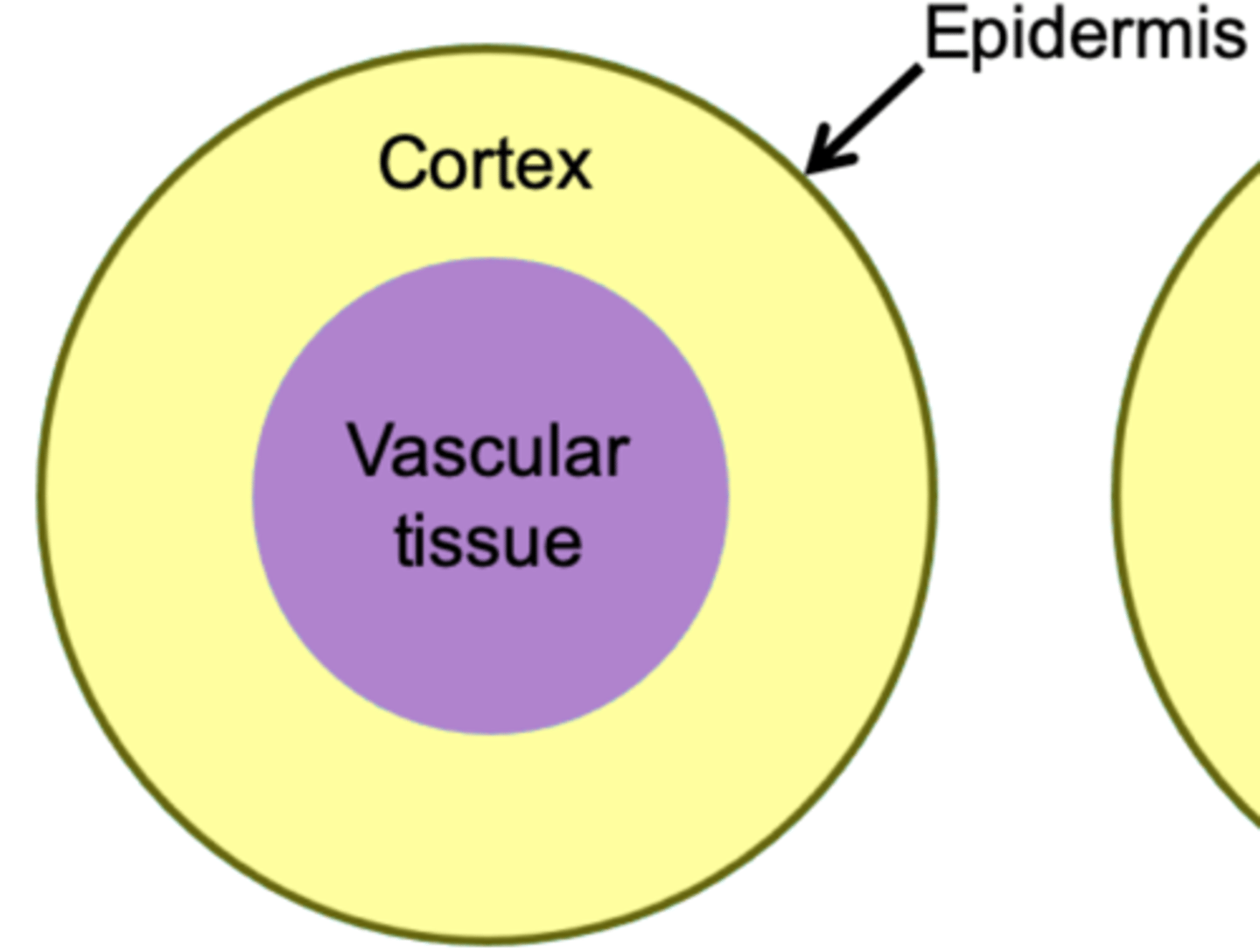
siphonostele
A type of stele containing a hollow cylinder of vascular tissue surrounding a pith.
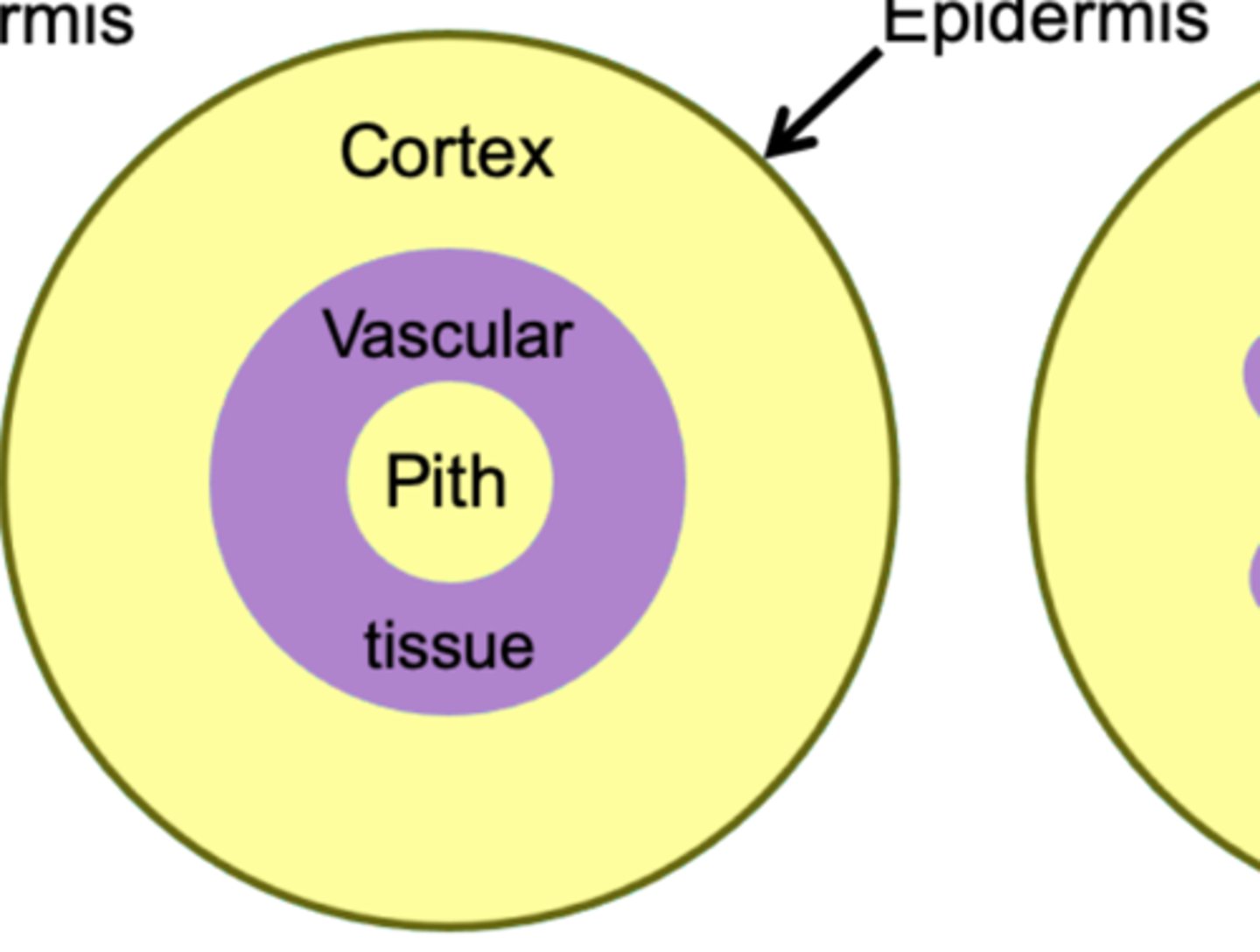
eustele
A stele in which the primary vascular tissues are arranged in discrete strands around a pith; typical of gymnosperms and angiosperms.
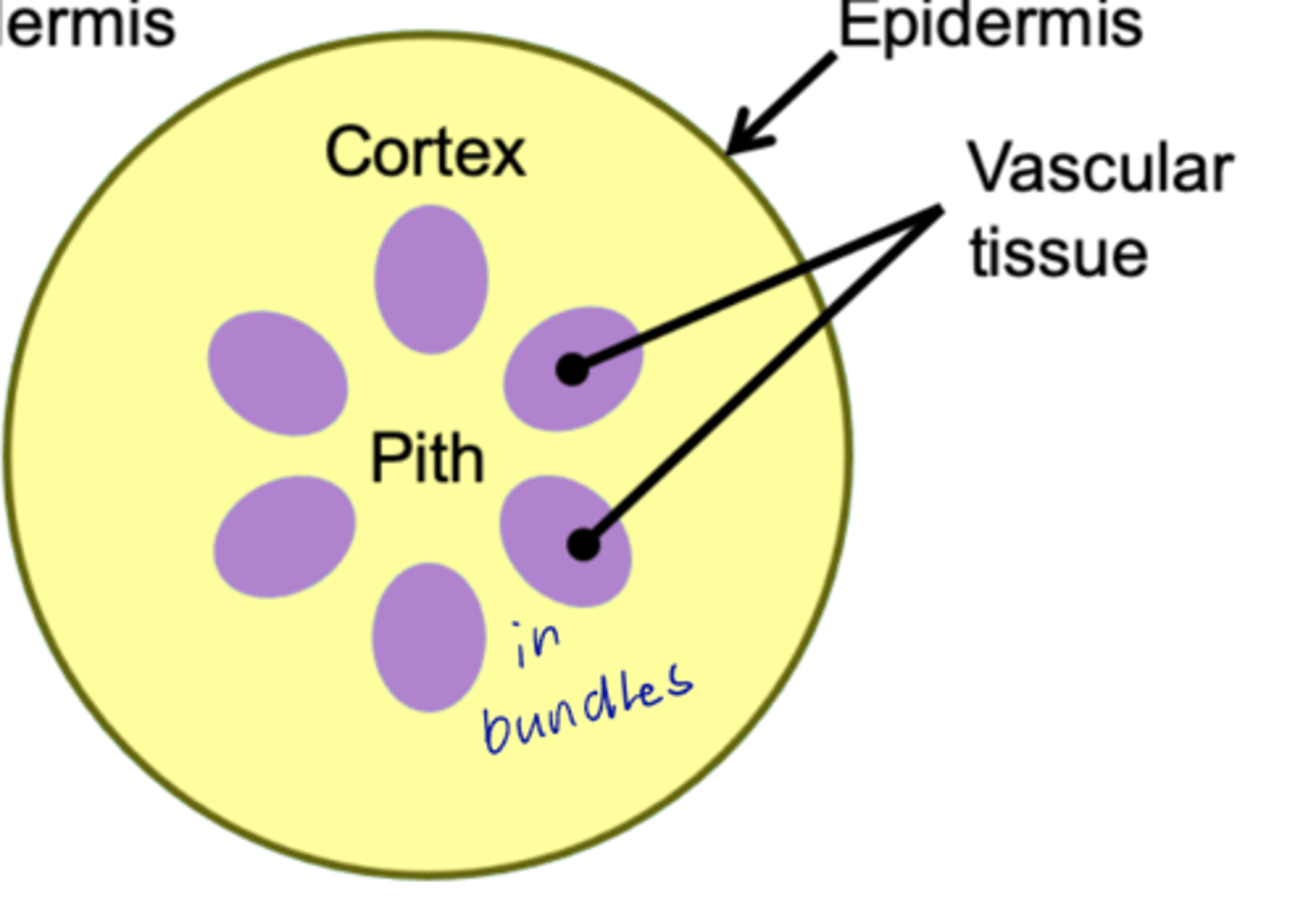
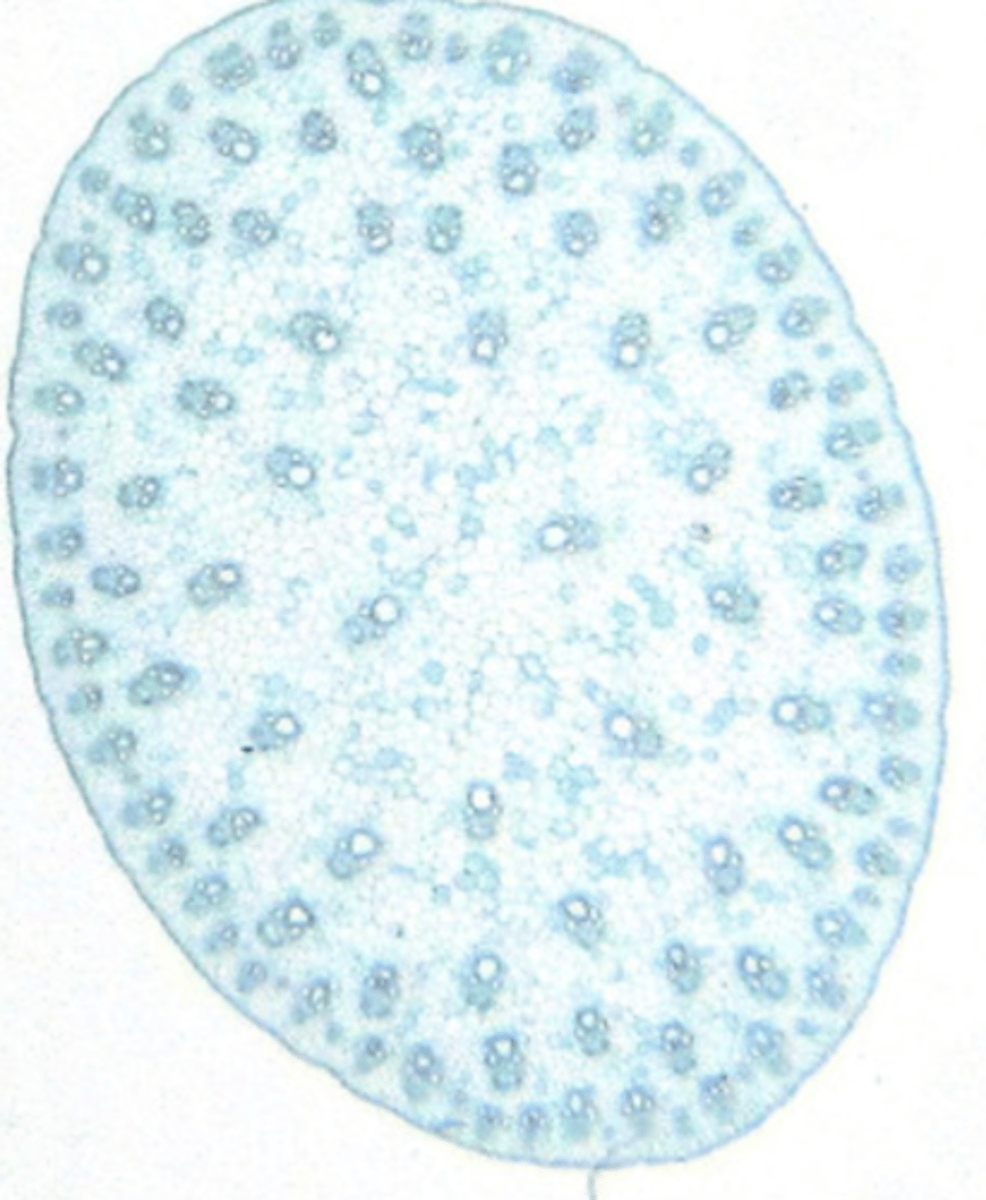
atactostele
- Stem contains a ring of vascular bundles, and then a spiral towards the centre.
- This represents the highest level of development of the vascular system in the stem.
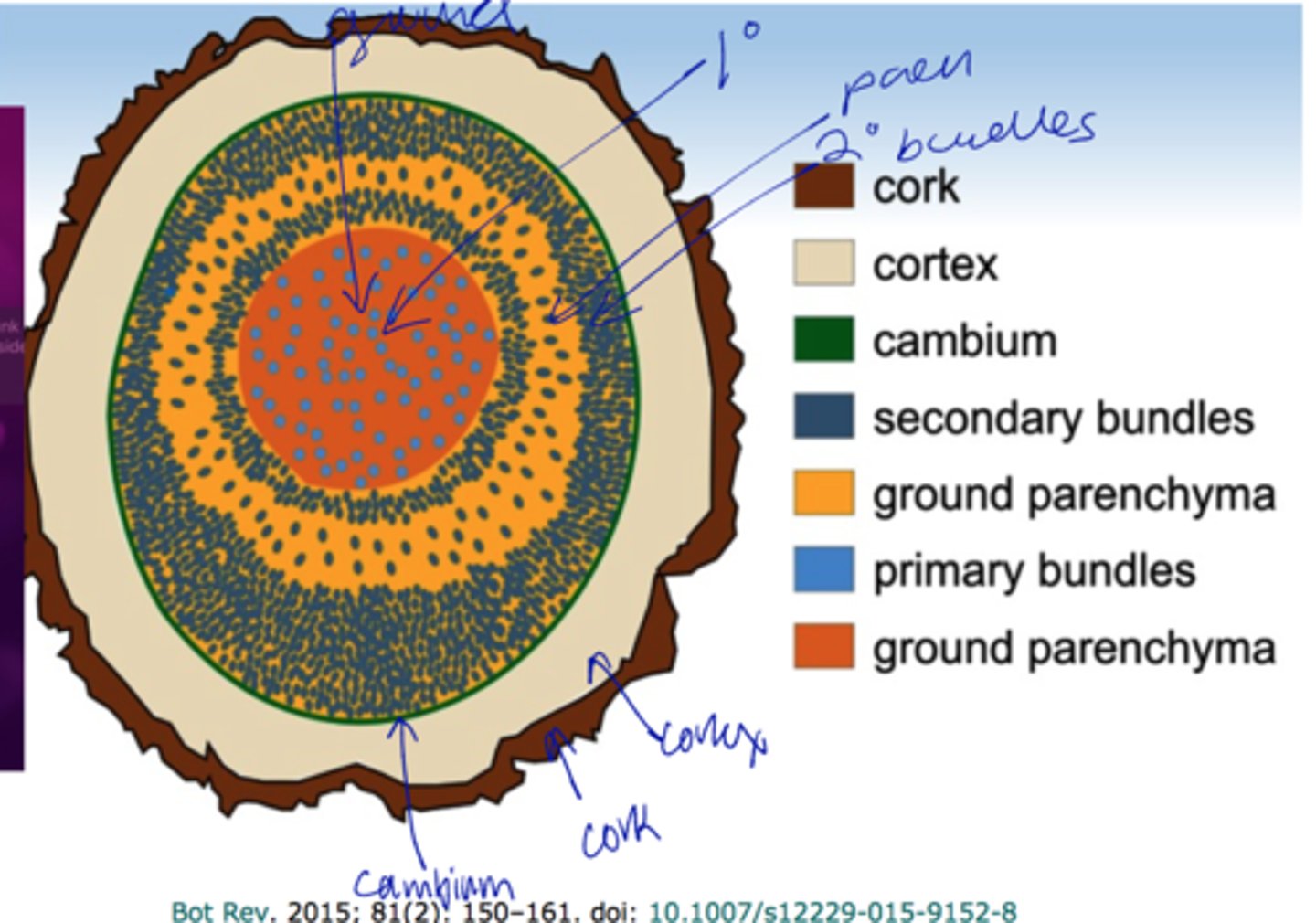
cortex
- betw epi and stele
- Mainly parenchyma (with some collenchyma and sclerenchyma)
- May see aerenchyma in aquatic plants
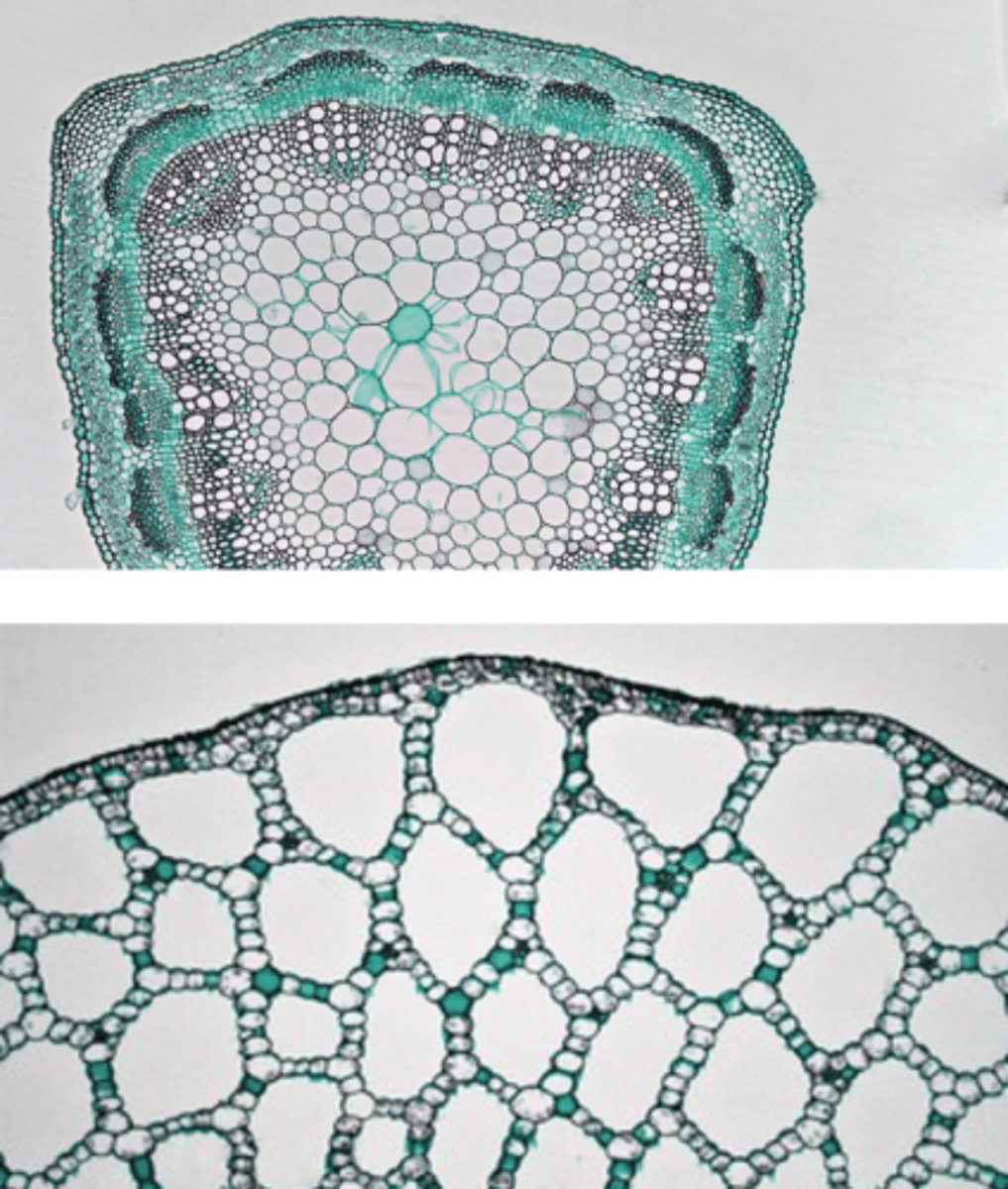
aerenchyma
a soft plant tissue containing air spaces, found especially in many aquatic plants
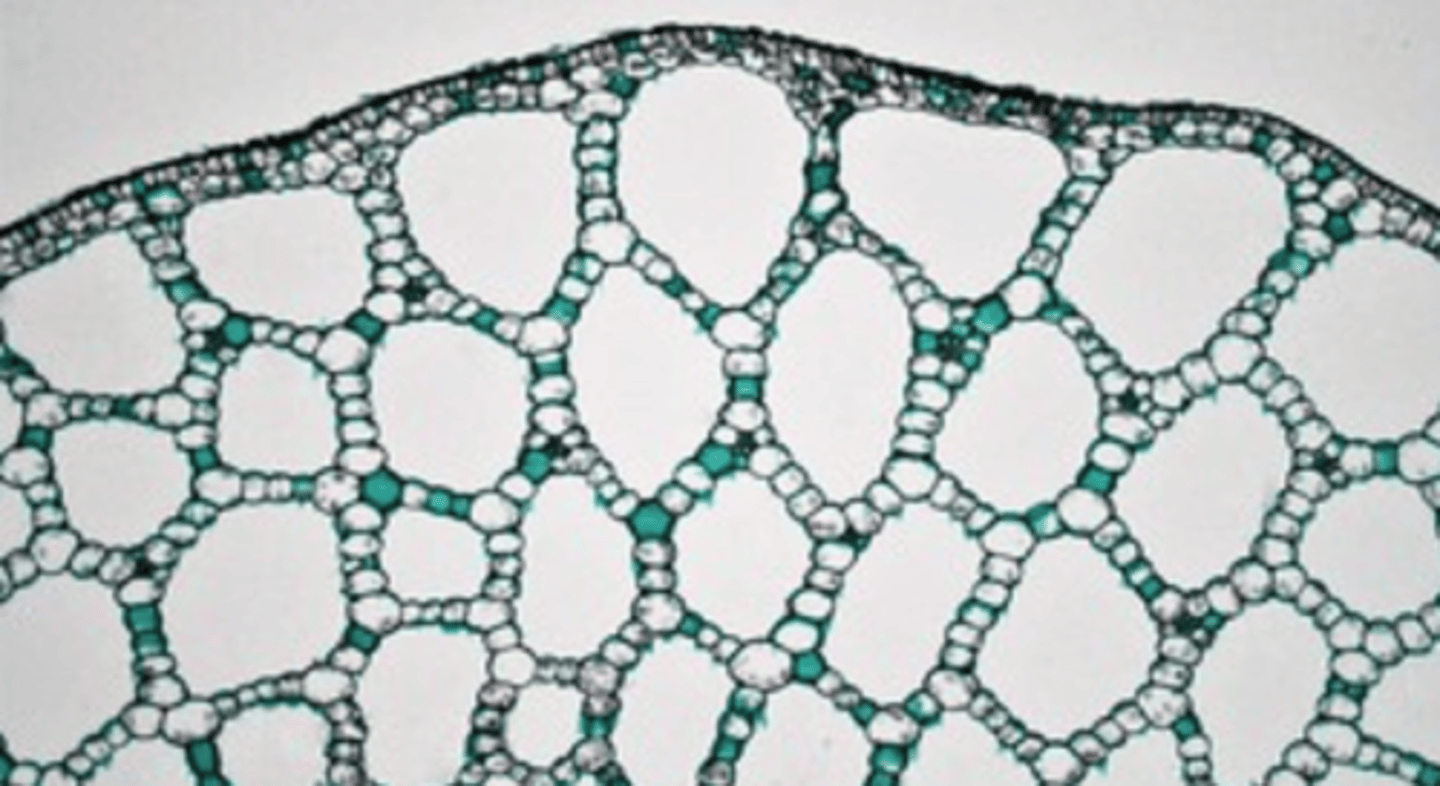
pith
- Internal from vascular tissue
- Typically parenchyma
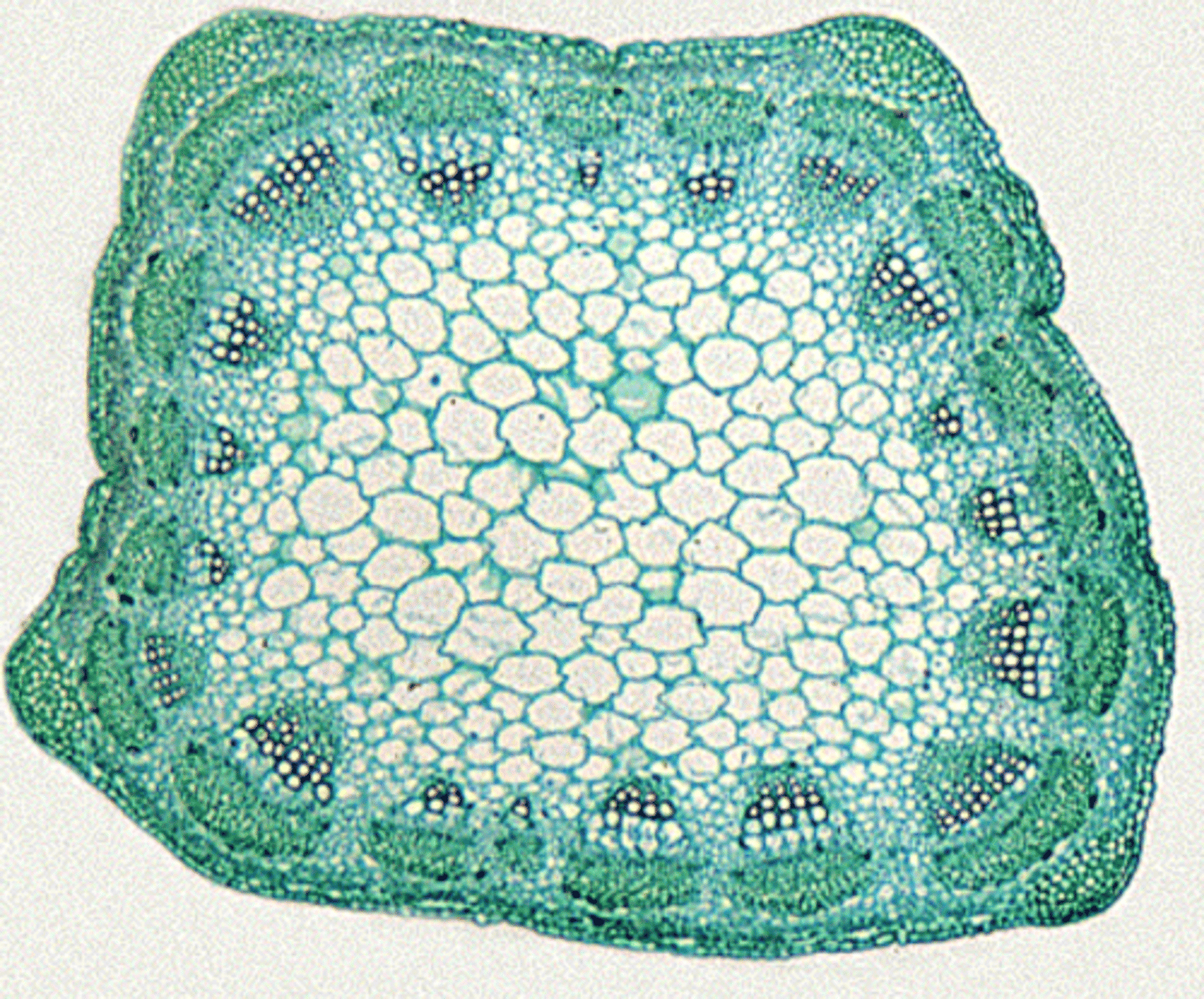
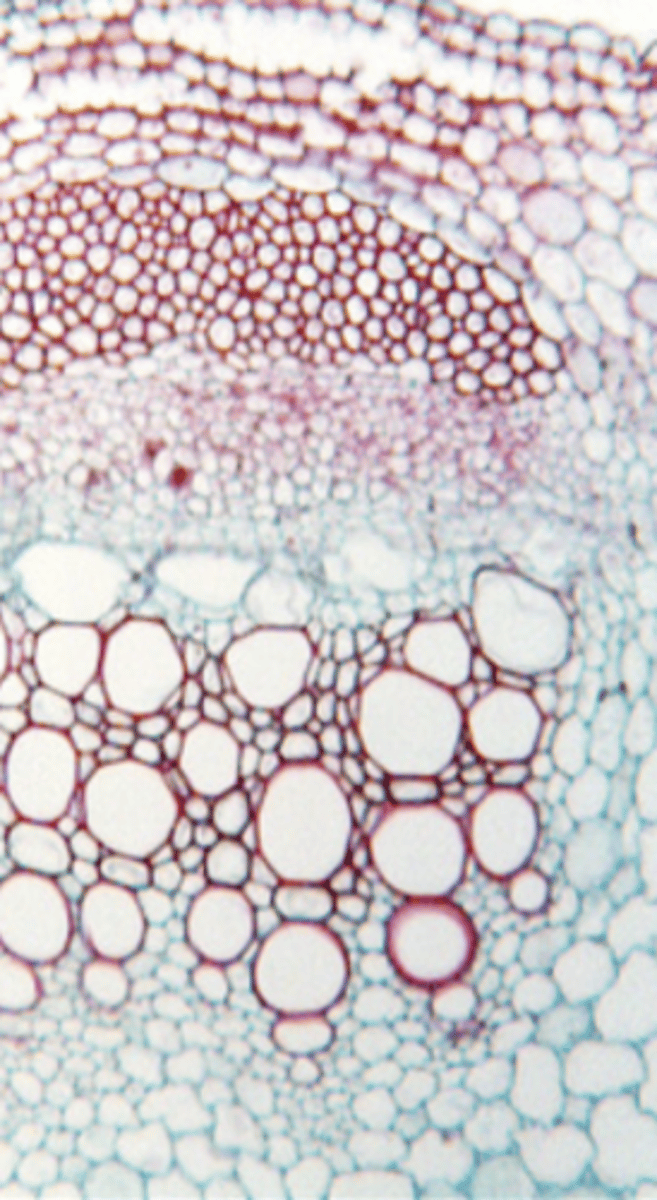
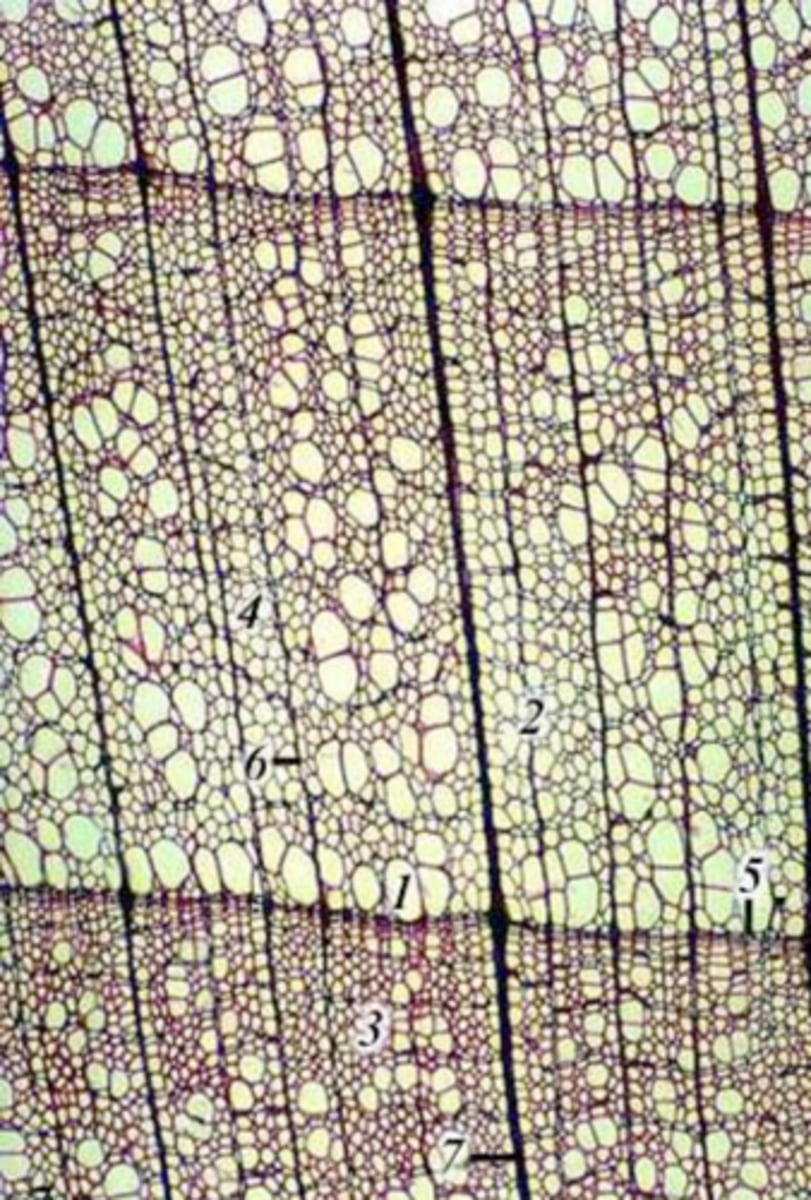
- cortex
- phloem fibers
- phloem
- metaxylem
- protoxylem
- pith
dicot stem parts
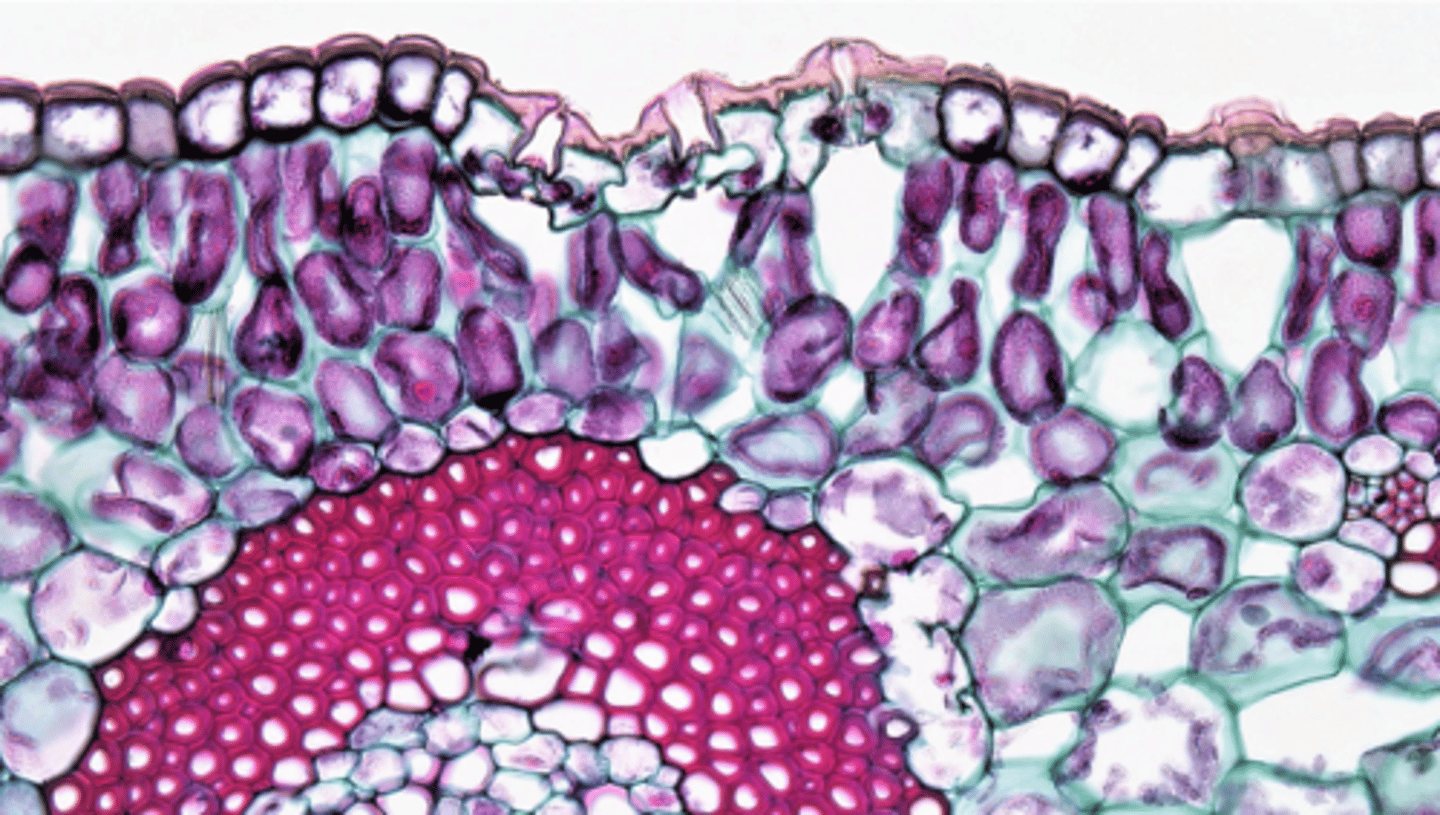
epidermis
- One layer thick with cuticle
- With trichomes
- Presence of stomatal apparatus
procambium
where do the vascular tissues form from
- Endarch pattern
- Protoxylem (first-formed primary xylem) is closer to the center of the axis
- Direction of maturation: centrifugal (younger outside)
Primary xylem differentiation
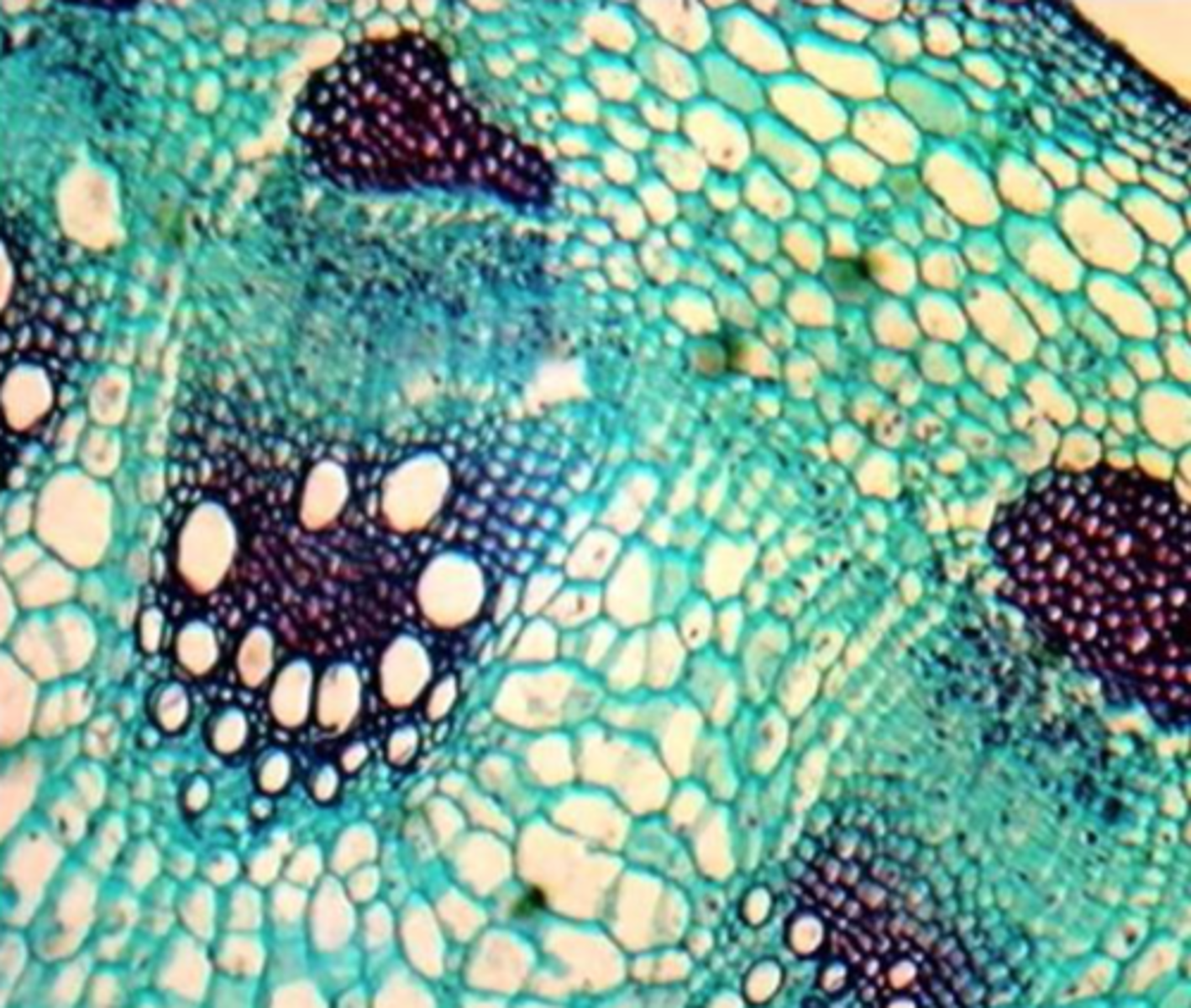
2ndary growth
- Responsible for increase in girth (diameter)
- Allows for much greater size and volume
- Great commercial value (wood and wood products)
- partially procambium
- IF parenchyma that dedifferentiates (mature --> meri)
kaya di siya TRUE secondary meristem
origin of vascular cambium
2ndary phlo and xy
products of vascular cambium
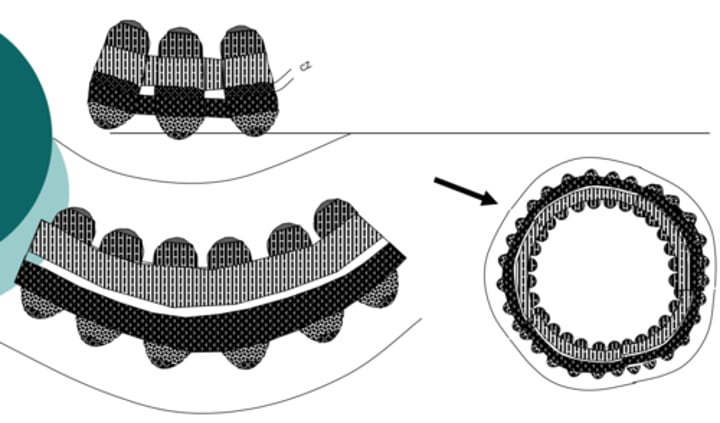
fascicular cambium + interfascicular cambium = vascular cambium
1. Development commences at the fascicular cambium (procambium in the vasc bundles)
2. Secondary xylem and phloem are produced by the fascicular cambium
3. The interfascicular regions begins to develop a cambium (interfascicular parenchyma --> interfascicular cambium thru dedifferentiation)
4. A widening band of secondary vascular tissue results.
5. The ring of secondary tissue is Complete. The interfascicular and fascicular cambia together form a vascular cambium
development of vascular cambium
does not activate, thus does not produce new phloem or xylem tissues
IF cambium in herbaceous stems
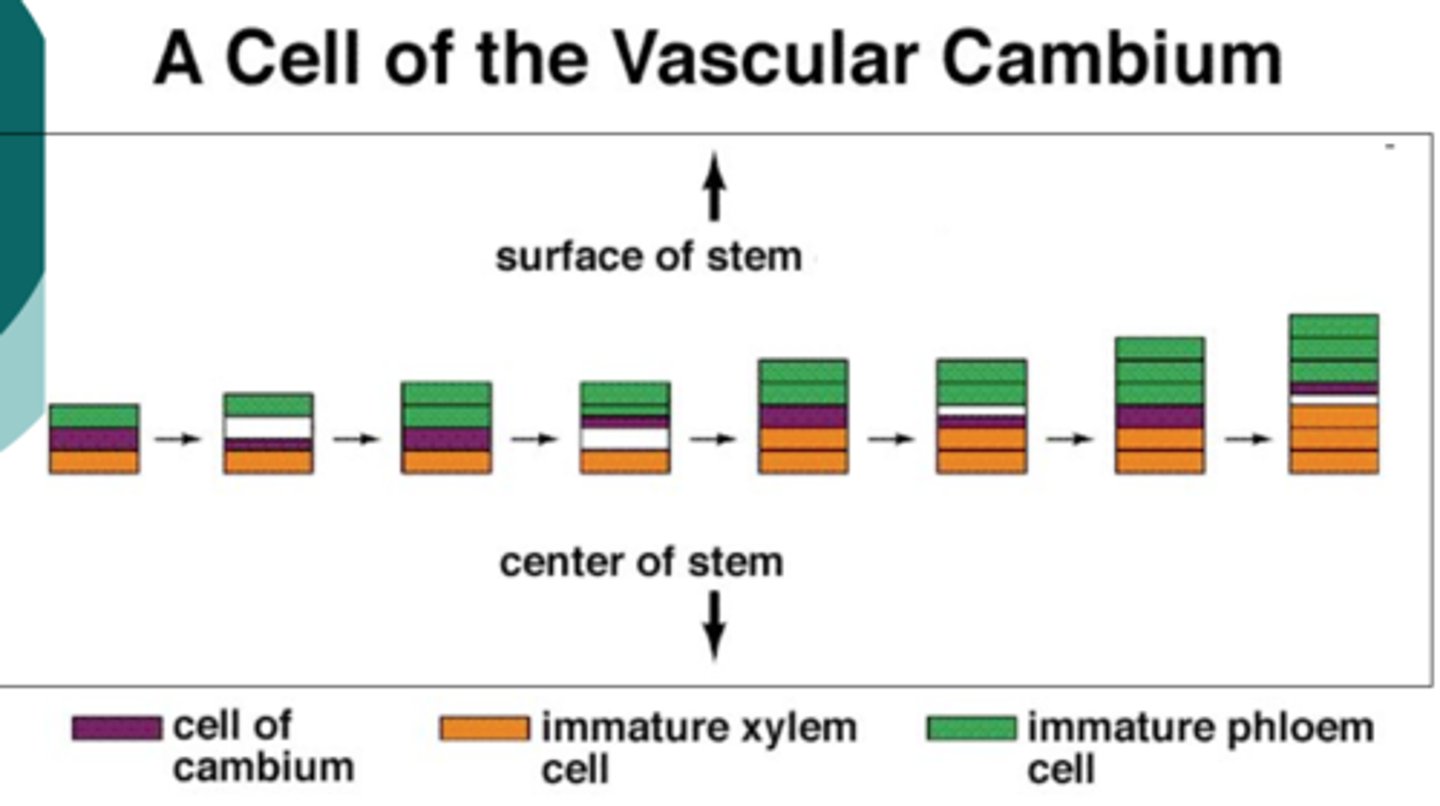
cell grows in volume; periclinal
- New xylem cells are formed inwardly
- New phloem cells are formed outwardly
activity of functional vascular cambium
- cortical parenchyma
- parenchyma of 1 and 2 phloem
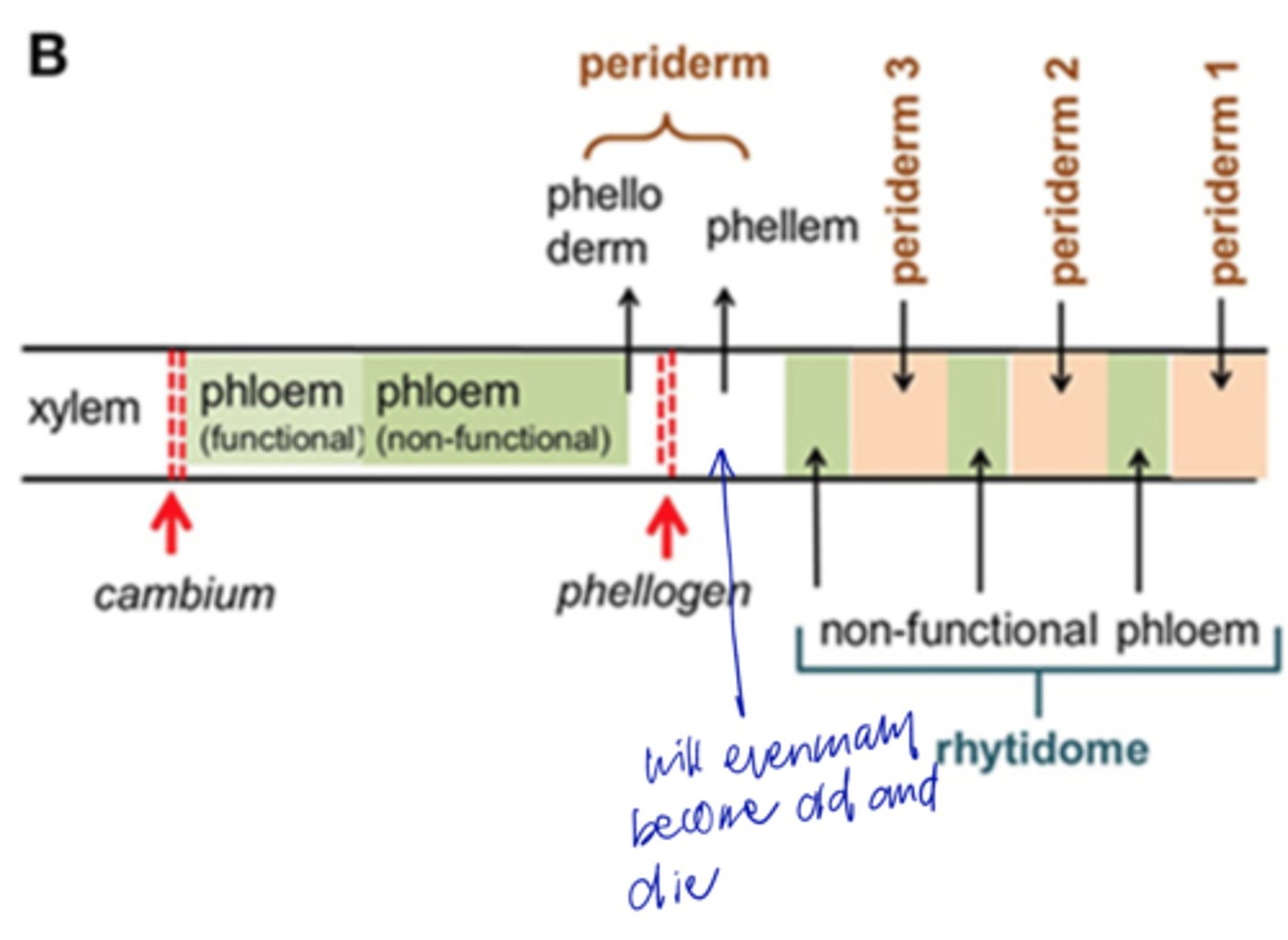
origin of cork cambium (phellogen)
cork (phellem) outside, phelloderm inside
products of cork cambium (phellogen) to form periderm
- secondary tissue
- replaces epidermis in roots and stems
- consists of phellem, phellogen, and phelloderm
periderm definition
- corky tissues
- non-living suberized cells to lessen water loss
- produced by the cork cambium (phellogen) to outside of stem
- produced more than phelloderm
phellem (cork) definition
- parenchyma-like cells
- produced toward inside of stem by the cork cambium (phellogen)
Phelloderm definition
1. increase in diameter of the stem occurs due to activity of vascular cambium
2. causes the protective epidermis to crack and split open
3. layer of cork cambium forms outside of the phloem
4. cylinder of cork cambium increases in diameter as stem increases in diameter
Forming the Periderm
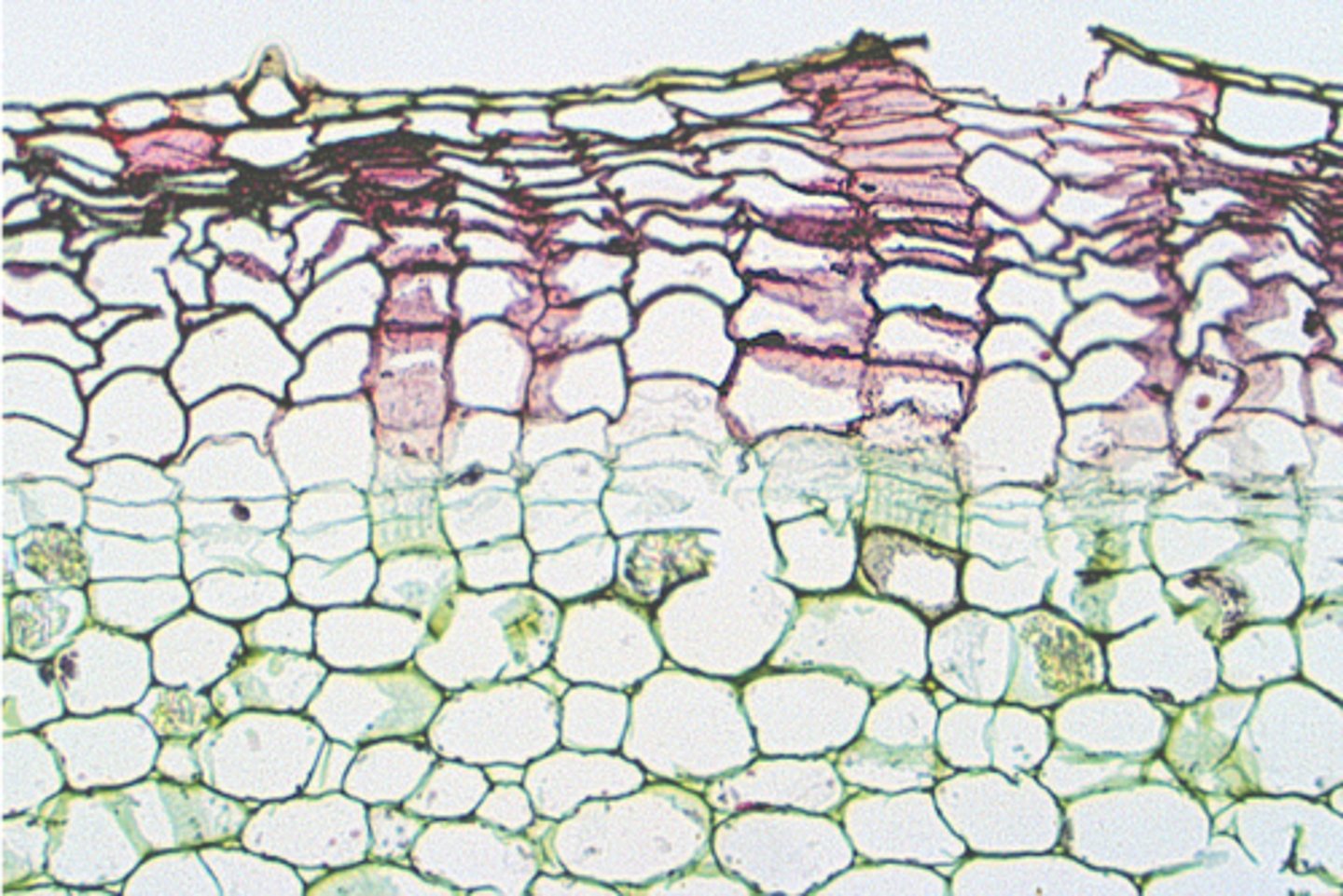
As the layers of cells outside the vascular cambium die, they are sloughed off as bark
bark definition
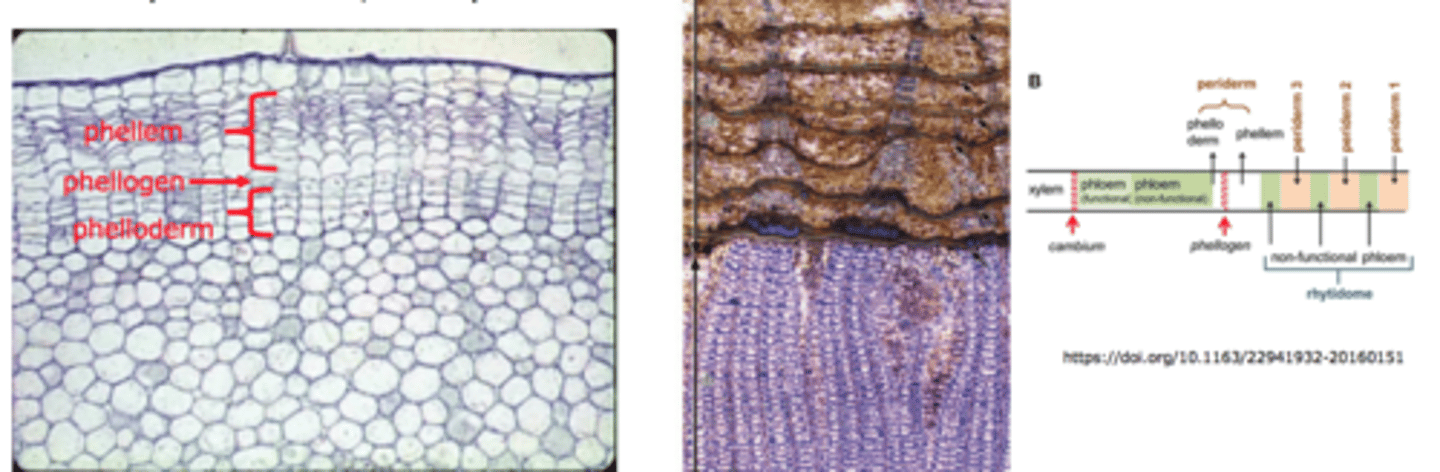
epidermis, cork, cork cambium, phelloderm, cortex, and phloem
In the young stem the bark contains
cork, cork cambium, phelloderm, and phloem
In the old stem the bark contains
a. Cortical cells just under the epidermis become meristematic
b. Produces a layer 1-2 cells thick of cork cambium called phellogen
cork formation in the young stem (1 year old or less)
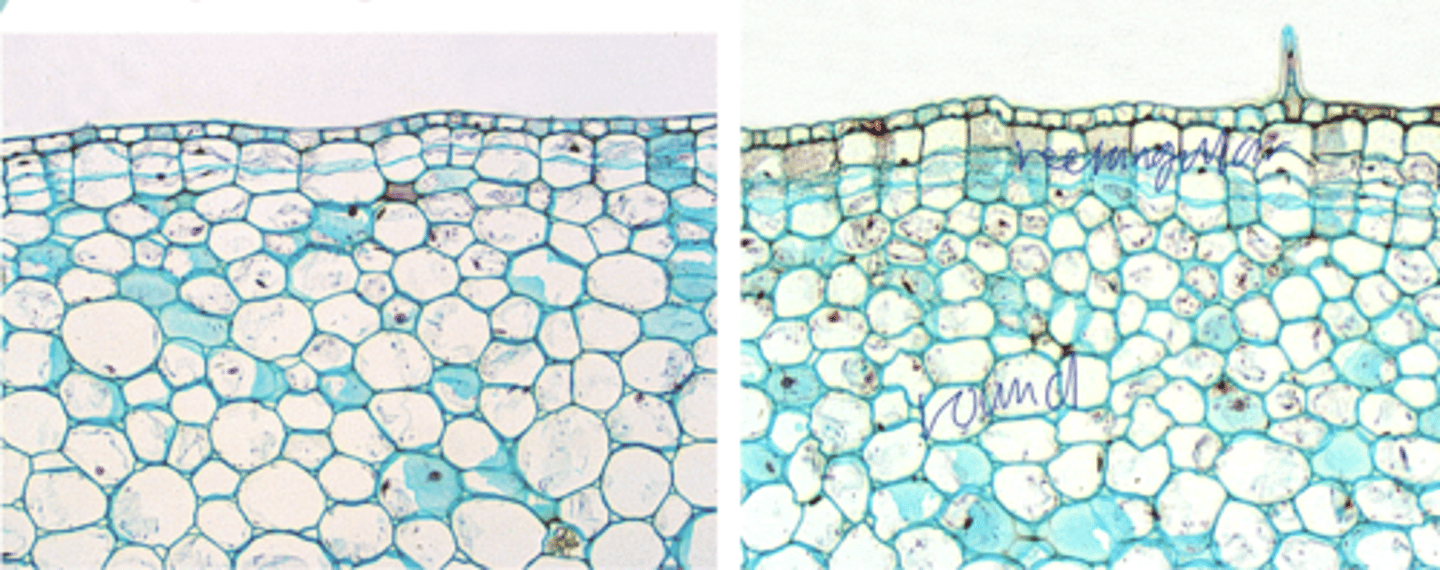
- Cork cells are flattened and cell walls contain suberin, a waxy substance
- new cambium forms because the former phellogen dies as it is crushed by expanding xylem
- forms in the outer region of the still-living phloem
- reforms every ~ 1 to 4 years depending upon the species of tree
cork in old stems (more than 1 year old, generally 3-4 years)
- cork is generally impervious to fluids and gases
- Special structures for gas exchange required to provide oxygen to the living cells of the secondary growth region, loose arrangement of cells
Lenticels definition
composite of dead phloem cells and old periderm layers (aging of bark)
rhytidome definition
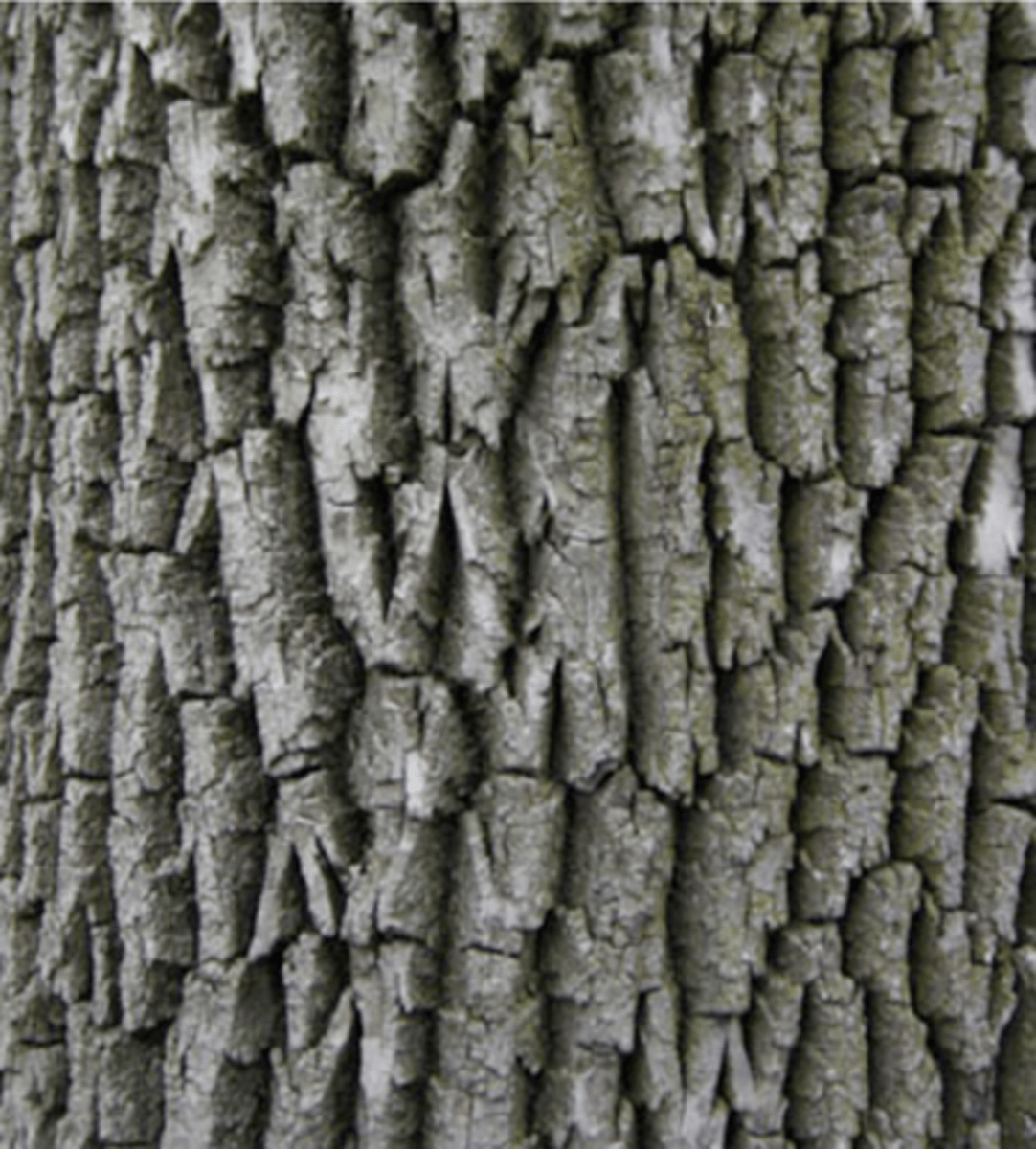

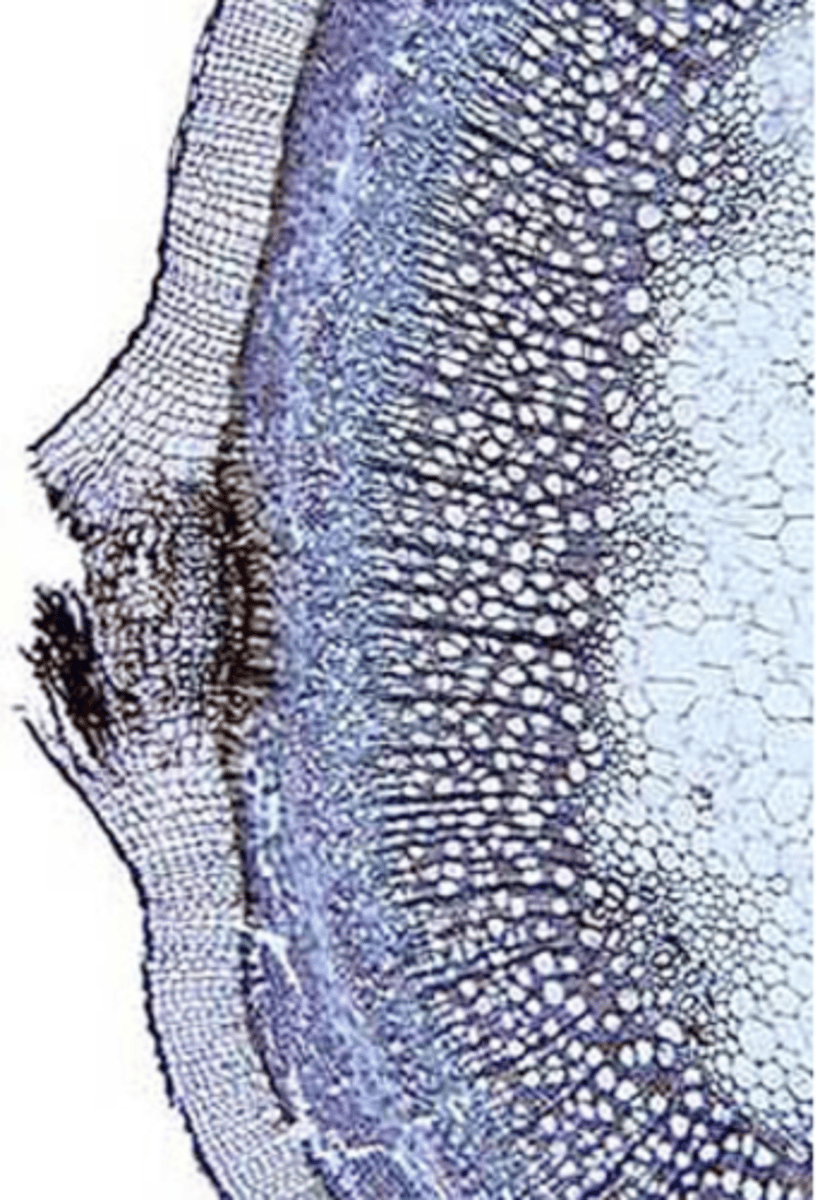
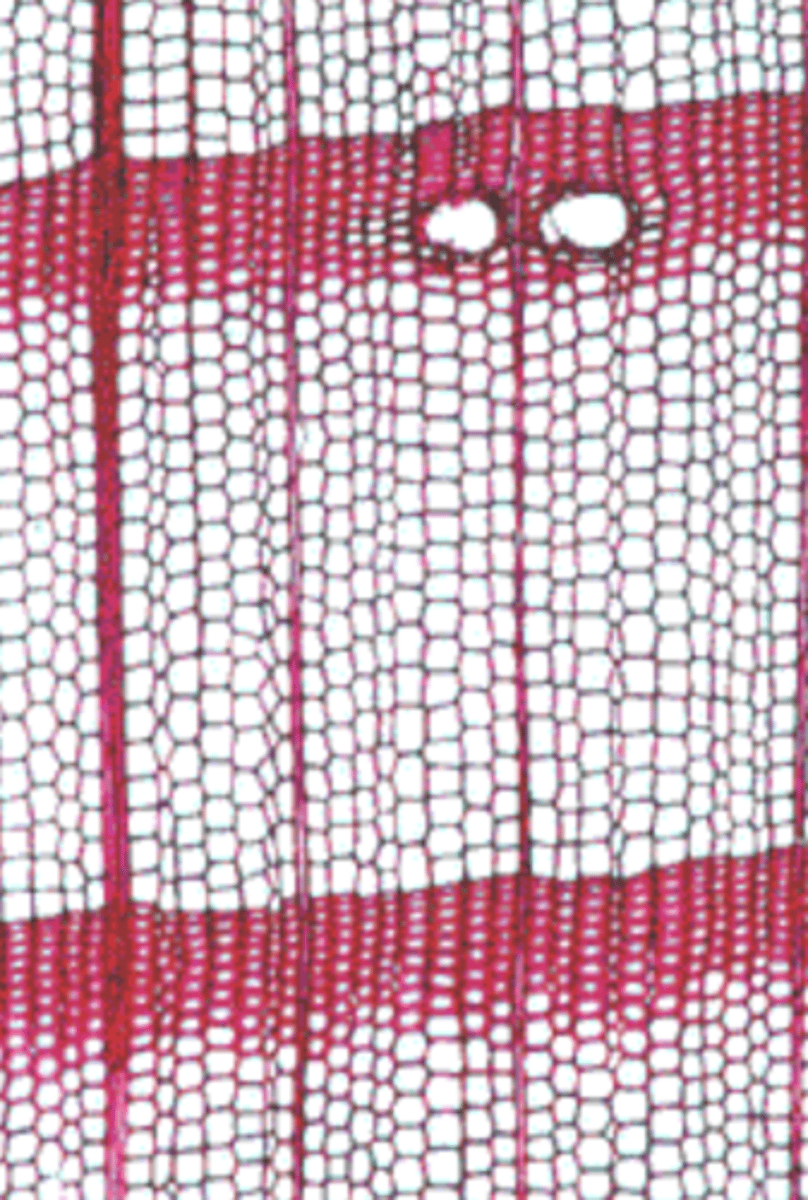
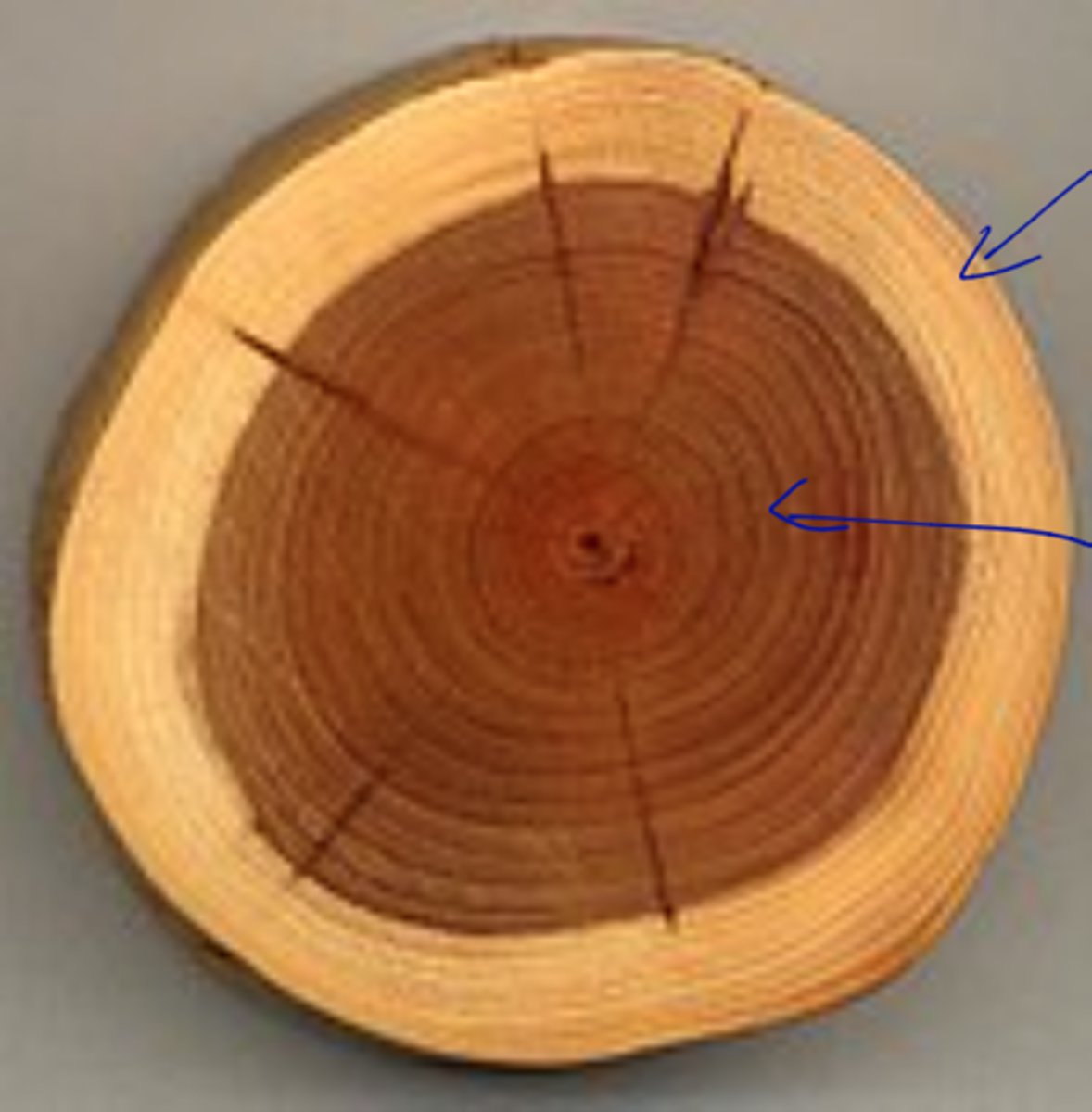
- active in spring and tapers in summer, ceasing in fall
- determine age of stem because texture of spring and summer cells is different
growth/annual rings

larger vessels (larger diameter compared to to tracheids), more porous, fewer and smaller rays
spring/early wood
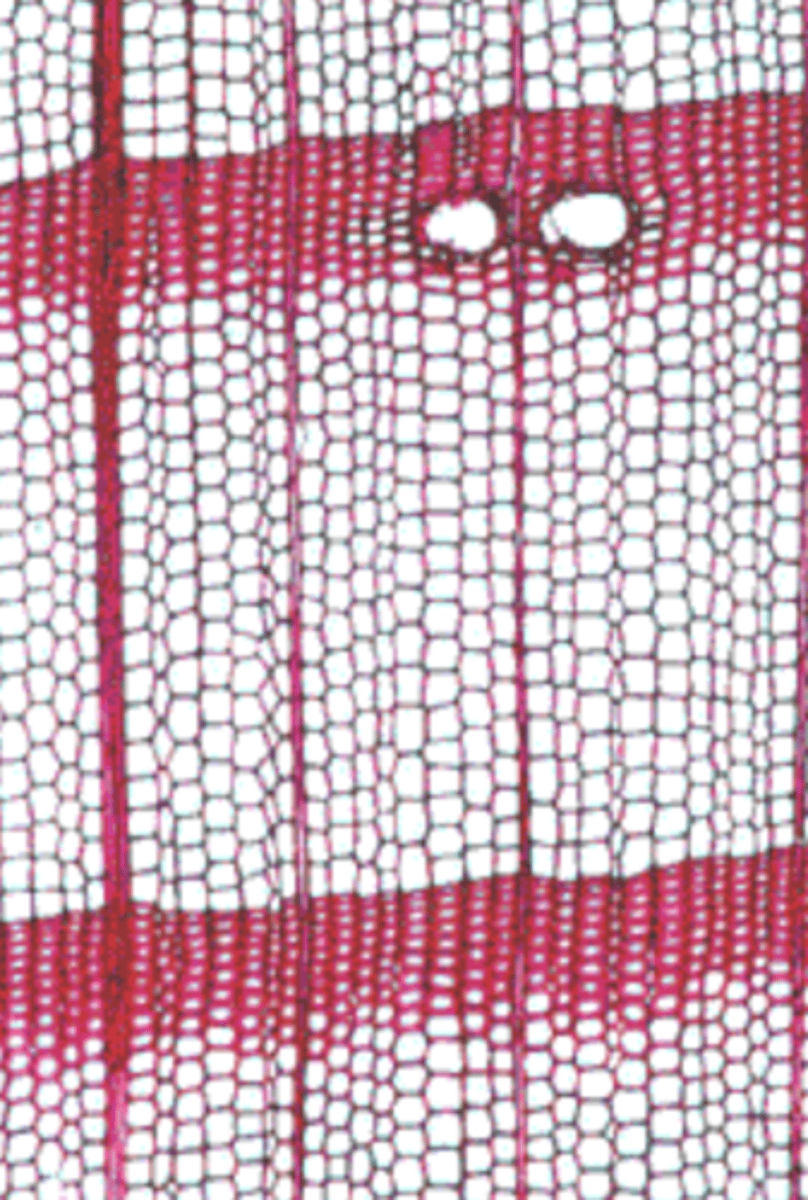
denser, smaller cells, thicker walls
summer/late wood
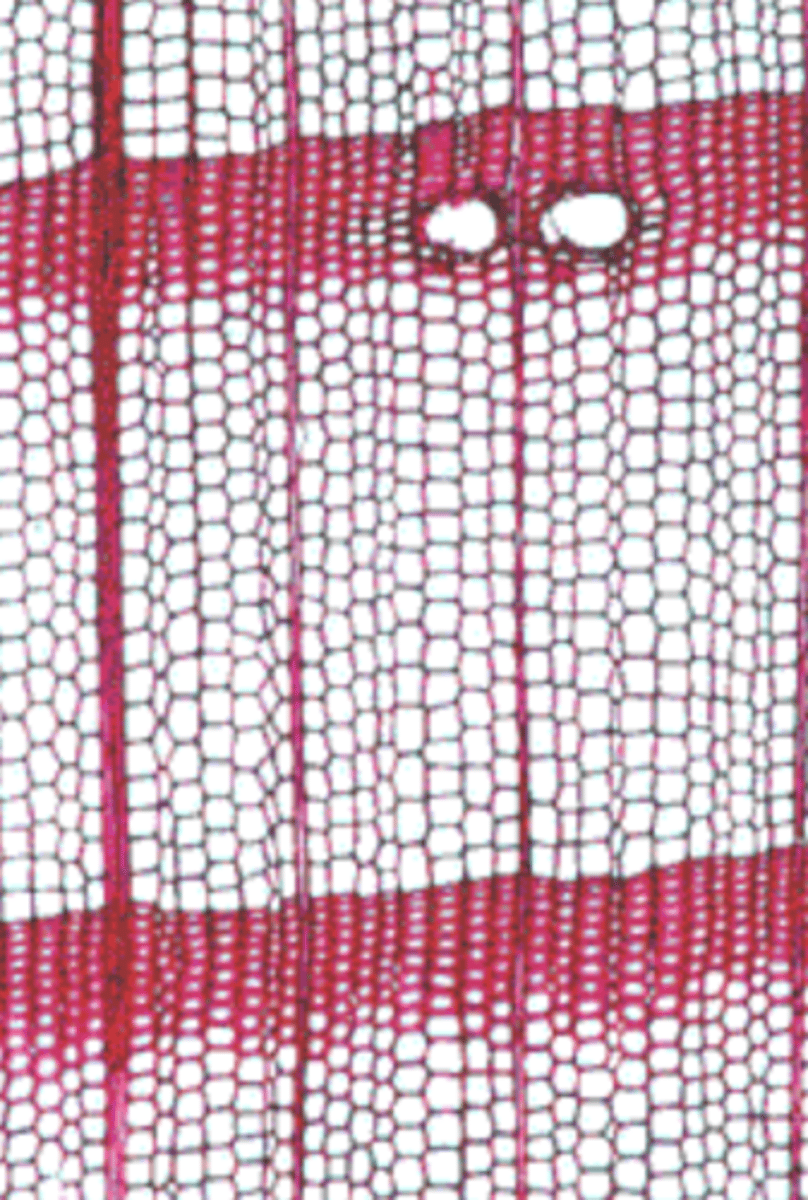
gymnosperm (conifers) bc it has resin ducts and only tracheids
gymnosperm or angiosperm?
- dump site for tree's waste prod.
- can rot away, leaving a hollow core filled with a variety of substances (oils, gums, resins, tannins)
- darker, denser more durable
- support a tree
heartwood definition
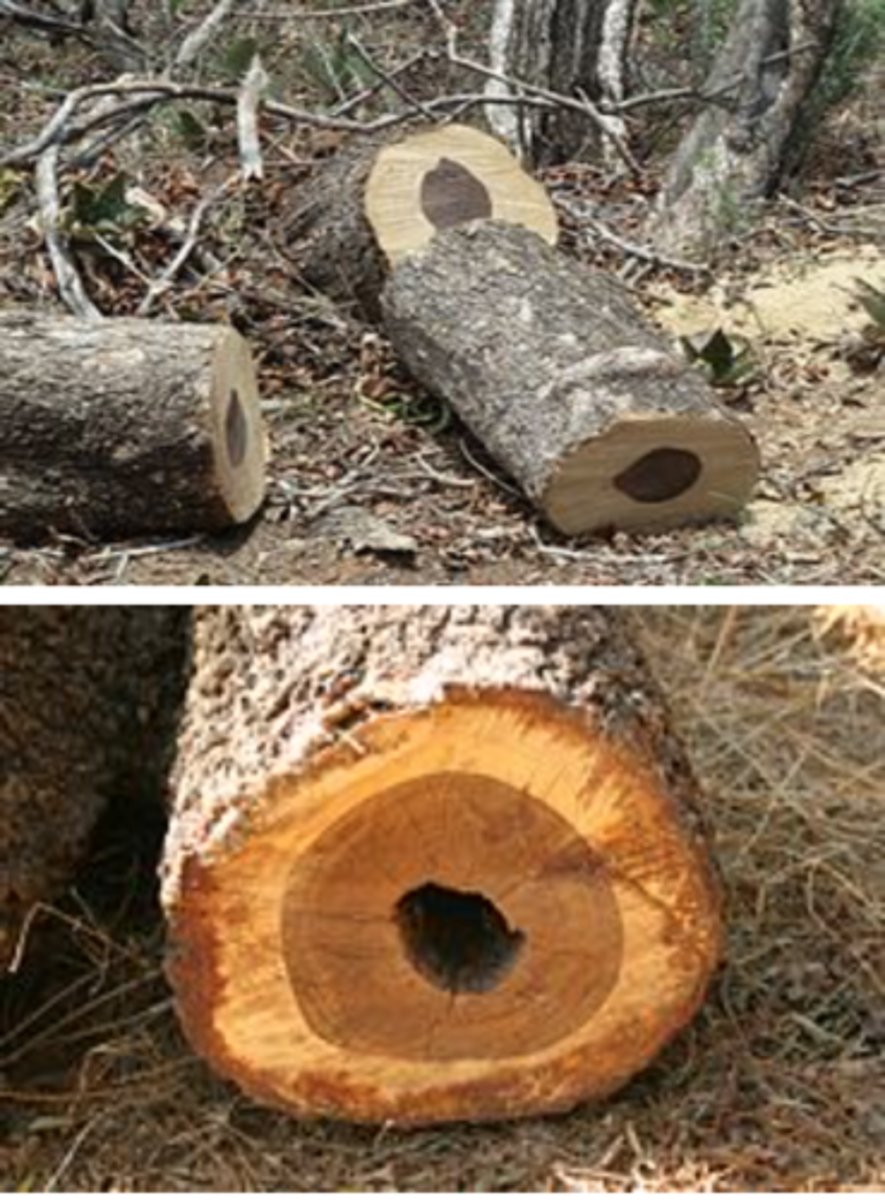

- functioning xylem toward the exterior
- usu. light, pale & weak
sapwood definition

softwood
Conifers (gymnosperms) are often any called
pine, spruce, fir, cypress, redwood
examples of conifers
- only tracheids, no vessels
- minimal parenchyma (appears more uniform)
- prominent bordered pits along their walls
conifers/softwood description
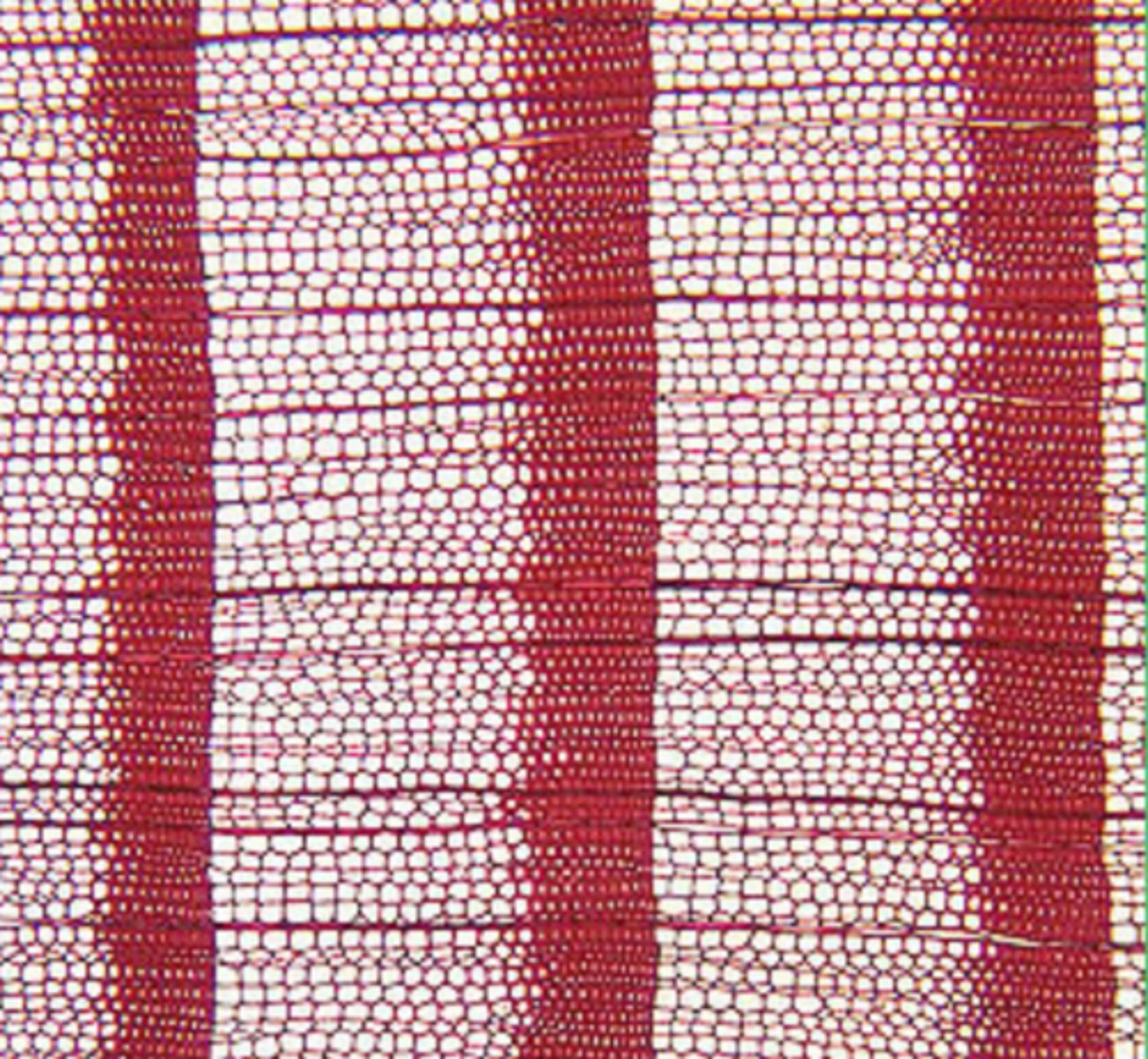
- conifers
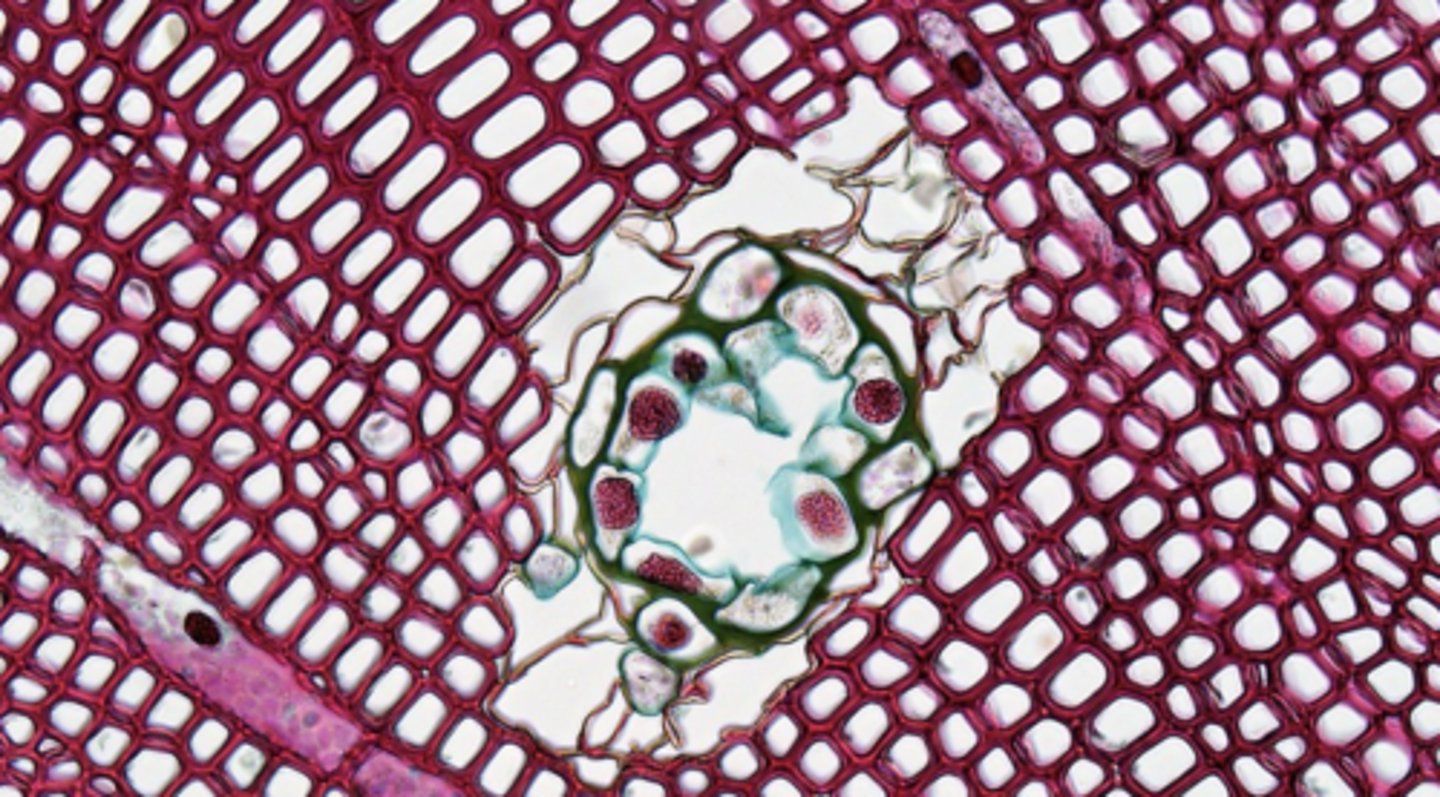
- lined by a ring of parenchyma cells.
- defense mechanism
Resin ducts (or canals)
- Comprised of vessels, fiber and parenchyma rays
- Frequently referred to as hardwood (but has no real meaning in terms of strength)
- Larger diameter vessels, and more numerous fibers
dicot/angiosperm wood description
oak, maple, birch, mahogany
dicot/angiosperm wood examples
- Most monocots are small and herbaceous
- Generally lack secondary growth bc no vascular cambium
Secondary Growth in Monocots

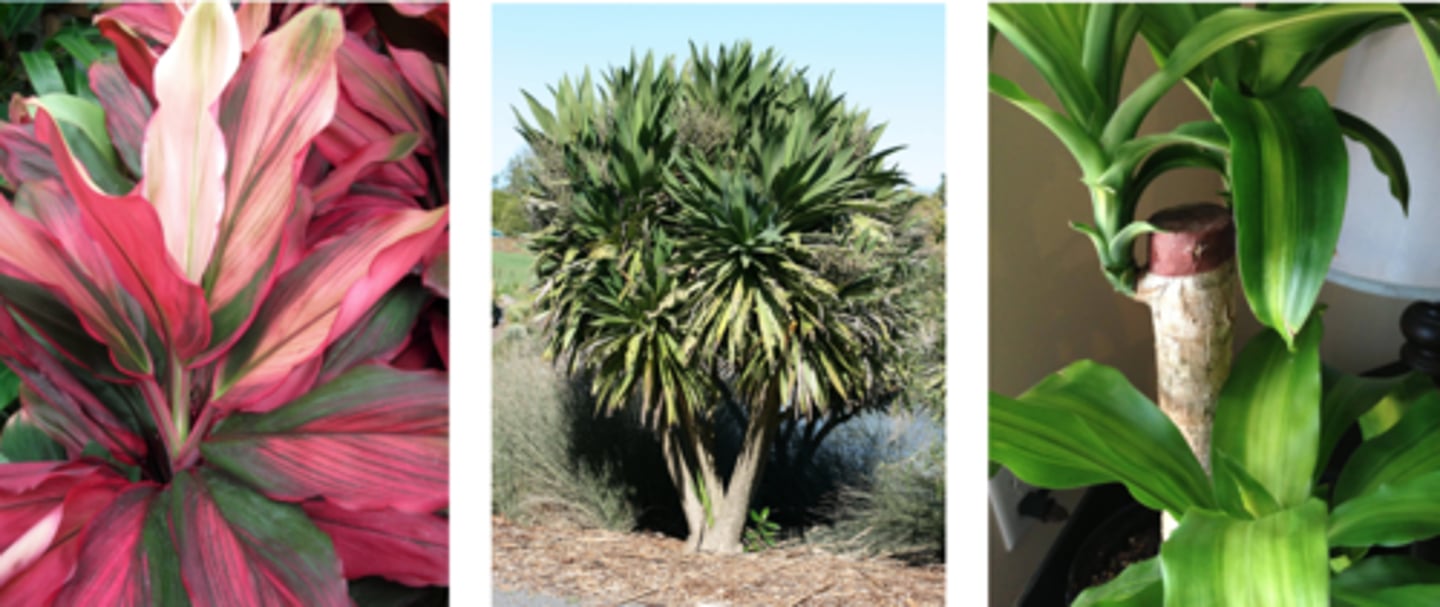
Aloe, Agave, Yucca, Dracaena, Cordyline
Woody monocots with secondary-like growth

ground tissue and entire vascular bundles
what does novel cambium produce sa inner side
- "Novel cambium"
- Derived from parenchyma of the cortex
Secondary thickening meristem; anomalous secondary growth
Cortical parenchyma
what does novel cambium produce sa outer side
hindi dumaan sa meristematic stage, bale mature tissue --> new tissue
why else is secondary thickening meristem not considered true secondary growth
Primary thickening meristem
where does STM arise from
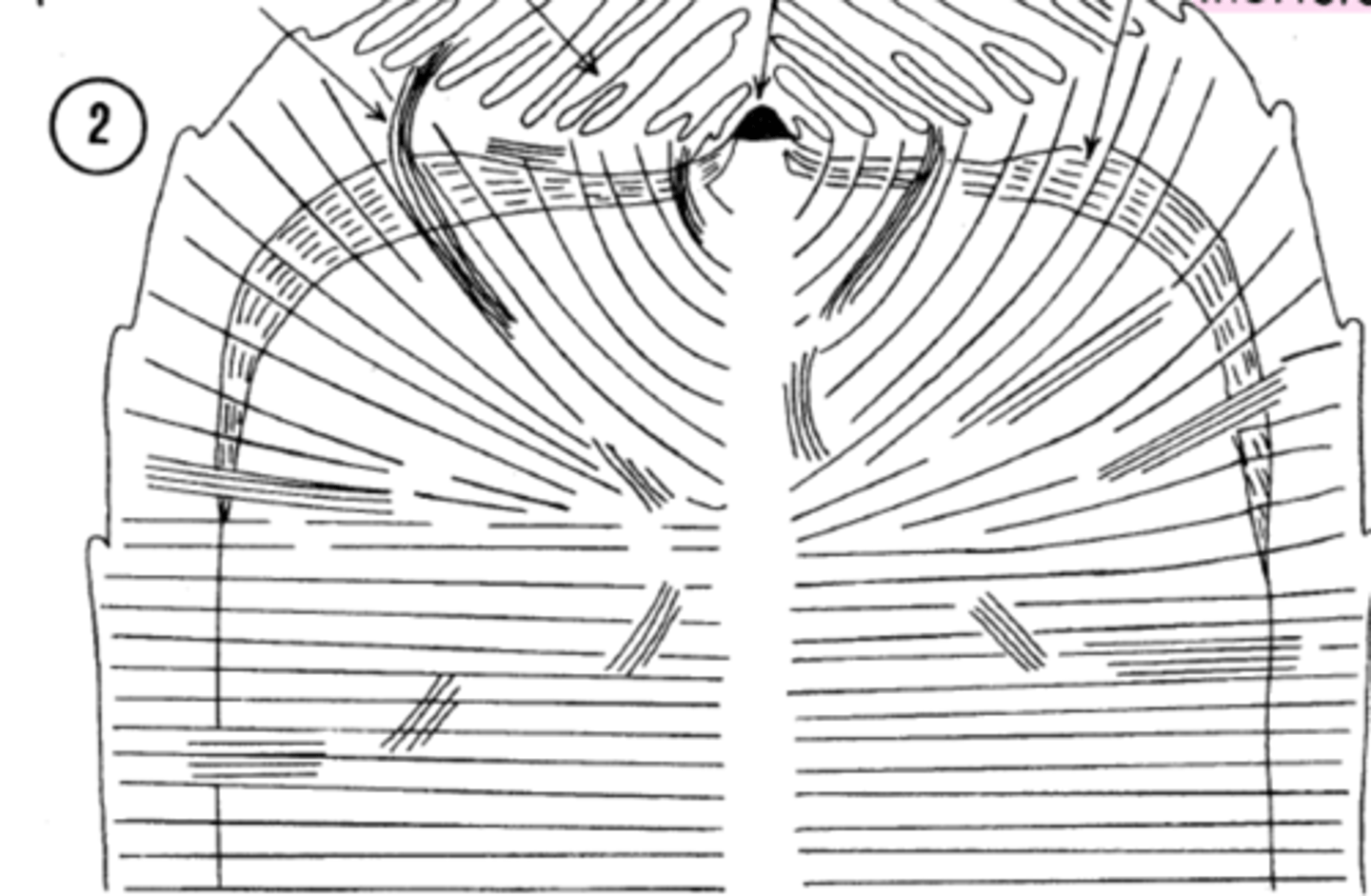
Primary thickening meristem
closer to shoot apex of palms (cocomt) so may "wood-like" structure
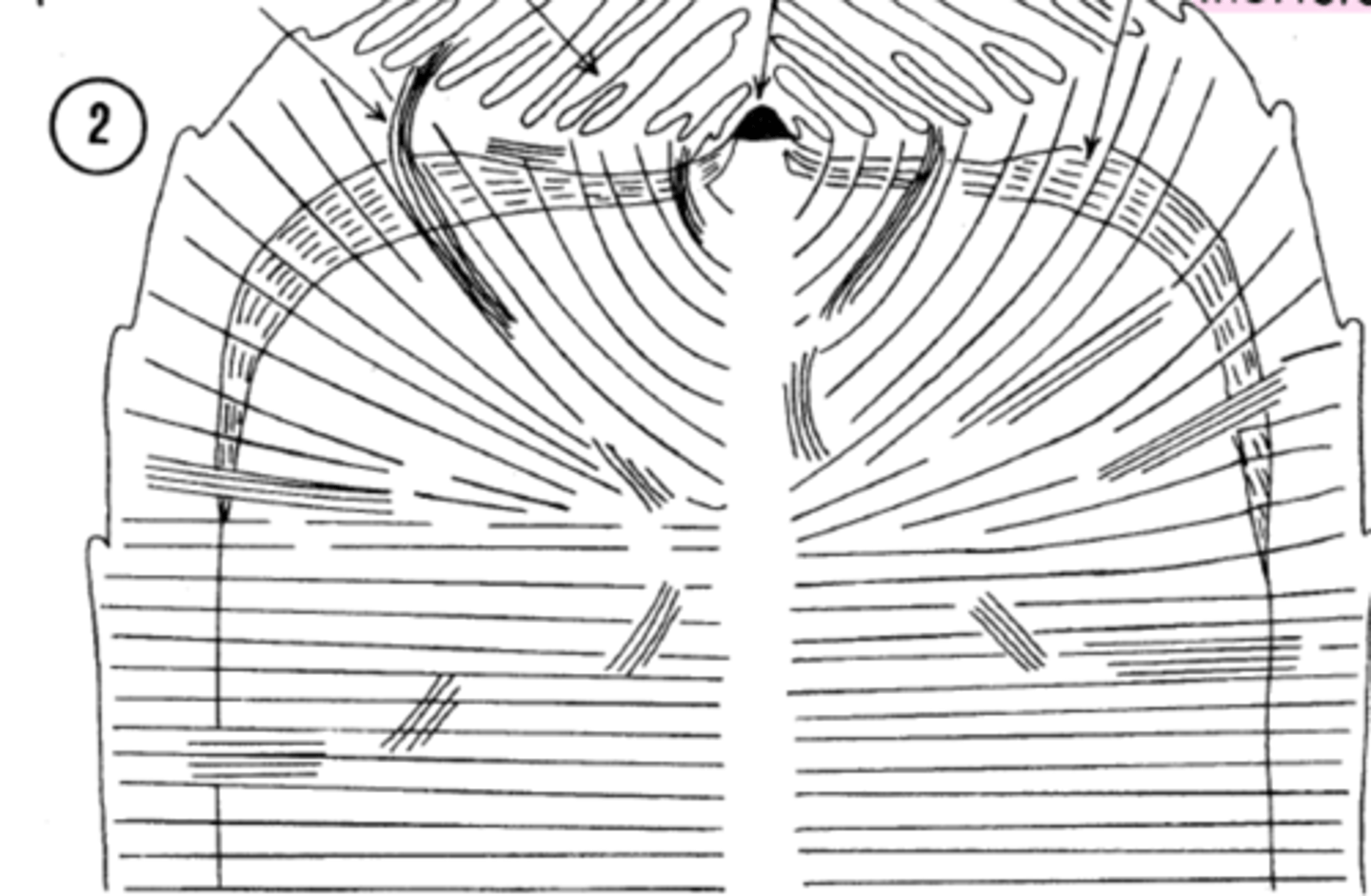
- u wont see 2ndary xy but many vascular bundles
- wide procambium region
- much vascular parenchyma
Secondary thickening meristem ng palms
