MODULE 2: FUNDAMENTALS OF PROGRAMMING
1/33
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
ALGORITHM
Set of instructions to perform a specific task
Well-defined step-by-step solution
FLOWCHART
graphical representation of an algorithm
PSEUDOCODE
method of describing algorithms using combination of natural language and programming language
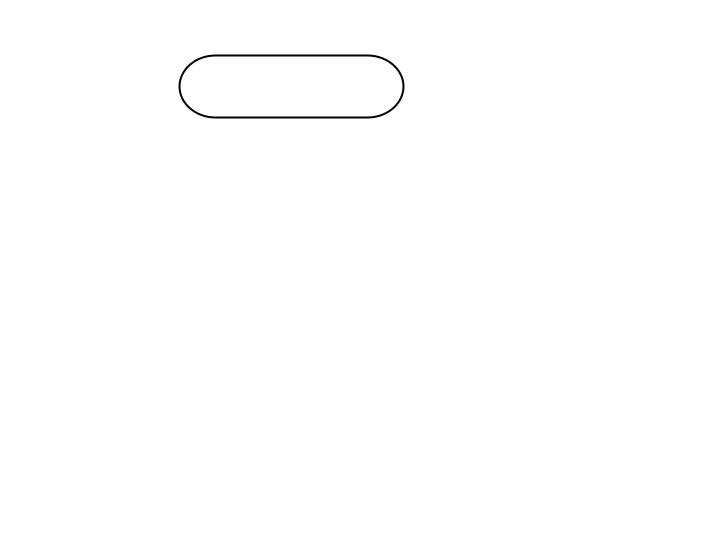
Terminal Box
Used to represent the beginning (Start) or the end (End) of a task
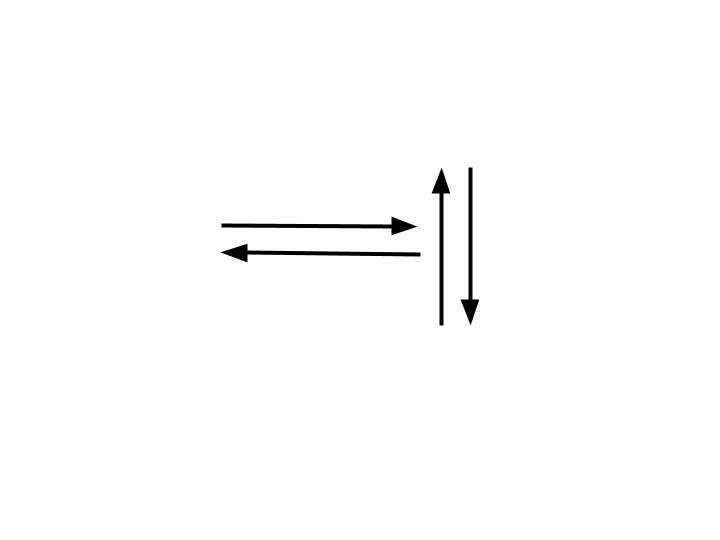
Flow Line
Used to connect symbols and indicate the flow of logic
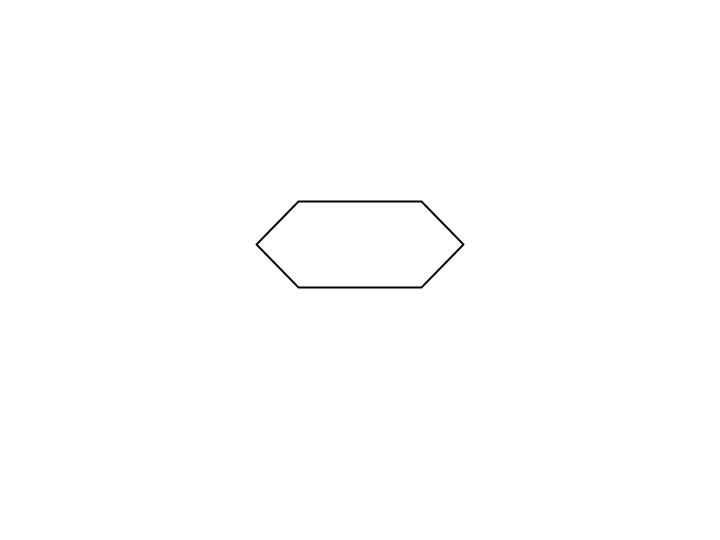
Initialization Box
Used to declare beginning value
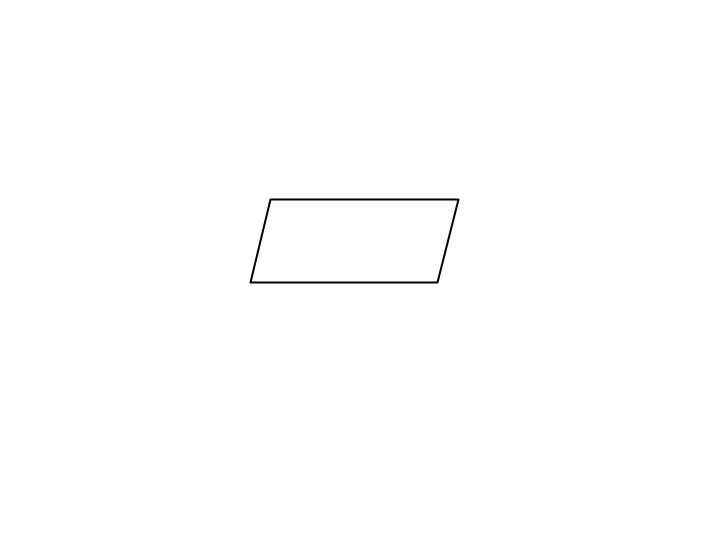
Input/Output
Used for input and output operations
Data to be read or printed are described inside
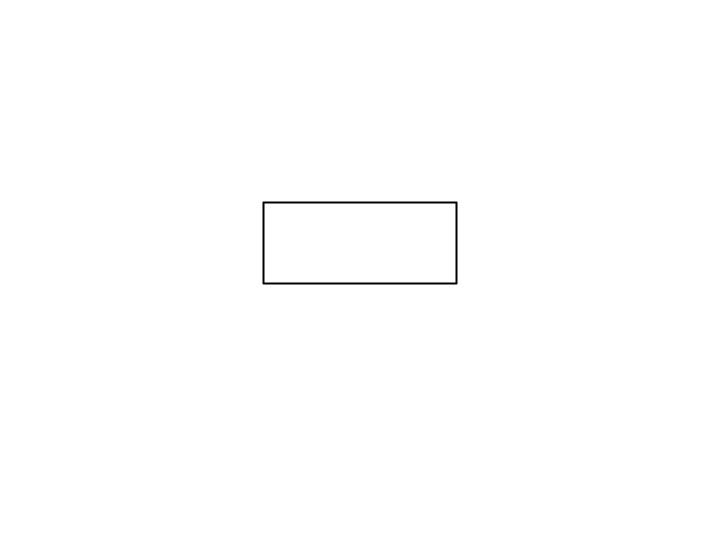
Processing
Used to connect symbols and indicate the flow of logic
Indicates any type of calculation
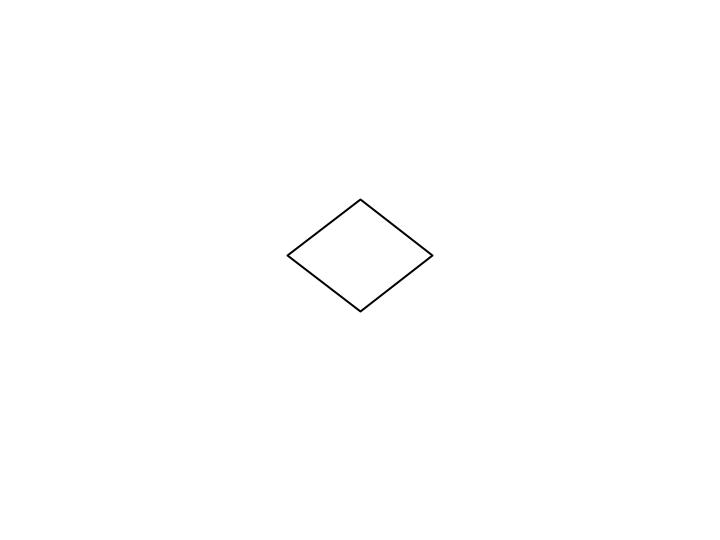
Decision Box
Used for any logic or comparison operations
Path chosen depends on whether the answer to a question is “yes” or “no” or “True” or “False”
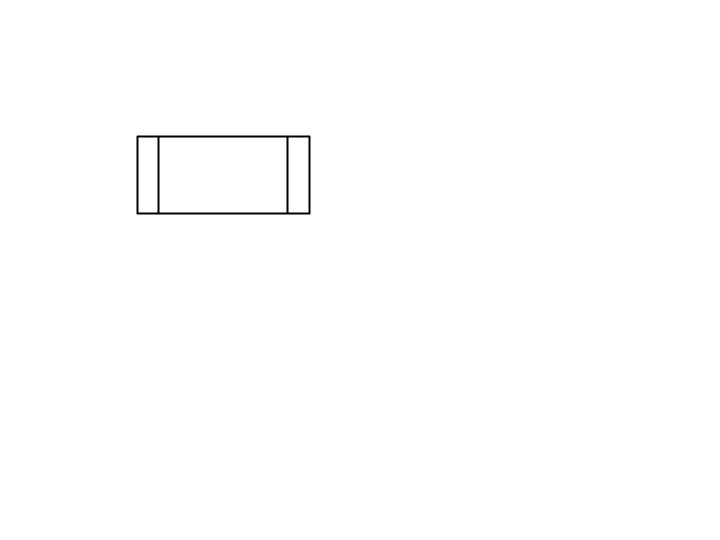
Pre-defined process
Marker for another process step or series of process flow steps that are formally defined elsewhere
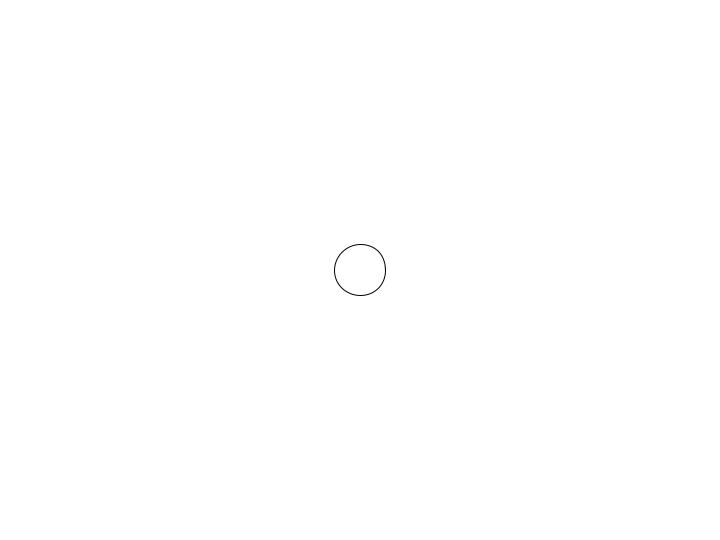
On-page connector
Allows flowchart to be continued on the same page
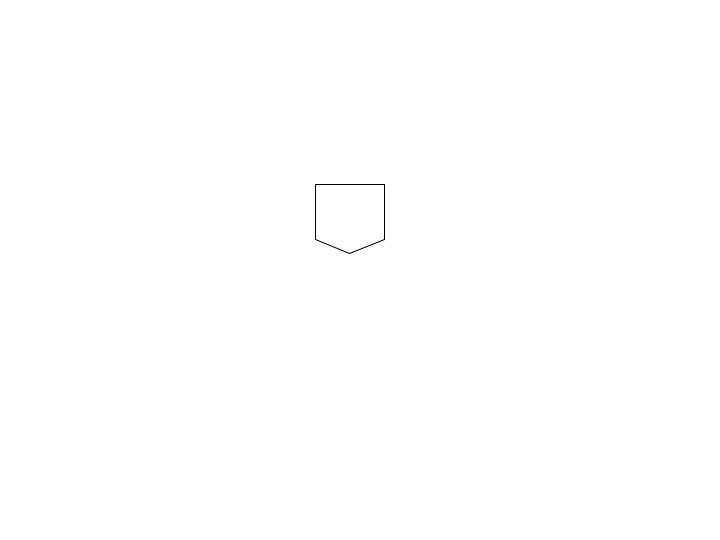
Off-page connector
Allows the continuation on other pages
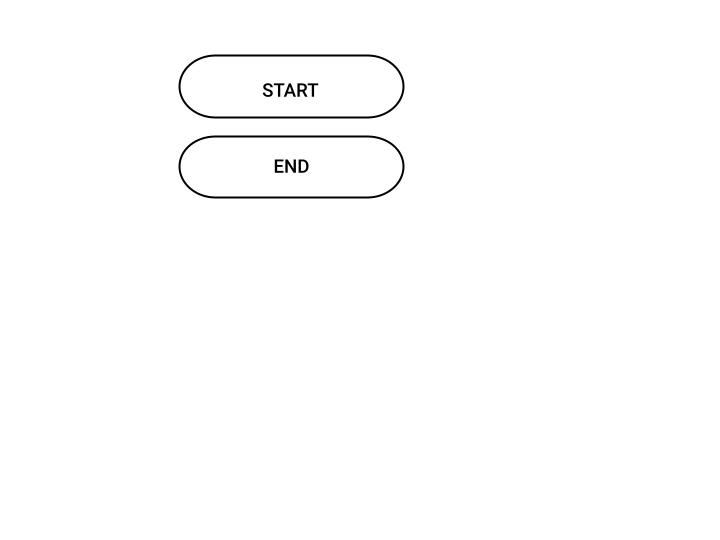
START AND END OPERATION
Signifies the start and end of the flowchart
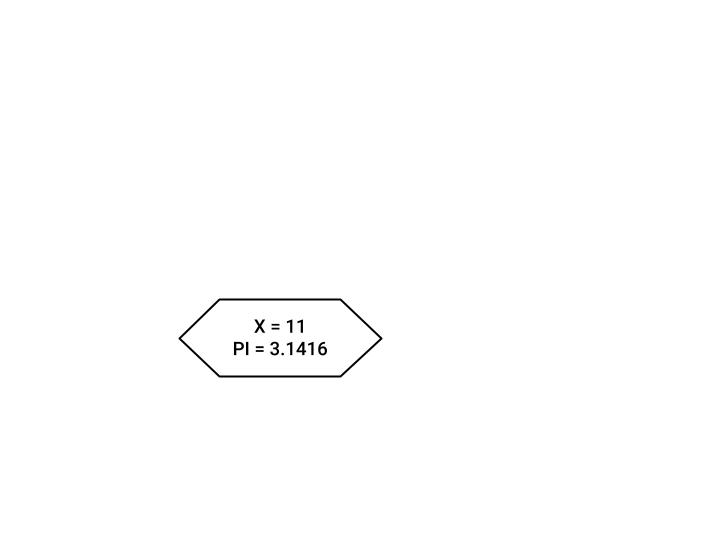
VARIABLE DECLARATION
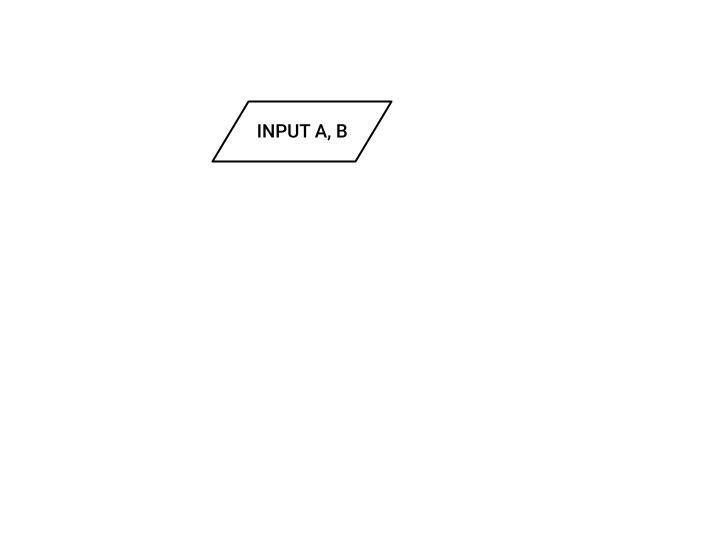
INPUT OPERATIONS
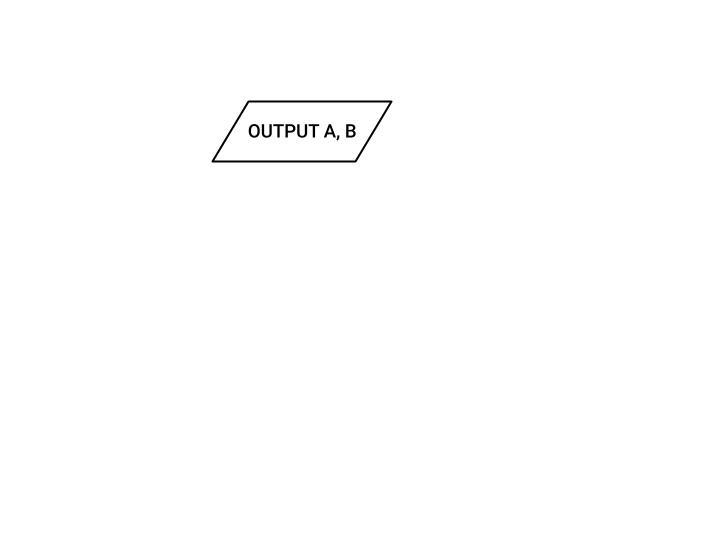
OUTPUT OPERATIONS
Standard Arithmetic Operators
+ (plus sign) – addition
- (minus sign) – subtraction
* (asterisk) – multiplication
/ (slash) – division
% (modulo) - remainder
Returns the remainder of a division operation
Rules of precedence
Also called the order of operations
Dictate the order in which operations in the same statement are carried out
Expressions within parentheses are evaluated first
Multiplication and divisionare evaluated next (from left to right)
Addition and subtraction are evaluated next (from left to right)
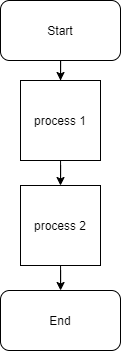
SEQUENTIAL OPERATION
Sequential is very simple design.
It does not involve conditional or iterative processing
Design in this types is normally from top to bottom or left to right
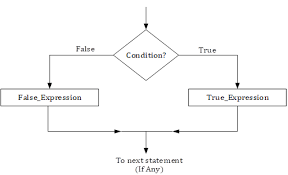
CONDITIONAL OPERATION
A step where a decision must be made
Ask questions and choose actions based on the available options
Boolean Expression
Value can be only true or false
Used in every selection structure
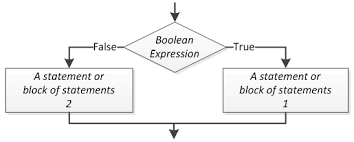
Dual-alternative (or binary) selection structure
Provides an action for each of two possible outcomes
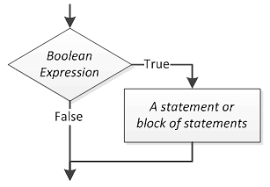
Single-alternative (or unary) selection structure
Action is provided for only one outcome
If-then
Relational comparison operators
Six types supported by all modern programming languages, <, >, =, >=, <=, !=
Binary
Two values compared can be either variables or constants
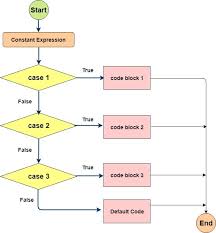
Case Structure Operation
A more open convenient way to handle multiple selections or multiple alternative.
Compound condition
Asks multiple questions before an outcome is determined
AND decision
Requires that both of two tests evaluate to true
Requires a nested decision (nested if)
nested if statements
Second selection structure is contained entirely within one side of first structure
else clause paired with last if
OR decision
Take action when one or the other of the two conditions is true
REPETITION OPERATION
The loop mechanism causes repetition of a sequence of statement/s based on the given condition/s. Most of the time, when a body of the loop is executed, the value of at least one variable changed. Therefore, most loop mechanism has cumulative effect.
Counter
a variable used to determine number of loops
Accumulator
a variable use to store results of an iteration
FUNCTION CALL OPERATION
Depicts a sub-process or sub-routine