4. DATA COLLECTION AND SAMPLING METHODS
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Data Collection Techniques (6)
Observation
Self-Report (Survey)
True Experimental Studies
Quasi-Experimental Studies
Archival Research
Sampling Techniques
Observation
Documentation of perceptual and behavioral processes
(related to looking at, listening to, touching, tasting, or smelling something)
No manipulations/high external validity
Behaviors coded after observations recorded using software
Observation downside?
Time consuming!
Self-Report (Survey)
A survey is a data collection tool used to gather information about
individuals (mail, telephone, online, etc.)Can be used in conjunction with experiments or observational studies or on their own
Important to use validated and reliable surveys
Self-Report (Survey) Tools?
Tools: Google Forms, Survey Monkey, and Qualtrics
Self-Report (Survey) Disadvantages?
Sampling error: location and time of year can skew data
Nonrespondents and low response rate
Open-ended questions (+)
response thorough and unrestrained
Open-ended questions (-)
answers may be difficult to read, interpret, or irrelevant
difficult to code and summarize
recent influence of ChatGPT on survey responses
Open-ended questions are best when?
Exploratory research
Focus groups
Close-ended questions (+)
easier to summarize
Close-ended questions (-)
not as comprehensive
Close-ended questions best when?
Good understanding of content
Theory testing
Develop Close-Ended Questions: Select Response Scales
Nominal/categorical scales
Mutually exclusive groups (i.e., religious affiliation, gender, yes/no question)
Ordinal scales
Rank order items (preference, importance, etc.)
Interval scales (using Likert format)
Evaluative: Strongly agree – Strongly disagree
Frequency: Never – Always
Usually 5 or 7 point scales, but can use 4 or 6 to force choice
Ratio Scales
# of times you took a nap in the past week; your weight
What to Avoid on Survey (4)
No abbreviations/acronyms, jargon words (i.e. SES)
No “double barreled” questions
Ex: Did the instructor provide a useful and interesting lecture?
No absolute answer options (always or never)
Avoid vagueness
Tips on Survey (3)
Limit length & order survey items from MOST to least important
Use pre-existing measures that have been validated
Make sure to put demographics/priming questions at end
True Experimental Studies
An experiment is a controlled study in which the researcher attempts to understand cause-and-effect relationships. In a true experiment, the researcher controls
True Experimental Studies (2 components)
how subjects are assigned to groups and which treatments each group receives
(random assignment used)
experimental control reduces effect of confounding variables
Quasi-Experimental Studies (3)
Similar to experimental designs, but lack the element of random
assignment often because it is making use of pre-existing groups
(experimental control somewhat involved)3 components:
Single Group Pre-Test Post-Test
Nonequivalent Control Group Post-Test
Nonequivalent Control Group Pre-Test Post-Test
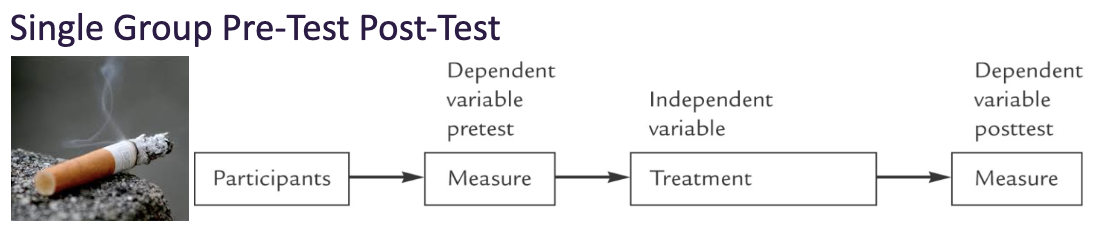
Single Group Pre-Test Post-Test
Placebo effect possible
Hard to generalize
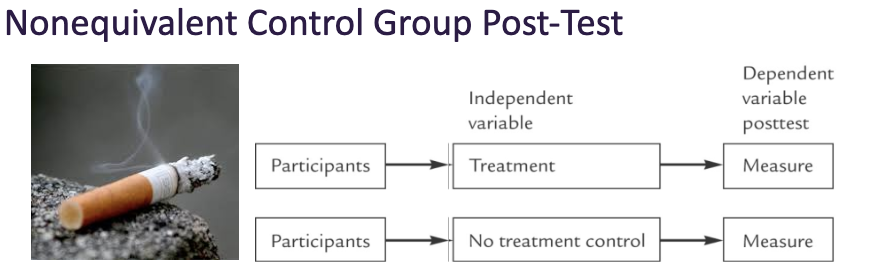
Nonequivalent Control Group Post-Test
Use naturally existing groups
Problem with selection bias
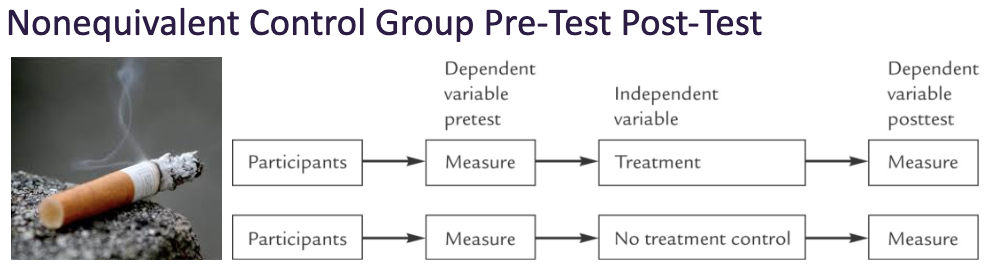
Nonequivalent Control Group Pre-Test Post-Test
Addresses selection bias problem. Group equivalence can be shown
Can measure a true change in the dependent variable
Archival Research
Rather than collecting your own data, you can use existing datasets when they contain your variables of interest
Meta-Analysis: Run statistics using data from several existing publications
Combining results from different studies, in the hope of identifying patterns among study results and resolving sources of disagreement among those results
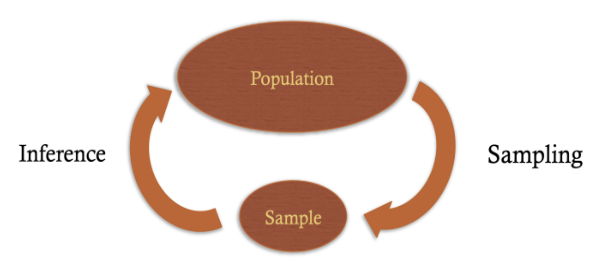
Sampling Techniques (2)
A subset of the population that is used to represent the entire population as a whole
2 components:
Probability Sampling
Non-Probability Sampling (no known chance of being selected)
Probability Sampling
Simple Random Sample
Systematic Random Sample
Cluster sampling
Stratified Random Sample
Non-Probability Sampling (no known chance of being selected)
Convenience/haphazard sampling
Snowball sampling
Purposive sampling
Quota sampling