Behavioral Neuroscience Exam 1
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/160
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:21 PM on 2/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
1
New cards
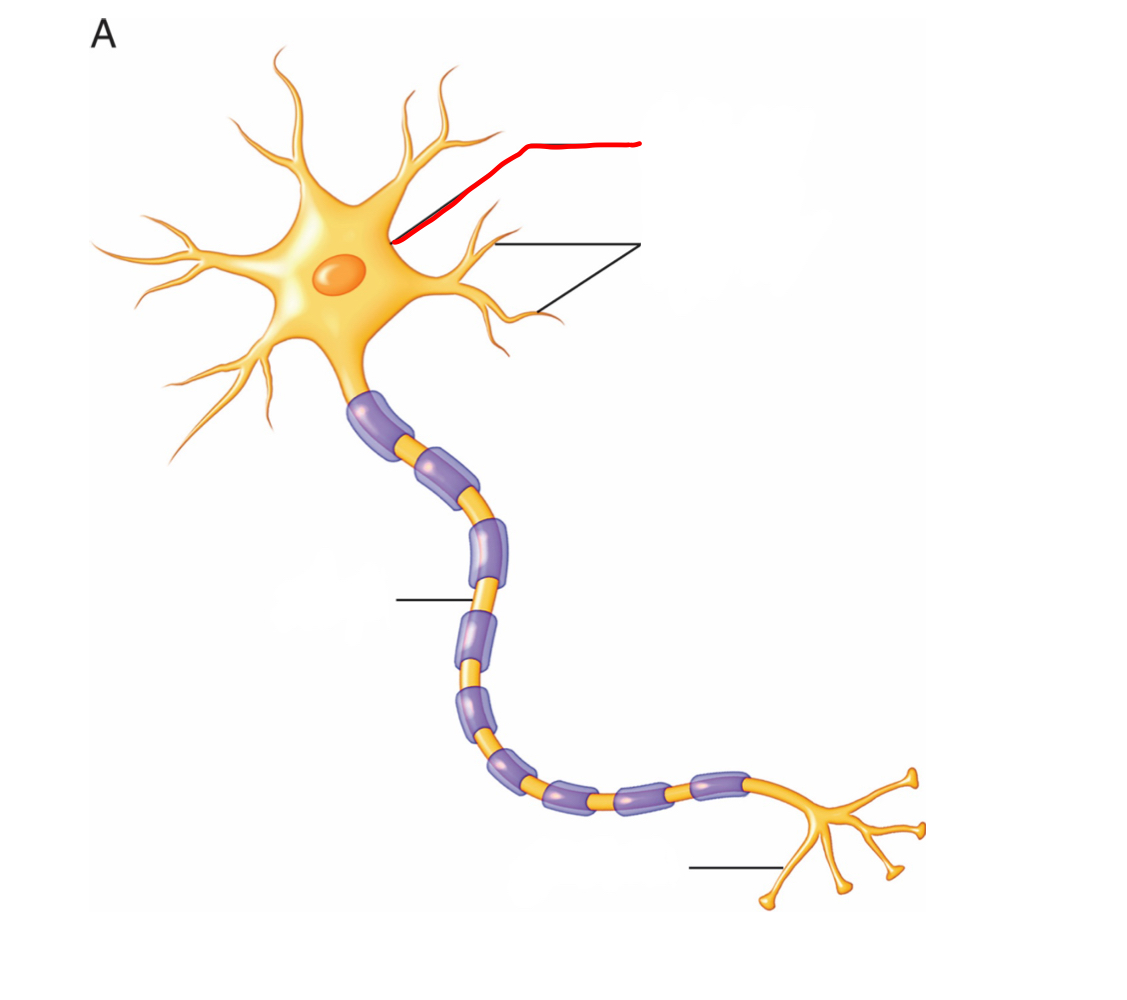
Cell body (soma) - collects information
What is the part of the neuron labeled in red and what is its function?
2
New cards
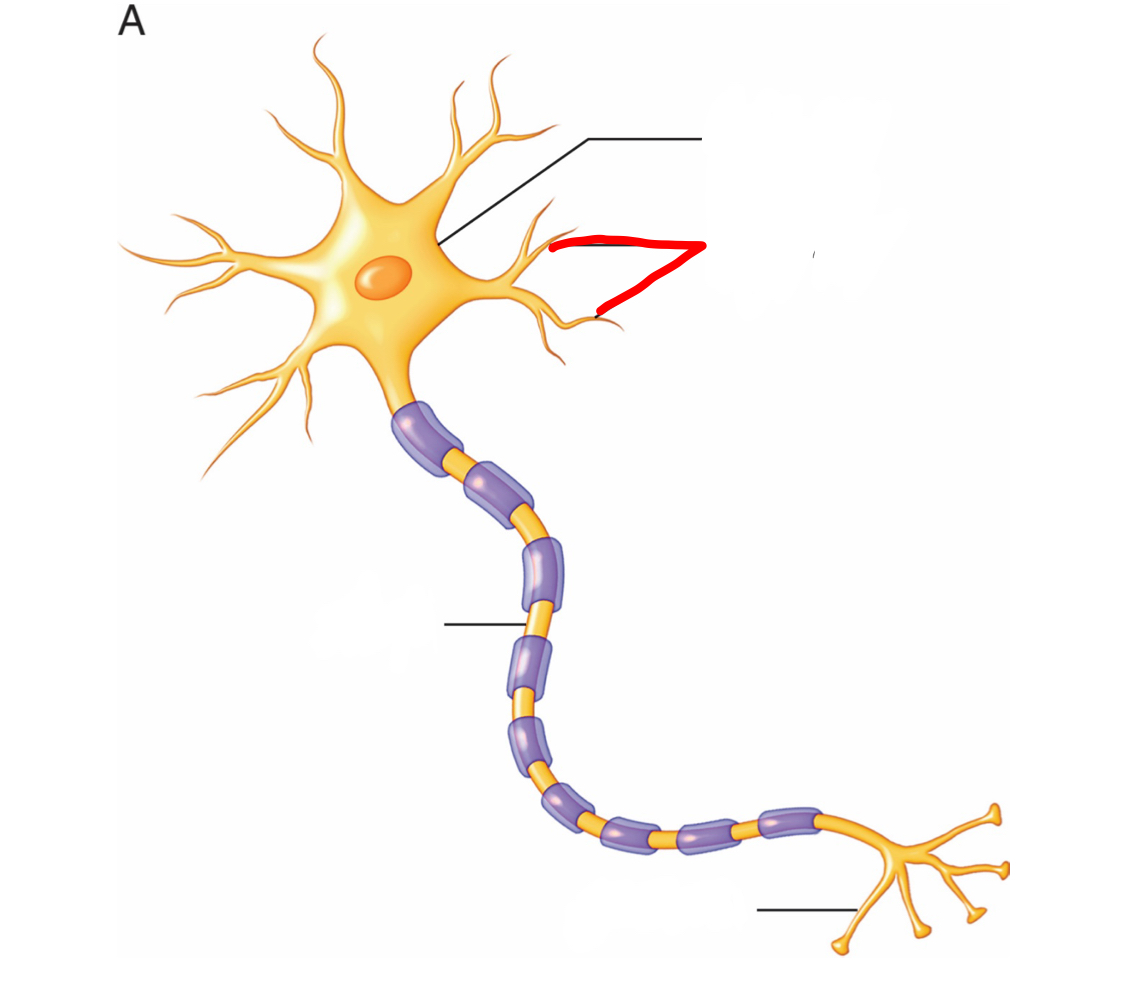
dendrites - receives information
What is the part of the neuron labeled in red and what is its function?
3
New cards
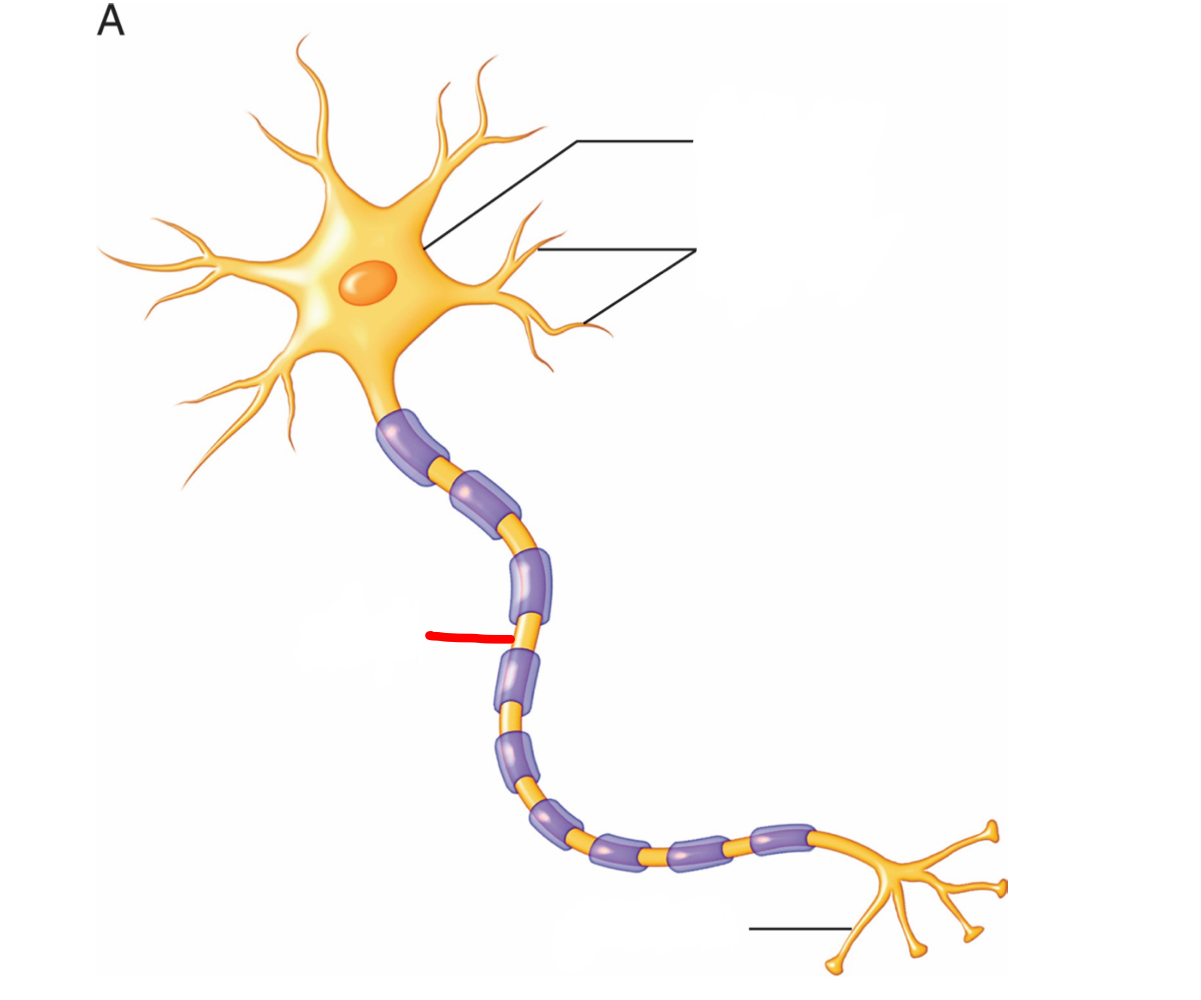
axon - transmits an electrical signal to the terminal
What is the part of the neuron labeled in red and what is its function?
4
New cards
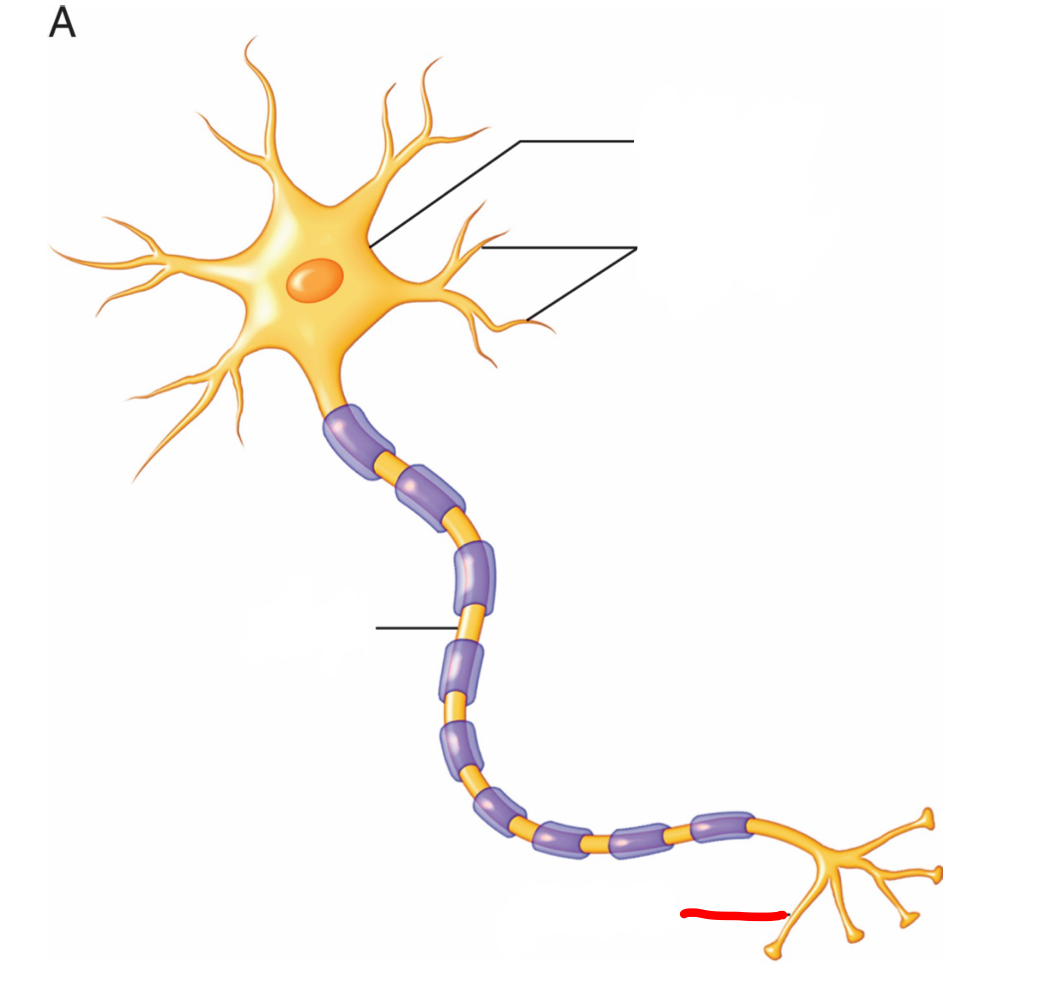
terminal - receives the electrical signal
What is the part of the neuron labeled in red and what is its function?
5
New cards
chemicals released from the axon terminal to help neurons communicate with one another
neurotransmitter
6
New cards
tiny gap where neurotransmitters cross
synaptic cleft
7
New cards
where neurotransmitters bind
receptors
8
New cards
axon
A signal moves down the ______ of the neuron.
9
New cards
glutamate and gaba
What are the most prevalent neurotransmitters?
10
New cards
excitatory neurotransmitter
glutamate
11
New cards
inhibitory neurotransmitter (more gaba means slower neuron firing)
gaba
12
New cards
neurotransmitter
The axon terminal releases a _____ into the synaptic cleft.
13
New cards
Neurons send a signal along the axon to the spinal cord and release an excitatory neurotransmitter which activates a neuron in the spinal cord and then the brain related to skin sensation.
How does touch information reach your brain?
14
New cards
carries information about environmental stimuli
sensory neuron
15
New cards
travel from one neuron to another
signals
16
New cards
causes muscles to contract
motor neuron
17
New cards
c) The brain recognizes that the cup is expensive and sends a signal (purple) that inhibits the spinal cord neuron.
If the hot cup is very expensive, can you hold onto it, at least for a while?
a) The sensory neuron responds to the heat of the cup
b) It sends a signal that excites the spinal cord neuron.
c) The brain recognizes that the cup is expensive and sends a signal (purple) that inhibits the spinal cord neuron.
d) The inhibitory signal from the brain cancels out the heat signal from the sensory neuron.
a) The sensory neuron responds to the heat of the cup
b) It sends a signal that excites the spinal cord neuron.
c) The brain recognizes that the cup is expensive and sends a signal (purple) that inhibits the spinal cord neuron.
d) The inhibitory signal from the brain cancels out the heat signal from the sensory neuron.
18
New cards
neurotransmitter, synaptic cleft, receptors
When a _____ (chemical) is released from a neuron's axon terminal, it crosses a ______ (tiny gap) and binds to ______ located on other neurons, muscles, or organs.
19
New cards
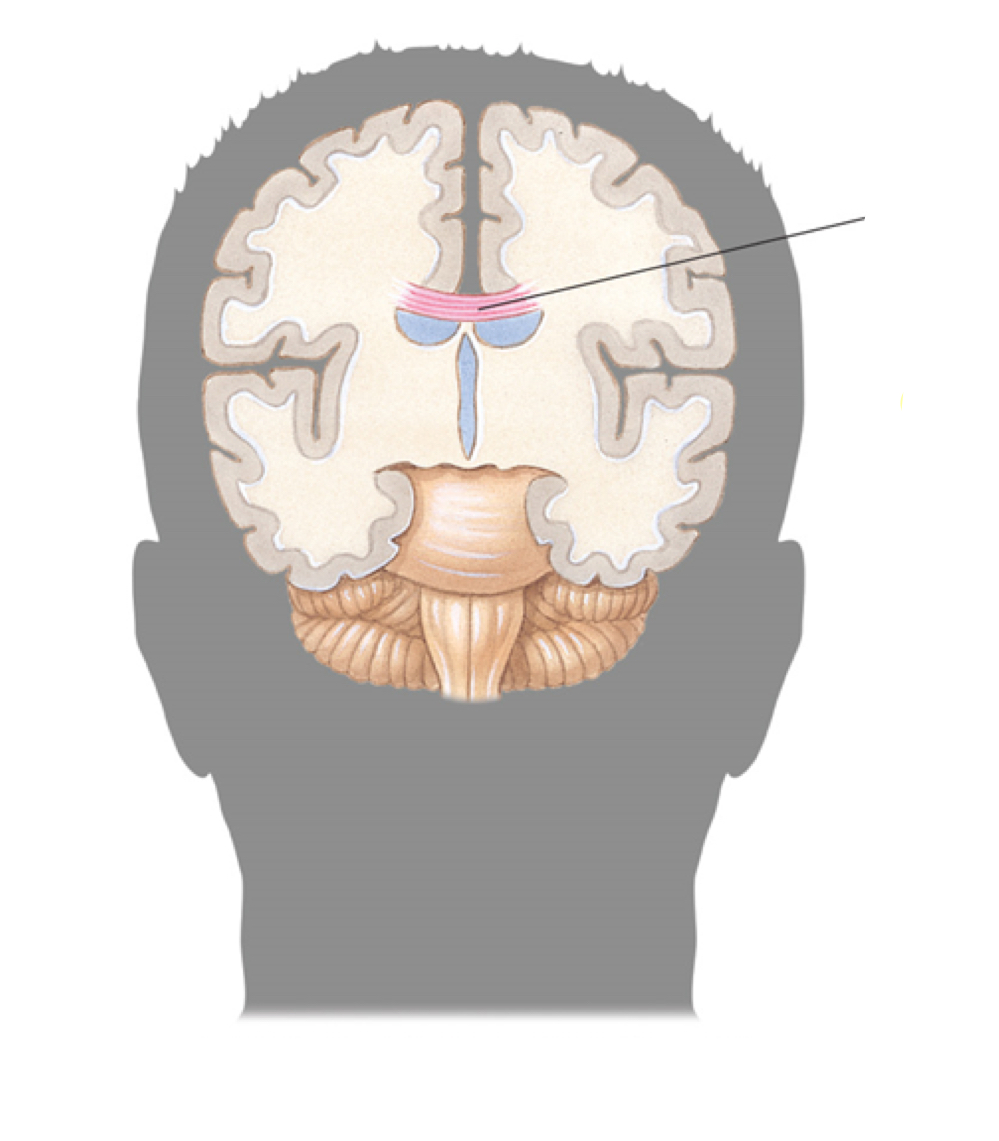
corpus callosum
What is the place labeled called?
20
New cards
bundle of fibers that cross between the left and right hemispheres of the brain
corpus callosum
21
New cards
language, interprets speech
left hemisphere of the brain specializes in?
22
New cards
right
What side of the body does the left hemisphere control?
23
New cards
The right hemisphere can still play a role in communication due to the corpus callosum
What happens if the left hemisphere of the brain is damaged?
24
New cards
crosses from one side of brain to contralateral (opposite) side of the body
movement information
25
New cards
crosses from one side of the body to the contralateral (opposite) side of the brain
tactile (touch) information
26
New cards
left
The right hemisphere receives most of its tactile information from what hand?
27
New cards
left
The right hemisphere of the brain predominantly controls movement of what arm?
28
New cards
A) the left hemisphere
Bob suffered a stroke and can no longer speak, write, or understand language. The chances are high that the stroke caused severe damage to ____ of his brain.
A) the left hemisphere
B) the right hemisphere
C) both hemispheres
D) the corpus callosum
A) the left hemisphere
B) the right hemisphere
C) both hemispheres
D) the corpus callosum
29
New cards
A) left hemisphere, speak
Bob receives an injection of an anesthetic into the blood supply serving the _____, and can no longer ____.
A) left hemisphere, speak
B) right hemisphere, speak
C) left hemisphere, access memories
D) right hemisphere, access memories
A) left hemisphere, speak
B) right hemisphere, speak
C) left hemisphere, access memories
D) right hemisphere, access memories
30
New cards
analytically/verbally
The left hemisphere processes information _______. It notices details.
31
New cards
holistically
The right hemisphere processes information _______. It notices the "big picture"/overall pattern.
32
New cards
intonation/melodies, recognizing faces
specializations of the right hemisphere
33
New cards
problem recognizing faces (issue with right hemisphere of brain)
prosopagnosia
34
New cards
right
Which hemisphere is active when we listen to music?
35
New cards
yes
If you were to meet a split-brain patient, would you be able to tell the two sides of the brain were divided?
36
New cards
right, left, corpus callosum
You pick up a pencil with your left hand; the tactile information about the shape of the pencil in your hand goes primarily to which hemisphere of your brain? ____ You are asked "what is in your hand?" Language is in the ____ hemisphere of your brain. In order to answer, the pencil information must be transferred from your right to left hemispheres via the _______.
37
New cards
right, I don't know, corpus callosum cannot transfer information from right hemisphere of brain to the left
You are a split-brain patient: You pick up a pencil with your left hand; the tactile pencil information goes primarily to your _____ hemisphere. You are asked "What is in your hand?" You answer ____. Why?
38
New cards
left, pencil
You are a split-brain patient: You pick up a pencil with your right hand; the tactile pencil information goes primarily to your _____ hemisphere. You are asked "What is in your hand?" You answer ____.
39
New cards
left
The right visual field goes to which hemisphere of the brain?
40
New cards
portion of the nervous system consisting of neurons in the brain and spinal cord
central nervous system (CNS)
41
New cards
section of nervous system lying outside of the brain and spinal cord (cranial and spinal nerves, autonomic nerves)
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
42
New cards
allow CNS to communicate with the periphery of the body
role of PNS
43
New cards
allow brain to communicate with the arms, legs, and other body parts
spinal nerves
44
New cards
muscles
Some spinal nerves originate in the spinal cord and send signals to the _____ of body parts, allowing us to move our body parts
45
New cards
spinal cord
Other spinal nerves originate in the body parts and send signals to the _____.
46
New cards
CNS
If a whole neuron is in the CNS, is it part of the CNS or PNS?
47
New cards
PNS
If a neuron starts in the CNS and ends in the PNS, what is it a part of?
48
New cards
allow the brain to communicate with the mouth, eyes, and other parts of the face
cranial nerves
49
New cards
muscles
Some cranial nerves originate in the brain and send signals to the _____ of the face (say the mouth), allowing us to move that part of the face,
50
New cards
brain
Some cranial nerves originate in the face (say the cheek or mouth) and send signals to the ____ allowing us to experience sensations (e.g., touch to cheek or taste in the mouth)
51
New cards
body parts, face
PNS:
spinal nerves to and from _____.
cranial nerves to and from the ____.
spinal nerves to and from _____.
cranial nerves to and from the ____.
52
New cards
move muscles and sense our environment
Cranial and spinal nerves allow us to _____ and to ________.
53
New cards
nerves that connect to the heart, lungs, and other organs
autonomic nerves
54
New cards
autonomic nerves, arousal: speeds up the heart, rate, respiration
sympathetic nervous system
55
New cards
relaxation: slows down heart rate, respiration
parasympathetic nervous system
56
New cards
CNS, organs
sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves communicate between the ____ (brain and spinal cord) and ____.
57
New cards
heart, lungs, liver, stomach
Autonomic nerves communicate with many organs such as ______.
58
New cards
relaxation
parasympathetic nerves relate to _____.
59
New cards
arousal (fight-or-flight)
sympathetic nerves relate to _____.
60
New cards
peripheral
autonomic nervous system is part of the ____ nervous system.
61
New cards
autonomic nerves that communicate with organs
autonomic division of PNS
62
New cards
cranial and spinal nerves that communicate with the face and body parts
somatic division of PNS
63
New cards
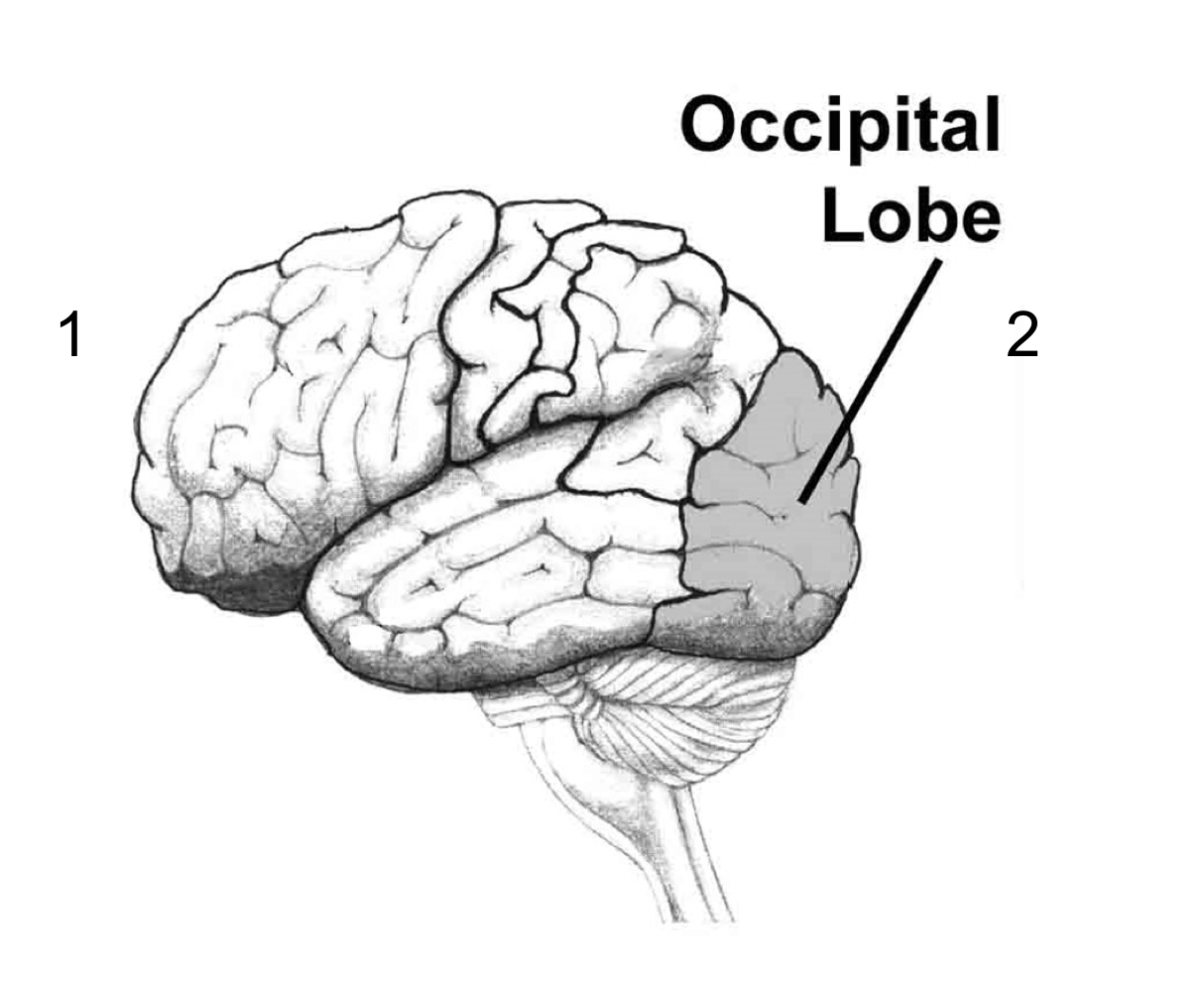
2
Which is posterior?
64
New cards
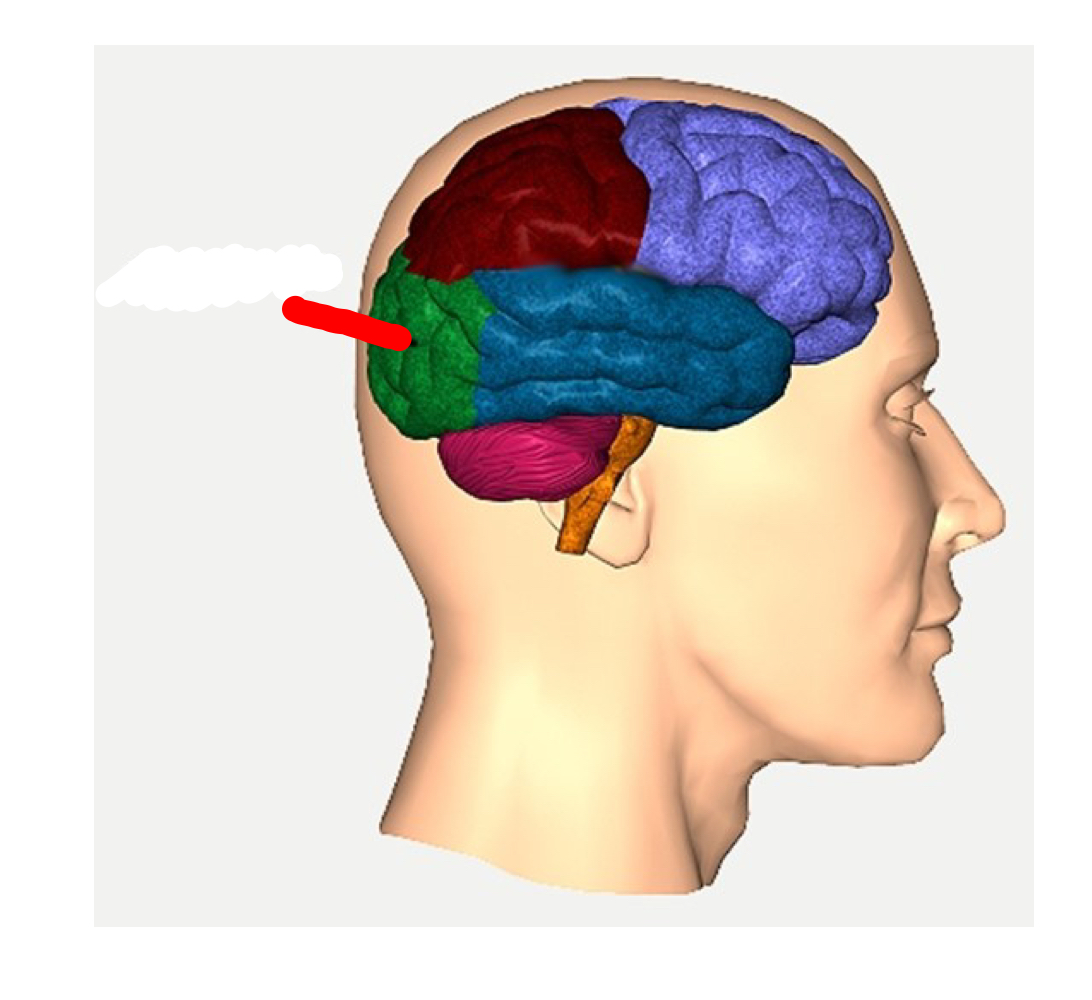
occipital lobe
What is this part of the brain called?
65
New cards
vision
The occipital lobe is associated with ____.
66
New cards
touch, anterior
The parietal lobe is associated with ____. It is ____ to the occipital lobe.
67
New cards
thalamus
The optic nerve sends visual information to the ____, which in turns send visual information to the occipital lobe.
68
New cards
thalamus
Touch information (from hands, arms, legs, and so on) enters the brain and first arrives to the ___.
69
New cards
parietal
Neurons in the thalamus send touch information to the ____ lobe.
70
New cards
peripheral
Tactile stimulation of the fingers activates nerves of the ____ nervous system.
71
New cards
thalamus
Neurons "originating" in the spinal cord carry the tactile (touch) information to the brain, specifically to the _____.
72
New cards
parietal
Neurons in the thalamus send the tactile information to the ____ lobe.
73
New cards
peripheral
The neurons (nerves) that carry touch sensation from your fingers to the central nervous system are in the ____ nervous system.
74
New cards
anterior
Sensory strip is in the most ___ part of the parietal lobe
75
New cards
different parts of the sensory strip correspond to different parts of the body
sensory strip
76
New cards
gyri
bulges between sulci are called
77
New cards
sulci
grooves in the cortex are called
78
New cards
sensory strip
post central gyrus is also called the
79
New cards
hearing/auditory
temporal lobe is associated with _____.
80
New cards
thalamus
Sound activates the auditory nerve (in the ear). Auditory information reaches the _____ before it reaches the auditory areas of the temporal lobe.
81
New cards
primary auditory cortex in the temporal lobe
From the auditory part of the thalamus, the sound information reaches the ________.
82
New cards
posterior
The motor strip is in the most ____ part of the frontal lobe.
83
New cards
can cause muscles to move
motor strip
84
New cards
anterior
the frontal lobe is ____ to the parietal lobe
85
New cards
ventral
the temporal lobe is ____ to the frontal and parietal lobes
86
New cards
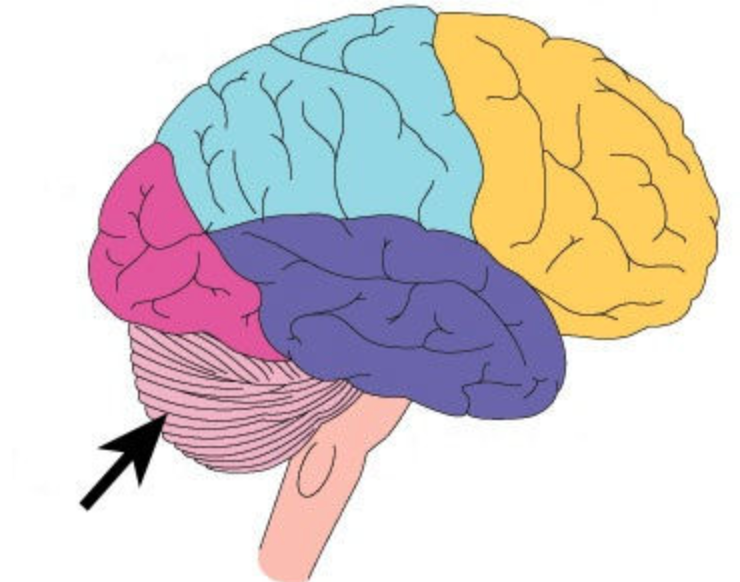
- movement coordination
- contributes to movement control
- contributes to movement control
cerebellum
87
New cards
outer surface of the brain
cerebral cortex
88
New cards
relay station
thalamus
89
New cards
associate with memory of past events/episodes
hippocampus
90
New cards
associated with fear learning
amygdala
91
New cards
active when you feel hungry, thirsty, cold, etc. (drives, basic motivations)
hypothalamus
92
New cards
midbrain (top), pons (middle), medulla (bottom)
oldest part of brain
oldest part of brain
the brainstem is composed of what 3 parts?
93
New cards
neurons in brainstem activate the higher brain regions to produce arousal/alertness
reticular activating system
94
New cards
fluid filled sacs contains cerebro spinal fluid
ventricles
95
New cards
protect spinal cord
meninges
96
New cards
neuron that makes synaptic contact with a muscle
spinal cord motor neuron
97
New cards
neuromuscular junction
The synapase (gap) between a motor neuron and a muscle is the _____.
98
New cards
muscle
The motor neuron makes synaptic contact with a _____.
99
New cards
neuromuscular junction, motor, muscle
Say a spinal cord motor neuron becomes activated. It releases its neurotransmitter into the _____ junction, i.e., into the synapse between the _____ neuron and the _____.
100
New cards
muscle
The neurotransmitter excites the ____ causing it to contract and move the limb
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
IB BIO - U1 L3 P2 - MICROSCOPES AND MICROSCOPE SKILLS (SCIENTIFIC DRAWINGS).
22Updated 900d ago0.0(0)
IB BIO - U1 L3 P2 - MICROSCOPES AND MICROSCOPE SKILLS (SCIENTIFIC DRAWINGS).
22Updated 900d ago0.0(0)