Cardio: Exam 2 Class ?s + EKGs
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
50 y/o male w/ hx of smoking and an LDL of 200 and TG of 170. No hx of cardiac events. Based on USPSTF guidelines, what primary prevention should he NOT be placed on?
statin
aspirin
smoking cessation
lifestyle modifications
aspirin
A 62 y/o apple-shaped female w/ hx of HTN presents w/ frequent urination and numbness in lower extremities. Fasting glucose was performed - resulted at 170. What condition are you most concerned for?
prinzmetal's angina
hypothyroidism
Cushing's syndrome
metabolic syndrome
metabolic syndrome
Patient is a 67 year old female presenting with history of mitral valve prolapse chief complaint of feeling like her heart is racing. She endorses some generalized fatigue. On exam you notice an elevated pulse, so you obtain an ECG. ECG shows atrial fibrillation, and P-Mitrale suggesting left atrial enlargement. On exam there is an apical holosystolic murmur that radiates to the axilla. What do you suspect?
mitral regurgitation
Mr. Bobby Man is a 56yom presenting to the ED as a STEMI alert by EMS.
EKG findings as follows
Rhythm: Irregularly Irregular
Rate: 92
Axis: Left Axis Deviation
2mm of elevation in II, III, aVF. No right sided involvement.
EMS reports they gave 324mg of Aspirin and 0.8mg SL NTG. He arrives on CPAP in respiratory distress with suspected flash pulmonary edema. When auscultating his heart, you hear a holosystolic murmur best heard at the apex which radiates to the axilla. S3 sound also noted.
What murmur do you suspect and how would an MI lead to this presentation?
Mitral Regurgitation (Acute) due to MI and chordal rupture will cause the pulmonary edema
Sarah is a 47yo patient presenting to the ED after chest pain from gardening. She states this occurs every time she gardens, episodes last about 10 minutes but the pain alleviates when she sits on her couch. Pt does not have any sx at this time. What condition does Sarah have?
STEMI
NSTEMI
Stable angina
Unstable angina
stable angina
You diagnose her with stable angina. What are your next steps in treating and discharging this pt?
a. Prescribe aspirin, statin, and BB for daily use. Prescribe nitroglycerin PRN then refer to cardiology for stress test.
b. Prescribe CCB and nitroglycerin then refer to cardiology for echocardiogram.
c. Admit pt and keep close observation while administering 325mg chewable aspirins.
d. Discharge pt since they have no sx at this time.
Prescribe aspirin, statin, and BB for daily use. Prescribe nitroglycerin PRN then refer to cardiology for stress test.
A 35-year-old woman presents to your clinic with DOE, fatigue, and palpitations. On physical exam, you note wide fixed splitting of S2. You also note a systolic ejection murmur at the 2nd/3rd ICS parasternally. What would be the best diagnostic test to evaluate the defect?
A.) nuclear stress test
B.)Bubble study
C.) cardiac cath
D.) chest x ray
b. bubble study
What is the most common type of atrial septal defect?
Patent foramen ovale
Secundum ASD
Primum ASD
VSD
Secundum ASD
A 30 y. male has been having pain over the last 45 mins with exertion. Tried using nitroglycerin prn which did not relieve his symptoms. EKG showed some ischemic changes but on labs had no elevated troponin. What do you suspect his diagnosis is?
STEMI
NSTEMI
Unstable Angina
Stable Angina
Unstable Angina
A 78 y/o female with DM has worsening fatigue and angina that comes on at rest with minimal exertion. EKG shows ST depression but not ST elevations. What should the initial treatment be?
Nitroglycerin/ ASA
BB
CCB
Supplemental oxygen
Nitroglycerin/ ASA
A 78 y/o F with PMHx of DM and arthritis presents w/ abdominal pain, N/V, and fatigue after playing a lengthy game of Monopoly. Patient is not stable enough for a stress test. Troponin comes back positive, and EKG reveals inverted T waves and ST depression..
What is the dx?
Unstable Angina
NSTEMI
STEMI
GERD
NSTEMI
Pt is dx with NSTEMI. She is at high risk. How soon are we trying to get her to PCI?
Within 2 hours
Within 24 hours
Within 72 hours
She does not need PCIi
Within 24 hours
RCA
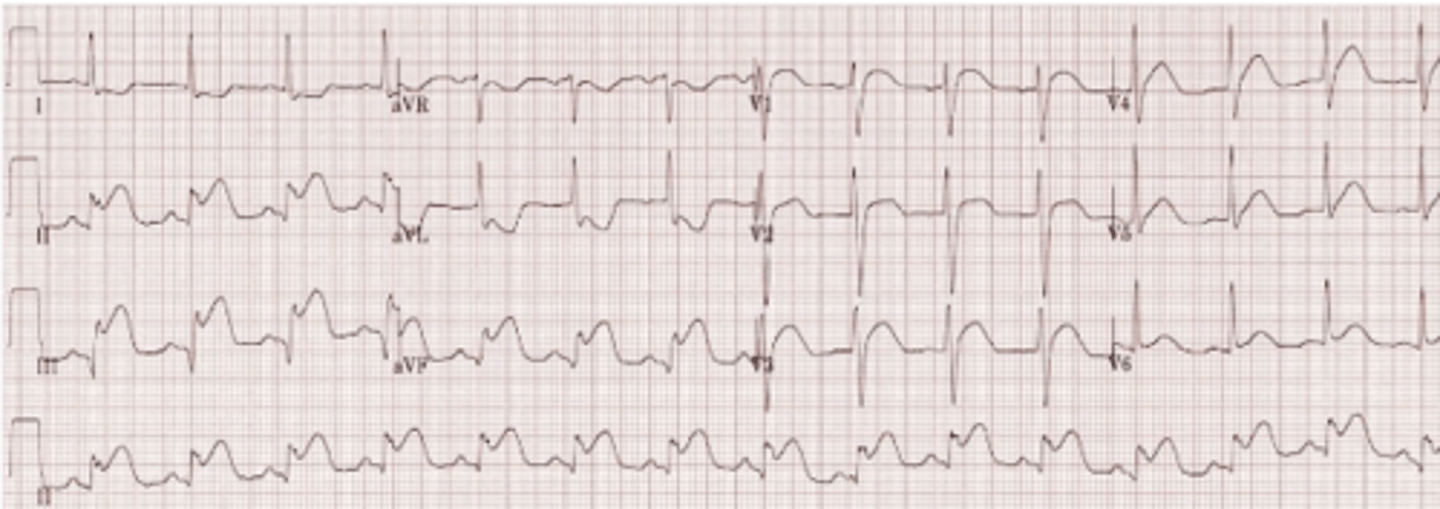
A 67 year old male with PMH of HTN and dyslipidemia presents to the ED with complaints of dyspnea and chest pain that began 4 hours ago. Upon interview, he states that the pain is radiating down his left arm. Cardiac biomarkers come back with positive troponins. EKG is shown below. Which coronary artery is most likely involved?
LAD
Circumflex
RCA
Distal LAD
This Patient was lucky enough to have access to a PCI hospital. What is the best first step in his care?
Stop platelets with high dose aspirin
Follow anti-platelet therapy with plavix
Give simple unfractionated heparin
Go to cath lab
All of the above
All of the above
A 74 yo male, with a Hx of HTN and 20 pack years presents for evaluation. He stated that "I fainted early this am, and now my chest hurts and can't catch my breath". What would you expect to hear on auscultation?
Opening snap
Diastolic decrescendo
Holosystolic
Mid-systolic crescendo-decrescendo
Mid-systolic crescendo-decrescendo
For a pt with aortic stenosis with what maneuver would you hear an increase in the sound and what maneuver would you hear a decrease?
I: Squating D: Standing
I: Standing D: Squatting
I: Standing and squatting
D: Standing and squatting
I: Squating D: Standing
24 y/o male patient presents with abnormally long limbs and on exam a harsh, medium pitch diastolic murmur is heard at the LLSB. The Murmur is increased when patient is sitting, leaning forward and fully exhaling.
What other clinical presentation may you expect to see on your physical exam?
· Grant Steel Murmur
· Quincke Pulse
· Cyanosis
·Ebstein phenomenon
Quincke Pulse
Patient is asymptomatic, however after echo, left ventricular ejection fraction is 42%.
What is the next best treatment option?
· Refer for surgery
· Reassurance
· ACE/ARB
·Percutaneous Balloon Valvuloplasty
Refer for surgery
A 50-year-old woman with a history of mitral stenosis presents to the emergency department with worsening shortness of breath and palpitations. An ECG reveals atrial fib and left atrial enlargement.
Which diagnostic test is considered the gold standard for assessing mitral stenosis and what specific measurements would you expect to see for severe mitral stenosis?
A. Echo - the size of the mitral orifice and gradient will be <1cm2
B. Echo - the size of the mitral orifice and gradient will be >1cm2
C. MRI - the size of the mitral orifice and gradient will be 1.0- 1.5 cm2
D. MRI - the size of the mitral orifice and gradient will be <1.5cm2
A. Echo - the size of the mitral orifice and gradient will be <1cm2
A 35-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with complaints of increasing shortness of breath, especially with physical exertion. She mentions that her symptoms have gradually worsened over the past few years. Her medical history is notable for rheumatic fever during childhood. On examination, you note a diastolic murmur best heard at the apex of the heart.
What is the most likely diagnosis, and what is the primary underlying cause?
A. Aortic Regurgitation
B. Mitral Regurgitation
C. Mitral Stenosis
D. Tricuspid Stenosis
C. Mitral Stenosis
13 year old female with no PMHx and no concerns presents for her annual visit. Physical exam findings are significant for a diastolic murmur heard over the LICS. The murmur is described as a high pitched blowing with a decrescendo configuration. What is the best initial treatment management?
Monitor
Surgical valve replacement
Beta blockers
Anticoags
Monitor
2. 8 year old male presents with a known history of a systolic murmur that is appreciated over the LICS. Patient is asymptomatic, and previous ECHO demonstrated a peak pressure gradient of 67 mmHg. PE findings are significant for palpable parasternal lift that is due to RVH. What is the best treatment?
Monitor
Balloon valvuloplasty
Beta blockers
Anticoags
Balloon valvuloplasty
A 4 yr old female is presenting today for her annual well child visit. During her visit, her mom mentions that the patient has had a persistent cough for the last three weeks. You go ahead an obtain and chest x-ray to rule out PNA or other causes. On XR, her lungs are clear but you note rib notching and what looks to be a "Figure 3" sign. Given the most likely diagnosis, what other abnormal finding might you expect to find?
Wide, fixed split of S2
RAE on ECHO
LVH on EKG
holosystolic murmur along LLSB
LVH on EKG
A mom presents today with her newborn for their newborn weight and color check. The mom is concerned because her baby has not been feeding and she has noticed "belly breathing". On examination, you notice the baby has bluish fingers and lips, she is tachycardic and both proximal and distal pulses are weak. Given history and physical exam, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Coarctation of the aorta
Transposition of GV
Ventricular septal defect
Patent foramen ovale
Transposition of GV
lateral MI
dx?
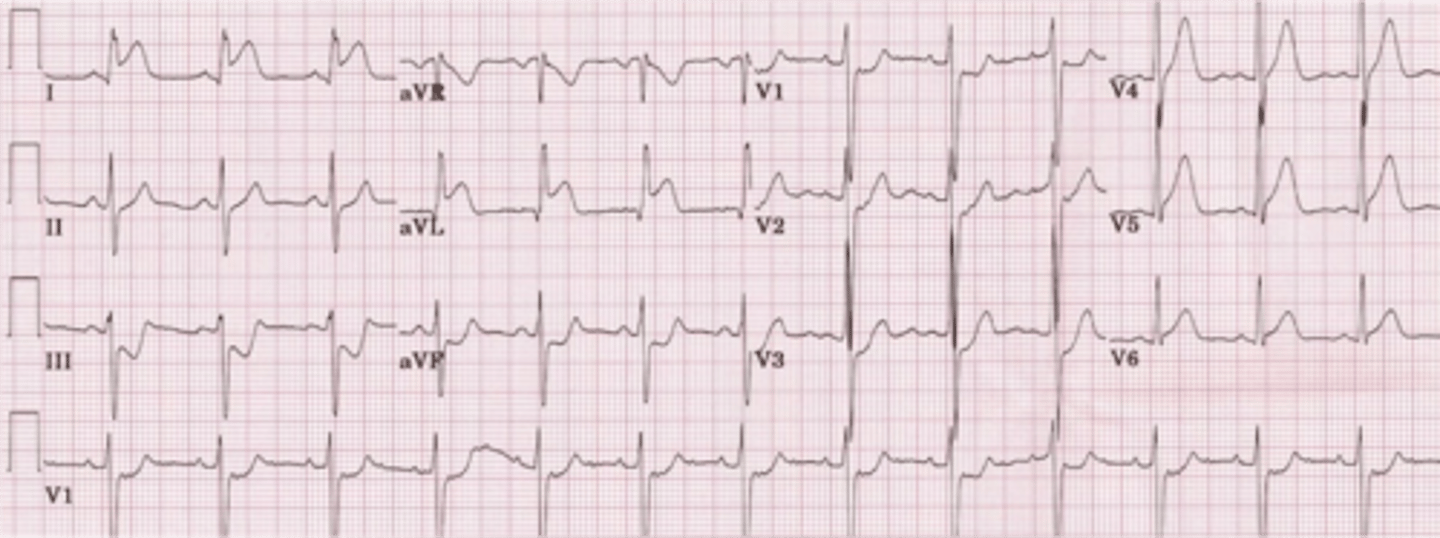
anterior wall MI
dx?
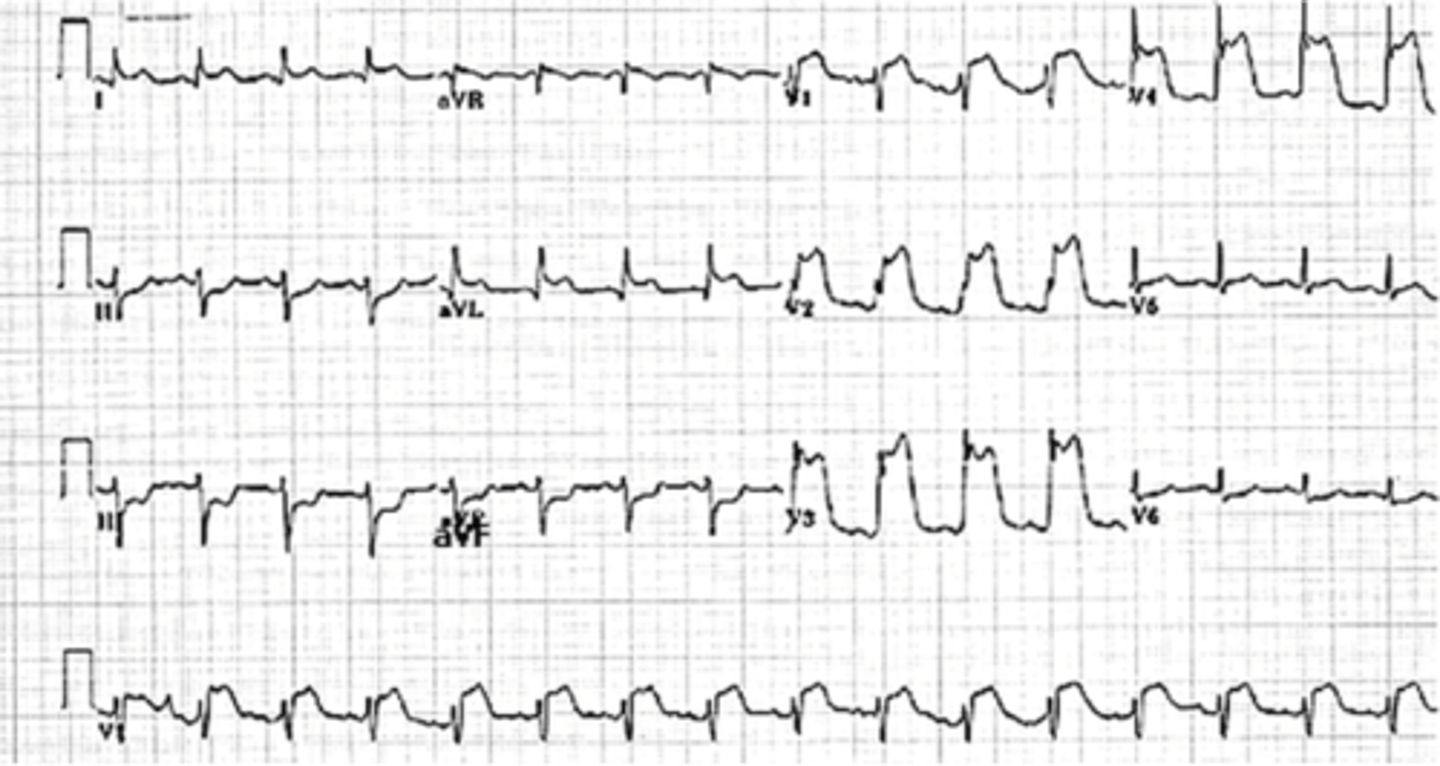
inferior wall MI
dx?
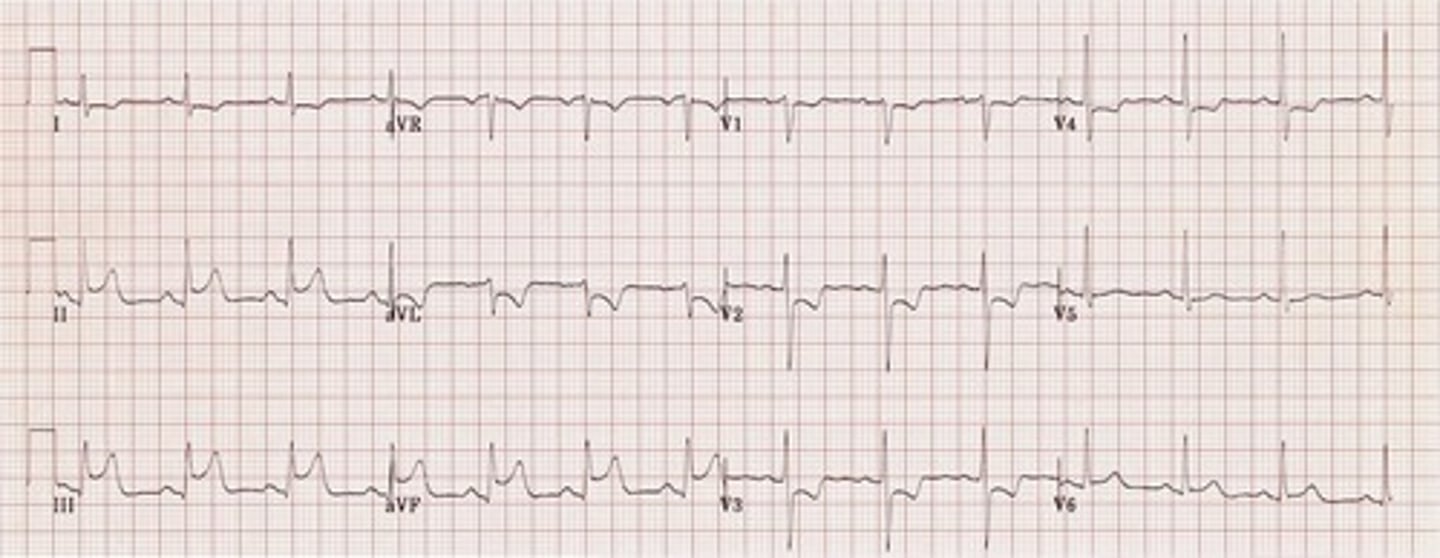
right venticular infarction
dx?
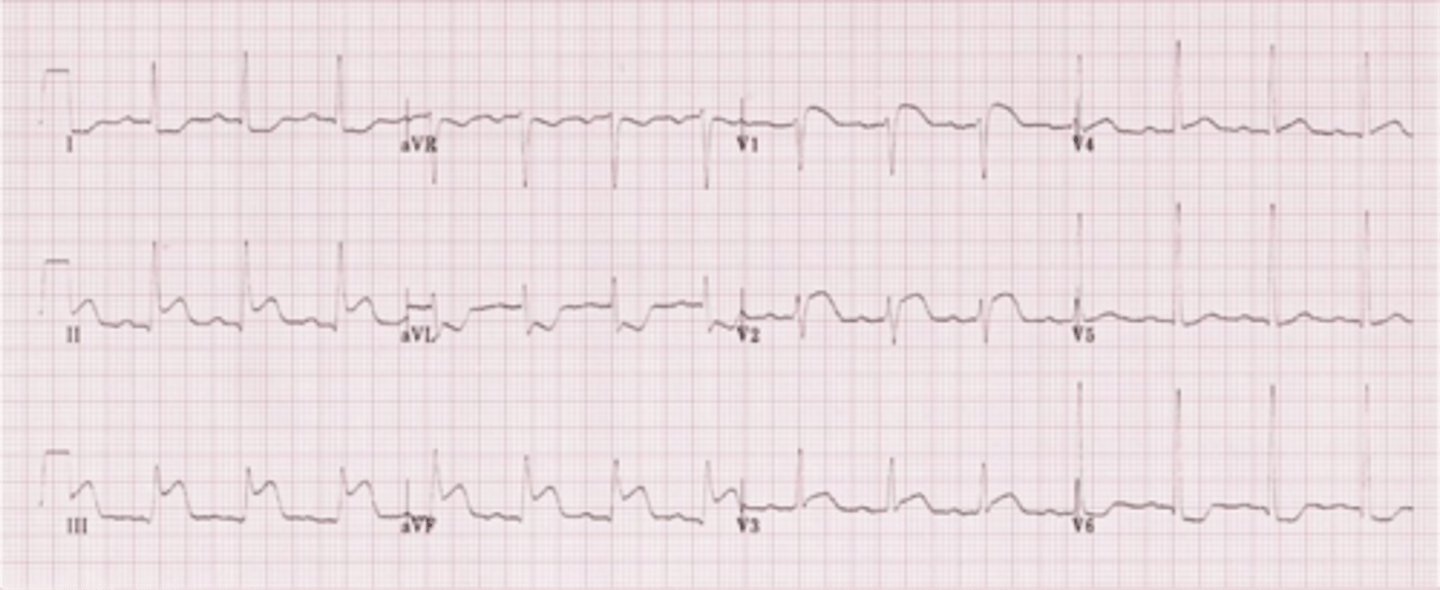
posterior MI
dx?
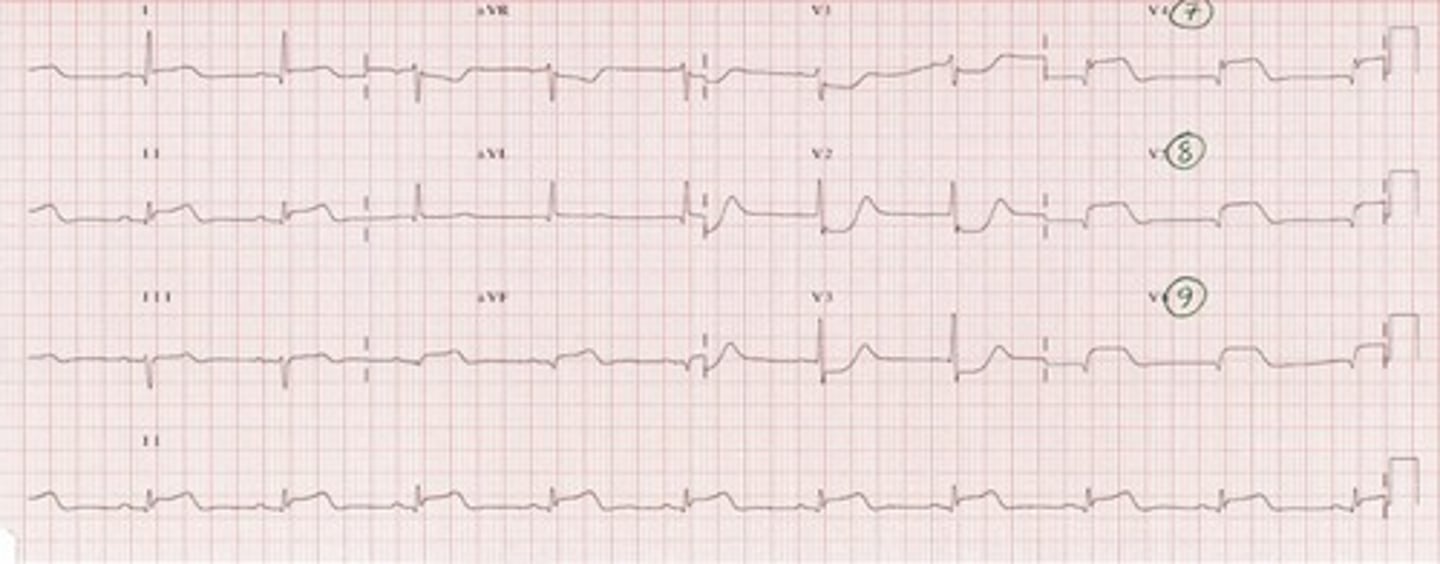
anterolateral MI
dx?
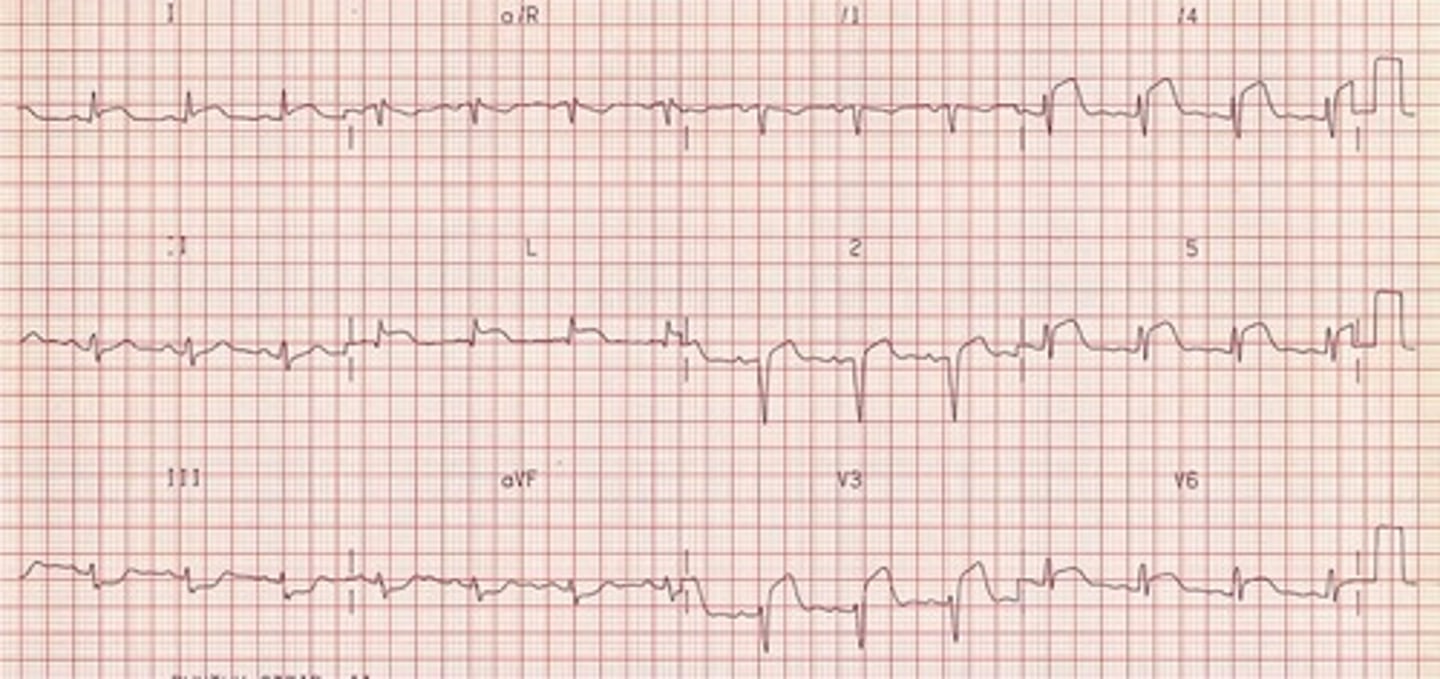
early repolarization
dx?
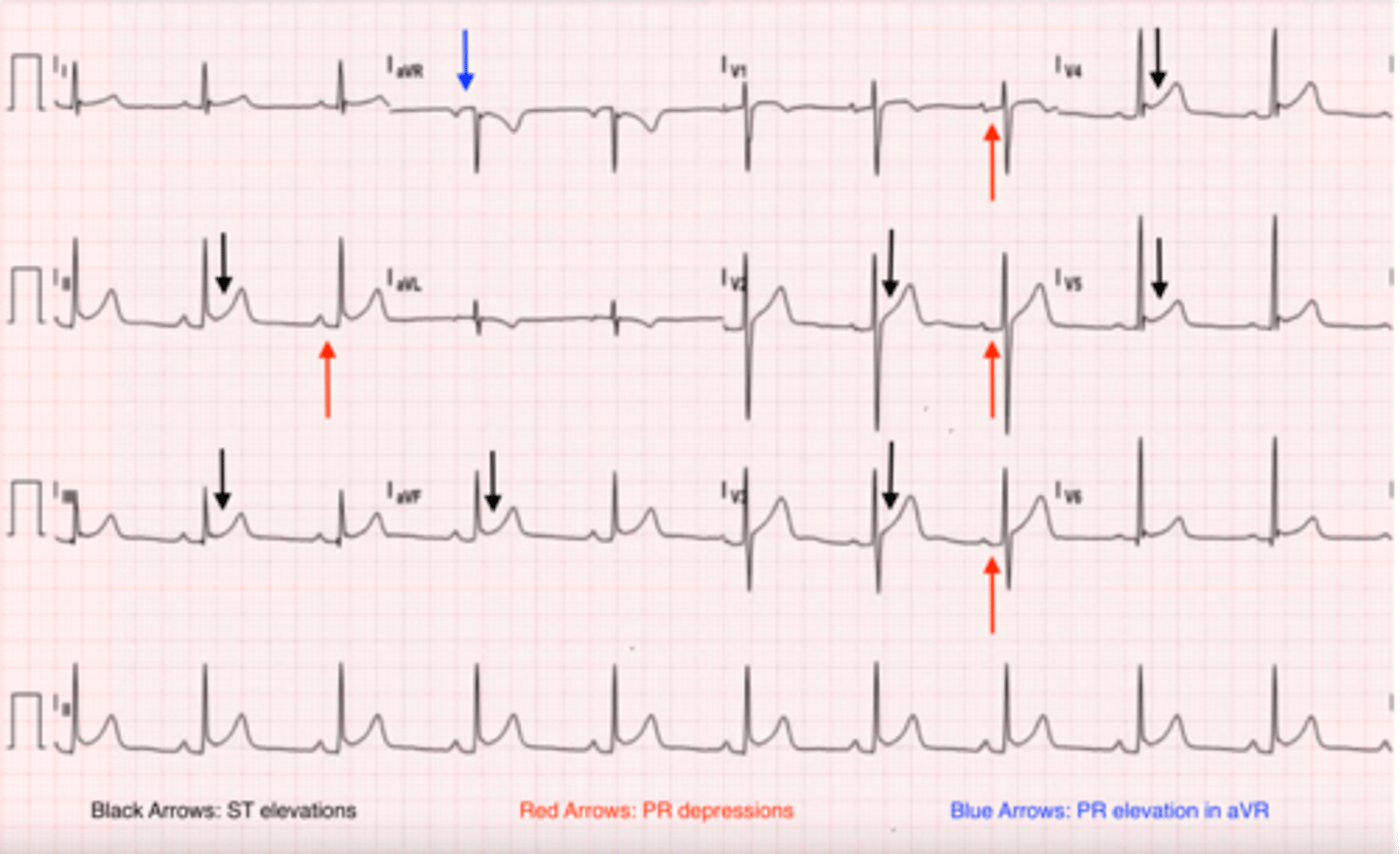
LVH
dx?
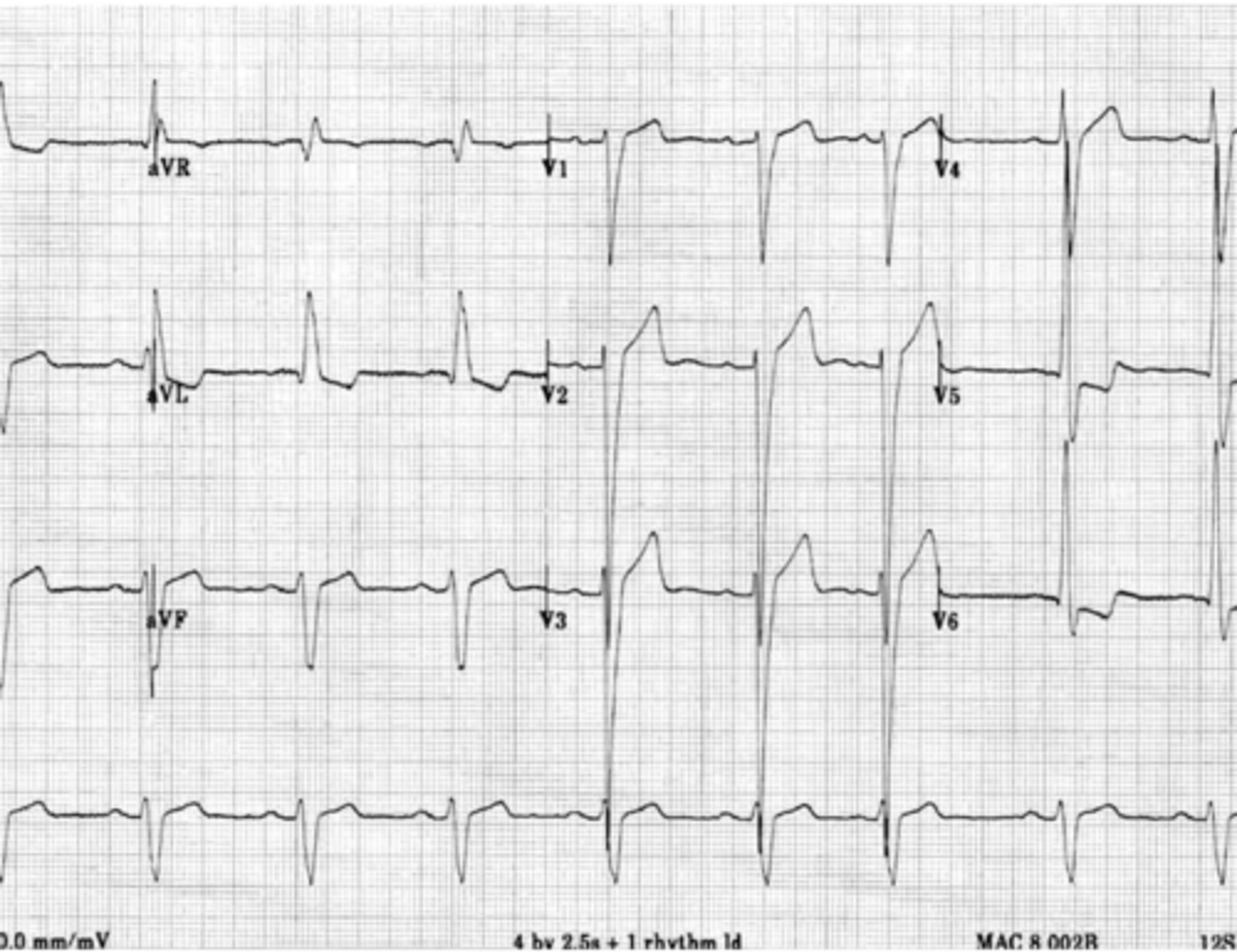
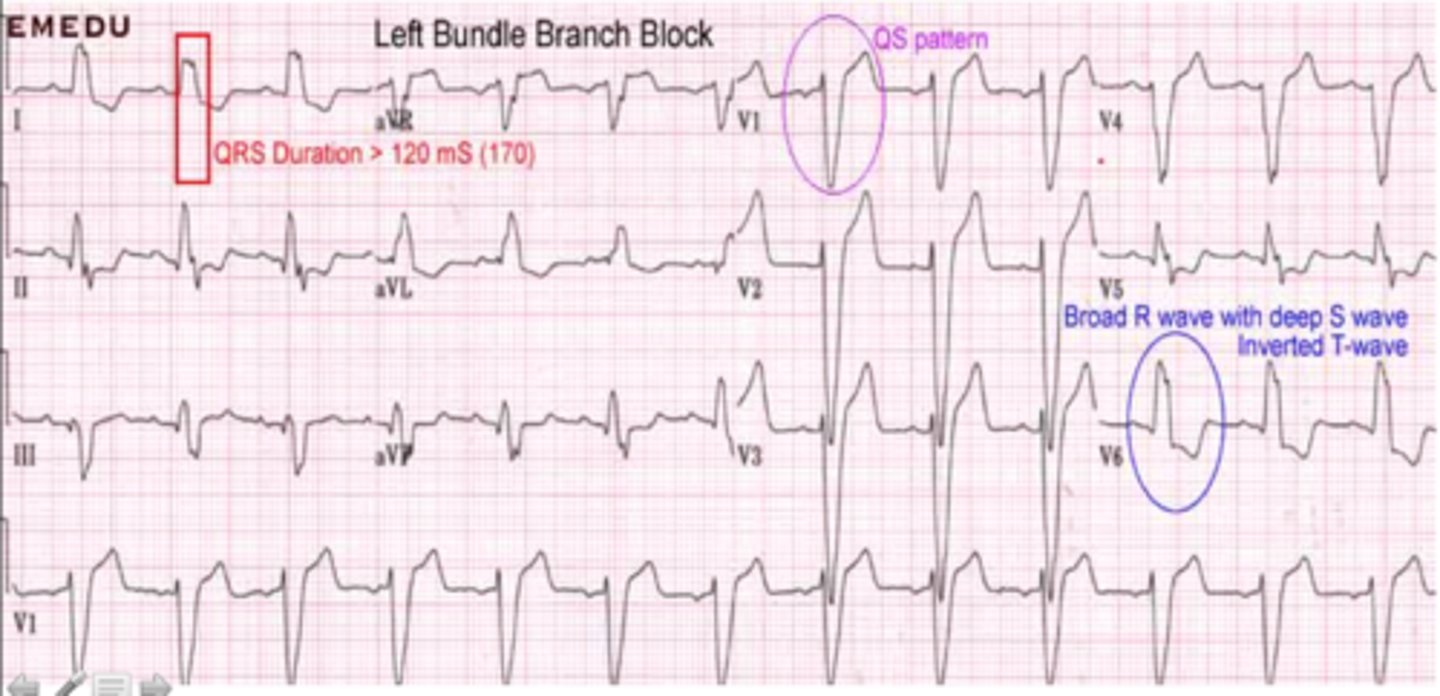
LBBB
dx?