Bio test cells and cell transport
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the 3 organelles all cells have in common?
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes
Why do scientists think chloroplasts and mitochondria were once free-living organisms?
They contain their own DNA and have 2 membranes - this is the Endosymbiotic Theory. These were once their own “creatures” and a eukaryotic cell engulfed/ate them and kept them around because they were useful.
Draw and label the cell membrane below using the words:
○
phospholipid, protein, hydrophobic, hydrophilic, polar, nonpolar
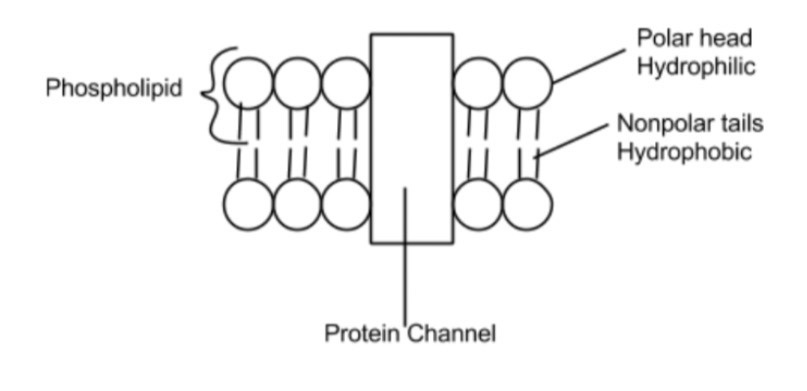
What’s the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic: something that doesn’t get along with water (nonpolar)
Hydrophilic: something that loves water (polar)
What does selectively permeable mean?
The cell membrane only allows certain molecules through.
What types of molecules are permeable to the membrane?
small molecules: O2, CO2, water
What types of molecules are impermeable to the membrane?
large molecules: glucose, enzymes, nucleic acids
What does “passive” mean?
No energy needed
What is diffusion?
molecules traveling across a membrane from HIGH to LOW concentration
What is facilitated diffusion?
molecules traveling across a membrane from HIGH to LOW concentration with the help of protein channels
What’s the difference between transport, receptor, and recognition proteins?
Transport: allows big and/or hydrophilic substances through membrane
Receptor: another molecule must bind for protein to open up and allow substance through membrane
Recognition: tells you what type of cell it is; has carbs on the end of the protein channel (glycoprotein)
What is osmosis?
The movement of WATER across a membrane from HIGH to LOW
What happens to a cell in an isotonic solution?
Stays the same = equal concentration of water inside and outside
What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution?
Shrinks = more water inside the cell, so water will leave it
What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution?
Grow = more water outside the cell, so water will rush in
What is osmotic pressure?
Plants have cell walls and the large vacuole that control the amount of water and contain the increase in pressure. Without this water pressure, leaves wilt (plant is dying without water).
What are 2 ways active transport is different from passive transport?
1. Active requires ENERGY
2. Active goes from LOW to HIGH concentration - against the normal concentration gradient
What is the compound for energy?
ATP
What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis?
Endocytosis: bringing something INTO the cell (eating)
Exocytosis: something exits or leaves the cell (excreting wastes)
What’s the difference between the 2 types of endocytosis?
Phagocytosis: eating large solids
Pinocytosis: “drinking” liquids
Desmosome
→ sewing or stitching cells together using protein filaments
○Skin doesn’t rip apart when we stretch
Tight Junctions
→ cell are sealed together to prevent leakage
○Sacs like the bladder
Gap Junctions
→ cells have protein-channel holes that connect their cytoplasms
○Brain and heart send hormones and nutrients
Plasmodesmata
→ holes in plant cells that connect their cytoplasms
○Transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
What’s the difference between arteries and veins?
Arteries take blood AWAY from the heart (filled with oxygen)
Veins bring blood BACK to the heart (less oxygen, more CO2)
What accessory organs help out the circulatory system; what do they do?
Liver → removes toxins from your bloodstream
Kidneys → remove excess water from your bloodstream, forms urine
What is the epiglottis?
The flap that covers your trachea when you swallow food so food particles do not go down into your lungs.
What is the order of the respiratory system organs when you breathe in?
Air enters nose/mouth → pharynx → larynx (voicebox) → trachea → bronchi → lungs → bronchioles → alveoli
Which respiratory organ is directly connected to a circulatory organ? Why is this important?
The alveoli inside your lungs have capillaries surrounding them. DIFFUSION forces the oxygen to go from your alveoli into your blood and forces the CO2 to go from your blood to your lungs to be breathed out. This is how you breathe! Your body’s cells need oxygen to make energy and have to get rid of waste (CO2).
Which digestive system organ is directly connected to a circulatory organ? Why is this important?
The villi in the small intestine have capillaries surrounding them. This is how digested FOOD/NUTRIENTS get into your bloodstream to be taken to all of your cells. Your cells need glucose in order to make energy.