A & P Digestive exam 4
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
THE GI TRACT IS LONG TUBE THAT
IS OPEN AT BOTH ENDS FOR THE TRANSIT OF FOOD DURING PROCESSING
NAMED PORTIONS OF THE TUBE INCLUDE THE
ESOPHAGUS, STOMACH, SMALLINTESTINE, LARGE INTESTINE, AND RECTUM
ACCESSORY STRUCTURES ARE
NOT PART OF THE GI TRACT, BUT THEY DO CONTRIBUTE TO FOOD PROCESSING
Pancreas
Liver
Gall bladder
ACCESSORY STRUCTURES INCLUDE THE
TEETH, TONGUE, SALIVARY GLANDS,LIVER, GALL BLADDER, AND PANCREAS
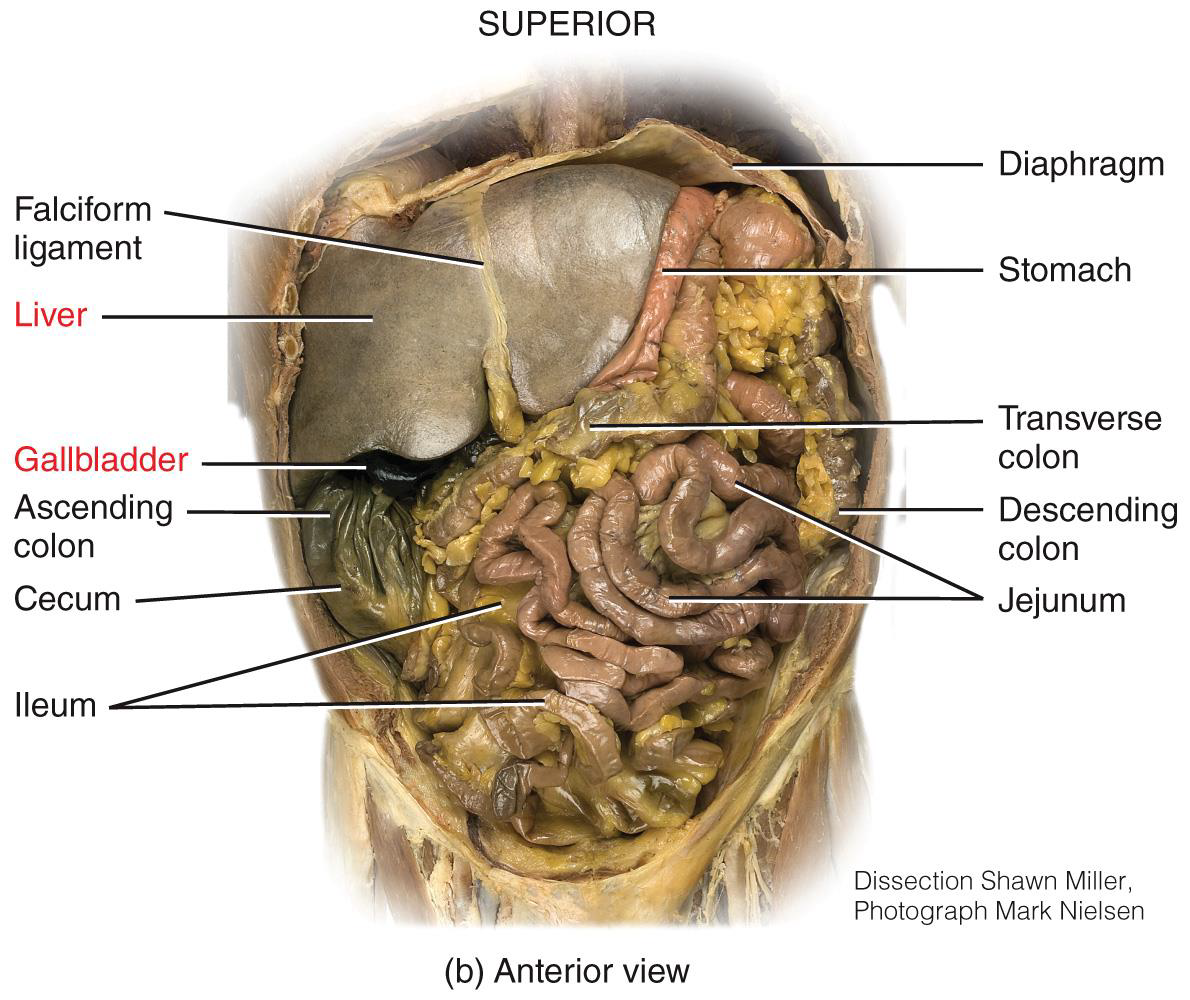
organs of the digestive system 2 photos
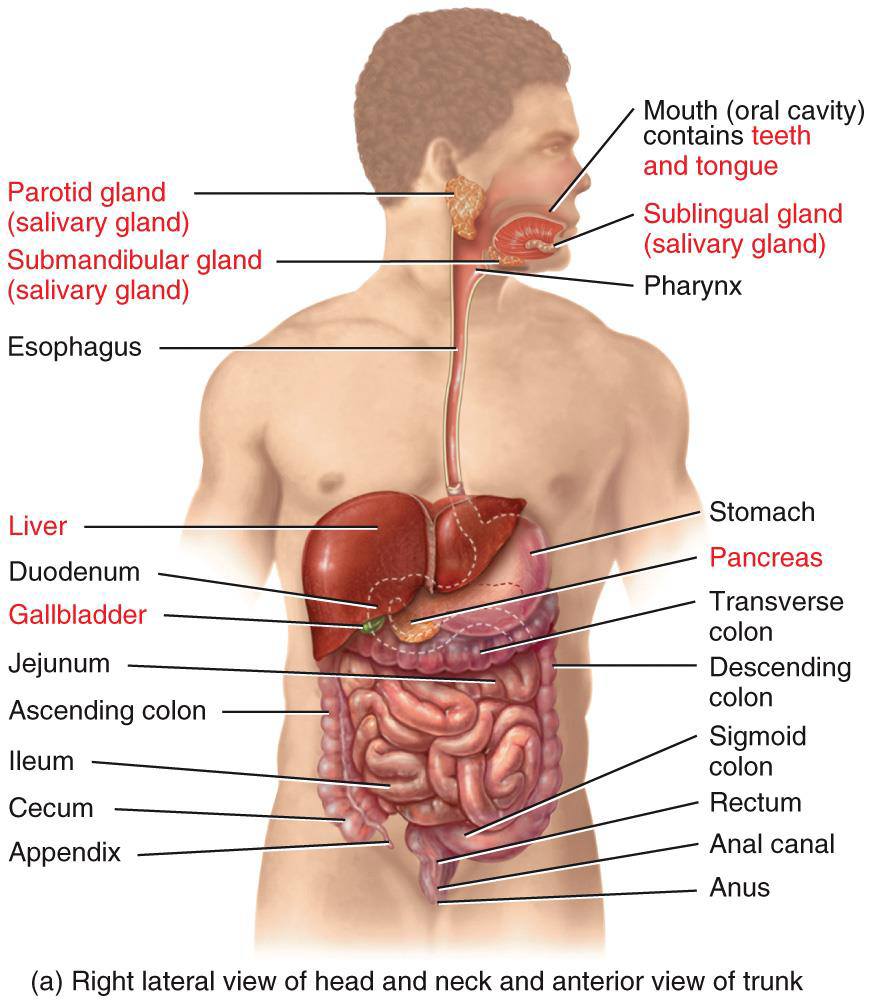
THERE ARE 6 BASIC PROCESSES INVOLVED IN DIGESTION photo
Ingestion
Secretion
Motility
Digestion
Absorption
Defecation
Layer of GI Tract photo
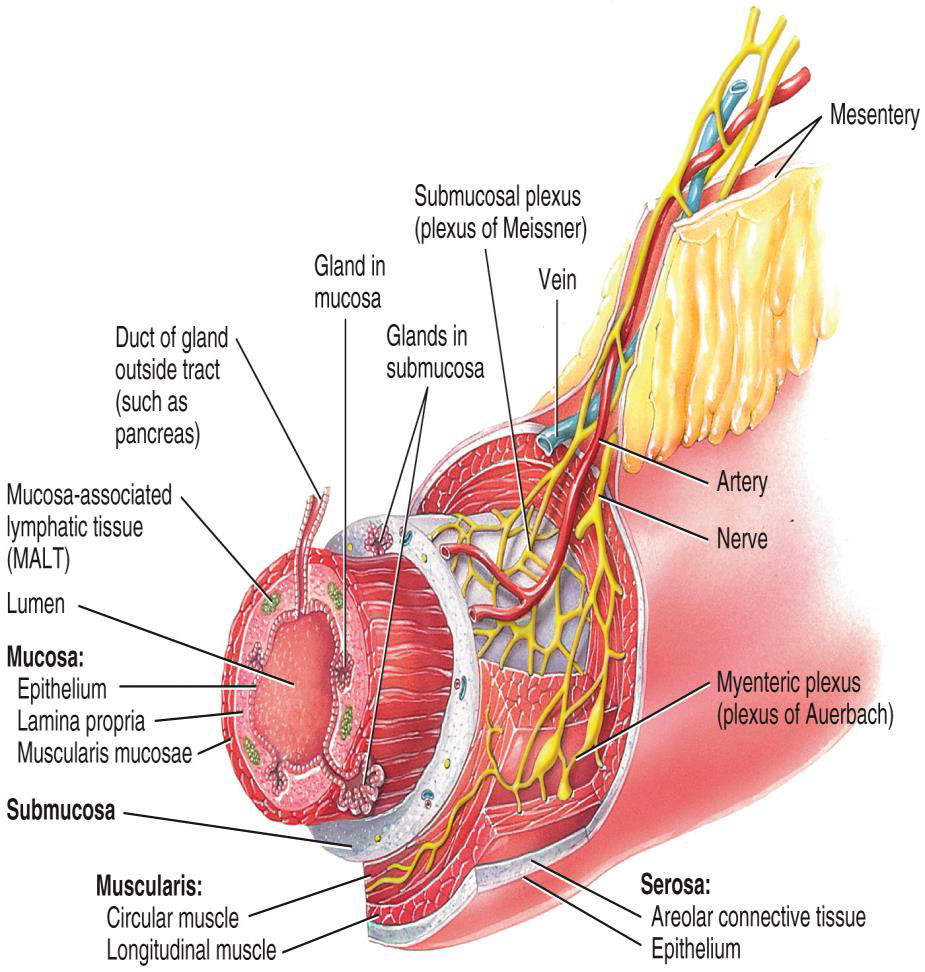
LAYERS OF THE GI TRACT
ESOPHAGUS TO LARGE INTESTINES
MUCOSA (INNER)
•MOIST, FRICTION RESISTANT
•SECRETES MUCUS, ENZYMES, HORMONES
LAYERS OF THE GI TRACT
ESOPHAGUS TO LARGE INTESTINES
2.SUBMUCOSA
•BLOOD VESSELS, NERVES, LYMPHATICS
LAYERS OF THE GI TRACT
ESOPHAGUS TO LARGE INTESTINES
3. MUSCULARIS EXTERNA
•SMOOTH MUSCLE FOR PERISTALSIS AND SEGMENTATION
LAYERS OF THE GI TRACT
ESOPHAGUS TO LARGE INTESTINES
4. SEROSA (OUTER)
•PERITONEUM
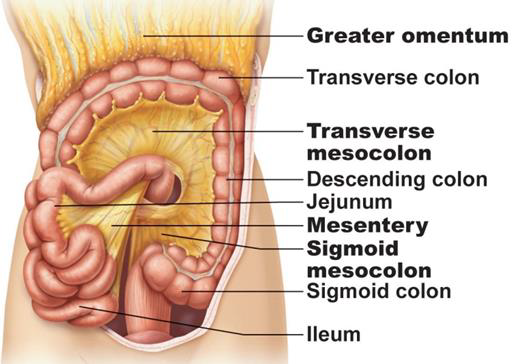
THE PERITONEUM IS THE 2 photos
LARGEST SEROUS MEMBRANE IN THE BODY
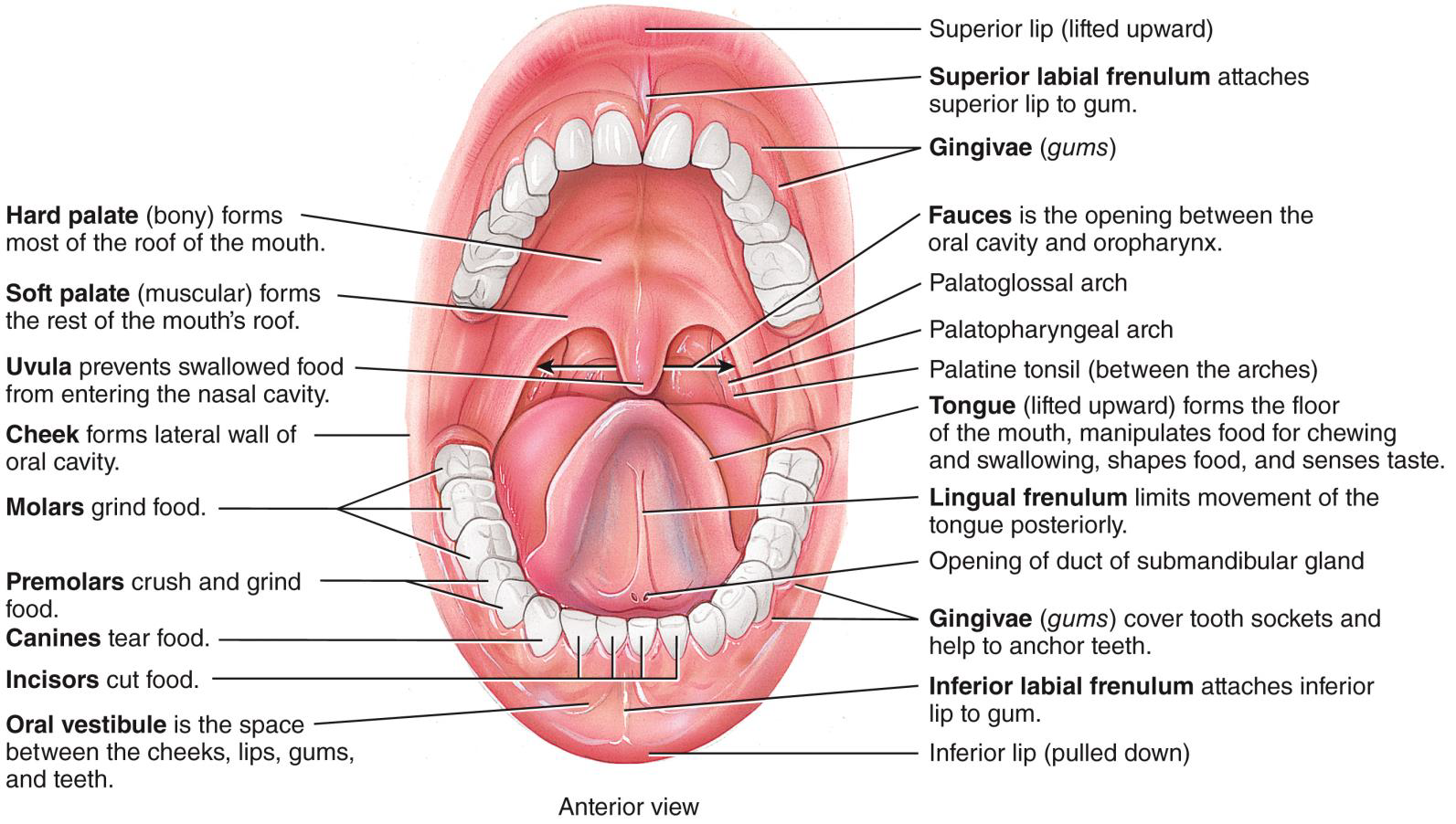
THE MOUTH IS FORMED BY
THE CHEEKS, HARD AND SOFT PALATES, AND TONGUE
SALIVARY GLANDS LIE OUTSIDE THE
MOUTH AND EMPTY THEIR CONTENTS INTO DUCTS WHICH DELIVER SALIVA INTO THE ORAL CAVITY
SALIVARY AMYLASE
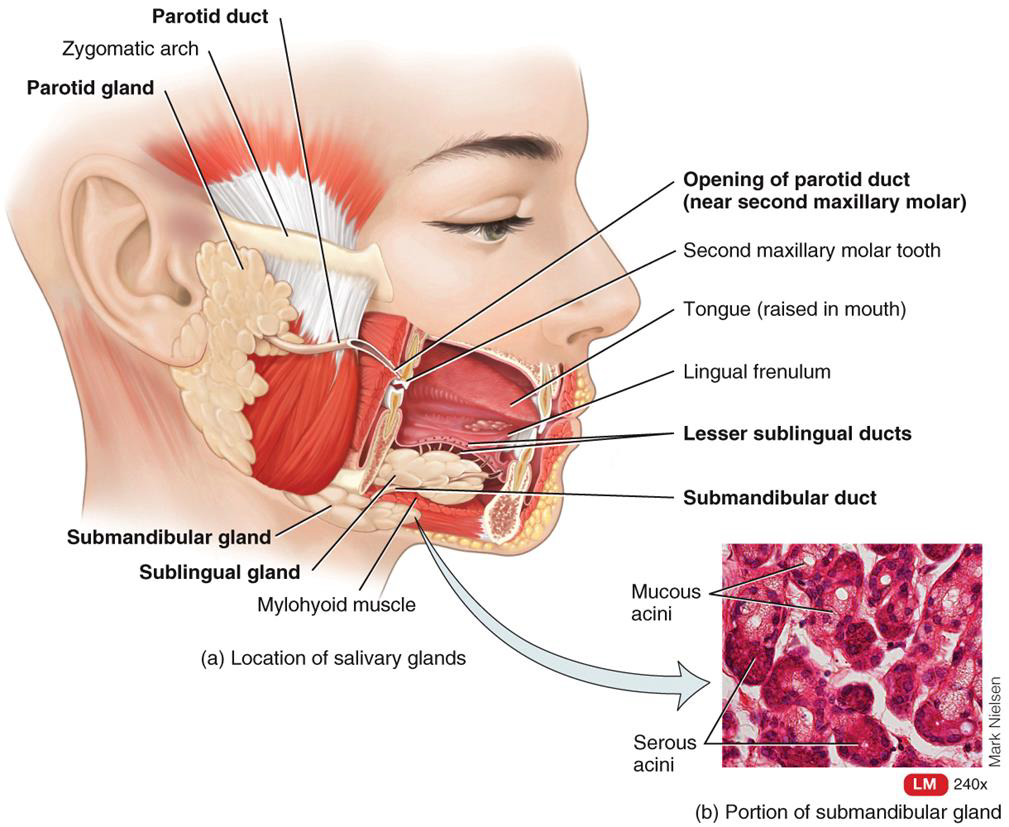
SALIVARY GLANDS 3 PAIRS:
1.PAROTID
2.SUBMANDIBULAR
3.SUBLINGUAL
TONGUE
TOGETHER WITH ASSOCIATED MUSCLE, FORMS THE FLOOR OF THE ORAL CAVITY
•COMPOSED OF SKELETAL MUSCLE COVERED WITH MUCOUS MEMBRANE
•PARTICIPATES IN CHEWING, SWALLOWING, AND SPEECH
•THE UPPER AND LATERAL SURFACES OF THE TONGUE ARE COVERED WITH PAPILLAE, SOME OF WHICH CONTAIN TASTE BUDS
•DO YOU REMEMBER THE 5 TYPES FROM YOUR NERVOUS SYSTEM STUDY?
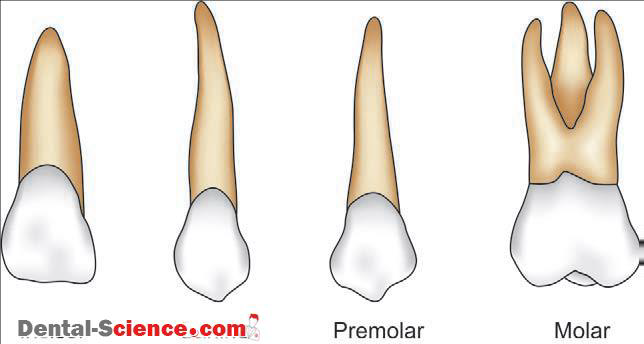
THE TEETH
PROJECT INTO THE MOUTH AND ARE ADAPTED FOR MECHANICAL DIGESTION
•PERFECTEXAMPLE OF THE PRINCIPLE OF COMPLEMENTARITY
•20 DECIDUOUS
•32 PERMANENT
Mechanical digestion
Chewing mixes food with saliva and forms a bolus which can be easily swallowed
Chemical digestion
•Salivary amylase converts polysaccharides to disaccharides
•Lingual lipase (mouth) converts triglycerides & other fats into fatty acids and diglycerides
Cheeks and lips summary
Keep food between teeth.
Foods uniformly chewed during mastication.
Salivary glands summary
Secrete saliva.
Lining of mouth and pharynx moistened and lubricated. Saliva softens, moistens, and dissolves food and cleanses mouth and teeth. Salivary amylase splits starch into smaller fragments
Tongue muscles summary
Move tongue from side to side and in and out; alter shape of tongue
Food maneuvered for mastication, shaped into bolus, and maneuvered for swallowing; speech
Taste buds summary
Serve as receptors for gustation (taste) and presence of food in mouth.
Secretion of saliva stimulated by nerve impulses from taste buds to salivatory nuclei in brain stem to salivary glands.
Lingual glands summary
Secrete lingual lipase.
Triglycerides broken down into fatty acids and diglycerides.
Teeth summary
Cut, tear, and pulverize food.
Solid foods reduced to smaller particles for swallowing.
HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE
•MUMPS
•DENTAL CARIES
•PERIODONTAL DISEASE
•CANKER SORES
•ORAL HERPES
•HALITOSIS
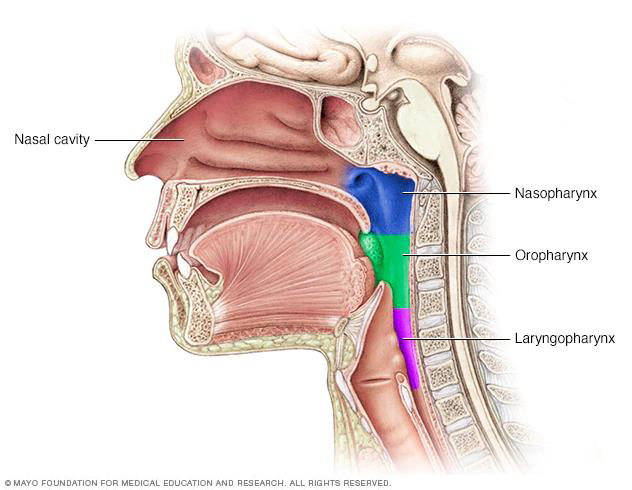
PHARYNX
A FUNNEL SHAPED TUBE THAT EXTENDS FROM THE INTERNAL NARES TO THE ESOPHAGUS POSTERIORLY AND TO THE LARYNX ANTERIORLY
COMPOSED OF SKELETAL MUSCLE AND LINED WITH MUCOUS MEMBRANE
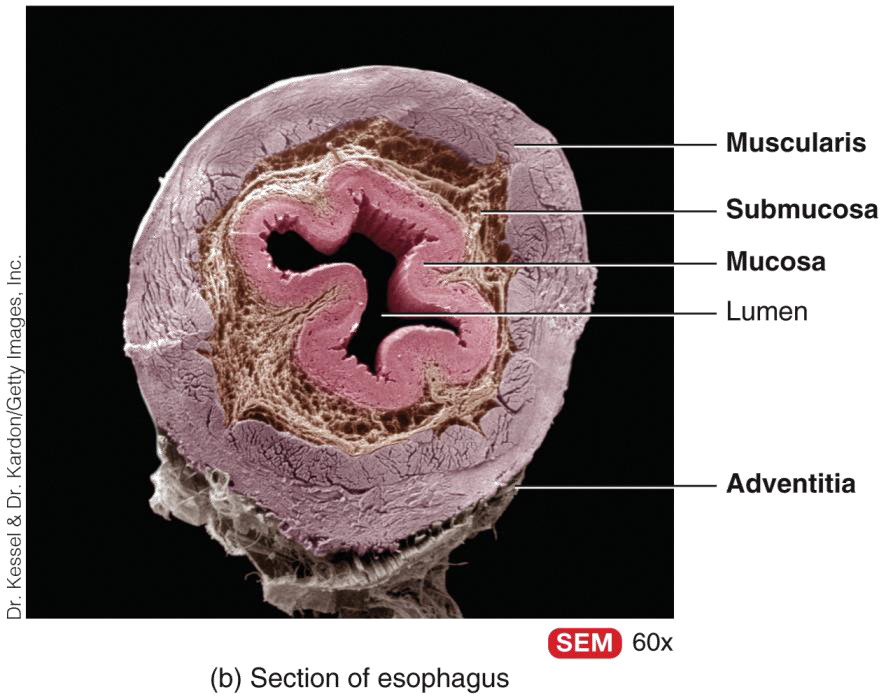
ESOPHAGUS
IS A COLLAPSIBLE, MUSCULAR TUBE THAT LIES POSTERIOR TO THE TRACHEA AND CONNECTS THE PHARYNX TO THE STOMACH
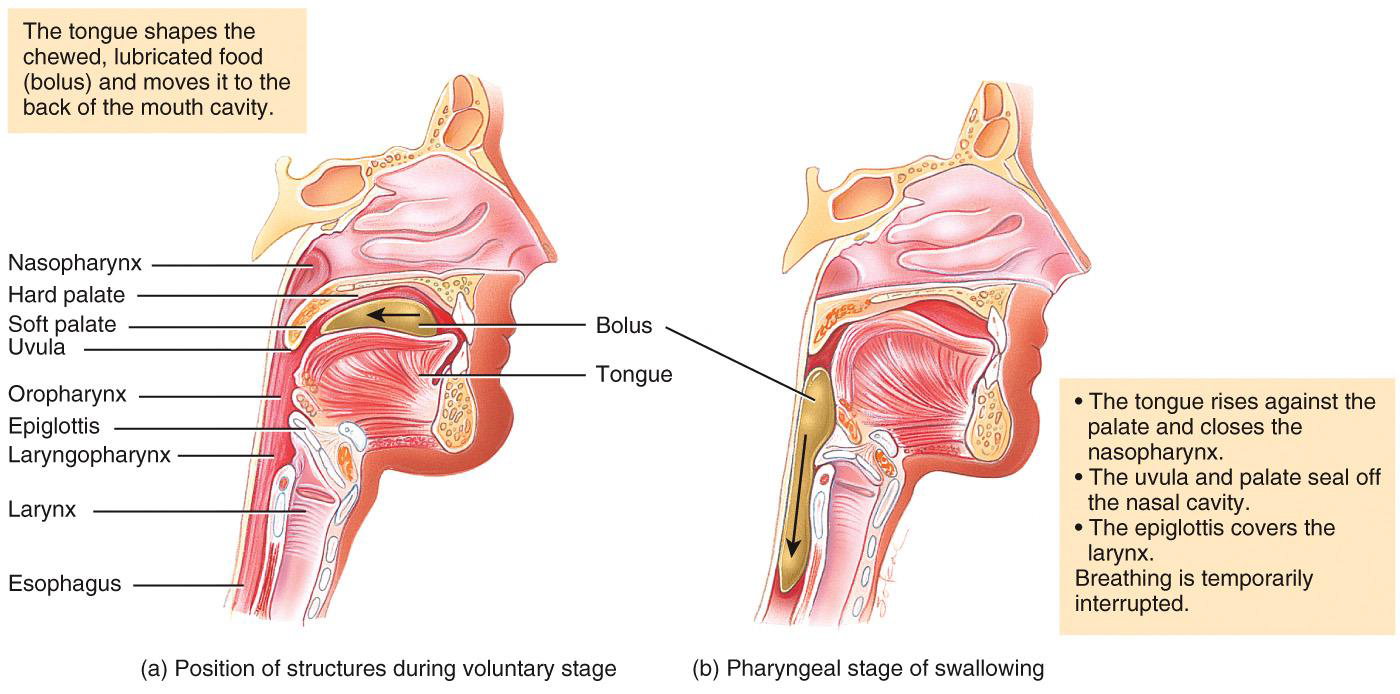
DEGLUTITION is 2 photos
Swallowing
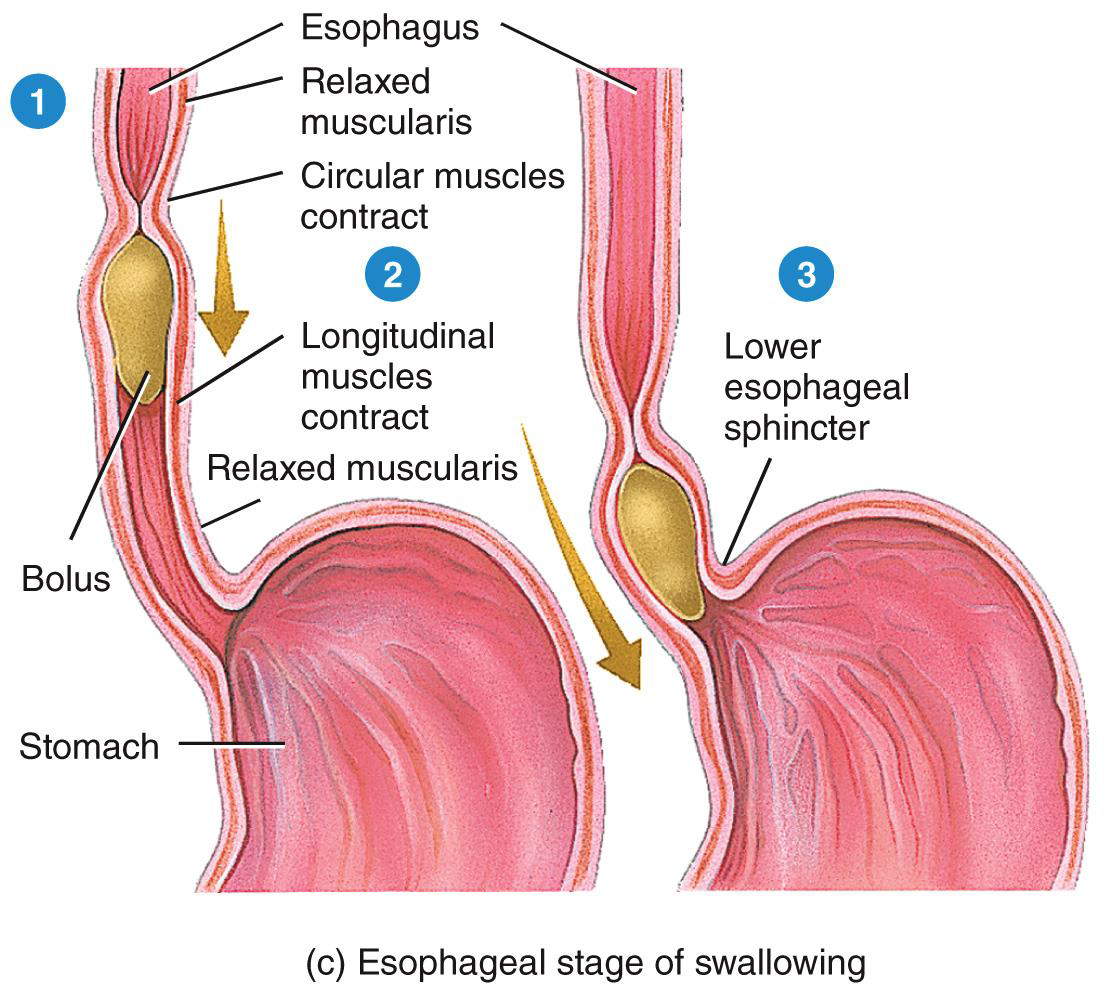
Pharynx summary
Pharyngeal stage of deglutition.
Moves bolus from oropharynx to laryngopharynx and into esophagus: closes air passageways.
Esophagus summaRY
Relaxation of upper esophageal sphincter. Esophageal stage of deglutition (peristalsis). Relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter. Secretion of mucus.
Permits entry of bolus from laryngopharynx into esophagus. Pushes bolus down esophagus. Permits entry of bolus into stomach. Lubricates esophagus for smooth passage of bolus.
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLEX
•HEARTBURN FIRST SYMPTOM
•ACIDIC REFLUX ERODES ESOPHAGUS
•STOMACH CONTENTS FORCED SUPERIORLY
•PREGNANCY, OBESITY, EATING/DRINKING IN EXCESS
HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCEs 2
•GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLEX
•HIATAL HERNIA
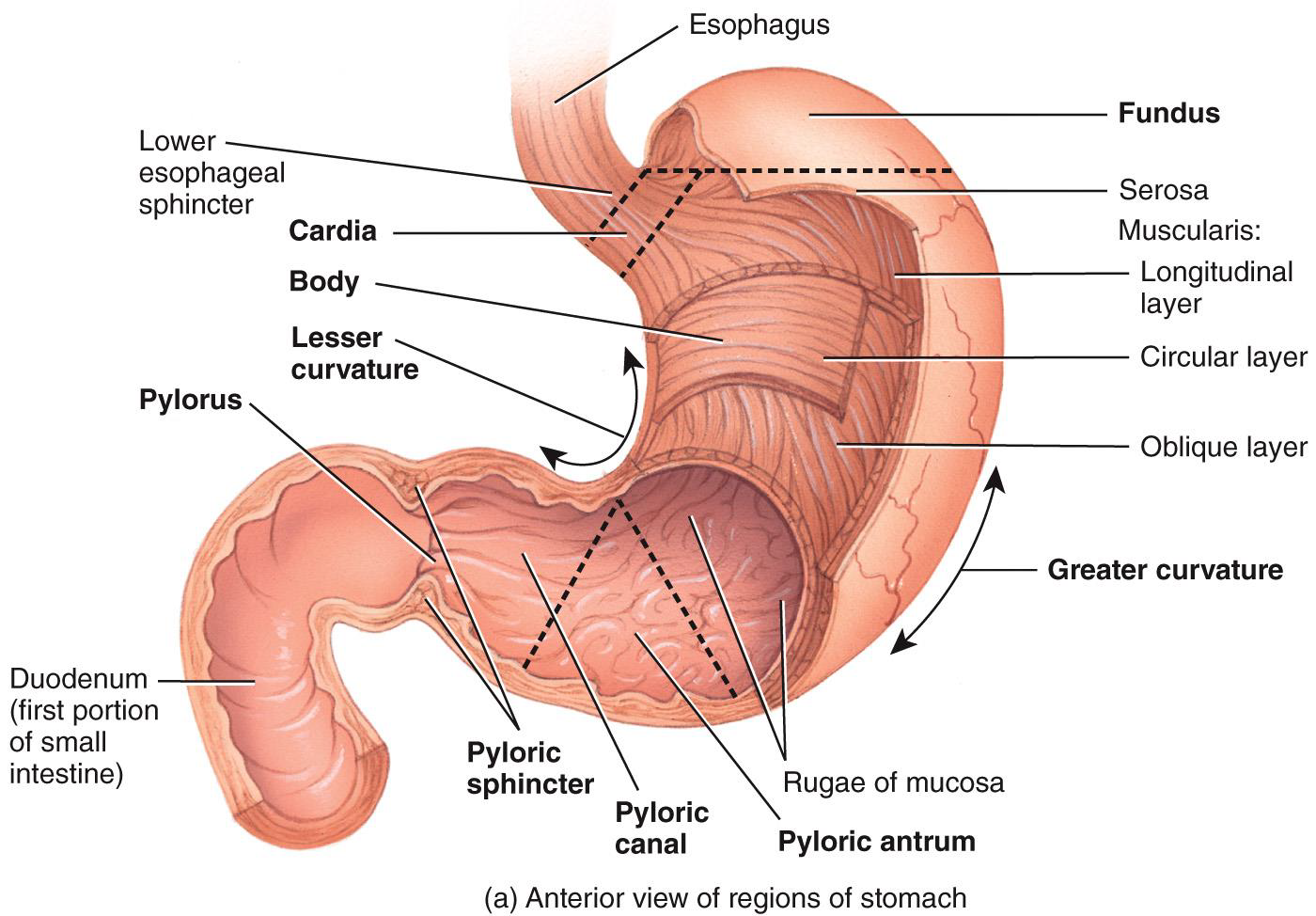
THE STOMACH IS A
J SHAPED ENLARGEMENT OF THE GI TRACT
Stomach Layers:
•Muscularis
•Mucosa
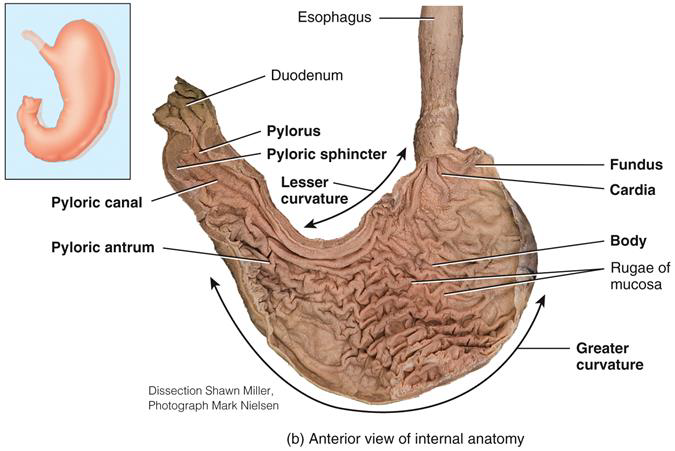
Stomach Regions:
•Cardiac
•Fundus
•Body
•Pylorus
FUNCTIONS OF THE STOMACH
Mixes saliva, food, and gastric juice to form chyme
Serves as a reservoir for food before release into the small intestine
Secretes gastric juice, which contains HCl, pepsin, rennin, intrinsic factor, and gastric lipase
Secretes gastrin into the blood
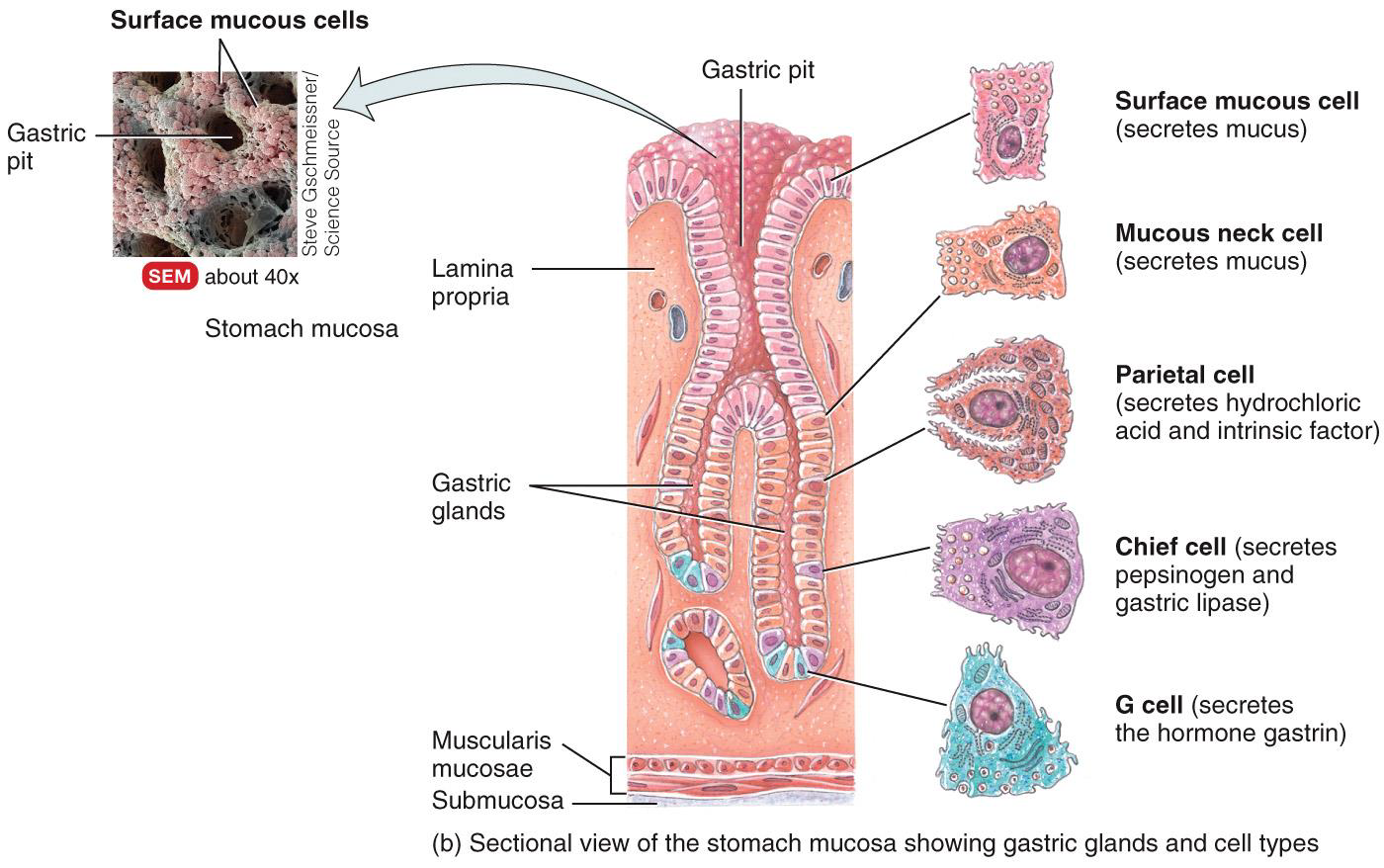
GASTRIC GLANDS AND CELLS IN THE STOMACH
Mucus, HCl, Intrinsic Factor, Pepsinogen, Gastric Lipase, Gastrin
Surface mucous cells and mucous neck cells summary
Secrete mucus.
Forms protective barrier that prevents digestion of stomach wall.
Absorption.
Small quantity of water, ions, short-chain fatty acids, and some drugs enter bloodstream.
Parietal cells summary
Secrete intrinsic factor.
Needed for absorption of vitamin B12 (used in red blood cell formation, or erythropoiesis).
Secrete hydrochloric acid.
Kills microbes in food; denatures proteins; converts pepsinogen into pepsin.
Chief cells summary
Secrete pepsinogen.
Pepsin (activated form) breaks down proteins into peptides.
Secrete gastric lipase.
Splits triglycerides (lipid) into fatty acids and monoglycerides.
G cells summary
Secrete gastrin.
Stimulates parietal cells to secrete HCI and chief cells to secrete, pepsinogen; contracts lower esophageal sphincter, increases motility of stomach, and relaxes pyloric sphincter.
Muscularis summary
Mixing waves (gentle peristaltic movements).
Churns and physically breaks down food and mixes it with gastric juice, forming chyme. Forces chyme through pyloric sphincter.
Pyloric sphincter
Opens to permit passage of chyme into duodenum.
Regulates passage of chyme from stomach to duodenum; prevents backflow of chyme from duodenum to stomach.
HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE 3
GASTRITIS (inflammation)
GASTRIC ULCER (erosion)
VOMITING
GASTRITIS
INFLAMMATION OF STOMACH WALL
GASTRIC ULCER
•EROSION OF THE STOMACH WALL
•BACK PAIN FELT 1-3 HOURS AFTER EATING
•FACTORS THAT INCREASE HCL AND DECREASE MUCOUS
•IBUPROFEN, SMOKING, SPICY FOOD, ALCOHOL, COFFEE, STRESS
•HELICOBACTER PYLORI BACTERIA CAN DAMAGE MUCOSA
•TREAT WITH BISMUTH, ANTIBIOTICS (IF BACTERIA PRESENT), TAGAMENT, ZANTAC
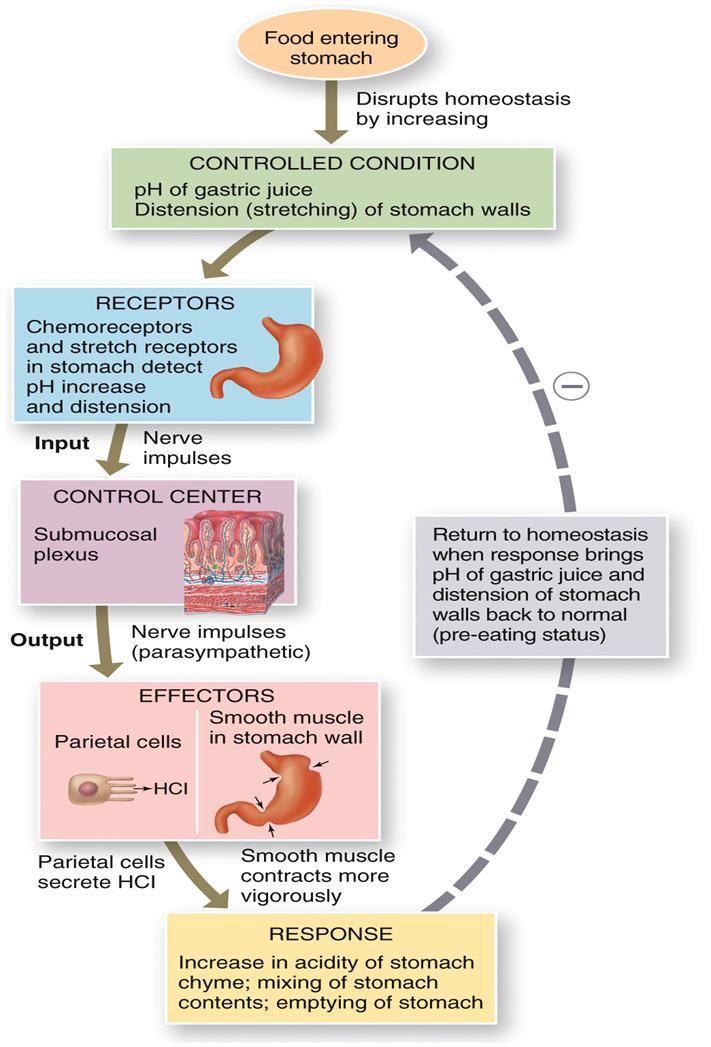
DIGESTIVE PHASES
1.CEPHALIC REFLEX
2.GASTRIC
3.INTESTINAL
DIGESTIVE PHASES
CEPHALIC REFLEX
•VAGUSNERVE-SIGHT, SMELL, TASTE OF FOOD
•PREPARES STOMACH BEFORE FOOD ENTERS mouth
DIGESTIVE PHASES
GASTRIC:
SECRETION AND MOTILITY
•STIMULUS-DISTENSION, PEPTIDES, AND LOW ACIDITY
•GASTRIN SECRETED
comes from g cells,
DIGESTIVE PHASES
3.INTESTINAL
•FOOD ENTERING DUODENUM INHIBITS VAGUS, ACTIVATES SYMPATHETIC NERVES
•SMALL INTESTINES RELEASE GASTRIN INHIBITING HORMONES, SECRETIN AND CHOLECYSTOKININ (CCK)
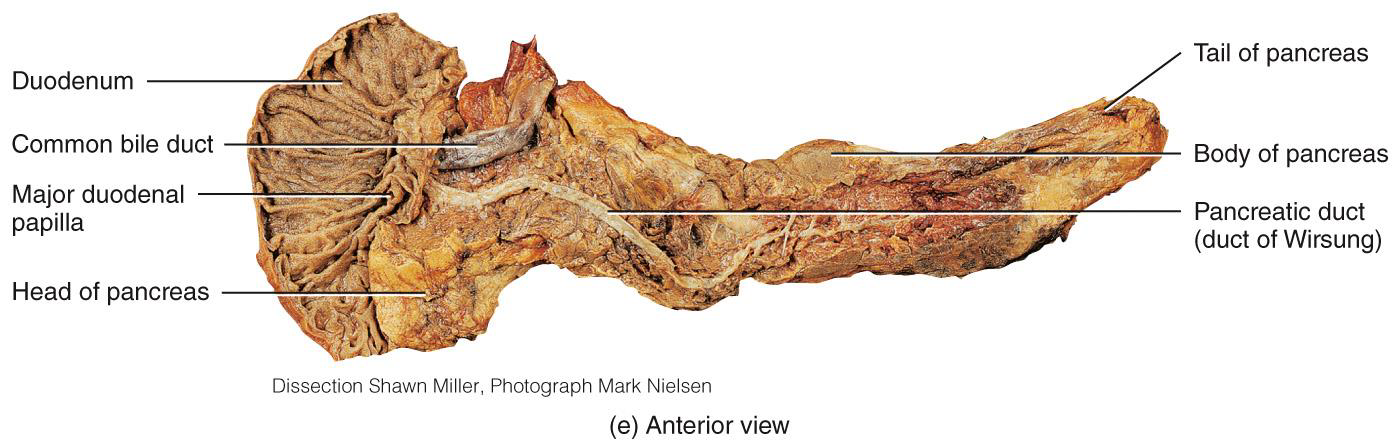
THE PANCREAS IS A GLAND THAT:
LIES POSTERIOR TO THE STOMACH
PRODUCES ENZYMES THAT DIGEST CARBOHYDRATES, PROTEINS, FATS, AND NUCLEIC ACIDS
EXOCRINE SECRETIONS INCLUDE AMYLASE, LIPASES, NUCLEASES, PROTEASES
(ENDOCRINE: ISLETS PRODUCE HORMONES!)
PRODUCES SODIUM BICARBONATE WHICH BUFFERS STOMACH ACID
NEUTRALIZES ACIDIC CHYME
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT????
EMPTIES ITS CONTENTS INTO THE DUODENUM
PANCREATIC ENZYMES
Pancreatic amylase carbs
Pancreatic acinar cells.
Starches (polysaccharides).
Disaccharides andtrisaccharides
PANCREATIC ENZYMES
Trypsin
Chymotrypsin
Pancreatic acinar cells.
Proteins.
Peptides.
PANCREATIC ENZYMES
Carboxypeptidase
Pancreatic acinar cells.
Amino acid at end of peptides.
Amino acids and peptides.
PANCREATIC ENZYMES
Pancreatic lipase
Pancreatic acinar cells.
Triglycerides (fats and oils) that have been emulsified by bile salts.
Fatty acids and monoglycerides.
PANCREATIC ENZYMES
Ribonuclease rna
Pancreatic acinar cells.
Ribonucleic acid.
Nucleotides.
PANCREATIC ENZYMES
Deoxyribonuclease dna
Pancreatic acinar cells.
Deoxyribonucleic acid.
Nucleotides.
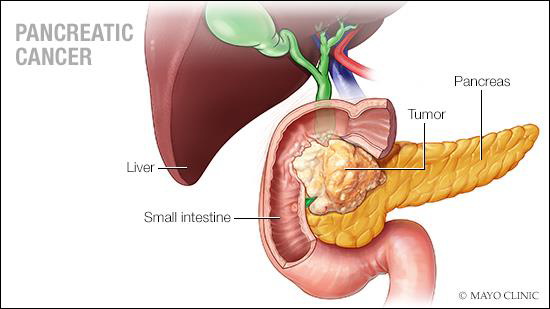
HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE 2 pancreas
•PANCREATITIS
•PANCREATIC CANCER
•SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS MAY INCLUDE:
•PAIN IN THE UPPER ABDOMEN THAT RADIATES TO YOUR BACK
•LOSS OF APPETITE OR UNINTENDED WEIGHT LOSS
•DEPRESSION
•NEW-ONSET DIABETES
•BLOOD CLOTS
•FATIGUE
•YELLOWING OF YOUR SKIN AND THE WHITES OF YOUR EYES (JAUNDICE)
PANCREAS, LIVER, AND GALLBLADDER photo
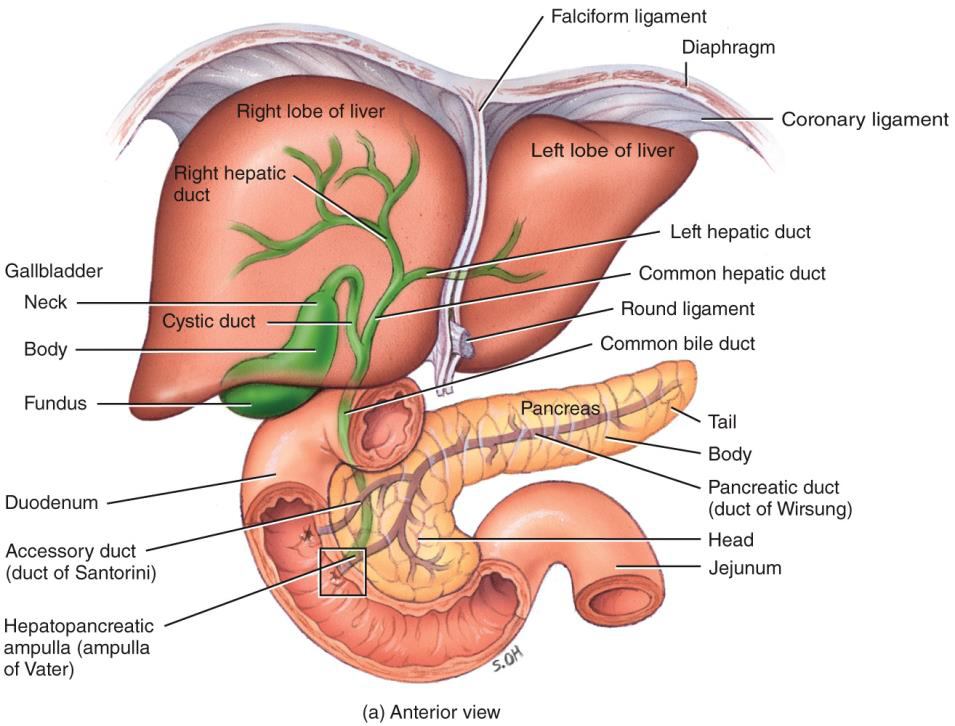
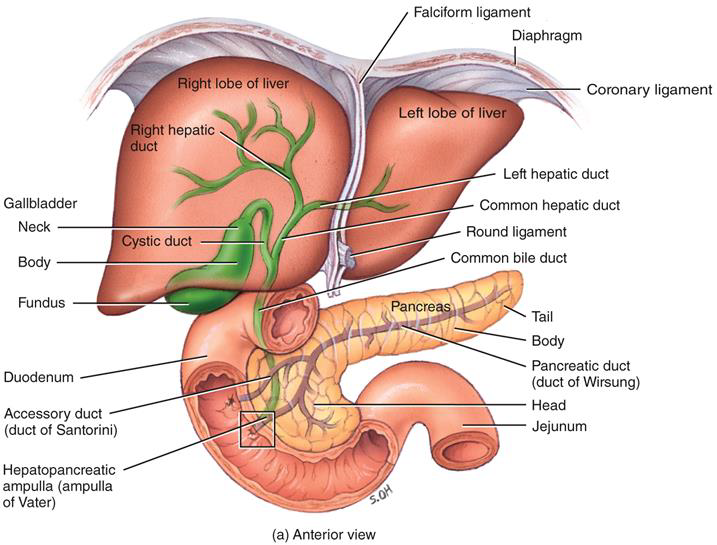
THE LIVER MAKES
BILE, WHICH IS IMPORTANT IN THE EMULSIFICATION OF FATS
THE GALLBLADDER STORES
BILE UNTIL IT IS NEEDED
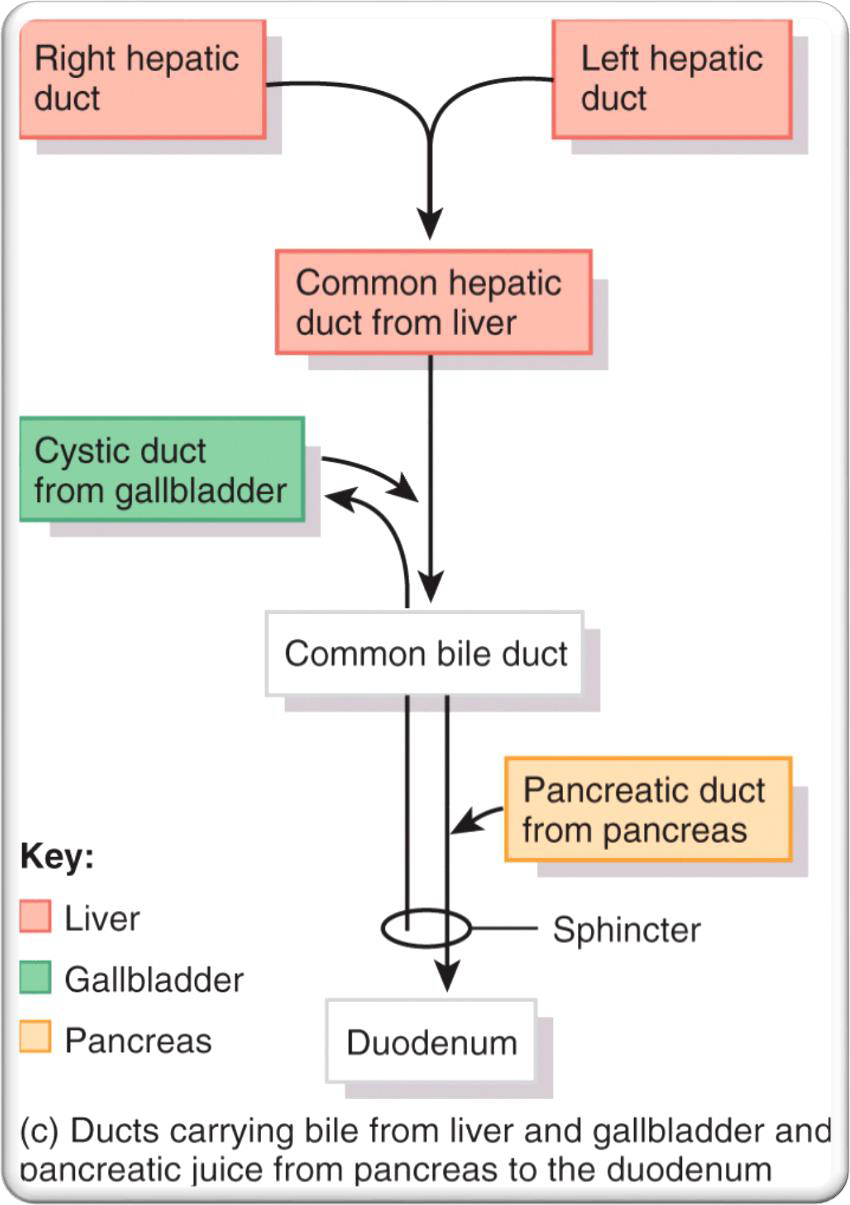
photo includes how direction bile goes into small intestine
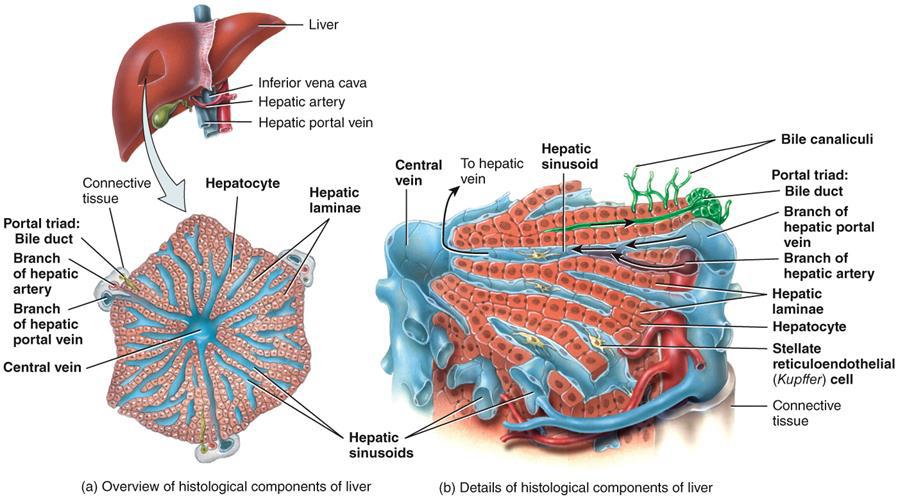
LIVER LOBULES - FUNCTIONAL UNIT
•KUPFFER CELLS - MACROPHAGES of liver, REMOVE DEBRIS, BACTERIA, OLD BLOOD CELLS
•HEPATOCYTES (liver cells)
•PRODUCE BILE
•PROCESS NUTRIENTS-CONVERT GLUCOSE TO GLYCOGEN
•STORE VITAMINS
•DETOXIFY BLOOD from drugs -CONVERT AMMONIA TO UREA
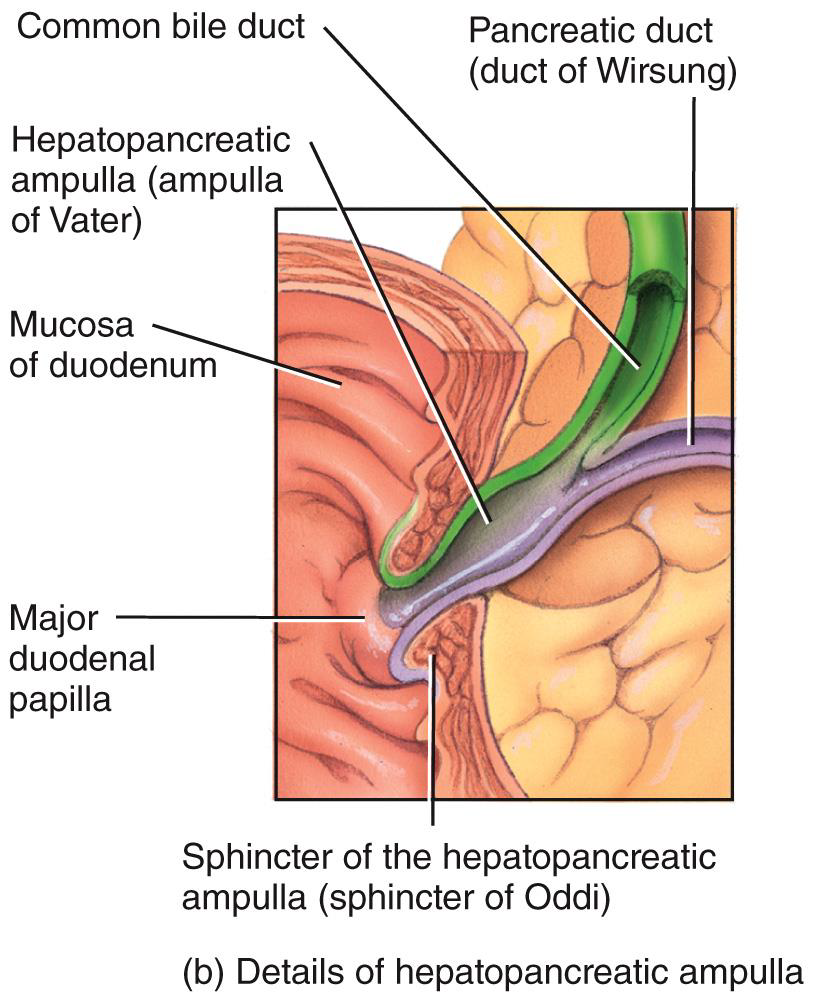
BILE RELEASE
HEPATOPANCREATIC SPHINCTER IS
CLOSED WHEN NOT DIGESTING
BILE RELEASE
CHOLECYSTOKININ (CCK) -INTESTINAL HORMONE
•RELAXES HEPATOPANCREATIC SPHINCTER
•STIMULATES GALLBLADDER TO CONTRACT FORCING BILE INTO DUODENUM
•STIMULATES SECRETION OF PANCREATIC JUICES
BILE RELEASE
VAGUS NERVE CAN
STIMULATE CONTRACTIONS OF GALLBLADDER
FUNCTIONS OF THE LIVER AND GALLBLADDER
Carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism
Processing detoxifying of drugs and hormones
Bilirubin excretion
Bile salt synthesis
Storage for bile
Phagocytosis
Vitamin D activation
HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE 4 LIVER
LIVER CIRRHOSIS
HEPATITIS
GALLSTONES
JAUNDICE
LIVER CIRRHOSIS
•CHRONIC INFLAMMATION DAMAGES HEPATOCYTES, SCAR TISSUE TO FORMS, ACTIVITY DEPRESSED
•CAUSED BY ALCOHOLISM, CHRONIC HEPATITIS (inflammation) irreversible
HEPATITIS
LIVER INFLAMMATION
VIRAL INFECTION
•HVA AND HVE-TRANSMITTED IN FOOD AND WATER
•HVB AND HVC-TRANSMITTED BY BLOOD
NON-VIRAL CAUSES INCLUDE DRUG TOXICITY AND WILD MUSHROOM POISONING
GALLSTONES
•CRYSTALLIZED BILE FROM TOO MUCH CHOLESTEROL OR TOO LITTLE BILE SALTS
•CONTRACTING ON SHARP CRYSTALS CAUSES PAIN
•OBESITY, ESTROGEN, DIABETES, CHOLESTEROL DRUGS…
•TREATMENTS-LASERS, ULTRASOUND, SURGICAL REMOVAL (BILE DUCT ENLARGES TO STORE BILE)
JAUNDICE
•YELLOWING OF SKIN DUE TO BILE DUCT BLOCKAGE OR LIVER DISEASE
buildup of bilirubin
•HEPATITIS, MALARIA, GALLSTONES, CANCER, PARASITES…
•YELLOW BILE PIGMENTS ACCUMULATE IN BLOOD
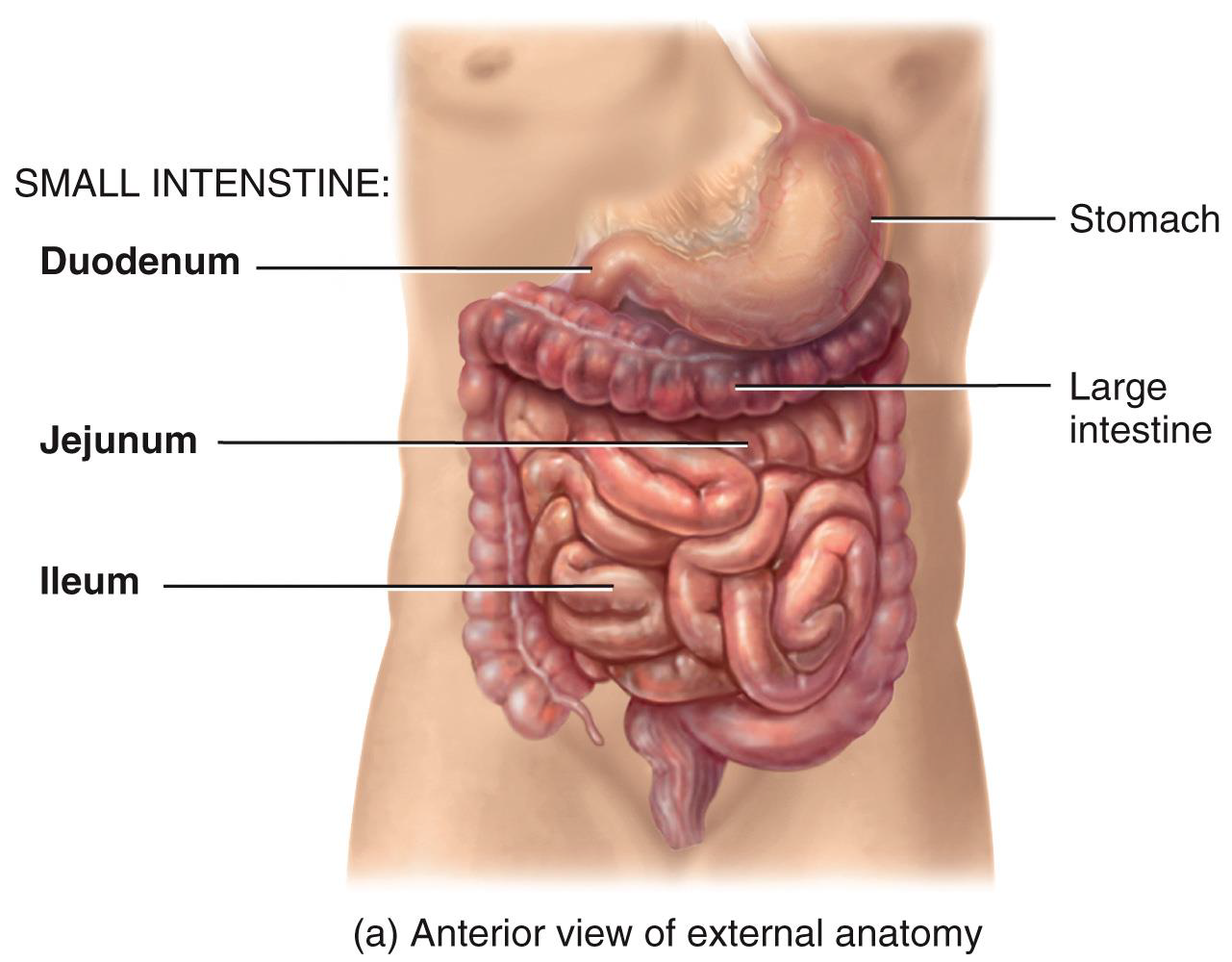
THE MAJORITY OF DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION OCCUR
IN THE SMALL INTESTINE
Parts of small intestine
Duodenum
jejunum
ileum
HISTOLOGY OF THE SMALL INTESTINE
•Circular folds increase the surface area for digestion and absorption in the small intestine
•Villi and Microvilli
INTESTINAL JUICE
provides a vehicle for absorption of substances from chymeas they come in contact with the villi
BRUSH BORDER ENZYMES
found on the surfaces of the microvilli of absorptive cells, break down food products; aids in digestion
FUNCTIONS OF THE SMALL INTESTINE
Segmentations (localized contractions) mix chyme with digestive juices and bring food into contact with mucosa for absorption; peristalsis (propulsive contractions) propels chyme through small intestine
Completes digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids; begins and completes digestion of nucleic acids
Absorbs about 90% of nutrients and water that pass through digestive SYSTEM
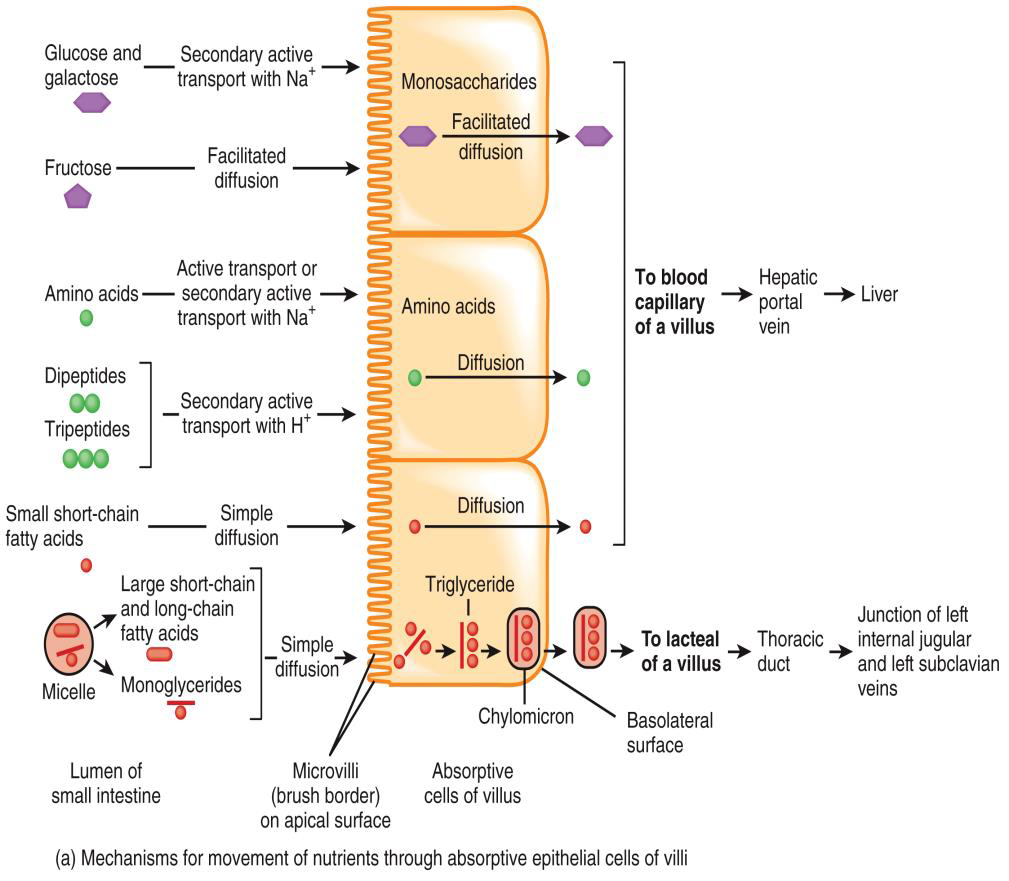
ABSORPTION IN THE SMALL INTESTINE PHOTO
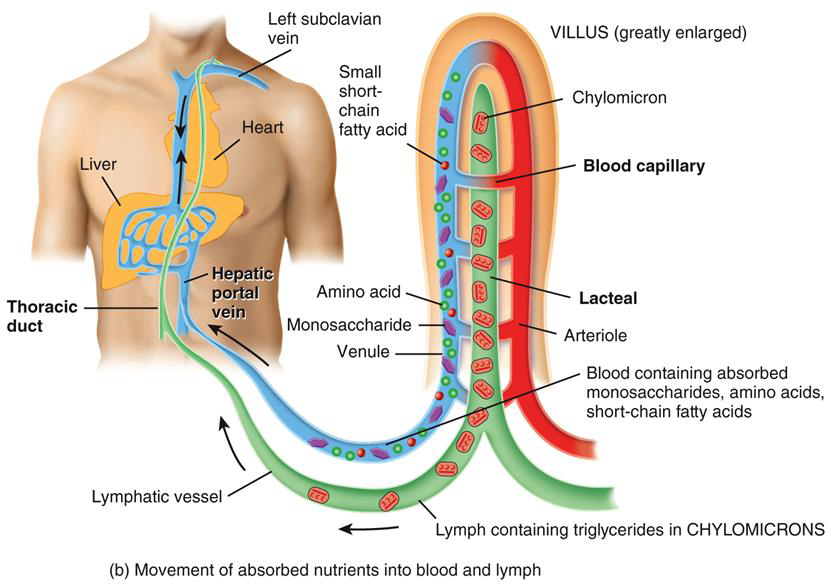
ABSORPTION ALCOHOL
•BEGINS IN STOMACH
•ABSORBS MORE RAPIDLY IN SMALL INTESTINE
ABSORPTION MALABSORPTION
•MAY BE DUE TO
•INADEQUATE CHEMICAL DIGESTION
•DAMAGE TO THE LINING OF THE SMALL INTESTINE
•IMPAIRMENT OF MOTILITY
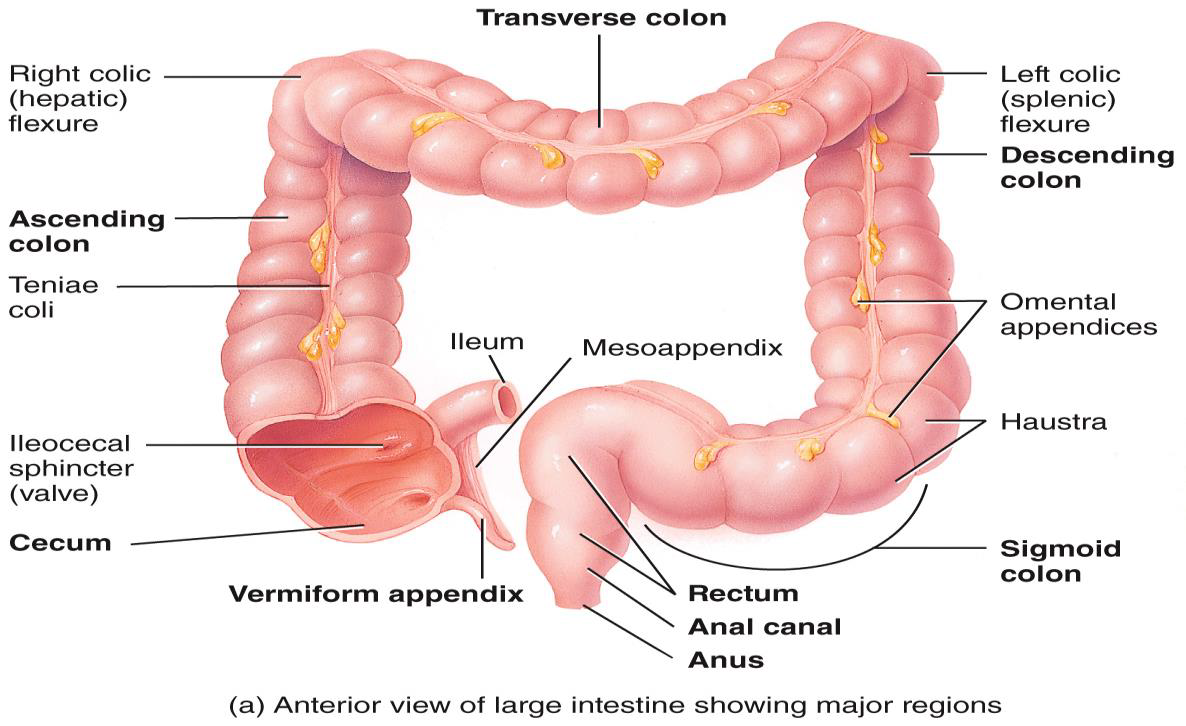
ANATOMY OF THE LARGE INTESTINE (COLON) photos
internal and external anal sphincter photo
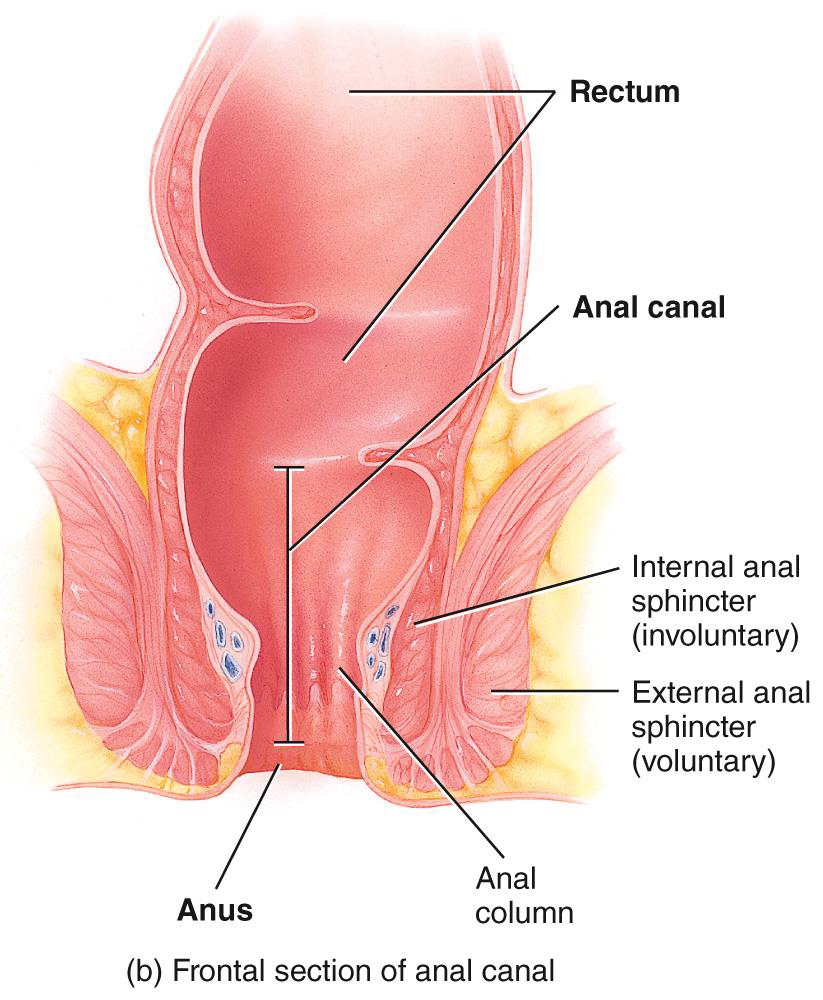
FUNCTIONS OF THE COLON
Haustral churning, peristalsis, and mass peristalsis drive contents of colon into rectum
Bacteria in colon convert proteins into amino acids, break down amino acids, and produce some B and k vitamins
Absorption of some water, ions, and vitamins
Formation of feces
Defecation
DEFECATION REFLEX
Motor impulses travel back to the descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and anus
Rectal wall distends and stretch receptors send sensory nerve
Longitudinal rectal muscles contract and the internal anal sphincter opens
HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCES 5
Appendicitis sharp abdominal pain
Polyps
•Colorectal cancer
Diarrhea
Constipation
Diverticula
AGING AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
AGING RESULTS IN:
•DECREASED SECRETORY MECHANISMS AND MOTILITY
•LOSS OF STRENGTH AND TONE OF DIGESTIVE MUSCULAR TISSUE
•CHANGES IN NEUROSECRETORY FEEDBACK
•DIMINISHED RESPONSE TO PAIN AND INTERNAL SENSATIONS
FOCUS ON HOMEOSTASIS PHOTO
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DISORDERS 3
LACTOSE INTOLERANCE
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME
Which of the following nutrients can the digestive enzymes of the pancreas breakdown?
All of the available answer options are correct
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates
What is the second part of the small intestine?
Jejunum
Which of the following refers to inflammation of the liver?
Hepatitis
Which of the following is released in the mouth?
Lingual Lipase
Where does the majority of digestion and absorption take place?
Small intestine