phosphorous cycle
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
give 6 phosphorous containing compounds:
DNA
ATP
RNA (mRNA, rRNA, tRNA)
phospholipids
NADP
triose phosphate
what is weathering?
the breakdown of rocks by wind, water or biological activity, releasing phosphate into soil and water, making it available for producers
what is deposition?
the process where particles, including phosphates, settle out of water and accumulate in layers
what is erosion?
the erosion of rock/soil particles, often containing phosphate, by wind/water/ice
what is sedimentation?
the buildup of layers of particles, like phosphate-rich sediments, at the bottom of bodies of water
what is run-off?
water flowing over land that carries dissolved phosphates into rivers/lakes/oceans
what is guano?
nutrient-rich bird droppings that add phosphate to soils when they decompose
what is the main store of phosphorous?
mainly found as a phosphate ion, in mineral form in sedimentary rock
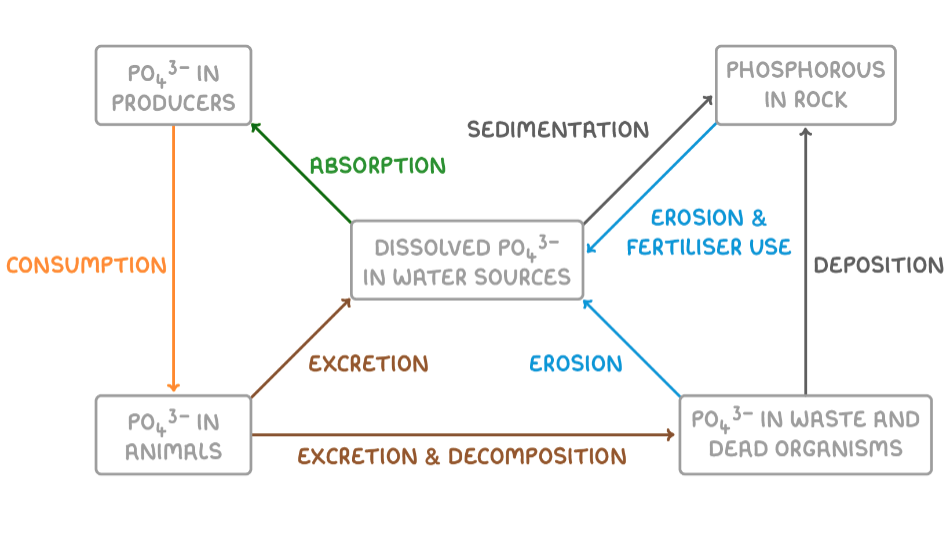
describe the phosphorous cycle:
phosphates in rocks are released into the soil and the sea through weathering, erosion and sedimentation
in the soil, phosphates are assimilated by the root network of the plants
saprobionts secrete extracellular digestive enzymes onto the dead and waste matter, hydrolysing cell tissues into smaller molecules
PO43- ions are released into the soil and assimilated by plants
PO43- ions absorbed by aquatic producers including algae before being passed along the food chain to zooplankton and fish and into seabirds
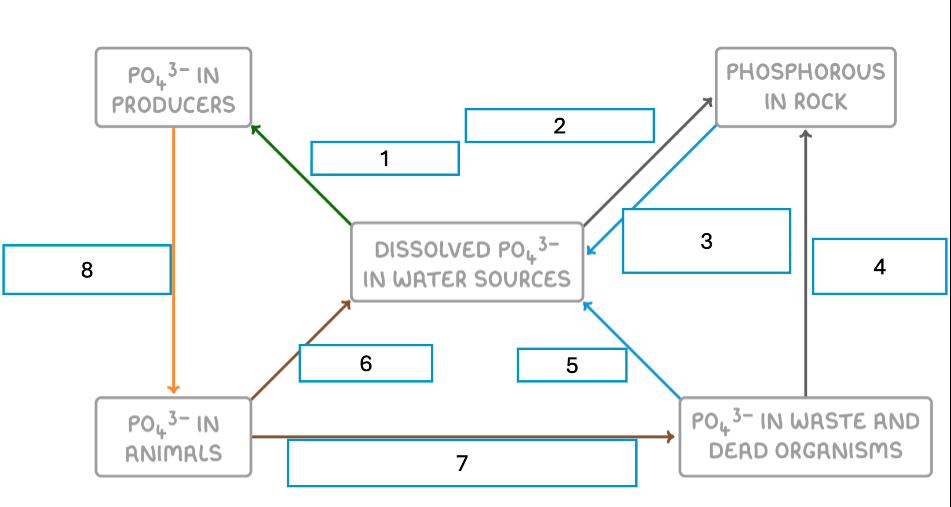
label this diagram!
absorption
sedimentation
erosion and fertiliser use
deposition
erosion
excretion
excretion and decomposition
consumption
what are mycorrhizae? what type of relationship do they form with a plant?
beneficial fungi growing in association with plant roots
form a mutualistic relationship with plant
how is mycorrhizae beneficial towards plant growth?
fungi increase SA for water and mineral absorption
mycorrhizae acts like a sponge so holds water and minerals around the roots
∴ makes plants more drought resistant and able to take up more inorganic ions
→ enables plants to take up more relatively scarce ions e.g. PO43- ions, improving plant growth
what do the mycorrhizae fungi receive in return as part of their mutualistic relationship with a plant?
carbon and sugar