Amines and Carbohydrates Concepts Review
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Naturally occurring amines isolated from plants are called …
alkaloids (i.e. morphine, cocaine, nicotine)
Some naturally occurring amines are…
vital to neurochemistry (adrenaline, dopamine, etc.)
nitrogen atom of amine is _________
trigonal pyramidal
Nitrogen atom of amine carries a…
partial negative charge on its lone pair
lone pair on N can function as
base or nucleophile
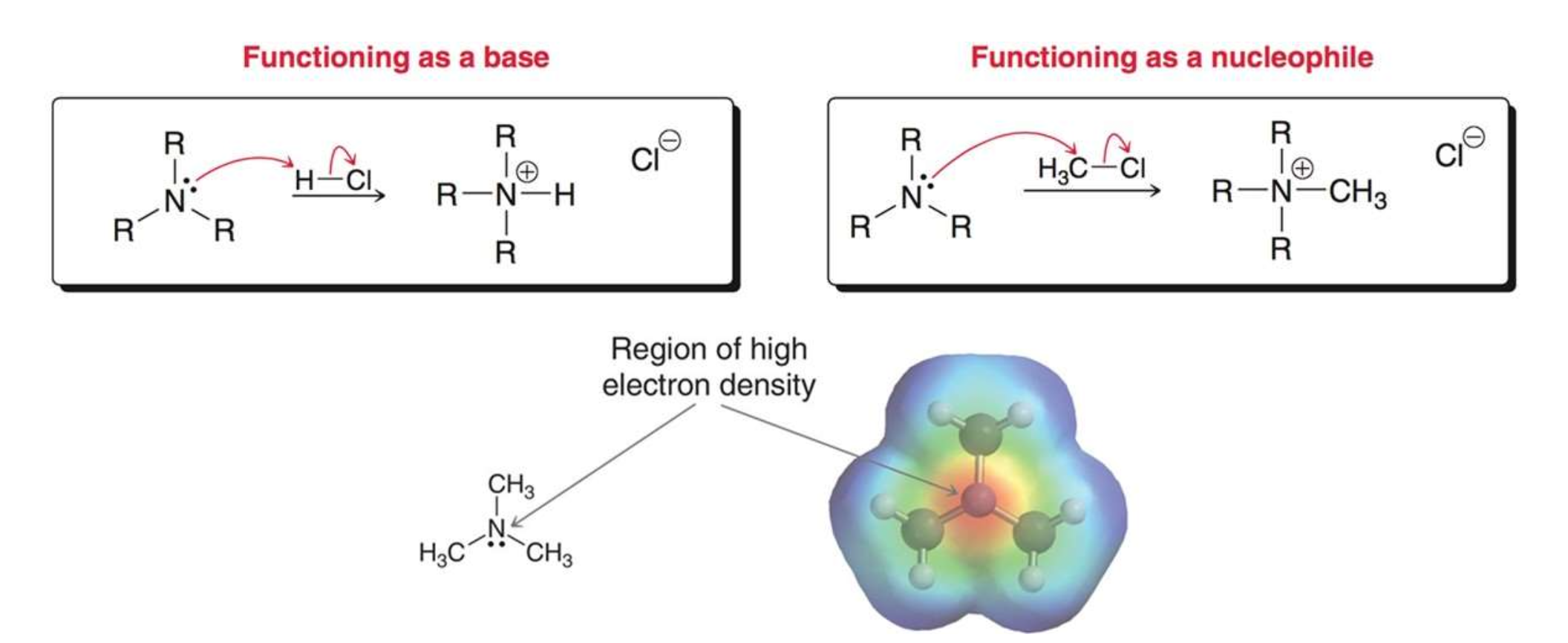
N atom in amines is ____ hybridized and the lone pair occupies _________.
sp3; an sp3-hybridized orbital
Amines with 4 different substituents are chiral but no optically active, why?
Rapid pyramidal inversion prevents a single stereoisomer from being isolated. The transition state between the two stereoisomers are of low energy so it does not take a lot of energy for inversion to occur at RT.
Amines with ________________ are soluble in water
fewer than 5 carbons
1º and 2º amines participate in ___________, and therefore have ___________ than 3º amines
H-bonding; higher boiling points
amines are ___________ than alcohols and ethers, this means that amines can be _______________.
stronger bases; readily protonated by weak and strong acids
Amines are typically strong bases given that…
The lone pair on N is free to accept a proton (should not be participating in resonance, delocalization, or aromaticity)
Aryl amines are less basic than alkyl amines because…
the lone pair on N gets delocalized in the aromatic system and thus is not as available for protonation
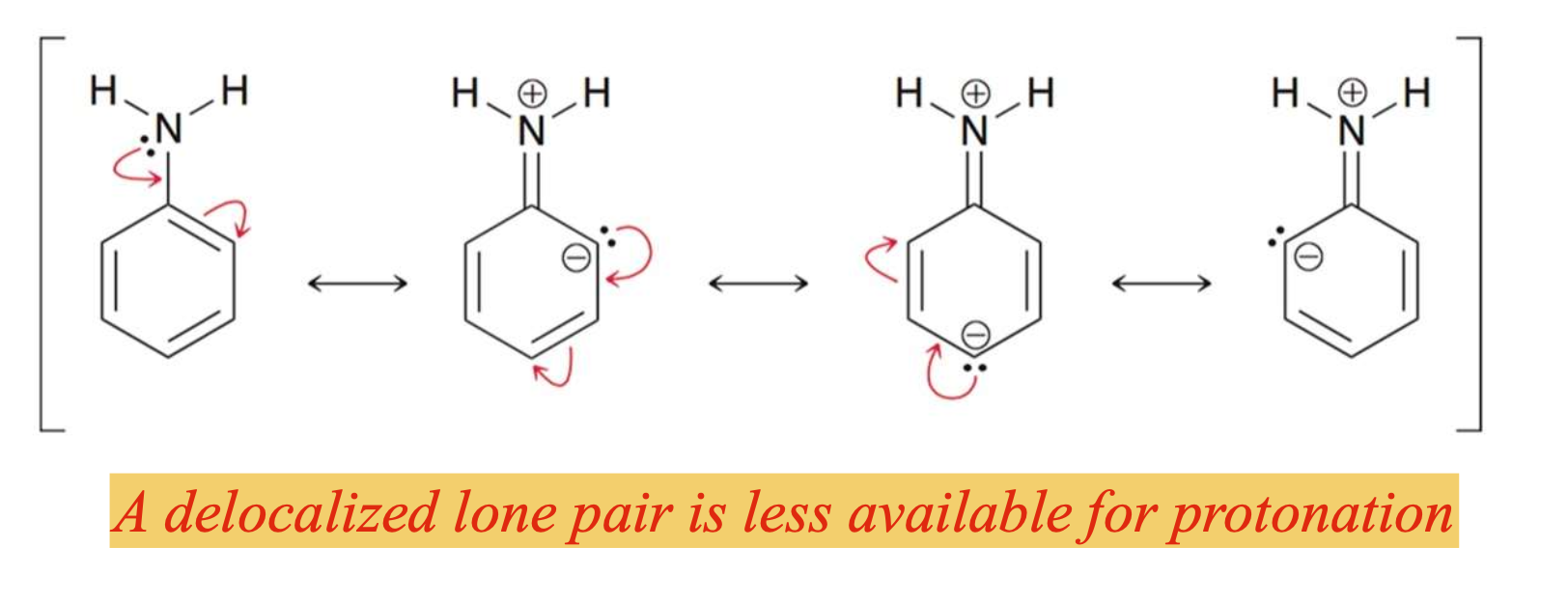
Electron donating groups, such as methoxy __________, while electron withdrawing groups, such as nitro ______________.
slightly increase the basicity of aryl amines; significantly decrease the basicity of aryl amines
are amides basic? why or why not
amides are not basic due to the lone pair on the N being delocalized into the carbonyl group
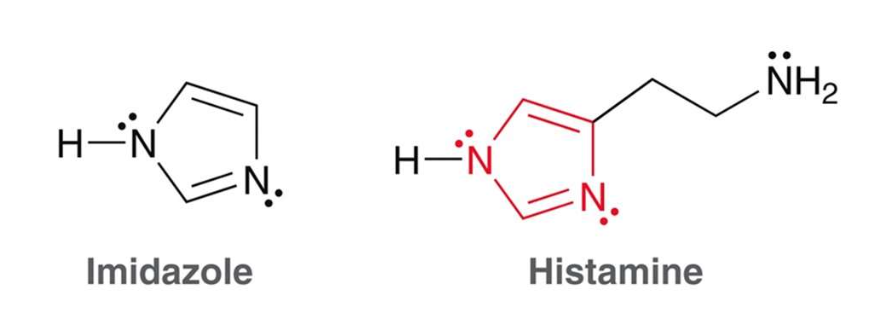
what is imidazole?
An imidazole ring is like pyrrole but has one extra nitrogen atom at the 3 position. Histamine is an example of an important biological compound that contains an imidazole ring.
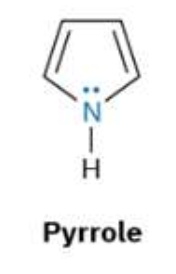
what is pyyrole?
Pyrrole is a simple, aromatic heterocycle
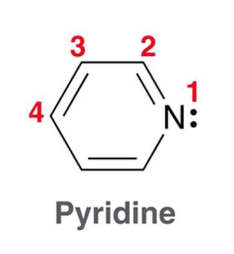
what is pyridine?
Pyridine is a six-membered heterocycle
The lone pair of the nitrogen atom is localized and occupies an sp2-hybridized orbital, and as a result, pyridine is a stronger base than pyrrole. Nevertheless, pyridine is still a weaker base than alkyl amines, because the lone pair occupies an sp2-hybridized orbital, rather than an sp3-hybridized orbital
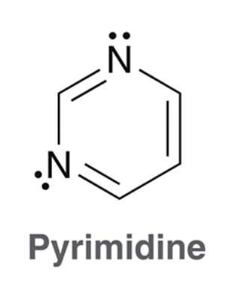
what is pyrimidine?
Pyrimidine is similar to pyridine but contains one extra nitrogen atom at the 3 position. Pyrimidine is a common moiety in biological molecules (e.g. DNA base pairs)
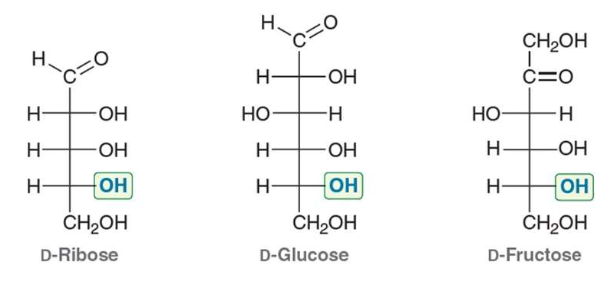
carbohydrates are…
polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones
D sugars have…
OH group at chiral center farthest from carbonyl on the right- hand side in the Fischer projection (R-confirmation)
How do we calculate the number of stereoisomers?
2n = X number of stereoisomers
where n = # of chiral centers
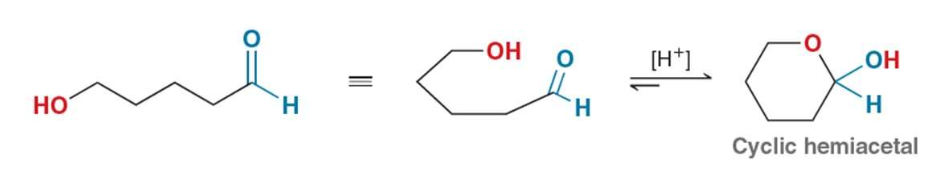
Describe ring formation for an aldose
An aldehyde can react with an alcohol to produce a hemiacetal under protic conditions
hemiacetal formation is favored for 5 and 6 membered rings
Do ketoses form rings?
Yes! ketones can also react with the alcohol (hydroxyl group) to product a hemiketal under protic conditions (also only favored for 5 and 6 membered rings)
During ring formation, what happens to the carbon at C1?
this carbon from a new chiral center
The stereoisomers formed upon cyclization are called _________ .
anomer’s
alpha anomer means…
the anomeric –OH group is trans to the –CH2OH group
beta anomer means…
the anomeric –OH group is cis to the –CH2OH group
describe mutarotation and how it can be accelerated
the interconversion between alpha and beta anomers and can be accelerated via an acid or base catalyst
describe the chair conformation of glucose
the only sugar where all substituents/groups are equatorial, thus is the most stable sugar and most abundant in nature
Recall we can acylate a pyranose ring, what is the purpose of this reaction?
OH groups converted to OAc groups will make them esters and will therefore increase the compound’s solubility in organic solvents.
Recall we can convert the anomeric OH to an OR (acetal) group, what would this compound be called?
glycoside
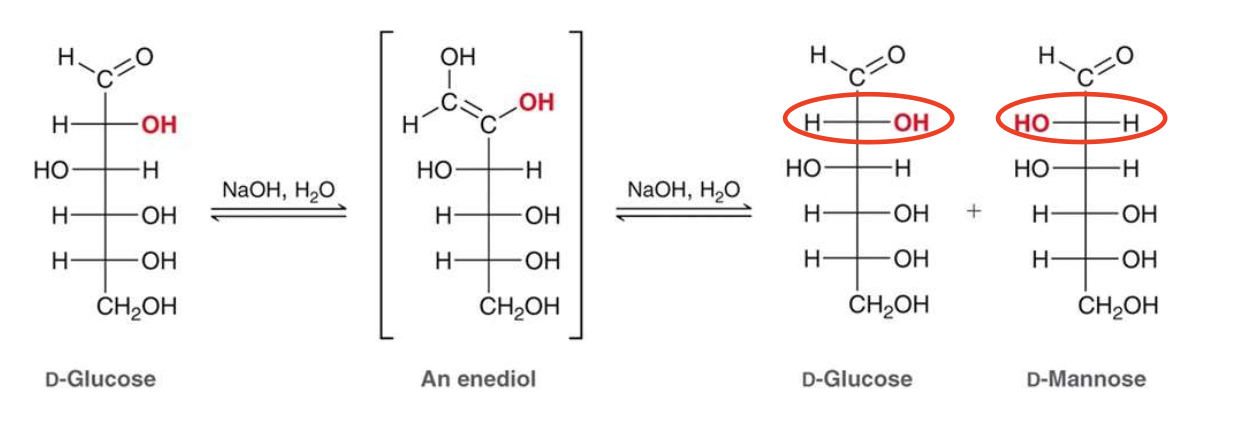
what happens if we put an aldose in strongly basic conditions?
The aldose will undergo epimerization at C2 carbon via the enediol (enol) intermediate —> epimers differ by one chiral center, so the C2 carbon will change configuration.
describe an alditol
a monosaccharide that has an aldehyde group which is reduce (via NaBH4 and H2O) to an alcohol group
What happens when an aldose is reacted with a mild oxidizing agent?
the aldehyde group converts to a carboxylic acid (forms aldonic acid)
What happens when an aldose is reacted with a slightly stronger oxidizing agent?
the aldehyde group and the 1º OH at the other end of the sugar is oxidized to a carboxylic acid (forms aldaric acid)
describe the difference between an alpha and beta glycoside linkage
alpha down, beta up
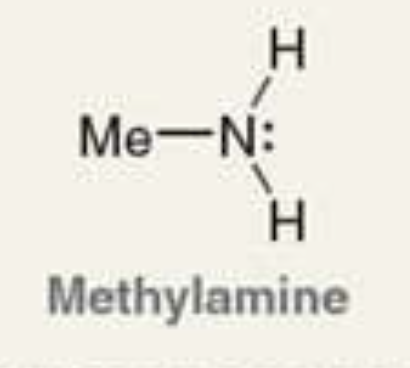
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
10.6
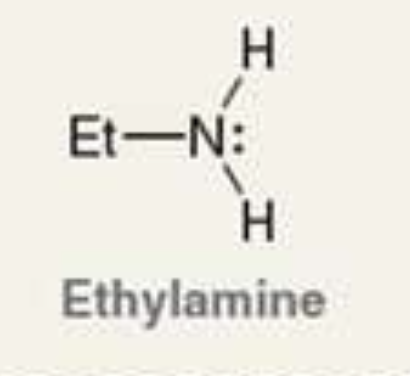
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
10.6
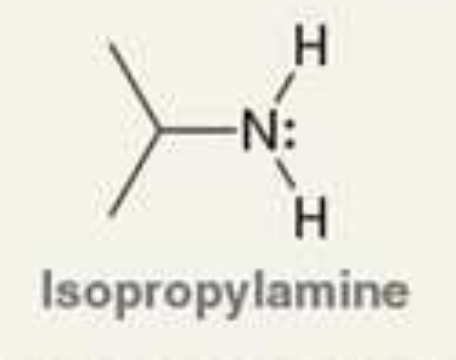
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
10.6
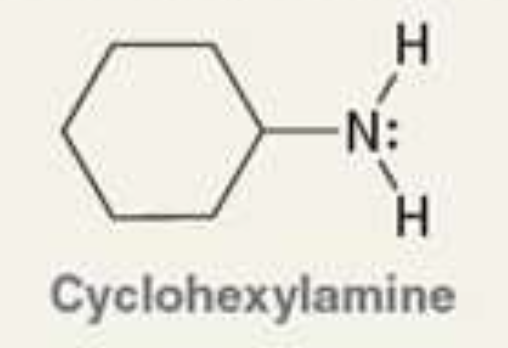
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
10.7
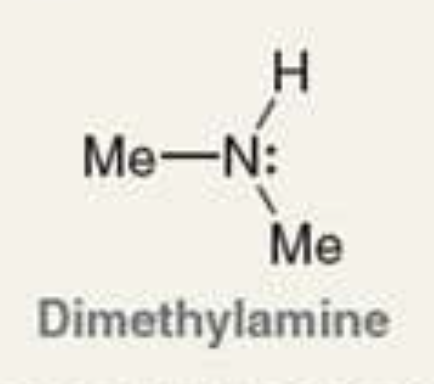
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
10.7
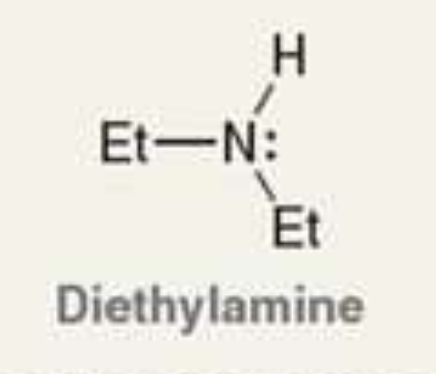
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
11.0
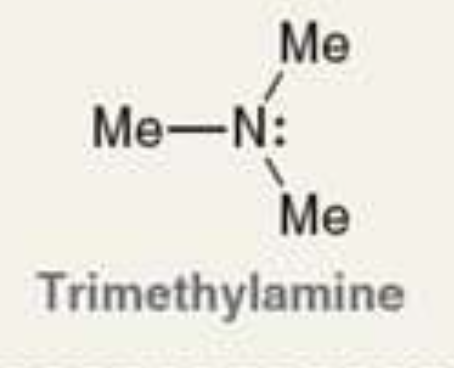
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
9.8
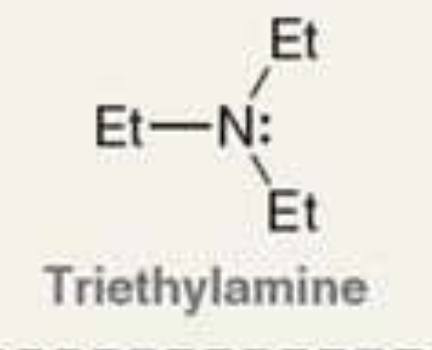
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
10.8
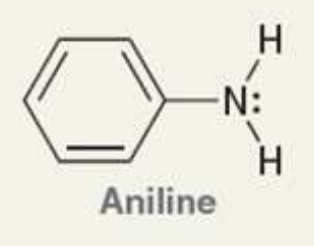
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
4.6
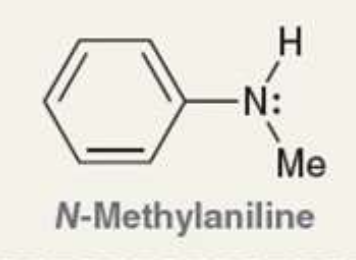
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
4.8
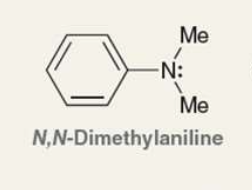
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
5.1
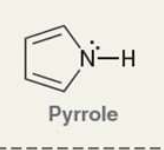
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
0.4
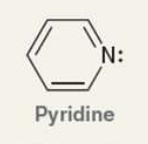
what is the Pka of the ammonium ion?
5.3
the stronger the para activating group…
the more basic the aniline will be
the stronger the para deactivating group…
the less basic the aniline will be
why is reacting ammonia (NH3) with CH3-I not a great way to monoalkylate ammonia?
Because each successive alkylation makes the amine more reactive towards alkylation, so it is basically impossible to isolate the monoalkylated amine.
why is sodium cyanogenborohydride used in reductive amination?
because it selectively reduces imines
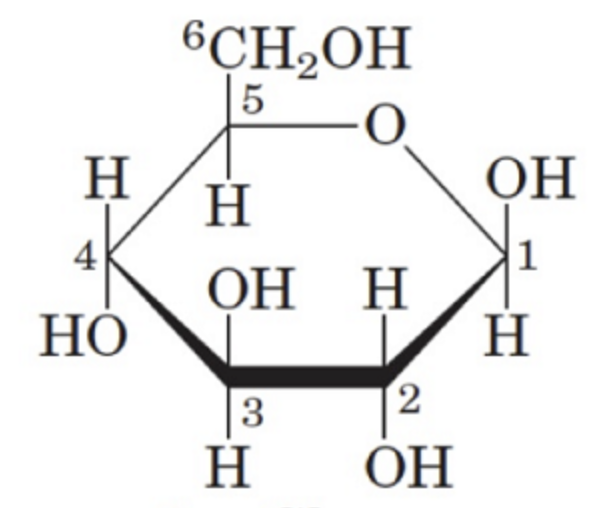
beta-D-glucose (Haworth)
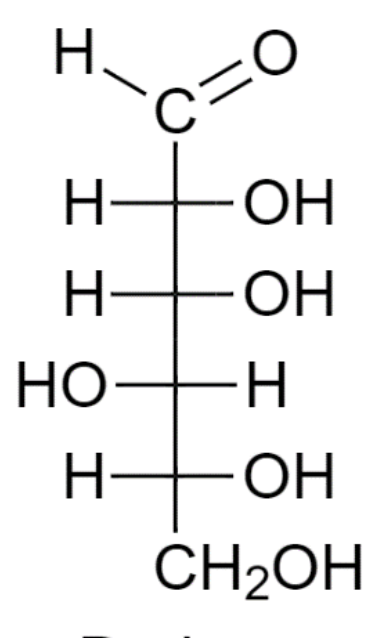
D-glucose (Fisher)
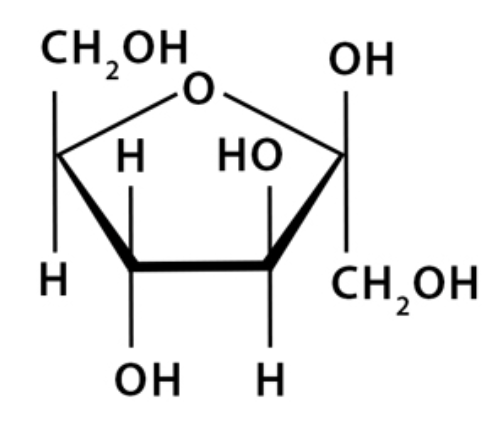
beta-D-fructose (Haworth)
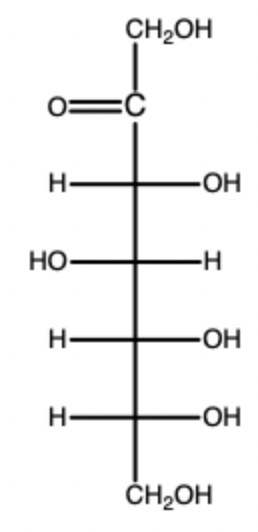
D-fructose (Fisher)
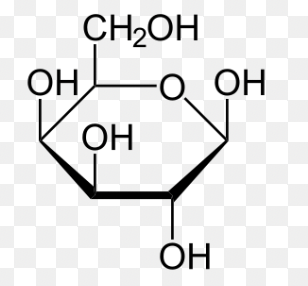
beta-D-galactose (Haworth)
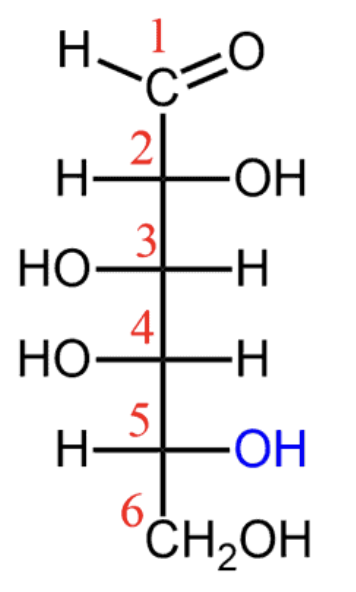
D-galactose
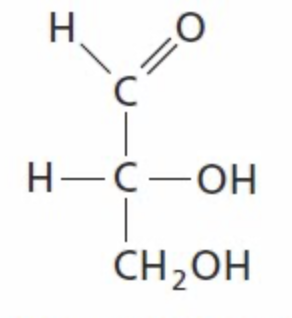
D-glyceraldehyde
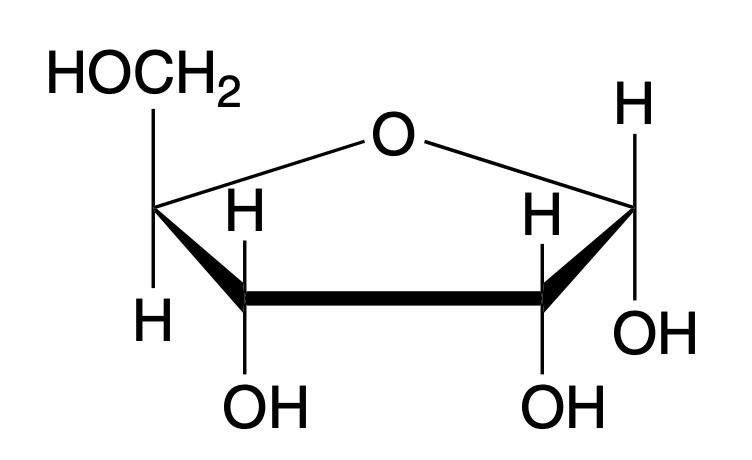
alpha-D-ribose (Haworth)
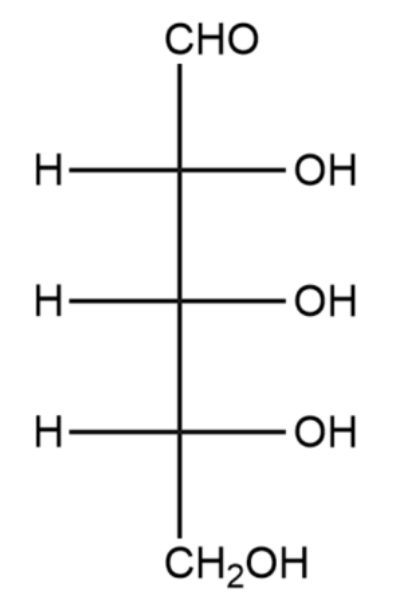
D-ribose (Fisher)
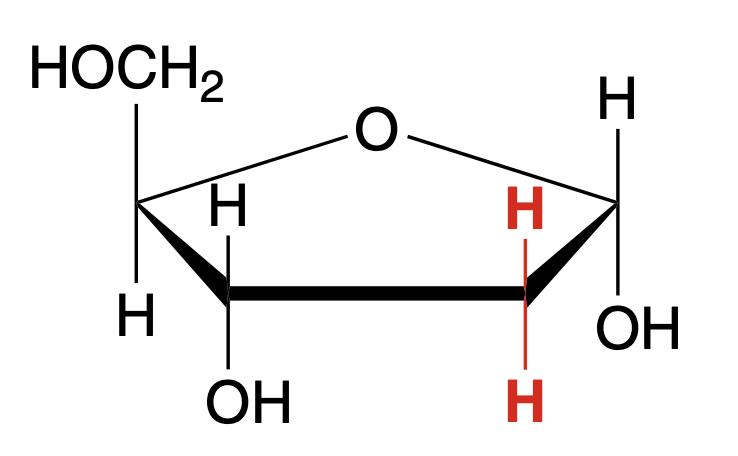
alpha-D-deoxyribose (Haworth)
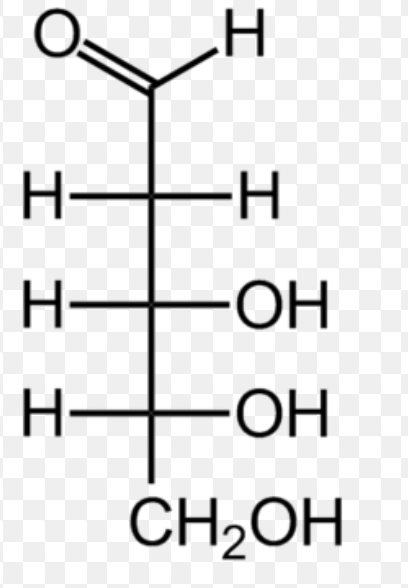
D-Deoxyribose (Fisher)
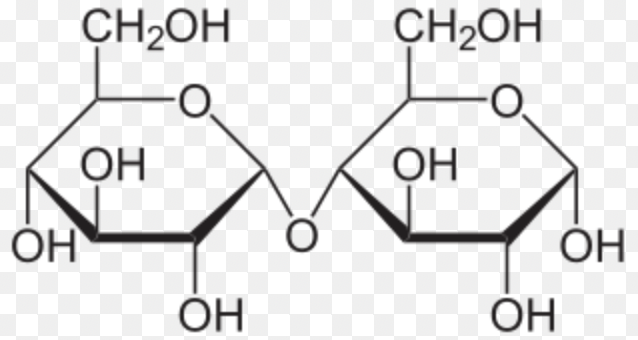
Maltose
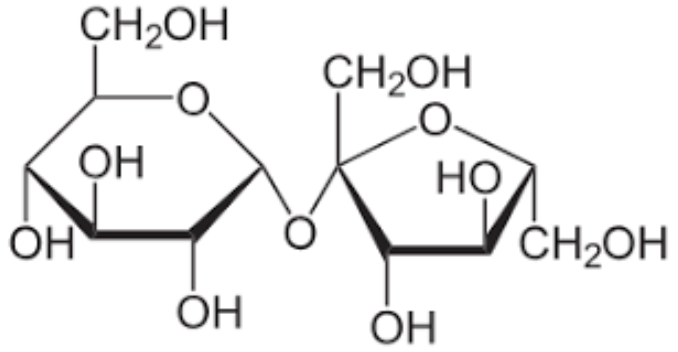
sucrose
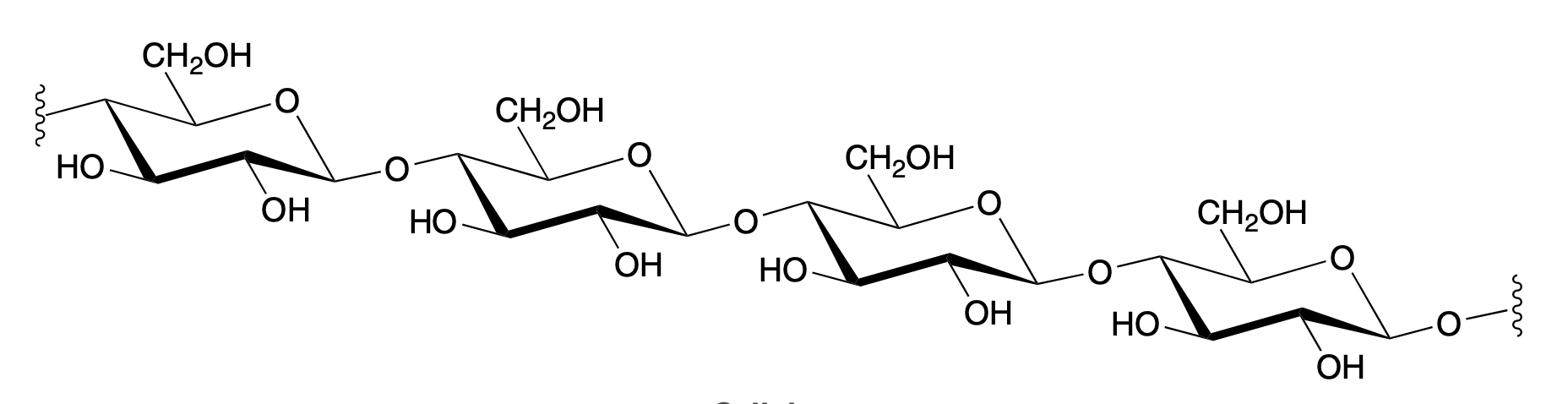
cellulose (beta 1—>4)
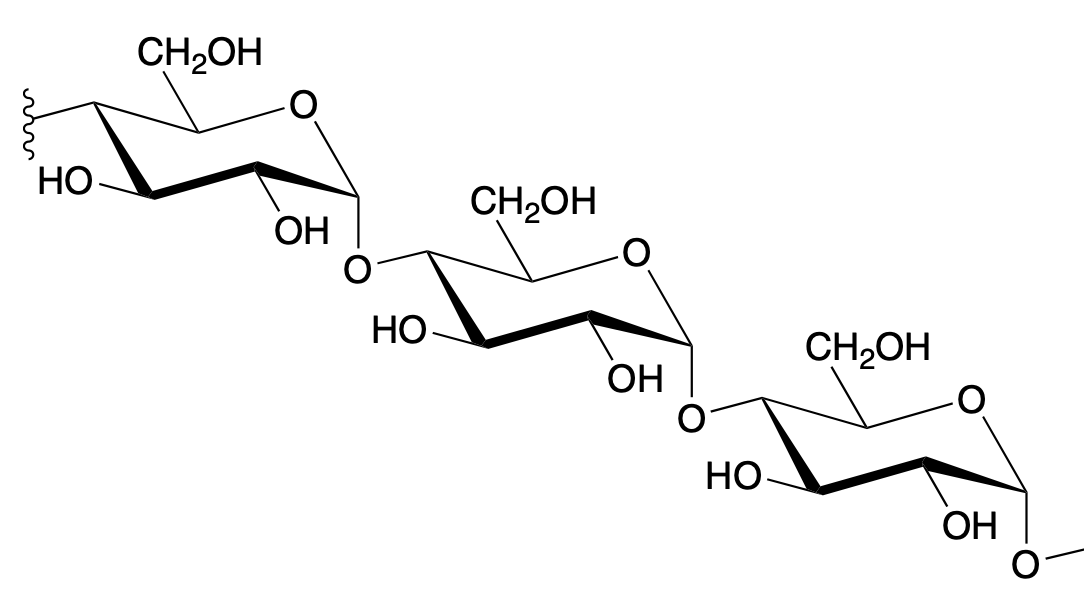
amylose (alpha 1—>4)