psyc 365: chapter 10
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Social ecological model
A model of acknowledging that the individual is influenced by a collection of larger, interrelated, and cumulative contexts such as organizations, communities and governments
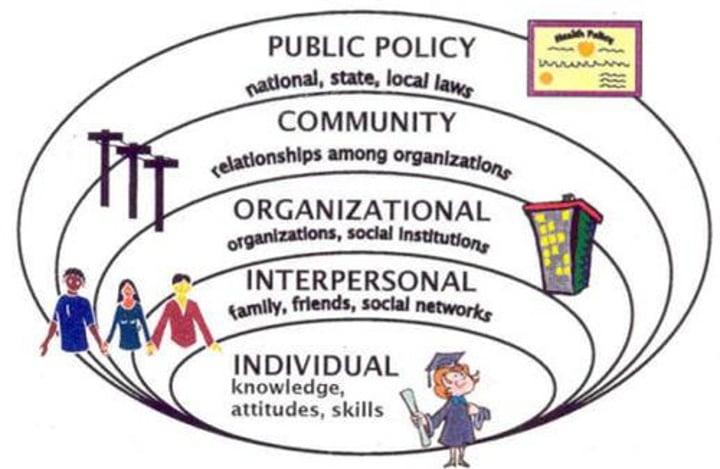
Social ecological model: Indvidual
Knowledge, attitudes, skills
Social ecological model: Interpersonal
Family, friends, social networks
Social ecological model: Organizational
Organizations, schools, workplaces
Social ecological model: Community
Design, access, connectedness, spaces
Social ecological model: Public policy
National, provincial/territorial, local laws and policy
Epidemiology
The study of changing patterns of health and disease across populations and geographic areas
Index case
The first identified instance of a medical problem
Pandemic
A large epidemic that occurs on a worldwide basis, crossing international boundaries; usually affects a large number of people
Pre-symptomatic
Someone who is confirmed to have the virus but is not yet showing symptoms
Asymptomatic
Someone who has not had the illness confirmed and has no symptoms
Viral mutation
Alteration in the genetic material of a virus that has the potential to increase virulency
Incubation period
The time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms
COVID-19 incubation period
2-14 days
Reproduction number (R)
The number of people, on average, an infected person ends up infecting
R < 1
Virus spreading is slow
R > 1
Virus spreading in increasingly
Prevalence
The number of cases that have been confirmed or presumed
Point prevalence
The number of cases present at a particular point in time
Period prevalence
The total number of cases that have occurred over the course of a time period
Current cases
The total number of cases minus those who have recovered or died from the disease
Incidence
The number of new cases that emerge in a given time period
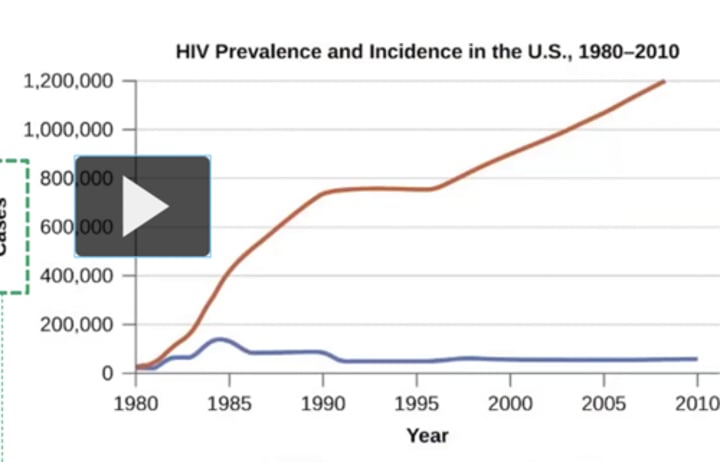
Prevalence graph
Red line
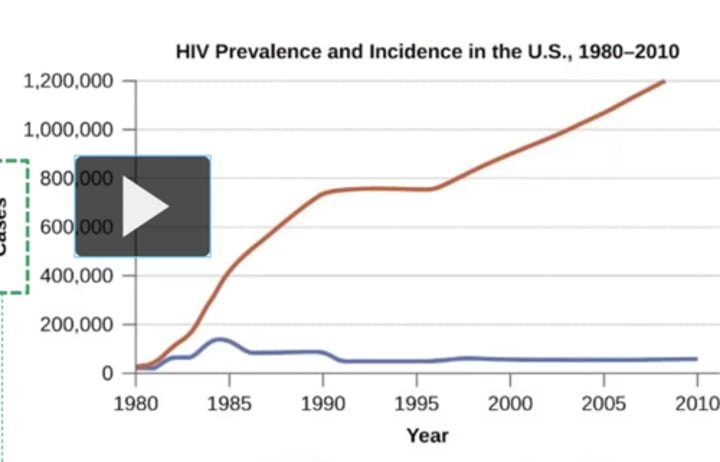
Incidence graph
Blue line
Explanations for differences in COVID-19 cases between Canadian provinces
- Spring vacations in schools
- Shelter-in-place orders
- Number and condition of seniors' care homes
- Outbreaks in industrial workplaces
Adverse behaviours associated with pandemics
Addiction, suicidality and depression
Behavioural activation
Mechanisms focused on positive responses that enhance resilience in the face of challenge
Three Cs associated with behavioural activation
Control (e.g., secondary control), coherence (e.g., acceptance-based coping) and connectedness
Secondary control
A process where we work on the things we can control in lieu of the things we cannot
Examples of secondary control in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic
- Social distancing
- Handwashing
- Sleeping adequately
- Exercising
- Establishing a routine
Acceptance-based coping
Paying attention to how one relates to emotions rather than letting the emotions take charge of one's behaviour
Gradients of health
The often-found positive relationship between socioeconomic status and health
Strategies when providing care to vulnerable patients
- Build connection to overcome perceived distance between patient and caregiver
- Develop medical expectations that are consistent with patients' social circumstances
- Establish collaborative relationships that empower patients
Wealth distribution as a predictor for health
The smaller the gap between the richest and the poorest citizens, the better the country's general health tends to be
Canadian healthcare spending compared to developed countries
Higher (+$1000) per person than the average among OECD countries
Cancer screening where Canada performs poorly compared to other developed countries
Lung cancer screening in women
Canadian health care satisfaction
Generally satisfied with quality of care but could improve wait times
Social determinants of health
Factors such as housing, employment, socioeconomic status and food availability that affect the health of populations
Upstream health causes
Economic and political causes of health (e.g., poverty and war)
Factors leading to vulnerability
- Increased exposure to a perceived threat
- Increased likelihood that the threat will become a real problem
- Lack of resources to deal with the threat
Examples of vulnerable populations
- Elderly
- Street youth
- Those living in poverty
Challenges with the term "vulnerable" to describe populations
May detract from systemic issues such as policies and stereotypes that contribute to inequitable health outcomes
Feelings common amongst unhoused people
- Alienation/loneliness
- Learned helplessness
Health conditions that more adversely affect rural-living Canadians
- Asthma
- COPD
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Heart disease
Harm reduction strategy
Attempts to reduce the harmful effects of a behaviour when faced with the reality that the health-compromising behaviour cannot be eliminated from a population
Characteristics of harm reduction
- Non-judgmental
- Emphasizes trust and compassion
- Operates under belief that comprehensive health services are a right for all
Critiques of harm reduction from those accessing services
- Does not improve life circumstances of those using drugs
- Can be difficult to access centres
Pragmatic belief
Holds that if a method yields positive results, it should be employed
Moral belief
Views some methods as not appropriate, even if evidence supports their efficacy
Harm reduction programs in BC
- Needle distribution
- Peer support
- Outreach and health education
- Substitute therapies (e.g., methadone clinics)
- Supervised consumption facilities
Infections prevalent in people who use IV drugs
- HIV
- Hep C
Benefits of fixed needle exchange sites
- Provides needles
- Handles housing and clothing requests
- Makes hospital and transportation referrals
- Provides counselling and education
- Instills feeling of safety for clients
- Reduces stigma for people accessing site
Drug efficacy
The extent to which the drug has the potential to yield its intended outcome under ideal circumstances
Drug effectiveness
A drug's ability to yield intended outcomes under realistic conditions
Process of drug development that is the most time-consuming
Effectiveness testing; involves thousands of participants
Challenge associated with COVID-19 vaccine trials
There could have be participants who became COVID positive, but did not experience symptoms and therefore were not tested for the disease; these people would have been asymptomatic transmitters
Challenge with vaccines requiring more than one dose
Roughly half of those who receive a first dose do not receive a second dose
Outcome measure
A quantifiable or objective means to determine the effectiveness of treatment
COVID-19 vaccine outcome measure
Absence of symptoms
Factors contributing to vaccine adherence
- Perceptions of effectiveness
- Side effects
Number of phases of vaccine development
3