Kidneys and Excretion
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
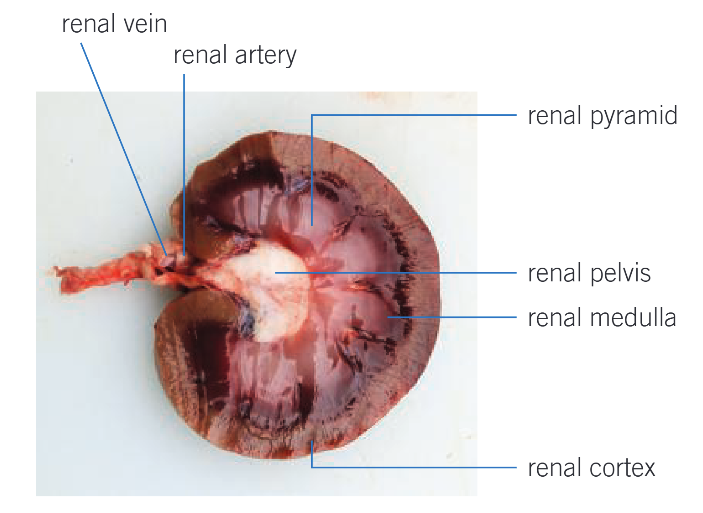
Gross structure of kidney
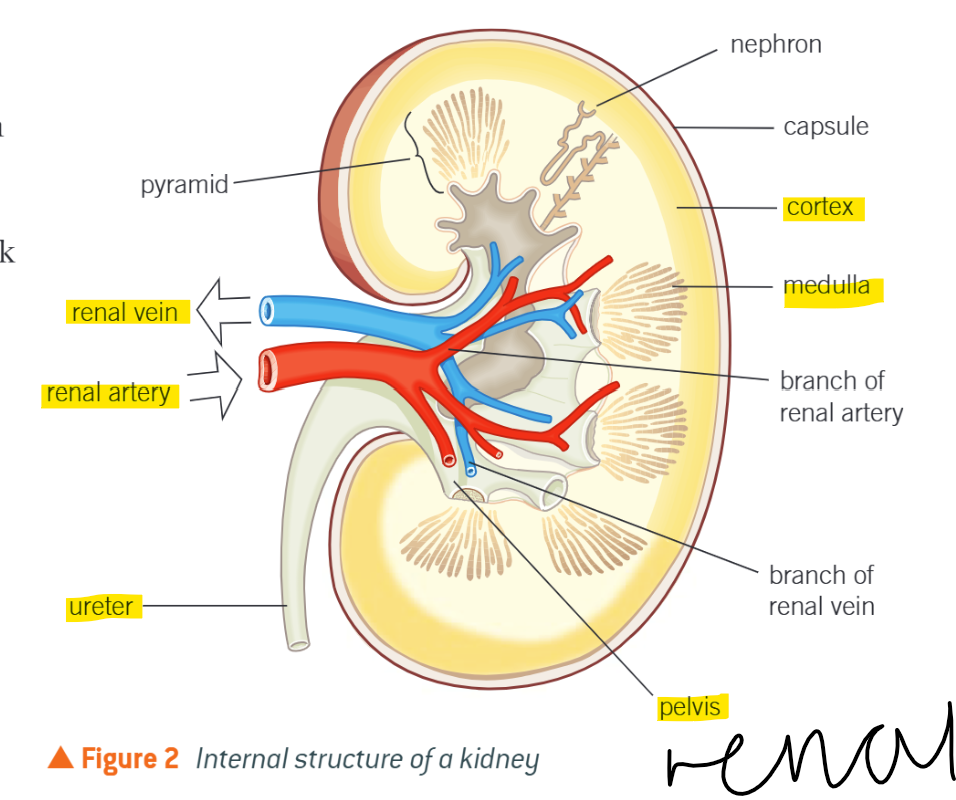
Renal Arteries
Branch off from abdominal aorta
Supply kidneys w. blood
Renal Vein
Removes circulated blood from kidneys, drains into inferior vena cava
Cortex
Dark outer layer
Filters blood
Has dense capillary network carrying blood from renal artery to nephrons
Medulla
Lighter than cortex
Contains tubules of nephrons that form pyramids of kidney and collecting ducts
(Renal) Pelvis
Where urine collects before passing down ureter
Mechanism of kidneys
Blood enters via renal artery and passes thru capillaries in cortex
Ultrafiltration
Selective reabsorption
Remaining unwanted substances (urea) pass along tubules, along ureter to bladder, where expelled as urine
Filters blood passes out of kidneys thru renal vein
Nephrons
Where blood is filtered ; removes nitrogenous wastes, balances mineral ions and water
1.5 mil in each kidney, providing huge SA for reabsorption of water, glucose, salts and other substances into blood
Structure of nephron
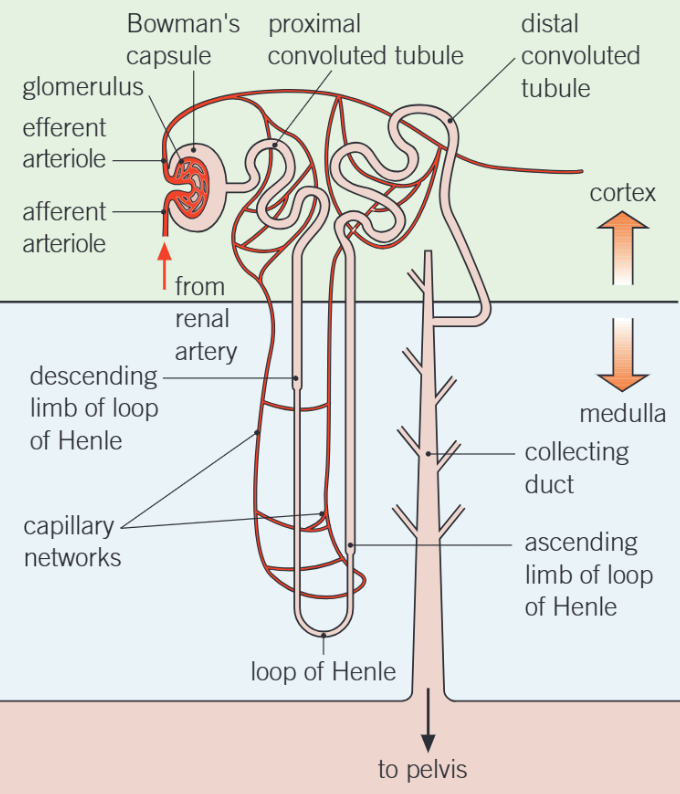
Bowman’s Capsule
Contains glomerulus, a tangle of capillaries
More blood goes in than out due to ultrafiltration process
Proximal convoluted tubule
First, coiled region of tubule after B.C
Found in cortex
Where substances needed by body are reabsorbed into blood
Loop of Henle
Long loop of tubule
Creates region w. v. high solute conc. in tissue fluid in medulla
Descending runs from cortex thru medulla to bend at bottom of loop
Ascending travels up thru medulla to cortex
Distal convoluted tubule
2nd twisted tubule
Fine-tuning of water balance occurs here
Permeability of walls to water varies in response to ADH levels in blood
Further reg, of ion and pH balance of blood occurs here
Collecting duct
Where urine passes down through medulla to pelvis
More fine-tuning of water balance occurs here
These walls also sensitive to ADH
Nephron and blood
Has network of capillaries around it; venule —> renal vein
Blood that leaves = reduces levels of urea, levels of glucose & amino acids roughly same as when entered
Mineral ion conc. in blood restored to ideal elevels
External structure of kidney
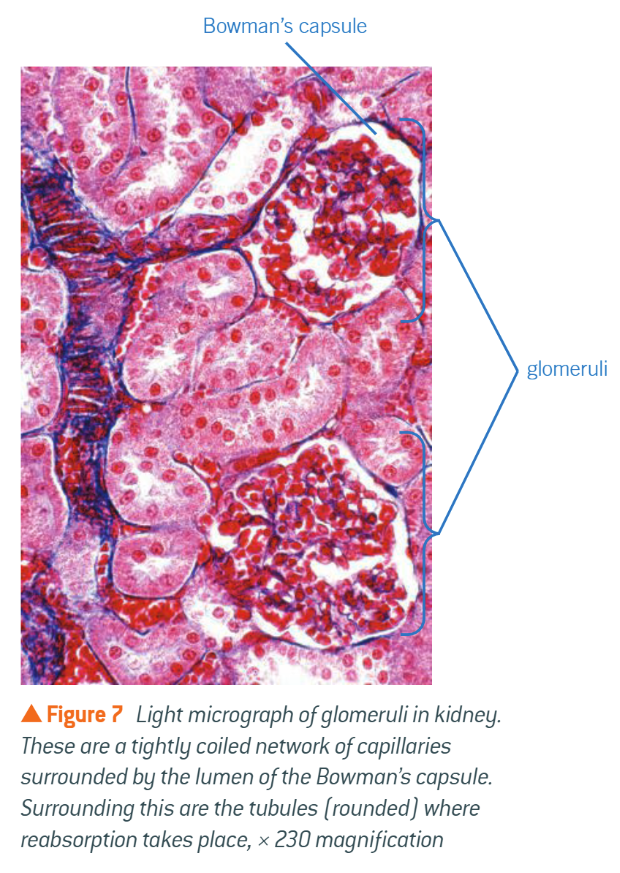
Internal histology of kidney
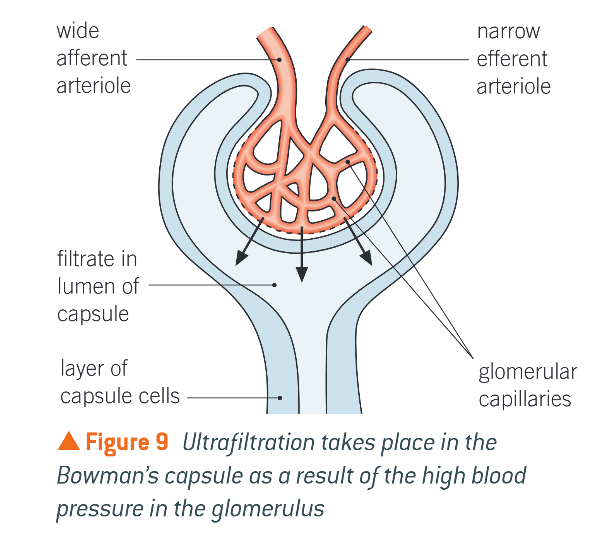
Ultrafiltration in glom
Blood enters glomerulus thru wide afferent arteriole, leaves thru narrow efferent arteriole
High pressure in capillaries forces liquid & small molecules in blood out of capillaries into B.C. via diffusion
RBCs & large proteins stay in capillary
Fluid passes thru basement membrane
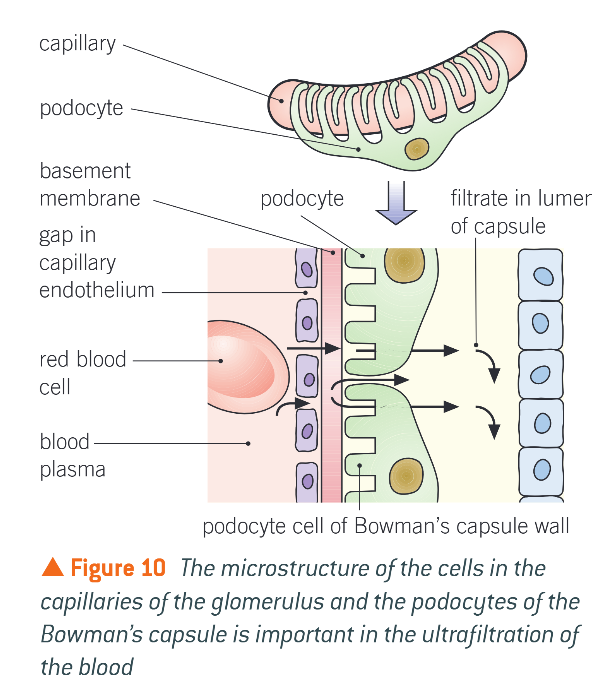
Basement membrane
Made of network of collagen fibres
Blood cells and many proteins retained due to large size
Ultrafiltration post glom
Podocytes ensure cells, platelets, large plasma cells don’t get thru to tubule
Filtrate enters B.C. lumen
Contains substances in same conc. as in blood plasma
Is hypotonic to blood plasma
Contains glucose, salt, urea
Passed along rest of nephron
Reabsorption in PCT
Glucose, amino acids, hormones, ions moved from filtrate into blood by active transport
Mg2+, Ca2+
80% of all filtrate
Approx, 85% of NaCl and wate reabsorbed
Na+ active, Cl- and water passive down conc. g.
Reabsorption amount is always the same
Cells lining PCT adaptations
Covered w. microvilli
Increases SA over which substances can be reabsorbed
Many mitochondria
Provide ATP need in active transport systems (Na+)
Co-transporter proteins
Once substances have been removed from nephron where do the useful ones go?
Diffuse down steep conc. gradients into extensive capillary network that surrounds the tubules
Maintained by constant blood flow thru capillaries
Flow along PCT, thru loop of Henle, along DCT
Loop of Henle
Allows mammals to produce urine
Diff areas have diff permeabilities to water
Acts as counter current multiplier
Uses energy to produce conc. g. that results in movement of substances
Cells use ATP to transport ions, producing diffusion g. in medulla
What happens in descending limb?
Water moves out of filtrate down conc. g. , into medulla
Medulla has low water potential due to high conc. of ions
Moves by osmosis into arteriole (neighbouring capillaries)
Features of descending limb
Leads from PCT
Filtrate entering is isotonic w. blood
Not permeable to Na+ and Cl- ions
No active transport occurs here
Fluid that reaches bend very conc. and hypertonic to blood in capillaries
Features of ascending limb
v. permeable to Na+ and Cl- ions
Actively pumped out into medulla = high Na+ and Cl- conc.
Impermeable to water
Fluid left in here becomes dilute
What happens to the medulla after Na+ and Cl- actively removed from ascending limb?
Has v. high conc. of ions
Essential for kidney to produce urine more conc. than blood
What is the fluid like once it has reached the top of the ascending limb?
Is hypotonic to blood
Enters DCT and Collecting Duct
What do the cells lining the DCT have?
Many mitochondria to carry out active transport
What happens with the DCT if body lacks salt?
Na+ and Cl- ions actively pumped out, down electrochemical gradient