Reflex Actions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is a reflex action?
A rapid, automatic, and involuntary response to a stimulus.
Why are reflex actions important?
They are protective, helping to prevent injury by providing a faster response than voluntary actions.

What are the three main components of a simple reflex arc?
Sensory Neurone
Relay Neurone (in the CNS)
Motor Neurone
What are the 3 key features of a reflex action?
Involuntary: The response is automatic and does not involve conscious thought (it bypasses the cerebrum).
Rapid: The neural pathway is very short, often involving few synapses, for a minimal delay.
Protective: The main purpose is to prevent or limit injury, giving it a high survival value.
What is the role of the relay neuron?
To connect the sensory neuron to the motor neuron within the Central Nervous System (CNS).
What is the survival value of reflex actions?
They provide a rapid, automatic response to potentially harmful stimuli (like heat, pain, or sudden imbalance). This allows the body to protect itself from injury before the brain has time to consciously process the danger.
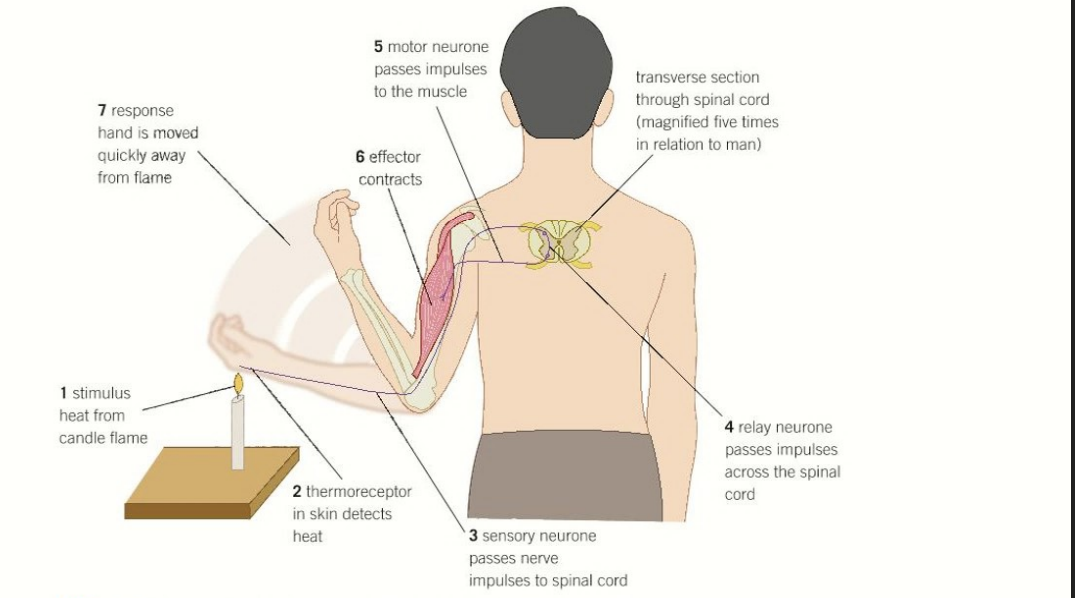
What is the pathway of neurons involved in a reflex action in order?
Receptor → Sensory Neurone → Relay Neurone → Motor Neurone
Receptor: Detects stimuli and creates an action potential in the sensory neurone
Sensory Neurone: Carries impulse to spinal cord
Relay Neurone: Connects sensory neurone to motor neurone
Motor Neurone: Carries impulse to effector
What is the specific stimulus and response in the knee jerk reflex?
Stimulus: Sudden stretching of the quadriceps (thigh) muscle, caused by a tap on the patellar tendon.
Response: Contraction of the quadriceps muscle, causing the lower leg to kick or "jerk" forward.
What is unique about the neural pathway of the knee jerk reflex?
It is monosynaptic, meaning it does not have a relay neurone.
The sensory neurone synapses directly with the motor neurone in the spinal cord. This minimal pathway makes it an extremely fast reflex.
(a) What is meant by the term 'reflex action'? (2)
(b) State the survival value of a reflex action. (1)
(a)An involuntary (1) and rapid (1) response to a stimulus.
(b) It helps to protect the body from harm / danger (1).
Describe the sequence of events that occurs during the knee jerk reflex after the patellar tendon is stretched.(4 marks)
Stretch receptors (muscle spindles) in the quadriceps muscle detect the stretch (1).
A sensory neurone transmits an action potential to the spinal cord (1).
The sensory neurone synapses directly with a motor neurone (1).
The motor neurone carries an action potential back to the quadriceps (effector), causing it to contract (1).
Explain why the knee jerk reflex is so rapid.(3 marks)
It is monosynaptic, meaning it only involves one synapse (between the sensory and motor neurone) (1).
This means it does not involve a relay neurone (1).
It also bypasses the conscious parts of the brain (cerebrum), making the neural pathway as short as possible (1).
A person with severe spinal cord damage might show a normal knee jerk reflex but be unable to feel the tap on their knee. Explain this observation.(2 marks)
The knee jerk reflex arc only involves the spinal cord (and does not require the brain) (1).
Feeling the sensation requires sensory impulses to travel up the spinal cord to the brain, but this pathway is damaged (1).
In a typical reflex (like withdrawing a hand from a hot object), the sensory neurone synapses with a relay neurone in the spinal cord. Why is the knee jerk reflex, which lacks a relay neurone, an unusual example?(3 marks)
The knee jerk reflex is a stretch reflex primarily for posture and balance, not a pain/damage response (1).
Most reflexes involve a relay neurone, which allows for coordination (e.g., to also stimulate an antagonistic muscle to relax).
The knee jerk reflex is a simple monosynaptic arc, evolved for maximum speed to prevent falling (1), by contracting the same muscle that was stretched (1).