Haemaglobin and oxygen transport
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Dalton’s Law
The total atmospheric pressure exerted by a gas is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases
Henry’s Law
The amount of dissolved gas in a liquid is proportional to its partial pressure above the liquid
Fick’s Law
V’gas = D*A* ΔP/T
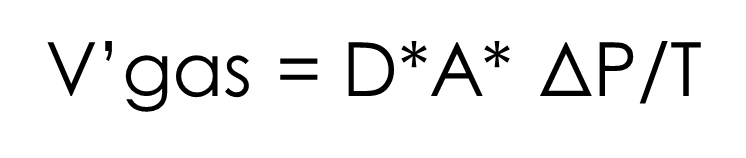
V’gas = Rate of gas diffusion across permeable membrane
D = Diffusion coefficient of that gas for that membrane
A = Surface Areas of the membrane
ΔP = difference in partial pressure of gas across the membrane
T = Thickness of the membrane
What are the types of shunting of blood at the lungs
Anatomical shunt: Blood bypasses the alveoli entirely, such as through the bronchial circulation or thebesian veins.
Physiological shunt: Blood flows through poorly ventilated alveoli, resulting in incomplete oxygenation.
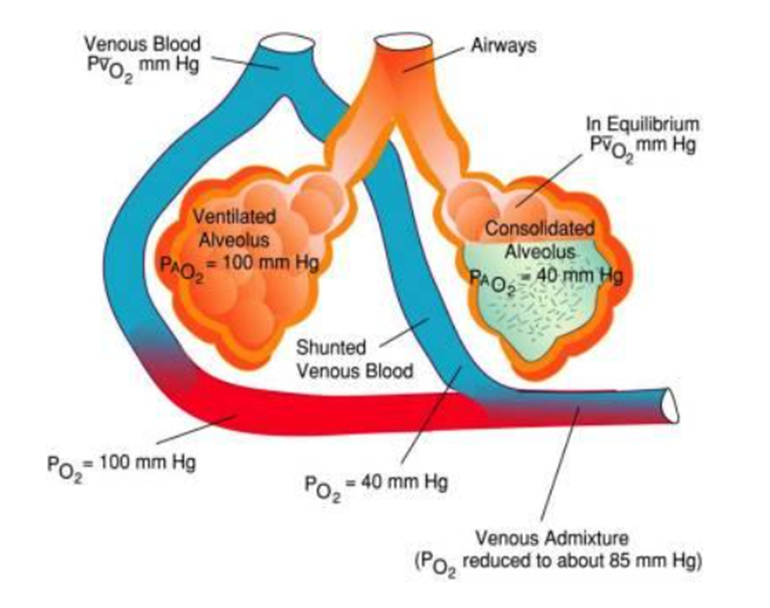
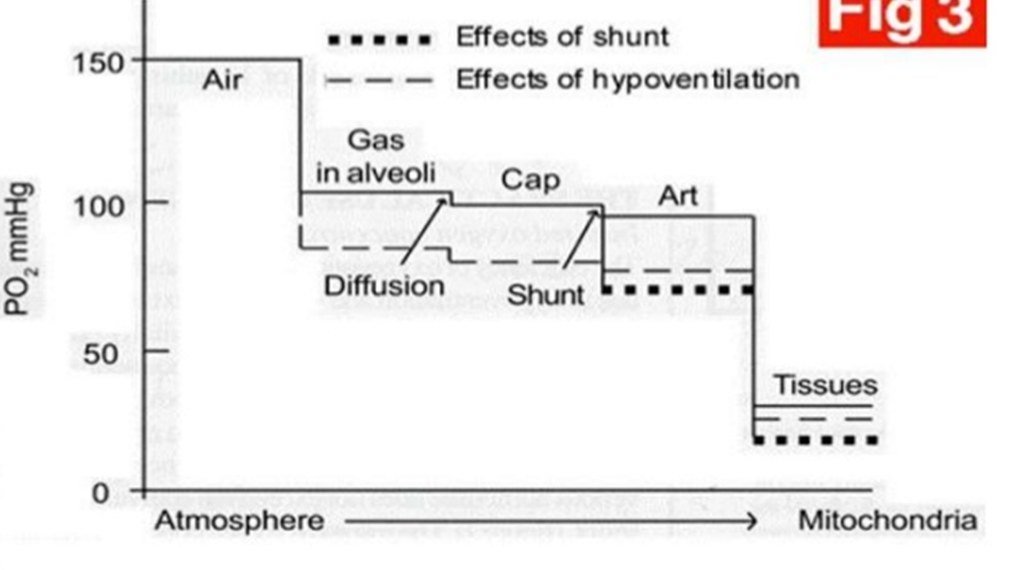
Describe the oxygen cascade
The progressive decrease in oxygen partial pressure (PO2) as oxygen moves from the atmosphere to the mitochondria in cells
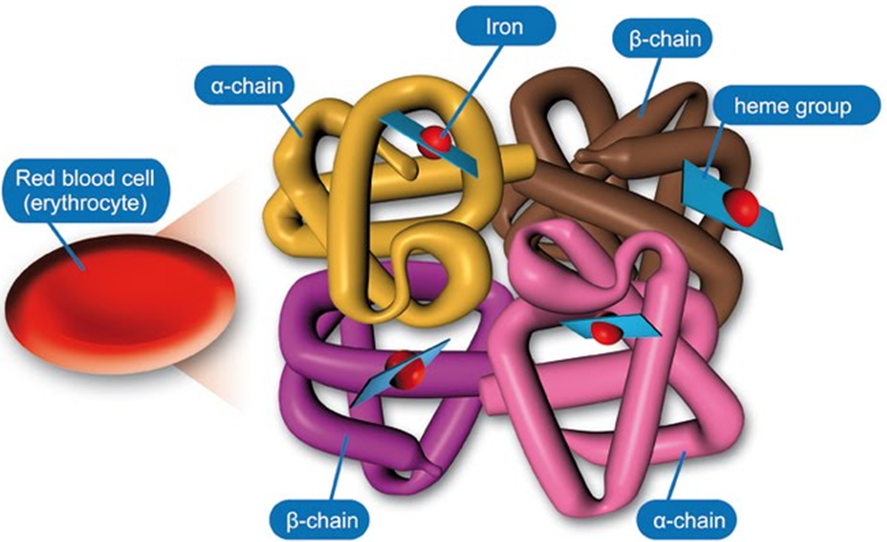
Describe the structure of Haemoglobin
Tetrametric
2 alpha chains
2 Beta chains
Binds a total of 4 oxygen molecules
Carries O2 from lungs to tissues
Co-operative binding of O2
Required to increase the solubility of O2 in blood
Describe co-operative binding of oxygen in haemoglobin
As oxygen binds to one subunit, it increases the affinity of the remaining subunits for oxygen. This means that binding of subsequent oxygen molecules becomes easier.
Oxygen binding causes a structural change in haemoglobin from the tense (T) state to the relaxed (R) state. This conformational shift is key to the cooperative mechanism.
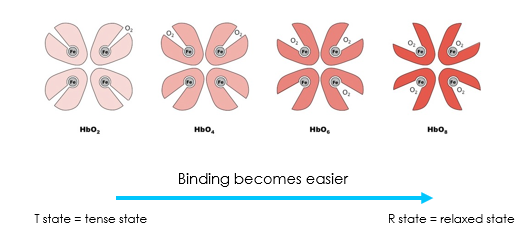
Describe how changes in pO2 affect the state of haemoglobin
Low pO2 in tissues favours T state: Oxygen unloading
High pO2 in lungs favours R state: Oxygen loading
What equation represents the binding of oxygen to haemoglobin
O2 + HHb = O2Hb + H+
O2 is oxygen
HHb is deoxyhemoglobin (also called reduced hemoglobin)
O2Hb is oxyhemoglobin
H+ is a hydrogen ion (proton)
Describe the effects of oxygen binding to haemoglobin
Oxygen binding: When oxygen binds to deoxyhemoglobin (HHb), it forms oxyhemoglobin (O2Hb).
Proton release: The binding of oxygen causes the hemoglobin molecule to release a proton (H+).
Bohr effect: The release of protons during oxygen binding is the basis of the Bohr effect. As pH decreases (more H+ ions), the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen decreases, facilitating oxygen release in tissues.
O2 + HHb = O2Hb + H+
What are the methods of CO2 transport
•Dissolved
•Bicarbanate and H+ ( Via carbonic acid)
•carbaminohemoglobin
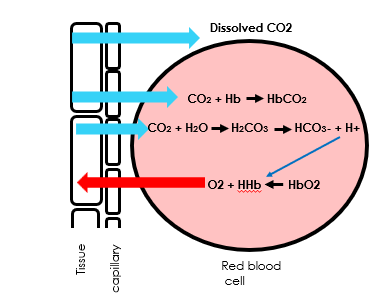
Describe the importance of the Bohr effect in terms of oxygen binding to haemoglobin
The release of protons during oxygen binding to haemoglobin is the basis of the Bohr effect.
As pH decreases (more H+ ions), the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen decreases, facilitating oxygen release in tissues.
O2 + HHb = O2Hb + H+
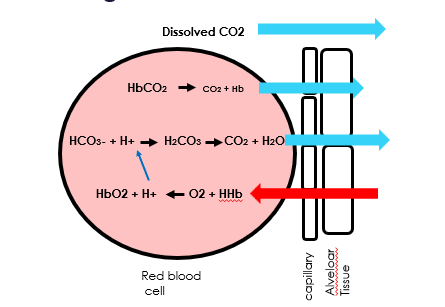
Draw a diagram of gas exchange in the alveoli
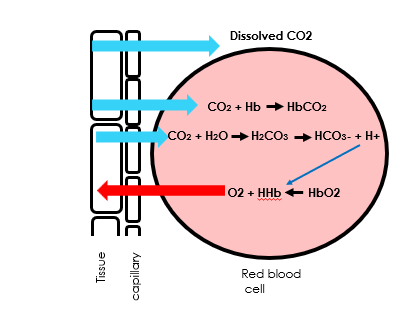
Draw a diagram of gas exchange in respiring tissues
Describe the effects of 2-3 DPG (aka 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate)
An intermediate product of glycolysis
Interacts with deoxygenated haemoglobin beta subunits
Stabilises the low oxygen affinity state (T state)
Decreases the affinity for oxygen
Promotes the release of the remaining bound oxygen molecules
Enhances the ability of RBCs to release oxygen near tissues
What are the signs of carbon monoxide poisoning
Sickness
Headache
Dizziness
Tiredness
Describe the effect of carbon monoxide on haemoglobin
Hemoglobin binds carbon monoxide (CO) 200 to 300 times more than with oxygen
Forms carboxyhemoglobin
The binding of one CO molecule to haemoglobin increases the affinity of the other binding spots for oxygen
Prevents oxygen unloading in peripheral tissue
Can have severe tissue hypoxia while maintaining a normal PaO2
Why does carbon monoxide prevent oxygen unloading at peripheral tissues
Stabilization of the R-state of hemoglobin: Carbon monoxide stabilizes hemoglobin in its relaxed (R) state, which has a higher affinity for oxygen. This makes the hemoglobin resistant to conformational changes that would normally allow oxygen unloading.
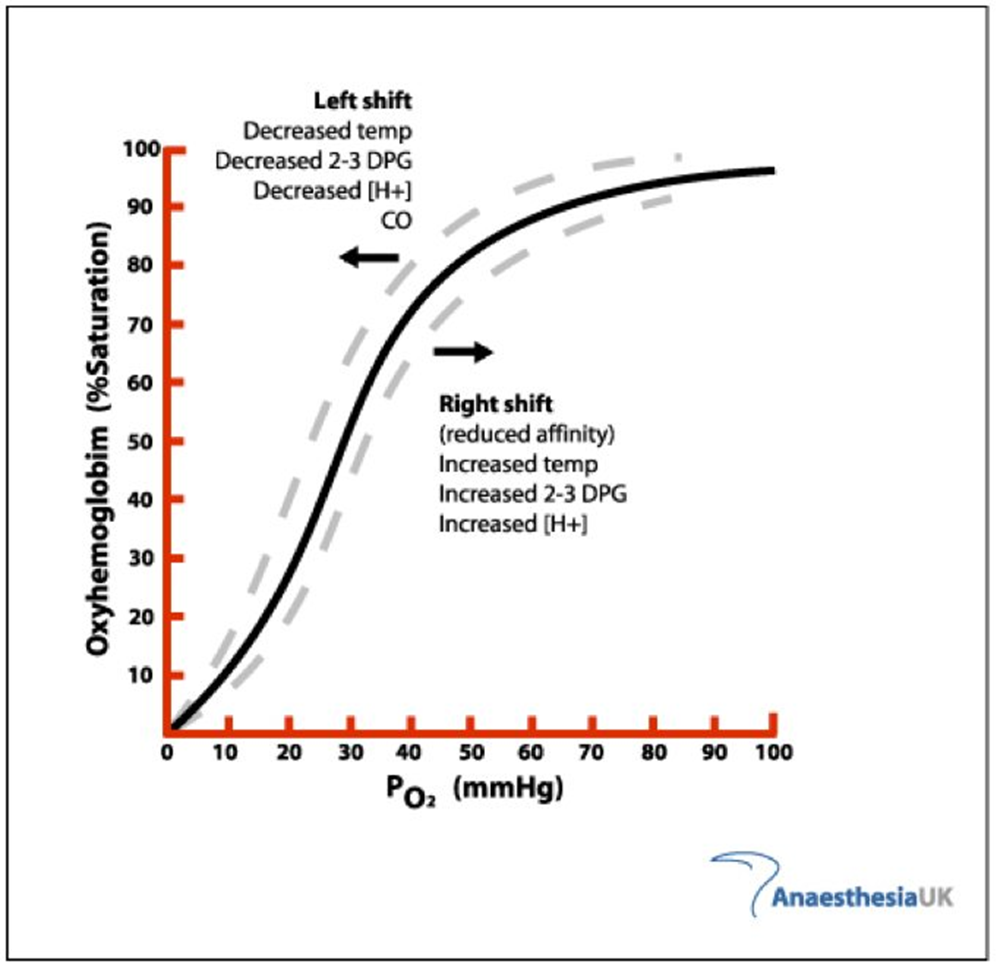
What causes a left shift in the oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve
Decreased Temp
Decreased 2-3 DPG
Decreased [H+]
Carbon Monoxide
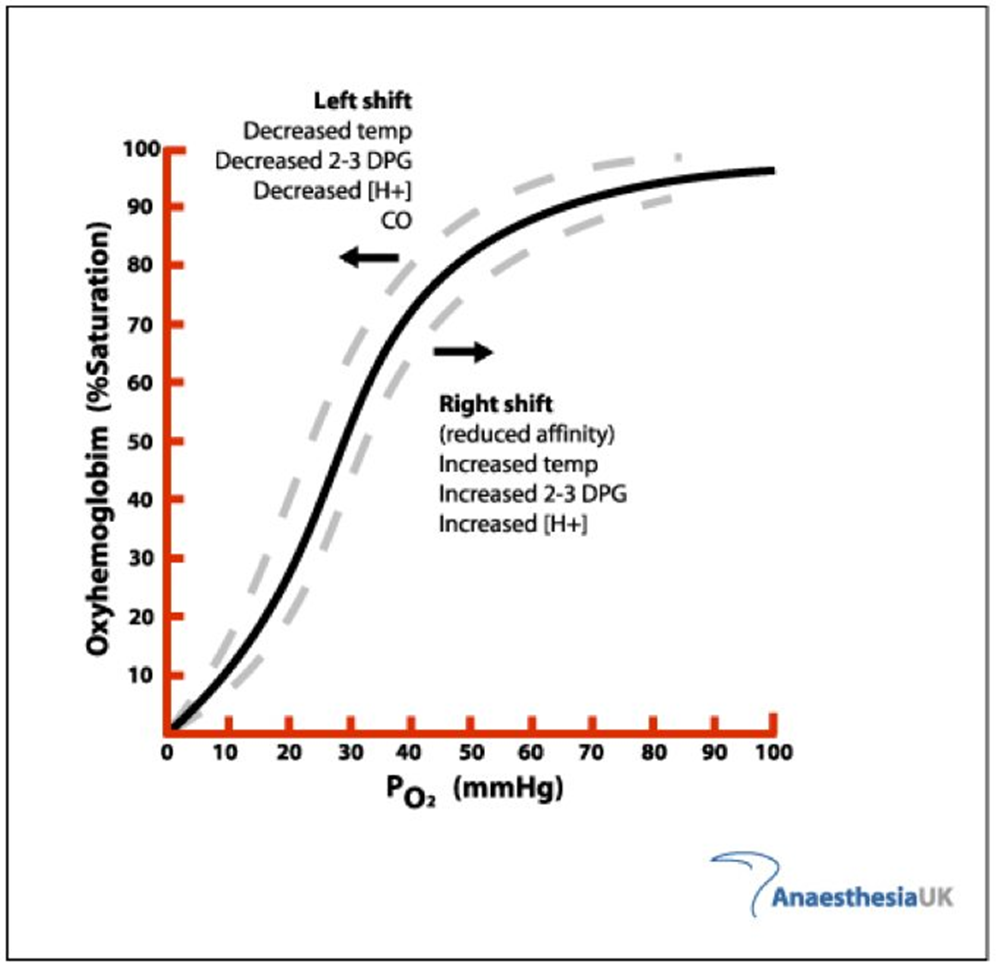
What causes a right shift in the oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve
Increased Temp
Increased 2-3 DPG
Increased [H+]
Describe the Bohr effect in haemoglobin
Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid
An increase in CO2 results in a decrease in blood pH (more free H+)
Hemoglobin proteins releasing their load of oxygen
A decrease in carbon dioxide provokes an increase in pH (less free H+)
Haemoglobin picks up more oxygen.
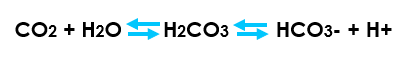
Define respiratory acidosis
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs cannot remove all of the carbon dioxide the body produces.
Define respiratory alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition marked by a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood due to breathing excessively.
List the causes of respiratory acidosis
asthma and COPD
pulmonary fibrosis
scoliosis
narcotics (opioids)
benzodiazepines
Severe obesity
Obstructive sleep apnea
List the causes of respiratory alkalosis
Anxiety or panic
Fever
Overbreathing (hyperventilation)
Pregnancy (this is normal)
Pain
Tumor
Trauma
Severe anemia
Liver disease
Overdose of certain medicines, such as salicylates, progesterone
Shortness of breath (lung disease)