Understanding Excitatory and Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Neurochemicals that increase the likelihood that a neuron will fire an action potential.
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP)
A voltage change due to a neurotransmitter that increases the chances that a neuron will fire an action potential.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Neurochemicals that decrease the likelihood that a neuron will fire an action potential.
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
A voltage change due to a neurotransmitter that decreases the chances that a neuron will fire an action potential - slight hyperpolarization.
Synapse
Space between two neurons.
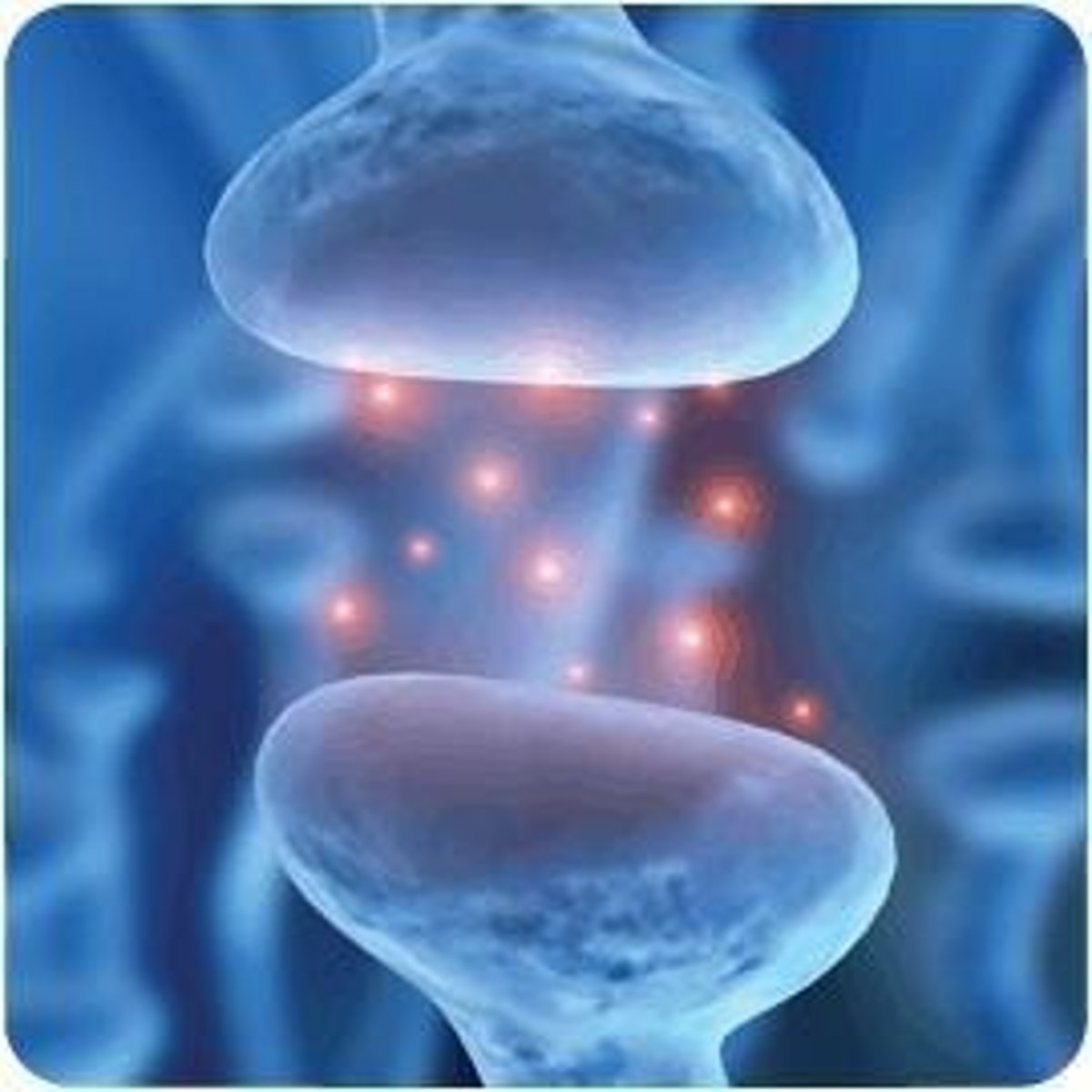
Synaptic cleft/gap
Narrow space between presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic dendrite.
Neurotransmitters
A chemical messenger in Nervous System, stored in vesicles, that travel across the synapse from one neuron to the next.
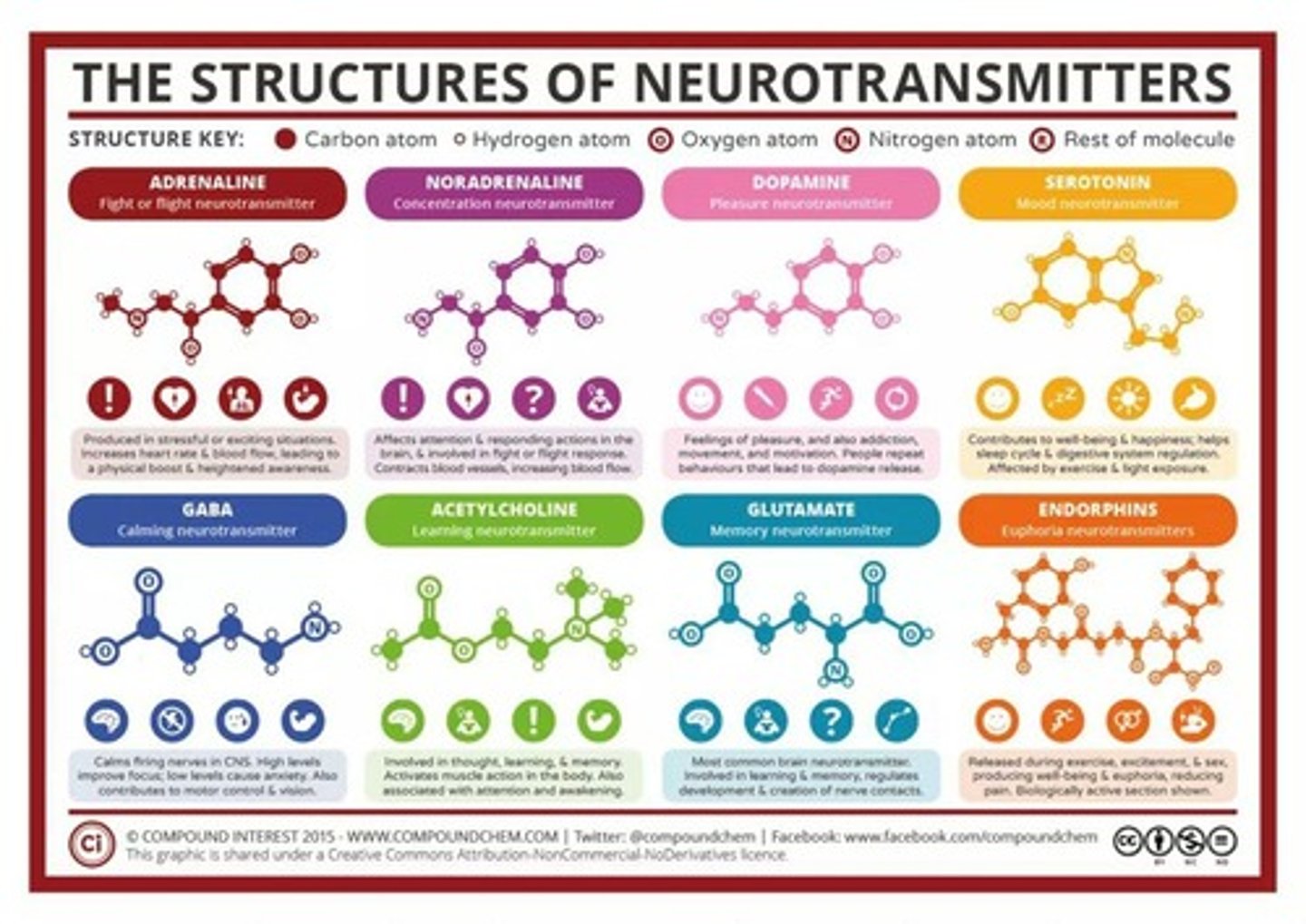
Dopamine (DA)
Function: Pleasure/Reward, Involved in drug addiction, Voluntary Movement, Learning, Attention, Emotion.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Function: Memory, Movement (between motor neurons and muscles), Learning, Attention, Sleep.
Serotonin (5-HT)
Function: Emotion, mood, Sleep, arousal, Appetite.
Norepinephrine (NE)
Function: Mood, Sleep, Learning, Eating, Control alertness and arousal, Fight or flight.
Glutamate
Function: Excitatory messages, used by more neurons than any other neurotransmitter, Long-term memory and learning.
GABA
Function: Sleep, Movement.
Endorphins
Function: Inhibits pain signals and regulates pleasure, released in response to pain or vigorous exercise.
Substance P
A neuropeptide that produces pain.
Lack of Dopamine
Linked to Parkinson's Disease, characterized by difficulty initiating movement and tremors.
Excess Dopamine
Linked to Schizophrenia.
Lack of Acetylcholine
Can't contract muscles (paralyzed), linked to Alzheimer's disease.
Excess Acetylcholine
Can cause muscle convulsions.
Lack of Serotonin
Linked to depression, eating, sleep disorders, and aggression.
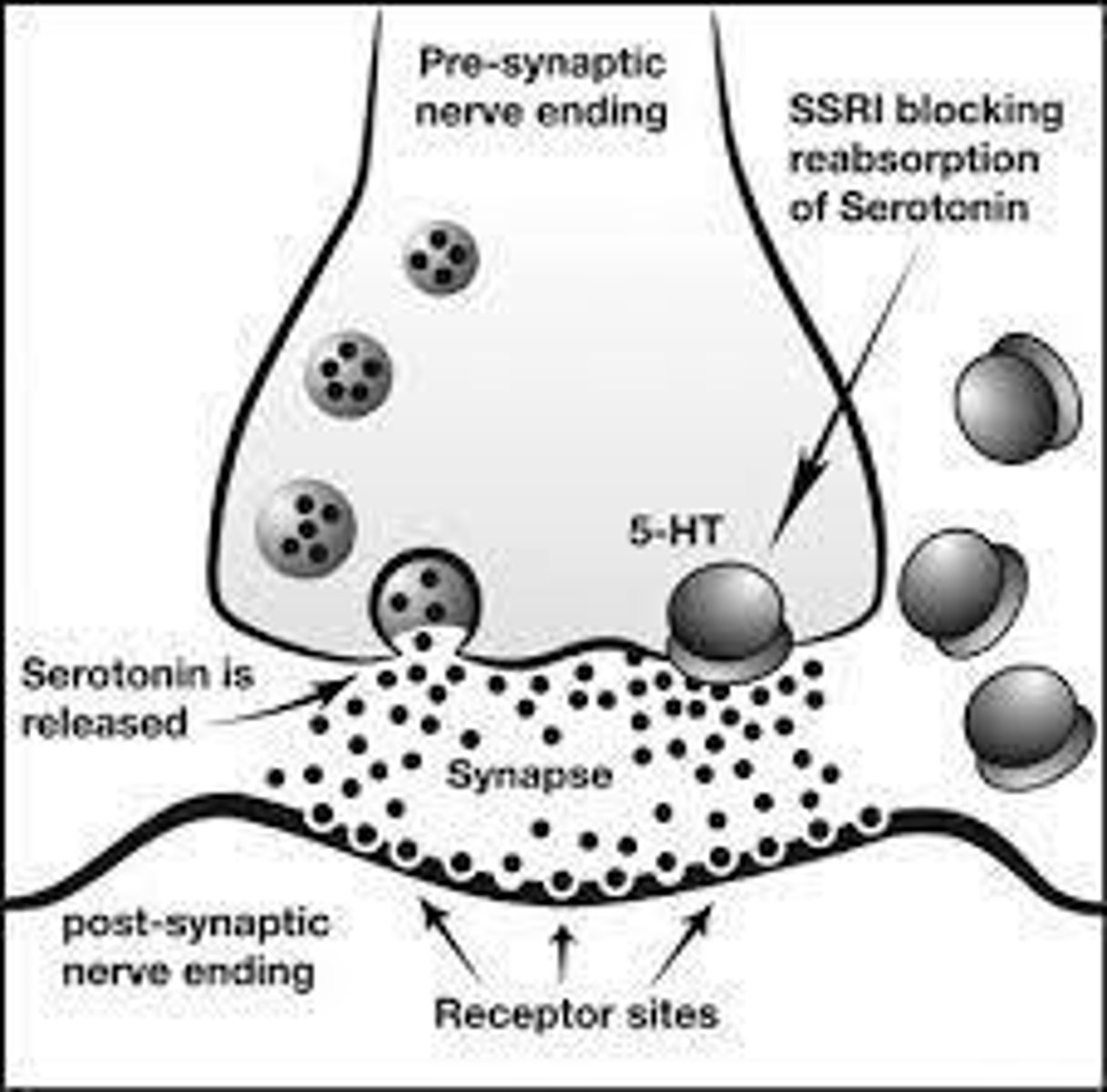
Excess Serotonin
Can lead to headaches, anxiety.
Lack of Norepinephrine
Can depress mood.
Excess Norepinephrine
Can cause anxiety, agitation, mania.
Lack of Glutamate
Problems in making or using glutamate have been linked to many psychological disorders.
Excess Glutamate
Can lead to migraines, seizures, insomnia.
Lack of GABA
Linked to anxiety disorders, seizures, tremors.
Excess GABA
Can lead to over relaxation and sedation.
Problems With Neurotransmitters
Neurons might not manufacture enough of a particular neurotransmitter, neurotransmitters may be reabsorbed too quickly, too many neurotransmitters may be deactivated by enzymes, too much of a particular neurotransmitter may be released.