F&W Ecol Lec Exam 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Phenetic Classification
Based on overall similarity of observational traits
Only considers structural and morphological characteristics
Cladistic Classification
Based on shared derived characteristics that can be traced to a recent common ancestor
Considers evolutionary relationships and ancestry
Taxonomic Ranks
(Domain), Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
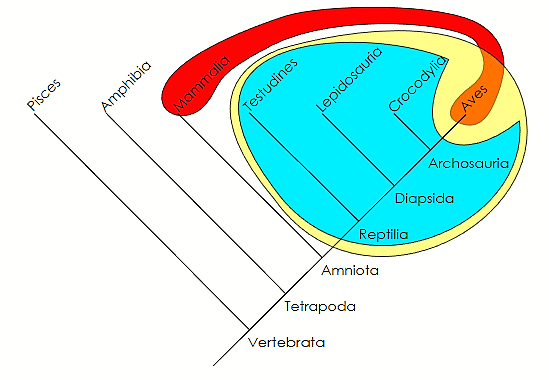
Monophyly
traceable to/descend from a common ancestor
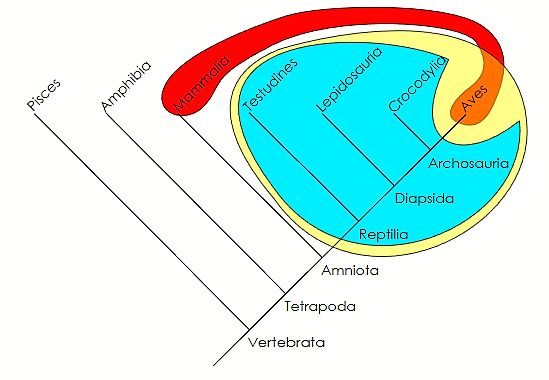
Paraphyly
doesn’t include all descendants from common ancestors
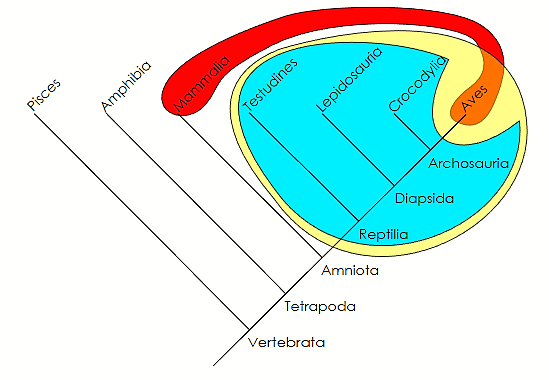
polyphyly
compares two unrelated groups
Characteristics unique to mammals (9)
mammary glands
hair/fur
3 inner ear bones
single dentary bone
dentary-squamosal jaw articulation
complex teeth
external ears (pinnae)
non-nucleate red blood cells
muscular diaphragm
Other mammal characteristics
endothermy
4-chambered heart
highly developed brain, nervous system
centrally placed limbs
Origin of mammals
synapsid reptiles
Anapsid
only eye and nasal fossa
turtles
synapsid
1 fossa
mammals
Diapsid
2 fossa
snakes, lizards, tuataras, crocodilians, birds
3 types of mammalian reproduction
monotreme
marsupials (metatherians)
placental (eutherians)
monotreme
egg-laying
marsupials (metatherians)
live-bearing with pouch
metatherians
placental mammals (eutherians)
live-bearing with placenta
eutherians
∼94% of living mammals
Skin Glands (4)
mammary glands
sweat glands
sebaceous glands
scent glands
mammary glands
nourish the young
sweat glands
evaporative cooling
sebaceous gland
oil to lubricate skin and hair
scent gland
mate attraction, territory marking, communication
Endothermy/Homeothermy
Endothermy: internal heat source (metabolic heat)
Homeothermy: constant body temperature
Advantage: active over greater range of temperatures—nocturnal lifestyle
Disadvantage: greater energy demands
Heterothermy
endotherms that have the ability to fluctuate their body temperature to save energy (for daily torpor and/or to hibernate)
skull, jaws, and teeth
large brain case
single dentary bone in lower jaw
inner ear bones evolved from articular and quadrate or reptilian jaw
stapes, incus, malleus
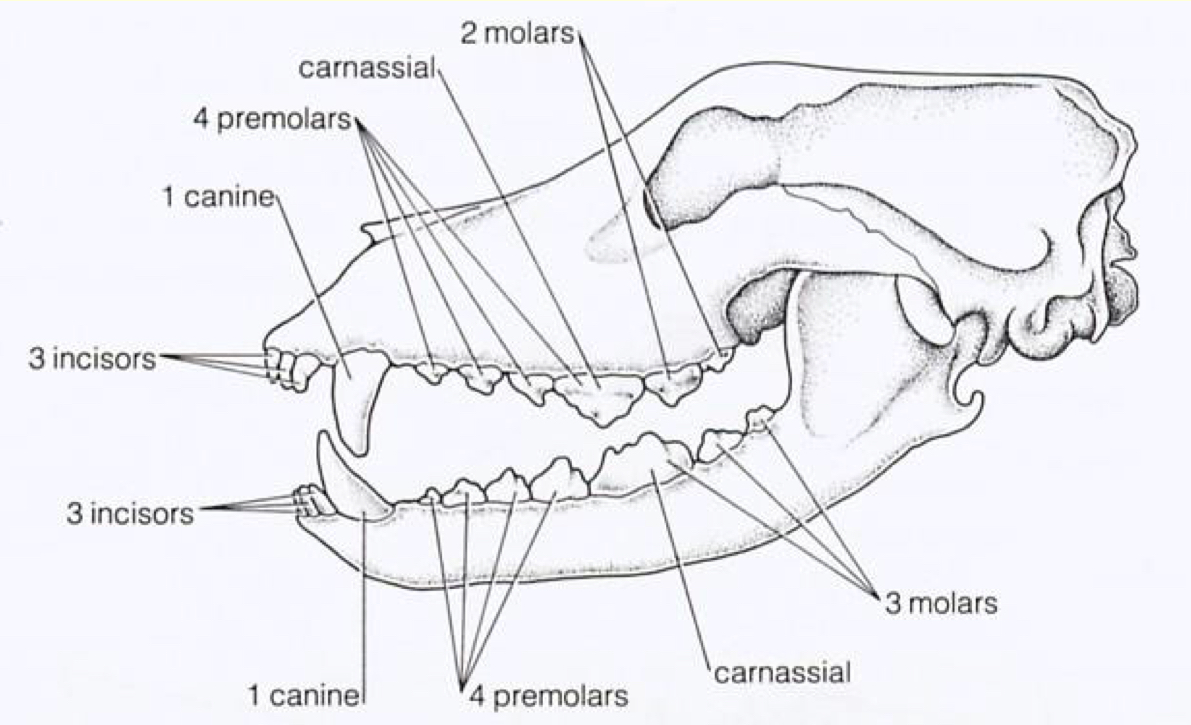
differentiated teeth
dental formula
I/I, C/C, P/P, M/M
upper/lower incisors, canines, premolars, and molars on ONE side of mouth
Example—dog & bear: 3/3 1/1 4/4 2/3
mammalian skeleton features
simplified and more completely ossified relative to reptile
centrally placed limbs, articulating knees and elbows
differentiated vertabrae
types of locomotion/stance (3)
plantigrade—walk on flat feet
digitigrade—walk on toes
unguligrade—walk on hooves
brain characteristics (3)
large, well-developed cerebrum
neocortex folded in many species to increase surface area
important role for memory, learning, rationalization, thought, etc
Senses (4)
olfaction
hearing
vision
touch
Olfaction
key role in foraging, mating, and social communication
hearing
highly developed in many species; some use hearing to echolocate
vision
variable; color vision poorly developed in most
touch
vibrissae (whiskers) act as tactile sensors
Subgroups of mammals
monotremes
marsupials
placentals
Order: Monotremata
2 families
5 species
Distribution: Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea
Monotreme characteristics
egg-laying
single opening (cloaca) at posterior end
long, leathery, sensitive snout
no functional teeth on adults
epipubic bones present
Monotreme Examples
Echidnas (Family Tachyglossiaae)
Duck-billed Platypus (Family Ornithorhynchidae)
Order: Marsupials
aka Metatheria
7 families (only need to know Didelphimorphia)
395 species
Distribution: (1) Australia, New Guinea, & eastern Indonesian islands (2) South, central, and north america
Marsupial characteristics (6)
Marsupium (pouch) in most species
Epipubic bones present
short gestation, prolonged lactation
small, narrow braincase
5/4 incisors
Didelphimorphia (Family) (Order of Marsupial)
American Opossums
126 species
opposable hallux on hind feet
prehensile tail
primarily in South an Central America
1 species north of Mexico (Didelphis virginiana—Virginia opossum)
Virginia opossum (Didelphis virginiana)
Family: Didelphidae
sharp sagittal crest, tiny brain case
Opposable hallux (Big toe)
omnivorous scavenger
Range: eastern US south through central americas, introduced to west coast
range expanding north
Placental orders in WI
Cingulata (armadillos)
Lagomorpha (lagomorphs—rabbits, hares, pikas)
Rodentia (rodents)
Eulipotyphla (shrews, moles, hedgehogs)
Chiroptera (bats)
Carnivora (carnivores)
Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates, whales, dolphins)
Most common mammal orders
Rodentia
Chiroptera (bats)
soricomorphs (shrews and moles
primates
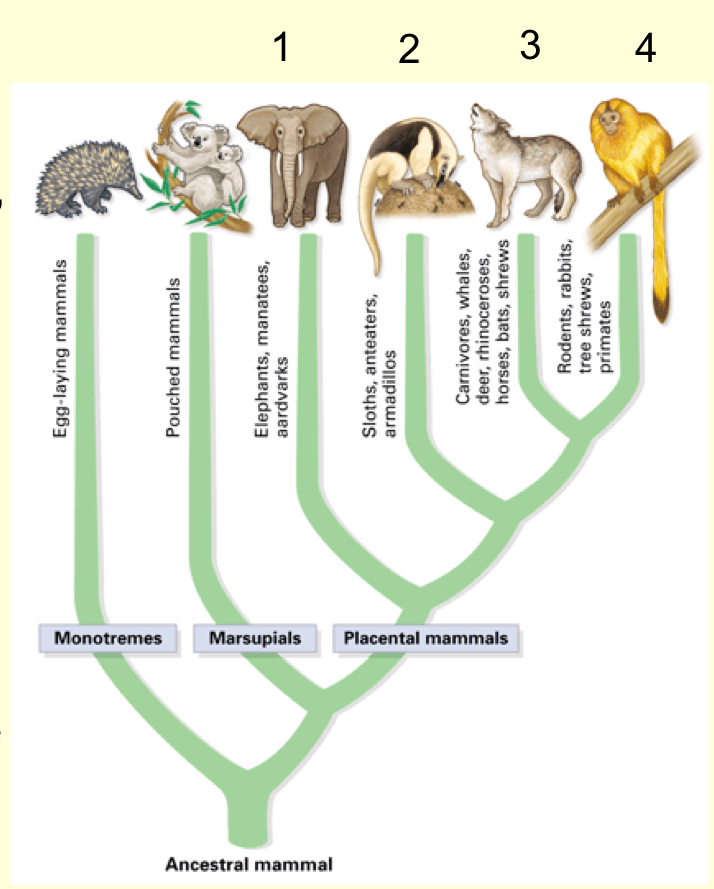
Placental mammal superorders
Afrotheria
Xenarthra
Laurasciatheria
Euarchontoglires
Cingulata (armadillos) characteristics
shell composed of bony plates covered with leathery skin
simple, peg-like teeth—homodont
short, thick limbs an large, heavy claws
most specials fossorial (burrow)
distribution: south an central America north to central US (1 species—Dasypus novemcinctus)
Dasypus novemcinctus (nine-banded armadillo)
unmistakable body armor with 9 bands in center
omnivorous
forests and brushland habitats
not established in WI but moving north slowly
Euliopotyphla (shrews, moles, hedgehogs)
distribution worldwide except Antarctica and Australia
5 families
(Euliopotyphla) Family Soriciae (shrews)
occurs worldwide except australia and antarctica
small narrow snout, small eyes and ears
NO zygomatic arches or auditory bullae on skull
high metabolic rate—eat 2x body weight daily
diet of mostly invertabrates
some venomous species
short-lived, multiple litters per year
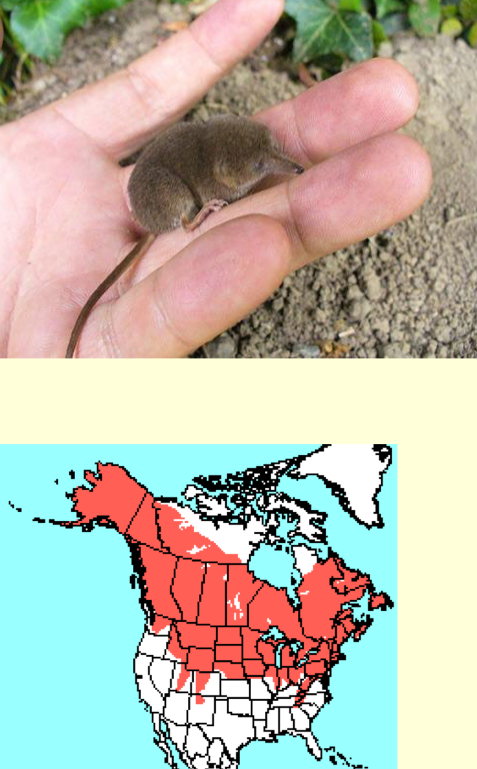

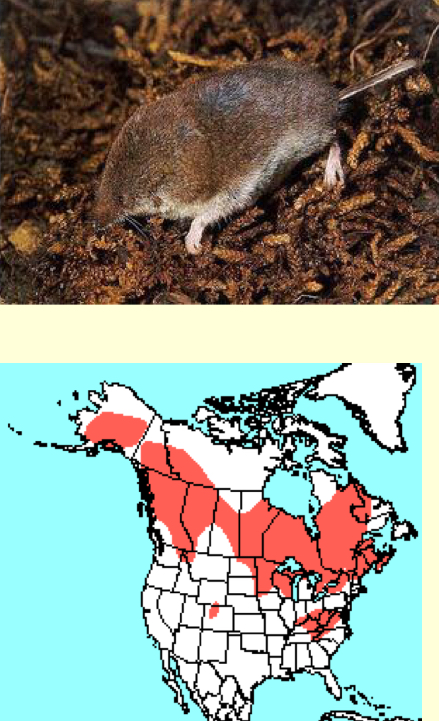
Sorex cinereus—Masked shrew
grayish brown fur
long tail
3-4inch total length
widespread in moist deciduous an coniferous forests in WI
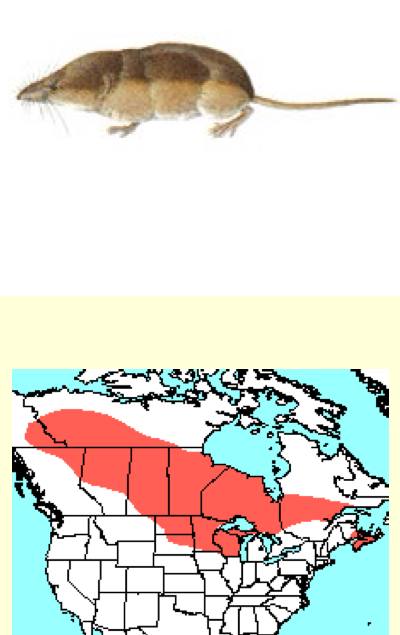
Sorex hoyi—Pygmy shrew
similar to S. cinereus—ONLY distinguishable by unicuspid teeth
smallest N american mammal (3.1-3.6in)
occurs in all but SW WI
less abundant than s. cinereus
Sorex arcticus—Arctic shrew
tricolor fur pattern
4-5in total
boreal forest species
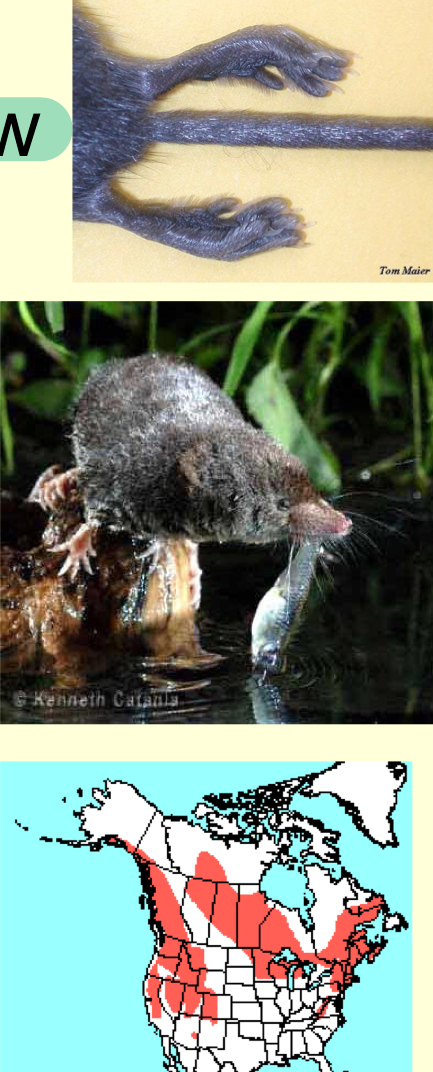

Sorex palustris—water shrew
5.4-6.5in
large feet w fringe of stiff hairs adapted for swimming
forages in and near water
found in marshes, bogs, and streams in N half of WI
species of special concern in WI
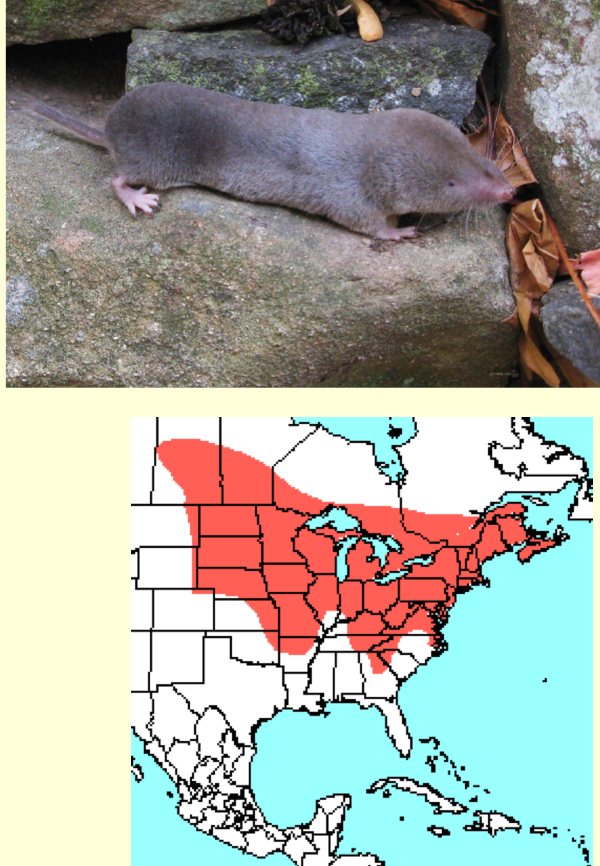

Blarina brevicauda—short-tailed shrew
dark fur, large body, short tail
4.3-5.5in
venomous saliva
eats small verts and inverts
common throughout WI
(Euliopotyphla) Family Talpidae (moles and desmans)
most mole species—fossorial
desmans—semi-aquatic
tiny eyes, flattened head, short legs, large claws
skull flattened, zygomatic arch and auditory bullae present
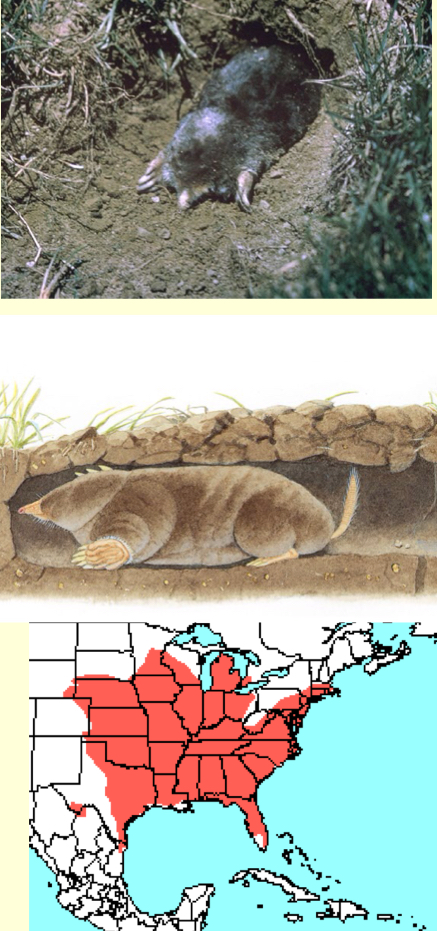
Scalopus aquaticus—eastern mole
grey-brown fur, plump body, short tail, large forelegs an claws
5.9-7.9in
digs tunnels in moist sandy or loamy soils
diet mostly inverts
solitary, annual breeder
occurs in S and W WI
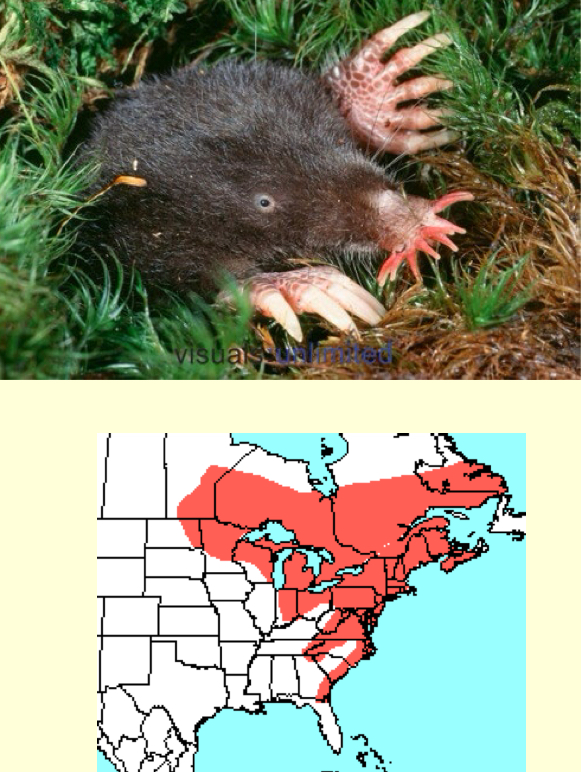
Condylura cristata—star-nosed mole
tentacles at tip of snout act as sensory organ
prefers wet soils near water
solitary, annual breeder
diet of terrestrial and aquatic inverts
occurs in N and E WI
Order Chiroptera (bats)
1 family in WI
8 species in WI
∼22% of all living mammal species
distributed worldwide except polar regions and highest mountains
bat characteristics
flight
nocturnal activity period
hibernation, daily torpor, migration
K-selected (long life span, low reproductive rate)
various diets
Bat size ranges
smallest: Kitti’s hog-nosed bat (bumblebee bat)—1.1-1.3in
largest: flying foxes—wingspan up to 5.6ft
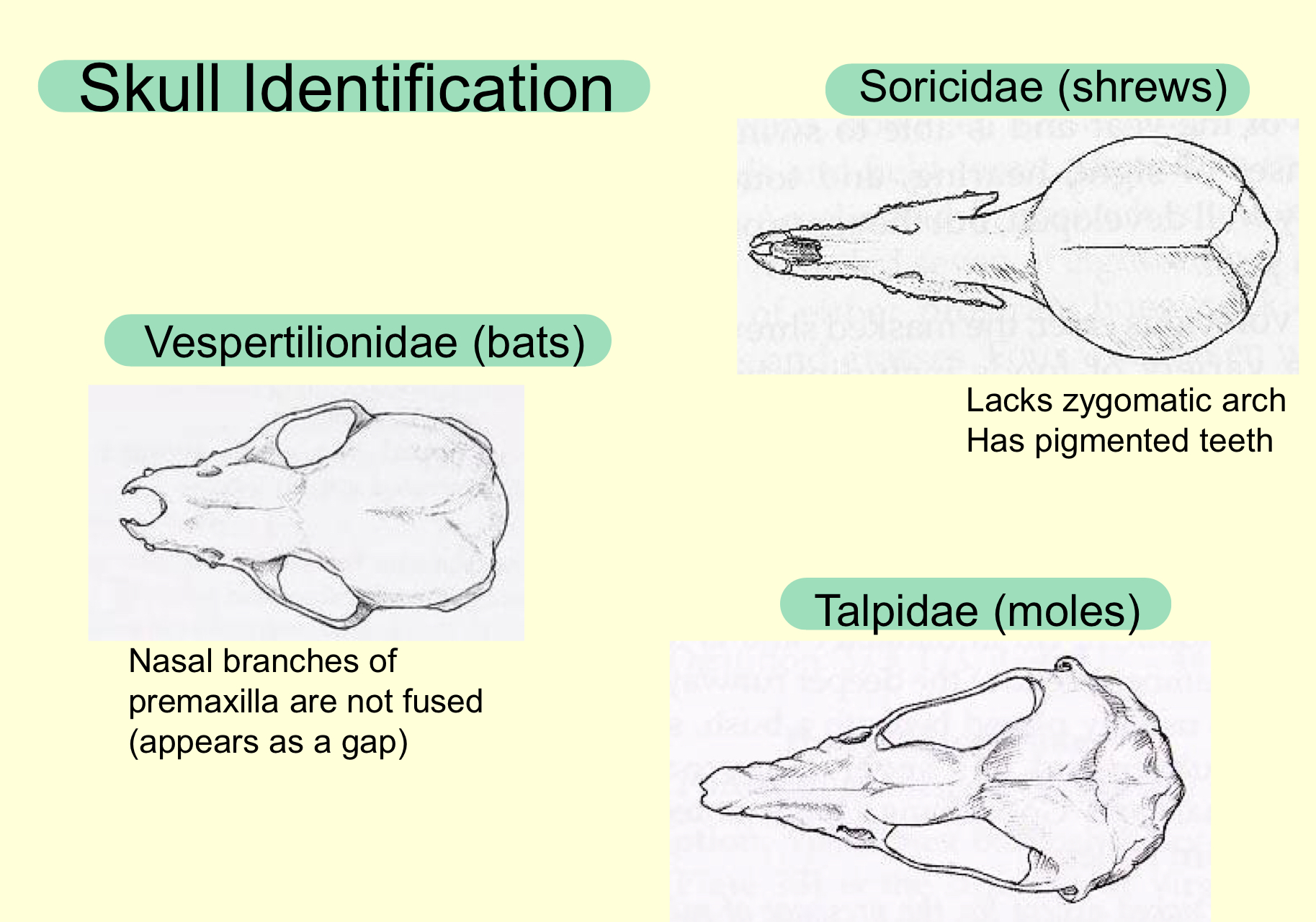
Skull identification bats vs shrews vs moles
bats—nasal branches of premaxilla are not fused (appears as a gap)
shrews—lacks zygomatic arch. has pigmented teeth
moles—zygomatic arch and auditory bullae present
Echolocation
used for foraging and navigation
ear and face morphology facilitates sound detection
Bat dietary specilizations (5)
bird-eating
frog-eating
fish-eating
sanguivorous (feeds on blood)
frugivorous/nectarivorous (most do not echolocate)
Bat benefits to ecosystem
role in food chain
pollination
seed dispersal
nutrient transfer (gunao—poop)
keystone species in some tropical forests, deserts, an cave ecosystems
Bat economic benefits
insect pest control
many bat-reliant tropical fruits and other plants
bat guano (poop) used as fertilizer
biomedical research—bat immune sys
Research on flight mechanics, echolocation, social behavior, etc
bats as disease vectors
low incidence of rabies (∼0.1% of bats) but most frequent vector for rabies in humans
serve as reservoirs for many human viruses (COVID, SARS, ebola, measles, mumps, etc)
White-nose syndrome (WNS)
deadly fungal infection affecting cave-dwelling bats in E US
causes bats to wake during hibernation, depleting energy reserves
Bats and wind turbines
significant source of mortality for migratory tree-roosting bats
most bats die from barotrauma
barotrauma: internal hemorrhaging caused by quick changes in air pressure
Bat conservation efforts
surveillance and monitoring of bat pops
protection of caves and other hibernacula
greater use of bat houses
4 bat species protected in WI