10-Pelvic Autonomics
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Erection Nerves and Arteries
Parasympathetic efferents from S2-S4 (pelvic splanchnics) form cavernous nerves that reach the helicine arteries of the penis, leading to dilation and engorgement of erectile tissues.
Erection (Triggering Factors):
Erection can be triggered or intensified by physical sensations carried by the pudendal nerve or by conscious thought.
Emission Nerves and Arteries
Sympathetic efferents trigger contraction of the ductus deferens, seminal glands, and prostate, adding sperm to the semen in the prostatic urethra.
Ejaculation:
Sympathetic efferents trigger contraction of the internal urethral sphincter.
Parasympathetic efferents cause contraction of urethral smooth muscle.
Somatic efferents (pudendal nerve) trigger contraction of the bulbospongiosus muscles, expelling semen through the external urethral orifice.
Remission:
Sympathetic efferents constrict the helicine arteries of the penis, causing it to return to its normal size.
Pelvic Pain Line - Sympathetic Afferents:
Sympathetic afferents travel back to the spinal cord via lumbar (T12-L2/3) and sacral splanchnics.
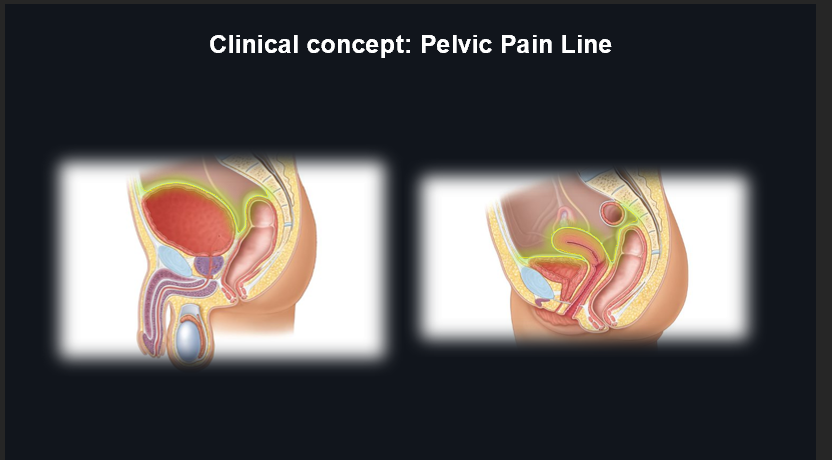
Pelvic Pain Line - Parasympathetic Afferents:
Parasympathetic afferents travel back to the spinal cord via pelvic splanchnics (S2-S4).
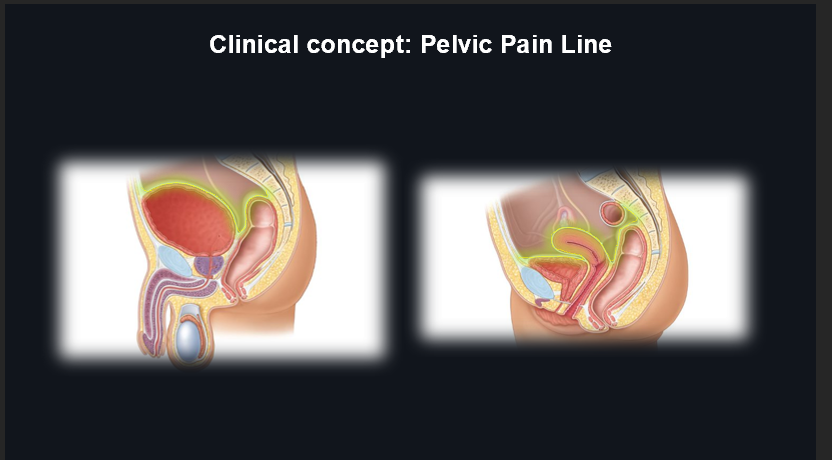
Pelvic Pain Line - Organs Above the Line (Detailed):
Organs above the pelvic pain line include:
Ureter
Superior part of bladder
Testis
Epididymis
Inguinal part of Ductus deferens (M)
Ovary & Uterine Tube (F)
Uterus (body & fundus) (F)
Nociceptive afferents travel back to the spinal cord with sympathetics (T12-L2/3 and sacral splanchnics).
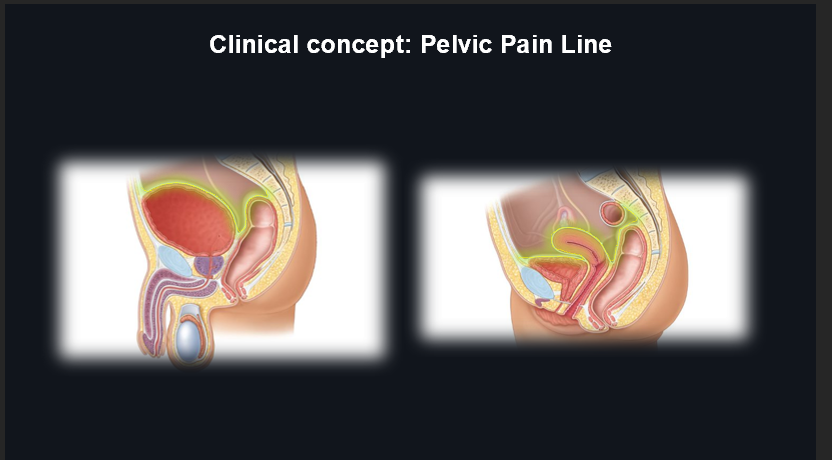
Pelvic Pain Line - Organs Below the Line (Detailed):
Organs below the pelvic pain line include:
Inferior bladder
Proximal urethra
Prostate (M)
Seminal vesicles & ejaculatory duct (M)
Rectum
Anal canal above pectinate line
Cervix & upper 2/3 of vagina (F)
Nociceptive afferents travel back to the spinal cord with parasympathetics (S2-S4 via pelvic splanchnics).
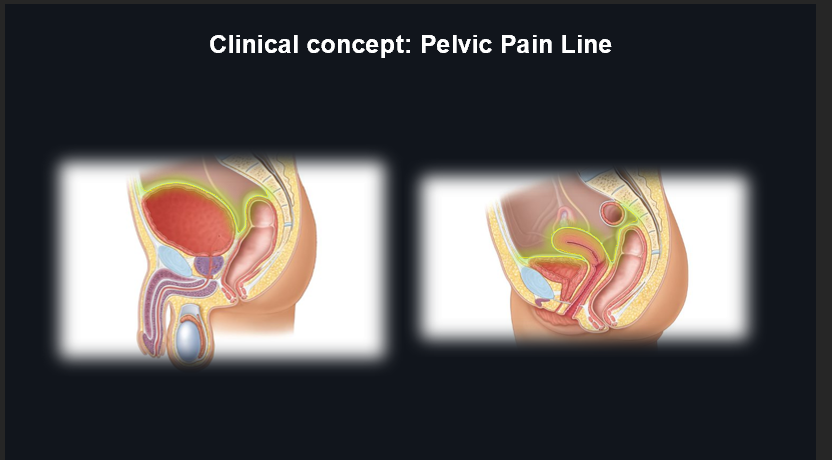
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Innervation to Ureters:
Sympathetic innervation relaxes the smooth muscle of the ureters.
Parasympathetic innervation contracts the smooth muscle.
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Innervation to Bladder:
Sympathetic innervation relaxes the detrusor muscle and contracts the internal urethral sphincter.
Parasympathetic innervation contracts the detrusor muscle and relaxes the internal urethral sphincter.
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Innervation to Ductus Deferens, Seminal Ducts, and Prostate:
Sympathetic innervation is responsible for emission and ejaculation by causing contraction of smooth muscle in the ductus deferens, seminal glands, and prostate.
The function of parasympathetic innervation to these structures remains unclear.
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Innervation to Penis:
Sympathetic innervation is not involved in producing an erection but is active during remission, causing constriction of the helicine arteries.
Parasympathetic innervation causes dilation of blood vessels in the erectile tissue, triggering an erection.
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Innervation to Uterus and Vagina:
Sympathetic innervation causes contraction of uterine smooth muscle.
Parasympathetic innervation relaxes uterine smooth muscle.
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Innervation to Vagina:
Sympathetic innervation to the vagina remains unclear.
Parasympathetic innervation causes engorgement of the clitoris and bulbs of the vestibule, and stimulates secretion of the vestibular glands, all related to sexual arousal.